Review_Exam1/REVIEW1
advertisement

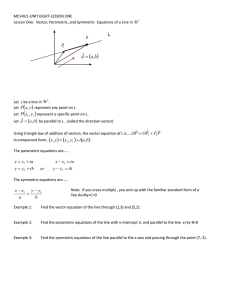
Mac2313 – Exam1 Review/Summer 2007 1 Review all conic sections, be able to classify them and sketch them based on their equations. 2 Be able to identify cylinders and quadratic surfaces. Know how to find the traces in the x = k, y = k and z = k planes. Practice sketching these surfaces in three dimensions. Know how to identify these surfaces, be able to match their graphs and equations. 3 Be able to sketch the graph of a curve given by a set of parametric equations. Know how to eliminate the parameter in a set of parametric equations. Be able to find a set of parametric equations top represent a curve. 4 Be able to find the slope of a tangent line to a curve given by a set of parametric equations. Know how to compute the arc length of a curve given by a set of parametric equations. Know how to find the area of a surface of revolution. 5. Understand the polar coordinate system. Rewrite rectangular coordinates and the equations in polar form and vice-versa. Sketch a graph of equation in polar form. Find the slope of the graph of the tangent line to a polar form. 6 The three-dimensional coordinate system, distance formula, and equations of spheres. Be able to sketch regions corresponding to given equations. 7 Definition of vectors (know both notations), length of vectors, operations with vectors. Be able to find unit vectors, know the special unit vectors and know how to split a vector into components. 8 The dot product. Know how to find the angle between two vectors, know how to decide if two vectors are orthogonal. Be able to calculate direction angles and direction cosines. Know how to find scalar and vector projections of a vector in the direction of an another vector. 9 The cross product. Know the determinant form definition, and remember that the cross product of a and b is orthogonal to both a and b. Know how to decide if two vectors are parallel. Be able to use cross product to calculate areas of triangles and parallelograms. Understand how the scalar triple product gives the signed volume of a parallelepiped. 10 Know the vector, parametric and symmetric form of the equation of a line. Be able to decide if two lines are parallel, orthogonal. Know the vector and scalar form of the equation of a plane. Be able to find the angle between two planes, the line of intersection of two planes, or the distance between them if they are parallel. 11 Be able to use cylindrical and spherical coordinates to represent the surface in space. 12 Analyze and sketch a space curve given by a vector valued function. Understand the concept of limit and continuity to vector-valued function. Review Problems recommended to practice on: 10.1#8,12,16,18,30,42,32, 46 10.2 # 8, 10,16, 22, 24, 52, 55,56 10.3#2,4,8,10,16,22,44,48,49, example 4, example 6 10.4 #2, 4, 8, 12, 14, 28, 32, 38, 42 11.1 # 4, 10, 14, 18, 26, 32, 34, 38, 42, 44, 46, 48, 50, 70,83 11.2 # 16, 26, 28, 38, 42, 44, 54, 72, 74, example 6, example 7 11.3 # 2, 6, 10, 12, 18, 20, 24, 28, 32, 34, 46, 50, 68, 70, 71 11.4 # 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 30, 32, 34, 42, 44, 46, 48 11.5 # 8, 10, 12, 15, 17, 22, 26, 28, 34, 48, 52, 58, 74, 84, 88, 91 11.6 # 8, 9, 10, 12, 20, 24 11.7 # 3, 5, 13, 15, 21, 26, 30, 35, 45, example 3 12.1 # 3, 10, 14, 24, 28, 60, 72, 74, 76