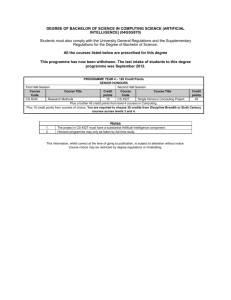
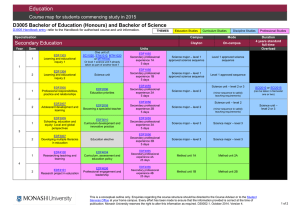
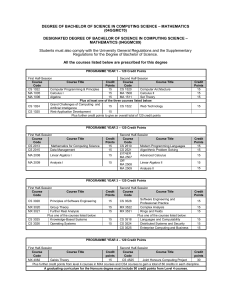
Downloadable version of course details in RTF
advertisement

Course details (2001) page 1 University Preparation Program (Abbreviation: UPP) Course code: E0D The University Preparation Program is a special enabling program. The course is designed to provide unqualified mature-age potential students with academic learning skills and the confidence and personal skills needed to succeed at University. The full-time one-year course features training in the use of technology for learning and a taster of University academic subjects across a broad spectrum of areas. Successful completion of the program will assist students to gain admission to undergraduate degree courses offered by the University of Tasmania. Admission & prerequisites The normal University Mature Age Entry requirements apply except for the deduction of one year from the minimum age. Students should have a demonstrated lack of access to higher education or educational opportunities; or have experienced a change in career or lifestyle. Students should also display a genuine intention to participate in higher education upon completing the UPP. Course objectives The UPP provides an opportunity for mature age students to revise, upgrade and establish skills relevant to higher education study in the current academic environment. Course structure The course is equivalent to one year full-time study but its unitised structure lends it to part-time study. UPP consists of 9 units, with a full time equivalent load of 8 units per year (4 per semester). Seven of these units are core or skills-based units including a bridging Mathematics unit. The other two offer introductions to current academic units. Special note on fees This course does not attract HECS fees but it does attract Austudy/Abstudy. Applications are made through the normal University Admission procedures. University Preparation Program: Schedule (North-West Centre) Unit Title campus-sem weight code Course details (2001) Study Skills Communications I Using Information Technology for Academic Purposes I Academic Studies I Communications II Academic Literacy Using Information Technology for Academic Purposes II Academic Studies II Bridging Maths page 2 B1/2~D1/2 B1/2~D1/2 12.5% 12.5% ESA010 ESA020 B1/2~D1/2 B1~D1 B2 B2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% ESA050 ESA070 ESA030 ESA040 B2 B2~D2 B2~D2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% ESA060 ESA080 ESA090 Details are subject to change. All details should be confirmed with the Course Coordinator, Mrs Jenny Oakley on (03) 6430 4905. Foundation Studies Program (Abbreviation: FSP) Course code: E0E International students who need to upgrade school results from their own country to gain entry to an undergraduate program at the University may apply for admission to the Foundation Studies Program. Students are guaranteed entry to all faculties of the University of Tasmania on successful completion of this course. There are two ways to study in the Foundations Studies Program : a Fast Track program of 24 weeks Academic English and academic studies and an Extended program of 34 weeks: 10 weeks Academic English followed by the Fast Track program. Admission & prerequisites Successful completion of: Indonesia SMA 3 Japan Upper Secondary School Certificate Korea High School Leaving Certificate Taiwan High School Leaving Certificate Thailand Mattayom 6 Hong Kong HKCEE: grade D in 4 subjects Malaysia SPM 6 passes; including 4 at credit or better MICSS Senior Middle Two: 6 passes Singapore GCE O levels: 6 passes including 4 at grade 4 Course details (2001) page 3 English language requirement is IELTS 5.0 or TOEFL 500 for Fast Track; and IELTS 4.5 or TOEFL 475 for the Extended program. Course objectives The course aims to provide students with the academic requirements for entry into a first year university program. It also aims to upgrade the language proficiency, study skills, research and computing skills and awareness of the expectations of the university environment in which they will study. Course structure FSP has three Core Subjects that are compulsory for all students: Academic English, Australian Studies, Computing Skills and Research Management. There are also Elective subjects; and FSP students choose three that are relevant to their degree program. Students may choose from: Biology, Chemistry, Mathematics, Accounting, Business Organisation and Management, Legal Studies, Australia in Asia and the Pacific, Psychology. Program schedule Unit title dates unit code Extended commences March ECS196 commences October ECS197 Fast Track commences January ECS198 commences June/July ECS199 Contact Phone: (03) 6226 2540. Introductory Academic Program (Abbreviation: IAP) Course code: <none> Course objectives Course details (2001) page 4 The Introductory Academic Program is an intensive short course offering students an introduction to Higher Education in Australia and an opportunity to prepare for the academic language demands of their award courses. A fee is payable. Course structure The course, which is suitable for students who are due to commence undergraduate and postgraduate studies at the University of Tasmania, includes: • • • • Introduction to Australian Higher Education Cross-cultural communication for International students Introduction to the course and School – – meeting with lecturers/supervisors – – assignments familiarisation with course content Computer skills – – – – – • • • • • word processing tables and graphs email internet course-specific computer skills Tutorial presentation and discussion skills Listening and note-taking in academic settings Reading for study Writing for academic purposes Excursions – – – – Australian culture Tasmanian history Tasmanian wilderness and wildlife. The course lasts for 5 weeks from early January to mid-February, involving 25 contact hours weekly. Class sizes average 12 students, with a maximum of 15. The program is offered by the English Language Centre in conjunction with the International Student Office and staff of academic schools of the University. Students receive a detailed written report on their language skills and advice on further English Language Support services. Satisfactory completion of the course is recognised by the awarding of a Certificate of Completion. Course details (2001) page 5 For further information: ph (03) 6226 2706. Riawunna – Centre for Aboriginal Education Murina (Pathway to Higher Education) Course code: W0D This enabling or bridging program is a non-award course which is offered at both the Hobart and Launceston campuses of the University of Tasmania to Aboriginal people 18 years and over. Course objectives The program is designed to provide Aboriginal people with the opportunity to develop their skills and knowledge-base for entry into mainstream undergraduate courses after successful completion of the Murina Program. The program assists students in building their self-confidence before progressing into an undergraduate course of their choice. The Murina Program, as a non-award course, does not attract the Higher Education Contribution Scheme (HECS) fees. However, students pay a University Entrance fee ($55 in 1999) and a Services and Amenities fee ($55 in 1999). Both of these fees will attract GST in 2001. Course structure The Murina Program is structured in two streams: 1) Core or compulsory skills-based units, and 2) Introductory or elective units that offer experiences in, and understandings of, undergraduate course content across a wide range of disciplines in the University. The program is offered over two 13-week semesters. Students may study at 100 and/or 200 levels. Aboriginal students who are undertaking mainstream studies may choose units in the Murina Program to enhance their academic success and broaden their skills base. Core units include: Academic Skills, Computer Skills, Nuritinga Palawa, Mathematics, and Aboriginal Writing and Literature. Introductory or elective units include: Psychology, Sociology, Physical Science, Social Science, Law, History, Government, Environmental Design and Architecture, Living Waters, Human Movement, Performing Arts, Fine Arts, Art History, Research Topic. For information on these units, please contact Riawunna Centre for Aboriginal Education. Course details (2001) page 6 Riawunna, Centre for Aboriginal Education Aboriginal higher education support units were established at the Hobart campus of the University of Tasmania in 1985 and at the Launceston campus of the Tasmanian State Institute of Technology in 1986. The amalgamation of the two units took place in 1992 with the establishment of the new University of Tasmania, and became Riawunna, Centre for Aboriginal Education. Riawunna offers a wide range of services to Aboriginal students enrolled at the University and to Aboriginal communities. The Centre also provides services to non-Aboriginal students and the University in general. This section of the 2001 University of Tasmania Handbook identifies the range of courses undertaken, and services offered, at Riawunna. For information on all units offered in the Aboriginal Studies sequence of study (HAB units) see pages B-xx and C-xx. Aboriginal Student Services Riawunna assists Aboriginal enabling, undergraduate and postgraduate students with the aim to successfully complete their study at the University through academic, social and cultural support programs. These services include; • • • • • • • • • • • Course advice, academic and personal counselling and support Tutorial assistance (ATAS) Cultural activities, community workshops and meetings Library resources Computer Lab facilities Private study facilities Orientation week Access to audio-visual and photocopy equipment Refreshment and kitchen facilities Community room Lockers Riawunna has indoor and outdoor space for Aboriginal students to relax and meet other students in a culturally conducive and friendly environment on campus at both Launceston and Hobart. Orientation and Assessment (O&A) Program The Centre conducts Orientation and Assessment Programs at Hobart, Launceston and the North West campuses for Aboriginal applicants who have applied for a University place within an undergraduate course, or who wish to enter university through the enabling program. The O&A Program is usually conducted over three days in December. It informs Aboriginal applicants of course options and support facilities offered at the University of Tasmania, and Course details (2001) page 7 provides Aboriginal people with the opportunity to be assessed for alternative mature age entry into mainstream University study. Please contact Riawunna Student Service Coordinators at Hobart or Launceston for further information about this program. Contacts Patsy Cameron, Coordinator, Aboriginal Student Services, Launceston, (03) 6324 3386. Caroline Spotswood, Coordinator, Aboriginal Student Services, Hobart, (03) 6226 2516. UniStart Course code: XAA001 UniStart is a preparation program for people who are unsure about: • • • • how to study at university what to expect what skills are needed for success who can help students develop those skills. The program is designed to meet a variety of needs. It is beneficial to anyone commencing University including school-leavers and mature age people who are returning to study. Course objectives The program aims to: • • • introduce students to the culture of life at the University of Tasmania introduce the types of learning tasks required at university assist students to develop a range of appropriate skills for University study. Career outcomes At the conclusion of the program, participants will be: Course details (2001) • • • page 8 better able to make the transition to university better prepared for the academic demands involved more likely to successfully complete their chosen course of study Course structure The program incorporates an essay assignment and consists of four core modules and elective options which are designed to assist students to complete this typical university task. It is taught by the Learning Skills Advisers (with the assistance of other Student Services staff), Library, and Information Technology Services (ITS) staff. In addition, academic staff on each campus provide sample lectures and tutorials. The UniStart modules are: Module 1: University Culture • • • Learning the culture Learning to learn University thinking Module 2: Study Skills • • • Lectures and note taking Academic reading and note making Summarising/paraphrasing Module 3: Preparing Academic Work • • • • • • Analysing a topic Writing analytically Structuring an essay Report writing Academic writing Oral communication – effective presentation Module 4: Information Literacy • • • Introduction to the University Library Searching electronic data bases Searching the Internet Module 5: Basic Numeracy (Optional) Course details (2001) page 9 Note: A basic level of computer literacy is necessary for Module 4 (and for success at University). There will be a 'Computers for Beginners' workshop prior to each UniStart. Enrolment in this workshop is essential for those with no or very minimal experience of computers. There will be opportunities during the UniStart program for students to practise their computer skills and learn about the university's facilities. UniStart really makes a difference. When compared to the general student population, students who have participated in UniStart – • • • Achieve better results Have less than half the failure rate. Are less likely to withdraw. Previous participants have made the following comments – "I feel I have a real headstart to going to Uni and I think everyone should do UniStart! Thank you!!" "It was VERY helpful (and fun) to meet so many other prospective students. We many concerns, interests, etc. in common." "I value the contacts I have made and will certainly start 2000 at Uni a lot more and less isolated." Cost? There are no fees for the UniStart program. When is it? December 2000 Hobart and Launceston Monday 4th Dec – Thursday 14th Dec. or January–February 2001 Hobart, Launceston and the North-West Centre Course details (2001) page 10 Monday 29th January – Thursday 8th February (NB The Hobart program will carry over to Fri 9th because of a public holiday) 9am – 4pm (some days are shorter) Monday to Thursday for 2 weeks How do I enrol in UniStart? Numbers are limited so booking is essential. To enrol or obtain more information please phone: Hobart phone: (03) 6226 2697 email:Mignon.Jolly@utas.edu.au Launceston phone: 03 6324 3787 email:Julie.Tubb@utas.edu.au North-West Centre phone: 03 6430 4949 email:Leanne.King@utas.edu.au Diploma of Fine Art and Design (Abbreviation: DipFAD) Course code: F2F This on-campus 2-year (minimum) full-time course is offered by the Faculty of Arts through the School of Visual and Performing Arts at Launceston. Part-time study is also available. Admission & prerequisites Applicants are required to submit a portfolio of recent art work (which may include slides, photographs or video) and to attend an interview. Applicants who are unable to attend an interview should provide a brief statement outlining their interest in the course and include any relevant qualifications or experience. Normally applicants should have successfully completed year 12 in an Australian school system. A person who possesses such other qualifications and experience deemed by the Faculty to provide an adequate preparation for study may apply for entry to the course. Course objectives Course details (2001) page 11 The course aims to provide students with: • • • • • • a para-professional qualification of high standard; a comprehensive course which articulates with the Bachelor of Fine Arts and the visual art streams of the Bachelor of Contemporary Arts; awareness and experience of recent technological developments in the visual arts; the necessary communication skills and flexibility to interact with the wider community; appropriate support studies to assist students in the development of high level visual art skills; the opportunity for students to gain a working knowledge of the academic, cultural, critical and technical language relevant to the visual arts. Articulation Students who have been awarded the DipFAD will, upon successfully applying for admission to the BFA or BCA, be credited with one-third of the BFA or BCA degree. Students who have not completed Art Theory as part of the DipFAD will be required to complete the compulsory level 100 Art Theory units within the BFA or BCA. Schedule of Units Unit Title campus-sem weight Level 100 Drawing 1A L1/2 12.5% Drawing 1B L1/2 12.5% and one of the following: Ceramics 1 Lf 75% Painting 1 Lf 75% Printmedia 1 Lf 75% Sculpture 1 Lf 75% Textiles 1 Lf 75% [a] Level 200 Either (FFD281 and FFD282) or (FFA100 and FFA101) Drawing 2A L1/2 12.5% Drawing 2B L1/2 12.5% Introduction to Cultural Practices 1 L1 12.5% Introduction to Cultural Practices 2 L2 12.5% and one of the following: Ceramics 2 Lf 75% Painting 2 Lf 75% code FFD181 FFD182 FFC180 FFP180 FFR180 FFS180 FFX180 FFD281 FFD282 FFA102 FFA103 FFC280 FFP280 Course details (2001) page 12 Printmedia 2 Lf 75% FFR280 Sculpture 2 Lf 75% FFS280 Textiles 2 Lf 75% FFX280 [a] The prerequisite for all level 200 units is the corresponding level 100 unit. Part-time students please note: Students enrolling the DipFAD part time enrol in one Drawing or Art Theory unit each year and a corresponding part-time major unit. Level 100 part-time codes end in 181 and 182; level 200 part-time codes end in 281 and 282. Thus Ceramics 1A (part time) would be FFC181 taught over a full year and weighted at 37.5%; Ceramics 1B would be FFC182, taught over a full year and weighted at 37.5%. Diploma in Languages (Abbreviation: DipLang) Course code: R2A This course is offered by the Faculty of Arts and is available at Hobart and Launceston, and may be undertaken part time over two years or a maximum of three consecutive years. In cases where study has been interrupted by illness or other unavoidable cause the Faculty may allow additional time in which to complete the course. The languages available are Chinese, French, German, Indonesian and Japanese at Hobart, and Chinese and Indonesian at Launceston. For an outline of units available, turn to the Bachelor of Arts Schedule of units which follows. Units at level 200/300 will be found listed under the entry for the relevant language. Admission & prerequisites Applicants must have passed the first year at university level in the language in which they wish to study or be deemed by the Head of School, Asian Languages and Studies or English and European Languages and Literatures to have reached an equivalent level of proficiency, eg TCE French or Indonesian Stage 4 (HA). Course objectives The course is intended to provide candidates with or without a degree the opportunity to improve their language competency. Candidates who have completed the Diploma will normally gain a level of competence in their chosen Course details (2001) page 13 language equivalent to that of a candidate who has studied the language as a major for the Bachelor of Arts degree. Course structure Candidates for the Diploma are required to study units in language with a weighting of at least 37.5% at level 200 and up to 62.5% at level 300 (a total of 100% HECS weighting). Articulation Students who hold an award from this University or another approved institution may be permitted by the Faculty to count units from the former award towards the Diploma. Students who graduate with a Diploma in Languages and wish to enter the Bachelor of Arts will be granted a total of 50% credit towards the BA, comprising 37.5% Group 2 and 12.5% Group 3. Students will be granted full credit towards the BA degree for subjects studies in an incomplete Diploma in Languages. Students who transfer to the BA from the DipLang and receive full credit cannot graduate with the DipLang. Diploma of Music (Abbreviation: DipMus) Course code: F2M This on-campus 2-year (minimum) full-time course is offered by the Faculty of Arts through the Conservatorium of Music at Hobart. Part-time study is also available. Admission & prerequisites All applicants are required to attend an audition and interview (where practicable) and to undertake a theory and aural test. Overseas and interstate applicants may submit a certified audio or video tape of recent performances and/or compositions. Instrumental and vocal applicants should prepare a program comprising three works of contrasting style and/or period; some technical work may also be required. Composition applicants should present a folio of at least three compositions. A person who possesses such other qualifications and professional experience deemed by the Faculty to provide an adequate preparation for study, equivalent to that provided for by the above prescriptions, may however be admitted to the course. Course details (2001) page 14 Course objectives The course aims to provide students with: • • • • • • a para-professional qualification of high standard; a comprehensive course which articulates with the Bachelor of Music; awareness and experience of recent technological developments in music; the necessary communication skills and flexibility to interact with the wider community; appropriate support studies to assist students in the development of high level musicianship skills the opportunity for students to gain a working knowledge of the academic, cultural, critical and technical language relevant to music. Articulation Students who complete this course satisfactorily will be granted credit for the first year of the Bachelor of Music if they are successful in their application for entry into the Bachelor of Music degree course. Schedule A Unit Title campus-sem weight code Level 100 General Musicianship Hf 25% FCG180 Practical Study Hf 50% FCP180 choose one of the following disciplines: Keyboard or Voice or Orchestral Instruments or Contemporary Music or Guitar or Composition Ensemble Study Hf 12.5% FCE180 and the following unit: Language Support Studies Hf 12.5% FCL180 Students normally enrol in FCL180. However, with special approval from the Director, students may undertake another unit in its place. Level 200 Core studies and Ensemble (all students) Aural and Listening 1 Hf 12.5% FCL100 Music Theory 1 Hf 12.5% FCT100 Performance and Communications 1 Hf 12.5% FCP100 Ensemble 1 Hf 12.5% FCE100 Principal Study and Related Studies CHOOSE ONE OF THE FOLLOWING DISCIPLINES: Keyboard Principal Study Keyboard 1 Hf 25% FCY100 Accompaniment 1 Hf 12.5% FCY150 Course details (2001) page 15 Voice Principal Study Voice 1 Hf 25% FCV100 French for Singers 1 Hf 25% FCV150 Orchestral Instruments Principal Study Orchestral Instruments 1 Hf 25% FCO100 Orchestra & Repertoire 1 Hf 12.5% FCO150 Contemporary Music Principal Study Contemporary Music 1 Hf 25% FCN100 Style and Analysis 1 Hf 12.5% FCN150 Guitar Principal Study Guitar 1 Hf 25% FCG100 Guitar Repertoire 1 Hf 12.5% FCG150 Composition Principal Study Composition 1 Hf 25% FCC100 Performance for Composers 1 Hf 12.5% FCC150 Complementary Studies CHOOSE ONE OF THE FOLLOWING: Principal Study Extension 1 Hf 12.5% FCB100 Musicianship Extension 1 [na] 12.5% FCB110 Improvisation 1 [na] 12.5% FCB120 Keyboard Skills 1 Hf 12.5% FCB130 Orchestration and Arranging 1 [na] 12.5% FCB160 Music Technology 1 Hf 12.5% FCB190 Voice students do not choose a Complementary Studies unit. Subject to Sub-Dean approval, students may take units offered by another school in the University up to a maximum of 12.5% in place of Complementary Studies units. Language for Singers (Italian or French or German) is offered by the Conservatorium of Music on a cyclical basis. In 2000 German was offered, in 2001 French is being offered. Bachelor of Arts (Abbreviation: BA) Course code: R3A Course details (2001) page 16 During 2000, changes were made to the structure of the BA degree. Students who commenced their study prior to 2001 should refer to the section headed 'Changes to the BA degree' at the end of this entry. This 3-year (minimum) course is available at Hobart, Launceston and the North-West Centre at Burnie. Some units are also available externally by distance education to Tasmanian residents who are unable to attend classes on either the Hobart or Launceston campus or at the North-West Centre. Students may study full time or part time and have nine enrolment years, including the year of passing the first unit for the degree, in which to complete course requirements. If students are studying by distance education their choice of units is limited and may be varied from time to time. They should check the availability of units before planning their course. Entry to the course normally occurs in February, but limited entry is also available in July. Admission & prerequisites Applicants are expected to meet the normal requirements set by the University for entry to degree courses. There are also several categories of special admission. No specific course or subject prerequisites apply. Course objectives The Bachelor of Arts offers the opportunity for a liberal education. Students are able to exercise choice across a wide range of disciplines. These include the humanities (Ancient Civilisations, Ancient Greek, Latin, English, History, Asian Languages, European Languages and Philosophy) and the social sciences (Geography, Political Science, Psychology, Public Policy and Sociology) as well as interdisciplinary studies (Aboriginal Studies, Asian Studies, Natural Environment and Wilderness Studies, Journalism and Media Studies, Social Ecology, and Women's Studies). The program develops general abilities in the following areas: • • • • • • • • • written expression linguistic skills creative self-expression capacity to analyse and interpret in a dispassionate and objective manner capacity for reasoned criticism data acquisition and analysis research techniques marshalling facts in support of arguments, and evaluating the possible outcomes of alternative courses of action, with the emphasis varying according to the particular program chosen. In short, the program helps students to operate in a complex and rapidly changing world. Course details (2001) page 17 Career outcomes In Australia and around the world, employers are increasingly seeing graduates who can speak and write clearly; who are computer literate and understand how to use technology; who know about other countries, cultures and societies; who can solve problems creatively; and who have developed that flexibility of thought which technical and vocational training rarely encourages. Graduates with a Bachelor of Arts degree find jobs in, for example: advertising, journalism, radio and television; the arts, heritage and museology; diplomacy, interpreting and tourism; management, marketing and administration; politics, the public service, the police force and the armed forces; teaching, research and publishing; psychology, counselling and community work. Course structure • • • • • • • Students normally complete a total of 300% (HECS weighting) of units made up of 100% first-year (level 100), 100% second-year (level 200) and 100% third-year (level 300). Students must also take sufficient units to complete two majors within the 300% total. A major is defined as sequential studies in one discipline made up of 25% at level 100 and 75% at levels 200/300 (a minimum of 100%). Details on how to meet the requirements for majors are contained in this Handbook under the relevant discipline heading. Please note that some majors have compulsory units and these are listed under the discipline entry. Students take a minimum of three years and a maximum of nine years to complete the degree Students may take one major (100%) from a discipline outside the BA schedule (see page B-xx) such as Fine Arts, Music, Management or Computing, with permission of the relevant Head of School. This is made up of 25% at level 100 plus 75% at levels 200/300. Note that units in Fine Arts have quotas and other units may have TCE prerequisites. Potential students should contact the relevant School for information on enrolment when applying for admission. At level 100, students normally study four different subject areas. At level 200 and 300, students take sufficient units to complete majors in two of the disciplines which they have studied at level 100. The remaining units to make up the 300% total can come from any of the other first-year subjects they have studied or more units towards the majors. Language students who enter the BA at level 200 in the language take only 75% of units at level 100 and take extra units at levels 200/300 in the language to make up the total required for the major and for the 300% required for the degree. Full-time students normally take a 100% load each year to complete in the minimum time. Students who are working in addition to their study may Course details (2001) page 18 take as little as 25% load in any one year, but should be mindful of the maximum time allowed for them to complete. Summary: • • • • • • • • No unit can count twice as part of two different majors The maximum percentage in any one discipline which can be counted towards the degree is 150% At least 25% of units in a major must be at level 300 At the end of year 1, students must declare their intended majors and confirm them at the end of year 2 The maximum percentage at level 100 for any single discipline is 25% Students must complete 25% at level 100 before progressing to level 200 units in that discipline Permission for an overload (more than 50% in any semester) must be obtained from a Sub-Dean Units cannot count towards the degree if the content is the same as another unit studied previously. The University Calendar has the full specifications for the degree. Students should remember that it is their responsibility to check that they have met the requirements for the degree. Typical courses EXAMPLE A Level 100 (Year 1) Sociology A and B 25% History 1 25% German 2 25% Government A and B 25% Level 200 (Year 2) Sociology German History 37.5% 37.5% 25% Level 300 (Year 3) Sociology 50% German 50% Sociology major (100% minimum) German major (100% minimum)<tbz> Course details (2001) page 19 EXAMPLE B Level 100 (Year 1) Ancient Civilisations 25% Journalism and Media Studies 1A and 1B Government A and B 25% English A and B 25% 25% Level 200 (Year 2) Journalism and Media Studies English 25% Political Science 25% 50% Level 300 (Year 3) Journalism and Media Studies 25% Political Science 50% English 25% Journalism and Media Studies major (100% minimum) Political Science major (100% minimum)<tbz> EXAMPLE C Level 100 (Year 1) Philosophy A and B25% History 25% Indonesian 1 25% Sociology A and B 25% Level 200 (Year 2) History 1 37.5% English 37.5% Philosophy 25% Level 300 (Year 3) History 50% English 37.5% Sociology 12.5% History major (100% minimum) English major (100% minimum)<tbz> Course details (2001) page 20 The Schedule of units which follows lists by discipline all units taught in the BA. Students should also consult the discipline entries in the Handbook to determine individual unit prerequisites plus the requirements for a major in the chosen discipline. Students intending to study a major in a discipline offered in another degree course (Groups 1A, 2A and 3A) eg Music, Management, Fine Arts, should consult the discipline entry in the Handbook to check the unit and major requirements in the particular discipline. Articulation Credit for previous study A person holding another award from this University or another approved institution may be permitted by the Faculty to count towards the BA, units from the former award to a maximum of 100% (an unspecified major). Students need to apply for credit when applying for entry to the BA. Units from courses offered by other Faculties of the University may be included in the degree provided they do not exceed the permissible weighting (see course structure on page B-xx). Examples of credit awarded towards a BA: Course/Award Credit awarded Total Completion of the Tasmania Police Recruitment course (TPRC) 25% Group 1A at level 100 plus 25% Group 2A at level 200 in the BA 50% Completed TAFE diploma or associate diploma 25% Group 1A level 100 25% Registered nurses, hospital trained 25% Group 1A level 100 25% Registered nurses, hospital trained and with further training, eg midwifery certificate 25% Group 1A level 100 and an additional 25% Group 2A level 200 50% Completed three-year degree 25% Group 1A, 37.5% Group 2A, 37.5% Group 3A (a major) 100% Articulation with other courses Students who have completed a BA degree with sufficient merit are eligible to apply for entry to the Bachelor of Arts with Honours (BA(Hons)) degree. Details on eligibility and how to apply are contained in the BA(Hons) section which follows. Students completing the Honours degree with sufficient merit are able to apply for entry to a research higher degree such as Master of Arts (MA) or Doctor of Philosophy (PhD). Information on these courses is obtainable from the Office for Research and the Research Higher Degrees Handbook. In addition, there are postgraduate diplomas and coursework master degrees. Information on these courses is included in the Postgraduate section of this handbook. Course details (2001) page 21 After completing two full years of study in the BA degree, students can apply for entry to the Bachelor of Social Work (BSW) degree course. The BA study must include two years of units in both Sociology and Psychology. The BSW is taught on the Launceston campus only. Interested students should consult the BSW entry included in this section of the Handbook. BA students may apply to transfer to the Bachelor of Social Science (Police Studies) or Bachelor of Tourism degree course (from 2001 offered in Launceston only). Interested students should consult the relevant entries which follow in this section of the handbook. BA students wishing to pursue a teaching career must also complete the two year Bachelor of Teaching (BTeach) degree (see page B-xx). This is a postgraduate qualification taken after graduating with a BA. The degree course is available on both the Launceston and Hobart campuses. Information brochures are obtainable from Student Recruitment offices on both campuses and from the contact number for the BTeach given on page xx. Students currently studying for a degree in another faculty are able to apply to transfer to the BA degree course and will receive some credit for their previous successful study. Changes to the BA Degree in 2001 During 2000 the Faculty of Arts authorised changes to the structure of the BA degree, the main one being the deletion of double majors. Students are now required to complete two majors in two different disciplines. Commencement prior to 2001 Students who commenced their study before 2001 will complete their degree according to the Rules under which they commenced. These are outlined in the Handbook for 2000 and are listed in full in the University Calendar (available at the Library, Student Administration, Faculty Offices). All re-enrolling students are strongly encouraged to attend one of the re-enrolment sessions to be held in Burnie, Launceston and Hobart during October, for advice on completing their degree. Alternatively, students may wish to attend an enrolment session for new students held in January 2001 (also held in Burnie, Launceston and Hobart). Students with queries may also discuss their options with Faculty Sub-Deans on each campus. In addition, staff in the Faculty Office are also available to assist students with their queries. Course details (2001) page 22 Students are strongly urged to check the individual discipline entries in the Handbook for information on unit offerings and cross-listed units. Commencement prior to 1998 Students who began their BA studies prior 1998 should consult the Course and Unit Handbook 2000. Enrolment restrictions – quotas All prospective BA students, including those currently enrolled in other courses in the University, should be aware that admission to the degree is subject to a quota and formal selection procedures. Students who are presently enrolled in another degree program and wish to be enrolled in a BA program will need to apply for a place in the course. Application forms are available from Student Administration, Hobart or Launceston. Similarly, entry into certain units in particular schools may be subject to quota restriction yet to be advised. Further information will be available at formal enrolment sessions. Enquiries may be made to academic schools or the Faculty Office, Hobart or Launceston, during the enrolment period. Enrolment outside the BA schedule Students who intend to enrol in subjects or units from another degree course as part of an Arts degree, must comply with the subject or unit prerequisites determined by that degree course. In all cases, specific prerequisites are listed in the relevant discipline entries. Restrictions apply to the number of units which may be studied. Schedule Note: (Unit) weight represents the proportion (%) of a normal full-time study load, and is used for calculating the services and amenities fee and the Higher Education Contribution Scheme (HECS) liability. For detailed information on the units, refer to the 'Unit details' section of this handbook where all units are listed in strict alphanumeric order of their unit code number. Note: Faculty reserves the right to correct errors or inconsistencies, with or without notice, and to make changes to this schedule. However, Faculty will endeavour to ensure that no students is disadvantaged by such changes. Course details (2001) page 23 [i] students need to study at least 3 (75%) and no more than 4 (100%) units from Group 1; [ii] students may enrol in 25% of units outside the BA schedule at 100 level; [iii] internal students may enrol in units offered by distance education. Group 1 Level 100 Unit Title campus-sem Aboriginal Studies Contemporary Indigenous Australia L1~H1~D1 Indigenous Australia to the 1950s L2~H2~D2 Ancient Civilisations Ancient Civilisations 1A: Gender and Politics in Classical Literature H2 Ancient Civilisations 1B: Introduction to Greek and Roman History H1 Ancient Civilisations 1 Hf Asian Studies Asian Studies 1A H1~Lv1 Asian Studies 1B H2~Lv2 Chinese Chinese 1 Hf~Lf English English 1A H1 English 1B H2~L2~B2~D2 Introduction to English: Australian Literature L1~B1~D1 French French 1 Hf Geography Population and Urbanisation L1~B1~D1 The Physical Environment L2~B2~D2 Geography Geography and Environmental Studies 1 Hf Geography and Environmental Studies 1A Hf German German 1 Hf History weight code 12.5% HAB102 12.5% HAB103 12.5% HTC101 12.5% 25% HTC102 HTC100 12.5% 12.5% HMA101 HMA102 25% HMC100 12.5% 12.5% HEA103 HEA104 12.5% HEA101 25% HEF100 12.5% 12.5% KJG101 KJG102 25% KGA100 25% KGA101 25% HEG100 Course details (2001) History 1 Hf 25% The Impact of Europe c. 1640–1780 H1~D1 12.5% (a) Age of Revolution and Empire c. 1780–1815 (b) The Modern World in Australia to 1860 H2 12.5% History 1 Lf~Bf 25% The History of Europe from c. 1620 to 1789 L1~B1 12.5% (a) The Impact of Europe from the French Revolution to the American Civil War; (b) The Modern World in Australia to 1860L2~B2~D2 HTA106 Indonesian Introductory Indonesian Hf~Lf 25% Japanese Japanese 1 Hf 25% Journalism and Media Studies Journalism 2: An Introduction to Media and Society H1 12.5% Journalism 1: An Introduction to Reporting and News H2 12.5% Latin Latin 1 Hf 25% Philosophy/Logic and Philosophy of Science Introduction to Philosophy 1A L1~D1 12.5% Introduction to Philosophy 1B L2~D2 12.5% Philosophy 1A H13 12.5% Philosophy 1B H2/3 12.5% Political Science Introduction to Government A H1~L1~B1 12.5% Introduction to Government B H2~L2~B2 12.5% Psychology Psychology 1A H1~L1~B1 12.5% Psychology 1B H2~L2~B2 12.5% Public Policy Introduction to Government A H1~L1~B1 12.5% Introduction to Government B H2~L2~B2 12.5% Social Ecology page 24 HTA100 HTA103 HTA104 HTA101 HTA105 12.5% HMN100 HMJ100 HEJ102 HEJ101 HTL100 HPA181 HPA182 HPA101 HPA102 HSG101 HSG102 KHA101 KHA102 HSG101 HSG102 Course details (2001) Sociology A Sociology B or 25% from the following units: Population and Urbanisation Community Health and Medicine I Geography and Environmental Studies 1A Health Care Where People Live and Work 1 Society, Culture and Health 1 Society, Culture and Health 2 Sociology Sociology A Sociology B Women's Studies Gender and Society The Representation of Gender page 25 H1~L1~B1~D1 H2~L2~B2~D2 12.5% 12.5% HGA101 HGA102 L1~B1~D1 12.5% KJG101 H1 12.5% CAM105 Hf 25% KGA101 L1 12.5% CNA126 L1 12.5% HGA138 L2 12.5% HGA139 H1~L1~B1~D1 H2~L2~B2~D2 12.5% 12.5% HGA101 HGA102 H1 12.5% HAF101 H2 12.5% HAF102 Group 1A 25% of units offered outside the BA schedule as the Faculty may approve. Groups 2 & 3 Where there are alternative unit codes (e.g. HSD206/306) the unit may be taken either at level 200 or level 300. When students enrol, depending on whether they wish to study a unit as a Group 2 unit or a Group 3 unit, they should use the appropriate code e.g. HSD206 is the Group 2 code for the unit Policy Process while HSD306 is the Group 3 code for the same unit. Students should note that they must complete units from each Group to a minimum weight as set out in the specifications. Students are advised to check the unit descriptions to see what the prerequisites, corequisites and mutual exclusions are for each unit. These may vary depending on the level of the unit. The maximum percentage for units at level 200/300 outside the BA schedule is 75%. Level 200/300 Unit Title Aboriginal Studies Aboriginal Arts Aboriginal Women campus-sem weight code [na] L1~H1 12.5% 12.5% HAB240/340 HAB232/332 Course details (2001) Contemporary Indigenous Tasmania Dynamics of Indigenous Cultures Indigenous Health Indigenous Identity and Place Indigenous Justice Issues Indigenous Life Histories Indigenous Tasmania and Colonial Dispossession Indigenous Tasmanians and the Bass Strait Islands 1830–1950 Indigenous Tourism Language in Aboriginal Society Special Topic in Aboriginal Studies A Special Topic in Aboriginal Studies B History of the Indigenous Peoples of North America Unit Title Ancient Civilisations Intermediate Ancient Greek A Intermediate Ancient Greek B Advanced Latin A Advanced Latin B Classical Tragedy: Euripides and Beyond Greek and Roman Epic Greek and Roman Mythology Greek Tragedy Intermediate Ancient Greek A Intermediate Ancient Greek B Intermediate Latin A Intermediate Latin B Latin 1 page 26 [na] 12.5% HAB206/306 H1~Lv1 L2 12.5% 12.5% HAB253/353 HAB213/313 [na] L2~D2 [na] 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HAB241/341 HAB208/308 HAB252/352 L1~D1 12.5% HAB256/356 L2~D2 H2 12.5% 12.5% HAB209/309 HAB210/310 L1~H1~D1 12.5% HAB214/314 L1~H1~D1 12.5% HAB201/301 L2~H2~D2 12.5% HAB202/302 L1~D1 12.5% HTA275/375 campus-sem weight code H1 12.5% HTC216 H2 H1 H2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HTC218 HTC317 HTC319 H1 [na] H1 [na] 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HTC213/313 HTC210/310 HTC223/323 HTC211/311 H1 12.5% HTC216 H2 H1 H2 Hf 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 25% HTC218 HTC217 HTC219 HTC215/315 Course details (2001) page 27 Love and Politics in Augustan Literature H2 Monuments of Rome: Image and Ideology [na] Roman Empire: Tiberius to Hadrian H1 Roman Imperial Society H2 Roman Republic 133–31 BC [na] The Later Roman Empire [na] The Pursuit of Empire: Philip, Alexander and Rome [na] Uncovering the Past H2 Women in Greek and Roman Antiquity [na] And the following units from other disciplines: English Medieval Writing [na] Shakespeare: Histories and Tragedies H2 Shakespeare: Comedy and Romance [na] Elizabethan and Jacobean Tragedy [na] Reading the Classics: Ovid and Chaucer [na] National Shakespeare [na] The Legend of King Arthur H1 History The Early Middle Ages: From Rome to the Millennium AD 410–1000 Hf Late Medieval and Renaissance Europe Hf Europe in an Age of Crisis 1560–1640 Europe in an Age of Crisis 1560–1640 Europe in the High Middle Ages, AD 1000–1300 Europe in the High Middle Ages, AD 1000–1300 Heresy and Inquisition in Medieval Europe AD 1100–1500 12.5% HTC205/305 12.5% HTC207/307 12.5% 12.5% HTC202/302 HTC203/303 12.5% 12.5% HTC201/301 HTC206/306 12.5% 12.5% HTC200/300 HTC204/304 12.5% HTC221/321 12.5% HEA213/313 12.5% HEA222/322 12.5% HEA223/323 12.5% HEA225/325 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HEA227/327 HEA262/362 HEA277/377 25% HTA201/301 25% HTA202/302 D2 12.5% HTA209/309 D2 12.5% HTA209/309 [na] 25% HTA212/312 [na] 25% HTA212/312 [na] 12.5% HTA225/325 Course details (2001) Unit Title Ancient Greek Intermediate Ancient Greek A Intermediate Ancient Greek B Intermediate Ancient Greek Grammar Advanced Ancient Greek A Advanced Ancient Greek B Advanced Ancient Greek Grammar page 28 campus-sem weight code H1 12.5% HTG216 H2 12.5% HTG218 Hf H1 H2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HTG220 HTG316 HTG318 Hf 12.5% HTG320 Unit Title campus-sem weight Asian Studies Australia and Asia H2~Lv2 12.5% Contemporary Asian Issues [na] 12.5% Ethnic Politics and Religious Nationalism in Asia H2 12.5% Issues in Contemporary China [na] 12.5% Reporting Asia: Western Media Perceptions of Asia H1 12.5% v Research Project Hf/1/2~L f/1/2 25%/12.5% And the following units from other disciplines: The Asia-Pacific Economies: Tigers H1 12.5% Contemporary Art of the Asia-Pacific Region H2 12.5% Cultures and Societies of Southeast Asia H2 12.5% Love, Family and Sexuality: East–West Comparison [na] 12.5% Chinese 2 Language Skills A Hf~LvfC3 25% Chinese 2 Language Skills B Hf~LfC3 25% Classical Japanese Literature [na] 12.5% Japanese 2 Language Skills A Hf~Lvf 25% Japanese 2 Language Skills B Hf 25% v Japanese Film H2~L 2 12.5% code HMA211/311 HMA221/321 HMA261/361 HMA246/346 HMA260/360 HMA300/301 BEA211 FST213/313 HGA254/354 HGA212/312 HMC201 HMC202 HMJ333 HMJ201 HMJ202 HMJ334 Course details (2001) page 29 Modern Japanese Literature Intermediate Indonesian (Reading and Writing) Intermediate Indonesian (Conversation) Survey of Indonesian Literature Advanced Buddhist Philosophy Indo–Tibetan Philosophy, History and Culture Introduction to Buddhist Philosophy Espionage, Terror and Global Disorder Globalisation and East Asian Politics Politics of Democratisation, East and West Asian Environmental Justice India since Independence Islam, Law and Women – Historical and Contemporary Perspectives Modern India till Independence War and Peace in the Pacific Geography of Asia Unit Title Behavioural Science Behaviour in the Workplace Child & Adolescent Development Health, Stress and Coping Human Abilities Research Project in Social Psychology Social Behaviour and Social Influence [na] 12.5% HMJ331 Hf~Lf 25% HMN201 H1~Lv1 12.5% HMN202 H1~Lv1 12.5% HMN304 H1 12.5% HPA297/397 C3 25% HPA276/376 H1 12.5% HPA219/319 H1 12.5% HSA270/370 [na] 12.5% HSA258/358 H1 12.5% HSA227/327 [na] H2 12.5% 12.5% HSD239/339 HTA222/322 H1 12.5% HTA223/323 [na] 12.5% HTA221/321 [na] H1 12.5% 12.5% HTA255/355 KGA202/302 campus-sem weight code L1 12.5% KHB215/315 L2 12.5% KHB205/305 L2 [na] 12.5% 12.5% KHB209/309 KHB211/311 [na] 12.5% KHB208/308 [na] 12.5% KHB207/307 Course details (2001) Unit Title Chinese Chinese 2 Language Skills A Chinese 2 Language Skills B Chinese for Tourism Chinese Reading and Writing Skills Chinese Special Topic A Chinese Speaking and Listening Skills Computer-Related Chinese Business and Office Writing Classical Chinese Modern Chinese Literature page 30 campus-sem weight code Hf~LfC3 25% HMC201 Hf~LfC3 H1 25% 12.5% HMC202 HMC205 H2~L2C3 Hf~Lf 12.5% 12.5% HMC302 HMC309 Hf~LfC3 25% HMC301 L2~H2 Hf H1~Lv1 12.5% 25% 12.5% HMC305 HMC306 HMC307 Unit Title campus-sem weight code Cultural Studies Note: Cultural Studies is being taught out. No new intake into this major in 2001. Cultural studies draws on the following units offered by various Schools: A Brief History of 20th-Century Art L1 12.5% FFA202/302 Wilderness and Natural Environment L1 12.5% FFA235/335 The Body in Art L2 12.5% FFA240/340 Landscape and Issues of Postcolonialism in Australian Art [na] 12.5% FFA241/341 Art and Design Theory 2/3 H1 12.5% FST200/300 Australian Art of the 1970s and 1980s H2 12.5% FST201/301 Cinema H1 12.5% FST202/302 Performance [na] 12.5% FST204/304 Picturing the Wilderness H3 12.5% FST205/305 Fashioning the Body H2 12.5% FST207/307 Feminist Aesthetics [na] 12.5% FST209/309 'Follow the White Rabbit': Fairy Tale, Fable and Cyber Fiction H2 12.5% FST210/310 Fantasy Decor H2 12.5% FST212/312 Course details (2001) Sexualities: Histories, Representation, Politics Power, Pleasure and Perversion Critical Theory National Shakespeare Popular Fiction: Texts and Audiences The Legend of King Arthur 'Just like in Thelma and Louise': Feminism and Film LA Noir: Film Noir and Hollywood Le grand écran: A History of French Cinema The German Film: More than One Hundred Years of German Cinema Post-1945 German Film Science, Technology and Contemporary Society Tourism, Sport and Leisure Cultures and Societies of Southeast Asia Sociology of Nature Change and Order in Contemporary Society Japanese Film Place and Environment Postmodernism and its Critics Politics in Literature and Film Heresy and Inquisition in Medieval Europe AD 1100–1500 Spreading the Word: A History of Image and Text Literature and Environment Unit Title English page 31 H1 12.5% HAF202/302 [na] H2 [na] 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HEA254/354 HEA260/360 HEA262/362 H1 H1 12.5% 12.5% HEA267/367 HEA277/377 [na] 12.5% HEA278/378 [na] 12.5% HEA279/379 [na] 12.5% HEF230/330 [na] H2 12.5% 12.5% HEG204/304 HEG212/312 [na] 12.5% HGA220/320 H1 12.5% HGA251/351 H2 [na] 12.5% 12.5% HGA254/354 HGA261/361 H2 H2~Lv2 [na] 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HGA302 HMJ334 HPA204/304 [na] 12.5% HPA206/306 [na] 12.5% HSA204/304 [na] 12.5% HTA225/325 H3 12.5% HTA226/326 H1 12.5% KGA272/372 campus-sem weight code Course details (2001) African Literature African Literature West and South American Women Writing (Nineteenth Century) Beautiful Lies: Recent Australian Writing British Literature 1800–1850 British Literature 1850–1900 Confessionalism: Post-Romantic Associations Confessionalism: Postmodernist Applications Constructing Modernity and the Metropolis Critical Theory Elizabethan and Jacobean Tragedy Gender and Nation 'Just like in Thelma and Louise': Feminism and Film LA Noir: Film Noir and Hollywood Medieval Writing Modern Drama Modernism in British Literature 1910–1930 Modernism in British Literature: Poetry National Shakespeare Popular Fiction: Texts and Audiences Postmodern American Poetry Power, Pleasure and Perversion Reading the Classics: Ovid and Chaucer Research Project Research Project Romantic Poetry Sexuality and the Subject in Fiction page 32 [na] 25% HEA259/359 [na] 12.5% HEA253/353 [na] 12.5% HEA258/358 H1 12.5% HEA205/305 H1 12.5% HEA257/357 [na] 12.5% HEA204/304 L1~Bv1~D1 12.5% HEA255/355 [na] 12.5% HEA261/361 H2 H2 12.5% 12.5% HEA215/315 HEA260/360 [na] H2 12.5% 12.5% HEA225/325 HEA289/389 [na] 12.5% HEA278/378 [na] [na] [na] 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HEA279/379 HEA213/313 HEA226/326 L1~Bv1~D1 12.5% HEA283/383 [na] [na] 12.5% 12.5% HEA284/384 HEA262/362 H1 12.5% HEA267/367 H1 12.5% HEA288/388 [na] 12.5% HEA254/354 [na] [na] H1/2~L1/2 [na] 12.5% 25% 12.5% 12.5% HEA227/327 HEA375 HEA376 HEA280/380 [na] 12.5% HEA286/386 Course details (2001) page 33 Shakespeare: Comedy and Romance [na] Shakespeare: Histories and Tragedies H2 The Body in the Text: 20th Century Australian Fiction [na] The Legend of King Arthur H1 The Literature of Tasmania H2 The Novel in the Nineteenth Century L2~Bv2~D2 Writing Narrative L2~H2 Writing Poetry and Short Fiction L1~H1 And the following units from other disciplines: Ancient Civilisations Love and Politics in Augustan Literature H2 Greek and Roman Epic [na] Greek Tragedy [na] Classical Tragedy: Euripides and Beyond H1 Latin 1 Hf Greek and Roman Mythology H1 Geography Literature and Environment H1 German The German Film: More than One Hundred Years of German Cinema [na] Post-1945 German Film H2 Music Ensemble 1 Hf 12.5% HEA223/323 12.5% HEA222/322 12.5% 12.5% HEA269/369 HEA277/377 12.5% HEA214/314 12.5% 12.5% HEA282/382 HEA290/390 12.5% HEA203/303 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HTC205/305 HTC210/310 HTC211/311 12.5% 25% 12.5% HTC213/313 HTC215/315 HTC223/323 12.5% KGA272/372 12.5% 12.5% HEG204/304 HEG212/312 12.5% FCE100 Bachelor of Arts Unit Title French French for Tourism and Business French Language Skills 2 French Language Skills 3 French Language Skills 3B campus-sem weight code H1 Hf Hf Hf 12.5% 25% 25% 25% HEF203/303 HEF201 HEF301 HEF302 Course details (2001) French Linguistics: An Introduction French Linguistics: Pragmatics French Literature: An Overview French-Canadian Women Writers Le grand écran: A History of French Cinema The French Novel (1900–1950) Twentieth Century French Theatre page 34 [na] 12.5% HEF210/310 H2 12.5% HEF213/313 [na] 12.5% HEF220/320 H2 12.5% HEF222/322 [na] 12.5% HEF230/330 [na] 12.5% HEF223/323 H1 12.5% HEF221/321 campus-sem weight code L1~D1 12.5% KJG201 L1~D1 L2~D2 25% 25% KJG301 KJG302 L2~D2 12.5% KJG202 Unit Title campus-sem Geography and Environmental Studies (Hbt) Biogeography and Climatology H1 Conservation Geomorphology H2 Environmental Impact Assessment and Decision Making H2 Environmental Management H1 Environmental Remote Sensing H1 Fauna Conservation Management H1 Geography of Asia H1 Historical Geography H2 Literature and Environment H1 Microclimatology H2 Natural Environment Field Techniques H3~L3~B3 weight code 12.5% KGA209 12.5% KGA327 12.5% 12.5% KGA381 KGA223/323 12.5% KGA365 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KGA332 KGA202/302 KGA240/340 12.5% 12.5% KGA272/372 KGA321 12.5% KGA213 Unit Title Geography Australian Natural Environments Environmental Geomorphology Globalisation Natural Resources Management Course details (2001) Sustainable Communities and Local Environments The Global Space Economy Urban Planning: Space, Place and Society Vegetation Management Wilderness and Natural Area Management: Natural and Cultural Values page 35 H2 H2 12.5% 12.5% KGA254/354 KGA208/308 H1 H1 12.5% 12.5% KGA253/353 KGA331 H2 12.5% KGA278/378 Unit Title campus-sem German Classical German Literature H2 Drama and Fiction from Realism to Naturalism [na] German for Tourism and Business H1 German Language Skills 2 Hf German Language Skills 3 Hf German Language Skills 3B Hf Medieval German Language and Literature H1 Post-1945 German Film H2 Post-1945 German Literature [na] The German Film: More than One Hundred Years of German Cinema [na] The Twentieth-Century German Novel [na] weight code 12.5% HEG310 12.5% HEG307 12.5% 25% 25% 25% HEG203 HEG201 HEG301 HEG302 12.5% 12.5% HEG305 HEG212/312 12.5% HEG213 12.5% HEG204/304 12.5% HEG311 Unit Title History African History African–American History Australia from 1918 to 1975 Australia from the 1850s to 1918 Australian History 1788–1990s Cold War Europe, 1945–1989 campus-sem weight code Lf~Df 25% HTA250/350 L2 12.5% HTA252/352 H1~L1 25% HTA207/307 Hf 25% HTA204/304 D1 12.5% HTA240/340 H2 12.5% HTA210/310 Course details (2001) Crime and the Law in Historical Perspective H2 Environmental History [na] Europe at War 1914–1945 H1~L1 Europe in an Age of Crisis 1560–1640 D2 Europe in the High Middle Ages, AD 1000–1300 [na] Gender in European Thought H2 Heresy and Inquisition in Medieval Europe AD 1100–1500 [na] Historiographical Studies [na] History and Heritage L2~H2~D2 History of the Indigenous Peoples of North America L1~D1 History of the USA [na] India since Independence H2 Islam, Law and Women – Historical and Contemporary Perspectives H1 Late Medieval and Renaissance Europe Hf Modern Europe 1815–1914 [na] Modern India till Independence [na] Revolution and Dissent [na] Special Topic in History Hf~Lf Spreading the Word: A History of Image and Text H3 The Early Middle Ages: From Rome to the Millennium AD 410–1000 Hf Third World Issues [na] Van Diemen's Land 1642–1850 H1 War and Peace in the Pacific [na] And the following units from other disciplines: Aboriginal Studies Indigenous Tasmanians and the Bass Strait Islands 1830–1950 L2~D2 Ancient Civisilations page 36 12.5% 12.5% HTA218/318 HTA271/371 12.5% HTA211/311 12.5% HTA209/309 25% HTA212/312 12.5% HTA205/305 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HTA225/325 HTA220/320 HTA290/390 12.5% 25% 12.5% HTA275/375 HTA241/341 HTA222/322 12.5% HTA223/323 25% HTA202/302 25% HTA203/303 12.5% 12.5% 25% HTA221/321 HTA216/316 HTA399 12.5% HTA226/326 25% 25% HTA201/301 HTA251/351 12.5% HTA229/329 12.5% HTA255/355 12.5% HAB209/309 Course details (2001) The Pursuit of Empire: Philip, Alexander and Rome Roman Republic 133–31 BC Roman Empire: Tiberius to Hadrian Roman Imperial Society Uncovering the Past Monuments of Rome: Image and Ideology Women in Greek and Roman Antiquity page 37 [na] 12.5% HTC200/300 [na] 12.5% HTC201/301 H1 H2 H2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HTC202/302 HTC203/303 HTC204/304 [na] 12.5% HTC207/307 [na] 12.5% HTC221/321 Unit Title campus-sem Indonesian Advanced Indonesian Language Skills Lf~Hf Advanced Indonesian Language Skills (Padang) C3 Indonesian Literature in Context (Padang) C3 Intermediate Indonesian (Conversation) H1~L1 Intermediate Indonesian (Conversation) (Padang) C3 Intermediate Indonesian (Reading and Writing) Hf~Lf Intermediate Indonesian (Reading and Writing) (Padang) C3 Interpreting and Translation [na] Popular Culture and Resistance in Indonesia Hv2~L2 Reading Indonesian Hf~Lvf Survey of Indonesian Literature H1~Lv1 Topics in Indonesian Literature [na] Wayang Shadow Puppet Theatre Lv2 weight code 25% HMN302 25% HMN306 12.5% HMN307 12.5% HMN202 12.5% HMN203 25% HMN201 25% HMN204 12.5% HMN303 12.5% 25% HMN309 HMN308 12.5% HMN304 12.5% HMN305 12.5% HMN210/310 Unit Title Japanese Classical Japanese Literature campus-sem weight code [na] 12.5% HMJ333 Course details (2001) Japanese 2 Language Skills A Japanese 2 Language Skills B Japanese Film Japanese for Tourism Modern Japanese Literature Professional Spoken Japanese Professional Translation of Japanese Reading Japanese Spoken Japanese Writing Japanese page 38 Hf~Lvf 25% HMJ201 Hf H2~Lv2 H1 25% 12.5% 12.5% HMJ202 HMJ334 HMJ203 [na] 12.5% HMJ331 Hf 12.5% HMJ330 H1 H1 Hf H2 12.5% 12.5% 25% 12.5% HMJ335 HMJ306 HMJ307 HMJ308 Unit Title campus-sem Journalism and Media Studies Advanced Print Journalism H1 Environmental Journalism [na] Newspaper and Magazine Design H2 Online Journalism H2 Photojournalism Theory [na] Professional Placement 1 H1 Professional Placement 2 H2 Professional Practices and Culture H2 Public Communications H1 Radio Journalism [na] Sub-editing [na] Television Journalism H1 Plus the following units from other disciplines: Law Media Law H1 Political Science Media and Politics H2 Public Policy Media, Mass Communication and Information Technology Policy [na] Sociology Popular Culture and the Mass Media H2 History weight code 12.5% 12.5% HEJ201/301 HEJ202/302 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HEJ220/320 HEJ219/319 HEJ204/304 HEJ206/306 HEJ218/318 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HEJ209/309 HEJ205/305 HEJ213/313 HEJ207/307 HEJ203/303 12.5% BLA652 12.5% HSA203/303 12.5% HSD227/327 12.5% HGA225/325 Course details (2001) Spreading the Word: A History of Image and Text page 39 H3 12.5% HTA226/326 campus-sem weight code H1 H2 12.5% 12.5% HTL217 HTL219 Hf H1 H2 Hf 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HTL220 HTL317 HTL319 HTL320 Unit Title campus-sem Logic and Philosophy of Science Chance, Coincidence and Chaos H1~Lw1~D1 Choice, Risk and Decision H2 Deviant Logic [na] Epistemology [na] w Introduction to Logic H1~D1~L 1~Bw1 Logic and Possibility [na] Paradoxes [na] Philosophy of Biology [na] Philosophy of Mathematics H2 w Time Travel H1/3~D1~L /1 Ways of Reasoning [na] weight code 12.5% HPA256/356 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HPA294/394 HPA295/395 HPA216/316 HPA291/391 HPA292/392 HPA217/317 HPA218/318 HPA246/346 HPA208/308 HPA275/375 Unit Title campus-sem Natural Environment and Wilderness Studies Geomatics 3c: Advanced Geographic Information Systems (GIS) H2 Biogeography and Climatology H1 Conservation Geomorphology H2 Natural Environment Field Techniques H3~L3~B3 Microclimatology H2 Vegetation Management H1 Fauna Conservation Management H1 weight code 12.5% KGG340 12.5% KGA209 12.5% KGA327 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KGA213 KGA321 KGA331 12.5% KGA332 Unit Title Latin Intermediate Latin A Intermediate Latin B Intermediate Latin Grammar Advanced Latin A Advanced Latin B Advanced Latin Grammar Course details (2001) page 40 Environmental Remote Sensing Environmental Impact Assessment and Decision Making Social & Environmental Accounting Tourism, Sport and Leisure Management and the Natural Environment Mass Social Movements Global Environmental Policy Australian Environmental Policy Asian Environmental Justice Environmental Management Wilderness and Natural Area Management: Natural and Cultural Values Wilderness and Natural Environment Drawing in the Landscape Art, Natural Environment and History Art, Natural Environment and Wilderness Literature and Environment The Literature of Tasmania Sociology of Nature Environmental Ethics Historical Geography Unit Title Philosophy Advanced Buddhist Philosophy Chance, Coincidence and Chaos Chinese Philosophy Choice, Risk and Decision H1 12.5% KGA365 H2 12.5% KGA381 H2 12.5% BFA207/307 H1 12.5% HGA251/351 [na] [na] 12.5% 12.5% BMA272/372 HGA233/333 H2~L2 12.5% HSD229/329 [na] 12.5% HSD230/330 [na] H1 12.5% 12.5% HSD239/339 KGA223/323 H2 12.5% KGA278/378 L1 [na] 12.5% 12.5% FFA235/335 FFD204/304 H3 12.5% FSZ250/350 H1 12.5% FSZ251/351 H1 12.5% KGA272/372 H2 [na] H1 H2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HEA214/314 HGA261/361 HPA277/377 KGA240/340 campus-sem weight code H1 12.5% HPA297/397 H1~Lw1~D1 [na] 12.5% 12.5% HPA256/356 HPA220/320 H2 12.5% HPA294/394 Course details (2001) Contemporary Philosophy: Biotechnology L1 Deviant Logic [na] Ecophilosophy [na] Environmental Ethics H1 Existentialism and Beyond H2 History of Philosophy 1: from Early Greece to the Renaissance H1~D1 History of Philosophy 2: Modern Philosophy H2~D2 Indo–Tibetan Philosophy, History and Culture C3 Introduction to Buddhist Philosophy H1 w Introduction to Logic H1~D1~L 1~Bw1 Law, Society and Morality [na] Logic and Possibility [na] Meaning and Understanding [na] Moral Philosophy H2 Philosophical Psychology [na] Philosophy 2001 H2 Philosophy and Literature [na] Philosophy and the Body [na] Philosophy of Art H1 Philosophy of Feminism H1~D1 Philosophy of Health Care [na] Philosophy of Mathematics H2 Philosophy of Mind [na] Philosophy of Religion [na] Place and Environment [na] Political Philosophy D1 Postmodernism and its Critics [na] Professional Ethics H2~Lv2 Science and Religion L2~D2 Self and Subjectivity L2 The Meaning of Life [na] The Philosophy of Kierkegaard [na] The Philosophy of Nietzsche [na] Time Travel H1/3~D1~Lw/1 page 41 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HPA253/353 HPA295/395 HPA278/378 HPA277/377 HPA225/325 12.5% HPA266/366 12.5% HPA268/368 25% HPA276/376 12.5% 12.5% HPA219/319 HPA291/391 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HPA242/342 HPA292/392 HPA245/345 HPA210/310 HPA203/303 HPA398 HPA201/301 HPA271/371 HPA215/315 HPA270/370 HPA269/369 HPA246/346 HPA207/307 HPA293/393 HPA204/304 HPA289/389 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HPA206/306 HPA212/312 HPA274/374 HPA233/333 HPA209/309 12.5% HPA202/302 12.5% 12.5% HPA230/330 HPA208/308 Course details (2001) Topics in the History of Philosophy: The Philosophy of Berkeley Ways of Reasoning page 42 [na] [na] 12.5% 12.5% HPA214/314 HPA275/375 Unit Title campus-sem Political Science Approaches to International Relations H1 Australian Foreign Policy [na] Australian Political System: Political Parties and Parliament H2 Approaches to International Relations H1 Espionage, Terror and Global Disorder H1 Globalisation and East Asian Politics [na] Media and Politics H2 Parliamentary Internship Political Ideologies H2 Political Thought: Liberal Democracy [na] Politics in Literature and Film [na] Politics of Democratisation, East and West H1 Race and Ethnic Politics [na] Tasmanian Politics and Australian Federalism [na] plus the following cross-listed units: Australian Environmental Policy [na] Business–Government Relations H1~L1 Sex, Drugs and Toxic Waste: The Politics of Regulation [na] Government and the Economy H2~L2 International Organisation: Globalism and Regionalism H1 Ethnic Politics and Religious Nationalism in Asia H2 weight code 12.5% 12.5% HSA202/302 HSA240/340 12.5% HSA241/341 12.5% HSA202/302 12.5% HSA270/370 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HSA258/358 HSA203/303 HSA361/432 HSA210/310 12.5% HSA212/312 12.5% HSA204/304 12.5% 12.5% HSA227/327 HSA201/301 12.5% HSA260/360 12.5% HSD230/330 12.5% HSD208/308 12.5% HSD207/307 12.5% HSD236/336 12.5% HSD232/332 12.5% HMA261/361 Course details (2001) Reporting Asia: Western Media Perceptions of Asia Social and Political Research Survey Research page 43 H1 12.5% HMA260/360 L1~H1 H3 12.5% 12.5% HGA203/303 HGA204/304 Unit Title Psychology Advanced Research Methods Clinical Psychology Cognition and Memory Developmental Psychology Educational Psychology Health & Rehabilitation Psychology Human Abilities Human Neuroscience Individual Differences Learning & Skilled Performance States of Consciousness Organisational Psychology Peace, Conflict & Law Assessment and Research Methods Psychology of Health & Stress Psychophysiology & Emotion Research Methods in Psychology Social Psychology campus-sem weight code H2 H1 H2 H2~L2 H1 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KHA308 KHA305 KHA306 KHA202 KHA319 H1 [na] H1 H1 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KHA209/309 KHA211/311 KHA303 KHA318 H2 [na] L1 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KHA314 KHA217/317 KHA215/315 H2 12.5% KHA212/312 H1 12.5% KHA301 L2 12.5% KHA213/313 H1 12.5% KHA304 H1~L1 [na] 12.5% 12.5% KHA201 KHA207/307 Unit Title Public Policy Asian Environmental Justice Australian Environmental Policy Australian Public Policy Business–Government Relations Executive Government campus-sem weight code [na] 12.5% HSD239/339 [na] H1~L1 12.5% 12.5% HSD230/330 HSD206/306 H1~L1 [na] 12.5% 12.5% HSD208/308 HSD235/335 Course details (2001) Global Environmental Policy Government and the Economy International Organisation: Globalism and Regionalism Media, Mass Communication and Information Technology Policy Policing and Governance Policy Analysis Regional Development Policy Sex, Drugs and Toxic Waste: The Politics of Regulation Sport and Tourism: Policy and Politics Women and Public Policy Approaches to Political Analysis plus the following cross-listed units: Australian Foreign Policy Australian Political System: Political Parties and Parliament Tasmanian Politics and Australian Federalism Social and Political Research Survey Research Understanding Organisations page 44 H2~L2 12.5% HSD229/329 H2~L2 12.5% HSD236/336 H1 12.5% HSD232/332 [na] H1~L1 [na] 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HSD227/327 HSD205/305 HSD209/309 H1~L1 12.5% HSD223/323 [na] 12.5% HSD207/307 H2~L2 [na] 12.5% 12.5% HSD210/310 HSD240/340 H2~L2 12.5% HSG200/300 [na] 12.5% HSA240/340 H2 12.5% HSA241/341 [na] 12.5% HSA260/360 L1~H1 H3 12.5% 12.5% HGA203/303 HGA204/304 H1 12.5% HGA236/336 Unit Title campus-sem Social Ecology Population and Society H1~L1 Social Ecology H2~L2 Social Ecology Internship H1/2 plus the following units from other disciplines: Australian Natural Environments L1~D1 Globalisation L2~D2 Community Health and Medicine Hf weight code 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HGE204/304 HGE203/303 HGE350 12.5% 25% KJG201 KJG302 25% CAM205 Course details (2001) Contemporary Indigenous Tasmania Crime and Criminal Justice Gender and Power Health Sociology Migrants in Australian Society Science, Technology and Contemporary Society Social and Political Research Social Inequality Sociology of Deviance Sociology of Nature Sociology of Youth Economics of Human Resources Environmental and Resource Economics Social & Environmental Accounting Sustainable Communities and Local Environments The Global Space Economy Urban Planning: Space, Place and Society Government and the Economy Policing and Governance Regional Development Policy Social Policy in Welfare States Perspectives on Ageing Unit Title Sociology Change and Order in Contemporary Society Crime and Criminal Justice Cultures and Societies of Southeast Asia Gender and Power page 45 [na] 12.5% HAB206/306 L1~D1 L1~D1 [na] 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HGA206/306 HGA272/372 HGA239/339 H1 12.5% HGA231/331 [na] 12.5% HGA220/320 L1~H1 [na] H1 [na] [na] 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HGA203/303 HGA262/362 HGA259/359 HGA261/361 HGA277/377 H1 12.5% BEA306 H1 12.5% BEA301 H2 12.5% BFA207/307 H2 H2 12.5% 12.5% KGA254/354 KGA208/308 H1 12.5% KGA253/353 H2~L2 H1~L1 12.5% 12.5% HSD236/336 HSD205/305 H1~L1 12.5% HSD223/323 H2~L2 L2 12.5% 12.5% HSD231/331 CNA246 campus-sem weight code H2 12.5% HGA302 L1~D1 12.5% HGA206/306 H2 L 1~D1 12.5% 12.5% HGA254/354 HGA272/372 v Course details (2001) Health Sociology Love, Family and Sexuality: East–West Comparison Magic, Spirituality and Religion Mass Social Movements Migrants in Australian Society Popular Culture and the Mass Media Qualitative Research Methods Science, Technology and Contemporary Society Social and Political Research Social Inequality Social Problems and Social Policy Sociological Analysis of Modern Society Sociology of Deviance Sociology of Nature Sociology of Youth Survey Research The Individual and Society Tourism, Sport and Leisure Understanding Organisations page 46 [na] 12.5% HGA239/339 [na] 12.5% HGA212/312 [na] [na] 12.5% 12.5% HGA219/319 HGA233/333 H1 12.5% HGA231/331 H2 12.5% HGA225/325 H1~L2 12.5% HGA230/330 [na] 12.5% HGA220/320 L1~H1 [na] 12.5% 12.5% HGA203/303 HGA262/362 [na] 12.5% HGA223/323 H2~L2~D2 H1 [na] [na] H3 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HGA202 HGA259/359 HGA261/361 HGA277/377 HGA204/304 [na] 12.5% HGA221/321 H1 12.5% HGA251/351 H1 12.5% HGA236/336 Unit Title campus-sem Women's Studies Contemporary Feminist Thought: Themes, Issues and Conflicts H2 Sexualities: Histories, Representation, Politics H1 plus the following units from other disciplines: Aboriginal Women L1~H1 American Women Writing (Nineteenth Century) [na] British Literature 1800–1850 H1 Gender and Nation H2 weight code 12.5% HAF215/315 12.5% HAF202/302 12.5% HAB232/332 12.5% HEA258/358 12.5% 12.5% HEA257/357 HEA289/389 Course details (2001) page 47 Medieval Writing [na] 12.5% HEA213/313 Power, Pleasure and Perversion [na] 12.5% HEA254/354 Reading the Classics: Ovid and Chaucer [na] 12.5% HEA227/327 Sexuality and the Subject in Fiction [na] 12.5% HEA286/386 Education of Women and Girls [a] H? 16.67% ESN773 Language, Gender and Communication in Education [a] H? 16.67% ESN771 Literature, Gender and Education [a] H? 16.67% ESN772 Love, Family and Sexuality: East–West Comparison [na] 12.5% HGA212/312 Fashioning the Body H2 12.5% FST207/307 Feminist Aesthetics [na] 12.5% FST209/309 Gender in European Thought H2 12.5% HTA205/305 Islam, Law and Women – Historical and Contemporary Perspectives H1 12.5% HTA223/323 Women in Greek and Roman Antiquity [na] 12.5% HTC221/321 Philosophy and the Body [na] 12.5% HPA271/371 Philosophy of Feminism H1~D1 12.5% HPA270/370 Sociology of Law H2 12.5% BLA616 [a] for availability and details of these units, please contact the Faculty of Education Groups 2A & 3A Units offered outside the BA schedule as the Faculty may approve with a combined weighting of not more than 75% at level 200/300. Fine Arts study in the BA BA students wishing to undertake study in Fine Arts may do so and still be within the specifications of their degree course. Students must attend an interview, bringing their portfolio with them. A Fine Arts major for a BA student can comprise a major in Art and Cultural Theory or a major which is largely based on studio units, but which must include a minimum of 25% Art Theory units. The total units studied must not exceed 100% (25% at level 100 and 75% over levels 200 and 300). Course details (2001) page 48 1. Sample major – Studio (Hbt) Year 1 Printmaking 125% Year 2 Printmaking 2A 25% Art Theory 1A 12.5% Year 3 Printmaking 3A 25% Art Theory 1B 12.5% Major total 100%<tbz> 2. Sample major – Art & Cultural Theory (Hbt & Ltn) Year 1 Theory 1 25% Year 2 Theory 2 25% Elective (eg Drawing) 12.5% Year 3 Theory 3 25% Elective (eg Drawing) 12.5% Major total 100%<tbz> 3. Sample major – Studio (Ltn) Year 1 Studio Survey 25% Year 2 Ceramics 25% Intro to Cultural Practices 1 12.5% Year 3 Ceramics 25% Intro to Cultural Practices 2 12.5% Major total 100%<tbz> Bachelor of Arts with Honours (Abbreviation: BA(Hons)) Course code: R4A This on-campus, 1 year full time (or, at the discretion of the relevant School, 2 consecutive years part time) course is available at Hobart and Launceston. Candidates whose work has been interrupted by illness or other unavoidable cause may be permitted to complete their course over a longer period of time. Candidates wishing to apply for a place must submit an application form, obtainable from Student Administration, by mid-December of the year before that in which they wish to commence study. The accompanying Schedule lists the disciplines which offer honours courses. Admission & prerequisites Candidates for the degree of Bachelor of Arts with Honours: Course details (2001) • • • • • page 49 must have qualified for admission to the degree of Bachelor of Arts, or another approved Bachelor degree, in this University or another approved tertiary institution; if a candidate from another approved tertiary institution, must have qualified for admission to a fourth year honours course in the proposed discipline of study or a cognate discipline; are required by Faculty to have a Grade Point Average (GPA) of 6.0 or better in the 200 and 300 level units forming a major in that discipline. Currently, the GPA is calculated on the basis of a HD=9, DN=7.5, CR=6.5, PP/FP=5.5; TP=5.0, NN=4.0 for the units at 200 and 300 level in the proposed discipline; if undertaking a combined honours program, should qualify for entry in both disciplines to be studied; should consult the following schedule for full details of discipline offerings as some disciplines prescribe additional units and a standard in the major higher than the Faculty minimum GPA for entry to their honours program. Admission in semester 2 is possible in some programs. Contact the relevant school for information. BA(Hons) course specifications are published in the Calendar, copies of which are held in the University Library, Student Administration, School Offices and the Faculty Office, and is available on the Web starting at http://www.admin.utas.edu.au/HANDBOOKS/handbooks.html Course objectives The Bachelor of Arts with Honours course allows candidates to pursue in-depth study in the discipline or disciplines of their choice and at the same time to demonstrate a level of excellence that will allow them to pursue higher degree studies. Career outcomes In Australia and around the world, employers are increasingly seeing graduates who can speak and write clearly; who are computer literate and understand how to use technology; who know about other countries, cultures and societies; who can solve problems creatively; and who have developed that flexibility of thought which technical and vocational training rarely encourages. Graduates with a Bachelor of Arts (Honours) degree find jobs in, for example: advertising, journalism, radio and television; the arts, heritage and museology; diplomacy, interpreting and tourism; management, marketing and administration; politics, the public service, the police force and the armed forces; teaching, research and publishing; psychology, counselling and community work. Course details (2001) page 50 Course structure A candidate for the degree must pursue either a single course of study in one honours discipline, or a joint course of study in two honours disciplines. The disciplines which may be studied as single honours courses are those listed in the schedule which follows. Unless exempted by the Faculty, a candidate may not enrol in the Honours course in a discipline listed unless the corresponding prerequisite requirements have been obtained. Joint honours courses consist of such combinations of the disciplines listed in the schedule as Faculty may from time to time approve. A candidate may not enrol in a joint honours course unless permitted to do so by the Faculty on the recommendation of the heads of the two Schools concerned. Candidates must either have passed the prerequisite units prescribed in the schedule for both the proposed disciplines or have otherwise satisfied the heads of the two Schools that they are sufficiently qualified to undertake the joint course. Candidates undertake a program comprising a number of coursework units and a research thesis. Candidates should consult individual discipline entries for full details (page references are given in the Schedule of Courses). Articulation A person holding an award from this University or another approved institution may be permitted by the Faculty to count towards the degree units from the former award in accordance with policies in force at the time of admission. Persons who have successfully completed the Bachelor of Arts with Honours may apply for entry to a higher degree (Masters or PhD) in accordance with policies governing candidature for such admission. General provisions The Dean may, on the recommendation of the head of School, grant a candidate an extension of time for the completion of a thesis where a thesis is required as part of an honours examination. Except by special permission of the Faculty there is no re-examination for honours in any one discipline. The classes of honours are First Class, Second Class, and Third Class. There is an upper and lower division in the second class. Candidates who have obtained honours in one course may proceed to honours in another course provided that they undertake a further year's work and Course details (2001) page 51 provided that the discipline or disciplines which comprise the earlier course are not included in the later course. Schedule of Courses Discipline campus-semprerequisites code Aboriginal Studies 4 (Honours) Hf~LfMajor in Aboriginal Studies or cognate discipline, including satisfaction of the Faculty Grade-Point Average HAB400/401 Asian Studies 4 (Honours) HfMajor, including satisfaction of the Faculty Grade-Point Average, plus a completed first year of a relevant language other than English, or equivalent. By the end of the honours year, students will have undertaken additional language study so as to demonstrate an ability to read competently in that language. HMA400/401 Chinese 4 (Honours) Hf~LfMajor with GPA of 7.0 or higher; or a double major with GPA of 6.5 or higherHMC400/401 Classics 4 (Honours) HfMajor in Ancient Civilisations (including Latin 1 – HTL or equivalent) OR a Major in Latin and satisfaction of the Faculty Grade-Point AverageHTC400/401 Geography Honours LfGeography major, including satisfaction of the Faculty Grade-Point Average (or an appropriate background approved by Faculty)KJG400/401 English 4 (Honours) H~LMajor, with Grade-Point Average of 6 or higher in 75% of English units at levels 200/300 HEA400/401 French 4 (Honours) H112.5% major with a GPA of 7 or better, and either an HD for HEF301 French Language Skills 3 or a DN for HEF302 French Language Skills 3BHEF400/401 Geography and Environmental Studies 4 Hfbachelor degree with a sound major in Geography and Environmental Studies or another discipline relevant to the thesis topic and satisfying the Faculty honours entry requirements for major and GPA.KGA402/403 German 4 (Honours) HfA 112.5% major in German and GPA of 7 or better. HEG400/401 History 4 (Honours) H~LMajor, with Grade-Point Average of higher than 6.5 HTA498/499 Indonesian 4 (Honours) Hf~LfMajor, with Grade-Point Average of 7.0 or better HMN400/401 Japanese 4 (Honours) Hfone Distinction (DN) and two Credits (CR) in HMJ306–308. Further passes in HMJ330–335 are recommended HMJ400/401 Philosophy 4 (Honours) Hf~LfMajor, including satisfaction of the Faculty Grade-Point AverageHPA400/401 Course details (2001) page 52 Political Science 4 (Honours) HMajor, with Grade-Point Average of 6.5 or higher HSA400/401 Psychology 4 (Honours) HfDouble major, containing at least 175% in the discipline, including KHA340 or KHA311, and satisfaction of the Faculty Grade-Point AverageKHA400/401 Public Policy 4 (Honours) H~LMajor, with Grade-Point Average of 6.5 or higher HSD400/401 Sociology 4 (Honours) Hf~LfMajor, including HGA202, HGA203/303 and satisfaction of Faculty Grade-Point Average. HGA400/401 Women's Studies 4 (Honours) HfFaculty requirement for entry to Honours, a major in Women's Studies and approval of the Coordinator of Women's Studies. HAF400/401 Bachelor of Contemporary Arts (Abbreviation: BCA) Course code: F3J This on-campus 3-year full-time course is offered by the School of Visual & Performing Arts in Launceston. Part-time study is also available. Admission & prerequisites Applicants are normally expected to have satisfied the University's admission requirements. Applicants intending to specialise in 2D Studies or 3D Studies will be required to submit a portfolio of recent artwork (which may include slides, photographs or video). Where there are circumstances which prevent an applicant attending for interview, a brief statement outlining interest in the course, including any relevant experience or qualifications, should be provided, including a portfolio of recent artwork. Applicants intending to specialise in Theatre Studies are required to attend an audition and interview. Overseas and interstate applicants may submit a video-tape of a recent performance. Students intending to specialise in Theory Studies are required to attend an interview in which they will either present a portfolio of recent artwork or present for audition, as appropriate. Course details (2001) page 53 Completion of either TCE Art, Craft & Design or Speech & Drama is desirable but not essential. Course objectives The educational objectives of the 3-year degree are: 1. 2. 3. To provide a foundation study in the methods, skills and processes involved in visual or performing arts practices; To familiarise students with conceptual concerns and theoretical debates surrounding contemporary visual and performing arts practices; To provide a program that creates an opportunity for students to go on to further study at Honours level or to undertake a degree program in a complementary area, eg cultural tourism, business, hospitality. Career outcomes Graduates from the Bachelor of Contemporary Arts will find employment in a variety of positions within the visual and performing arts professions. Students who complete a stream in either 2D Studies or 3D Studies or Theory Studies may work as curators, gallery administrators, researchers and teachers, as well as participating in individual and group-generated projects and studio practice. Students who complete the Theatre Studies stream may work in professional theatre as actors, stage managers or technicians, film and television, or public relations. Course structure To meet the requirements of the BCA, students must complete a total of 300%, of which normally 100% will be at level 100, 100% at level 200 and 100% at level 300. Students must also meet the requirements for a major stream in either Theatre Studies, 2D Studies, 3D Studies or Theory Studies. Year 1 All students must complete the core theory units Introduction to Cultural Practices 1 and 2 (2 x 12.5%). Students choose Year 1 core units from the schedules for one of Theatre Studies, 2D Studies, 3D Studies or Theory Studies. Year 2 All students complete 25% in Theory Studies units. Students who elect to do a major stream in either Theatre Studies, 2D Studies or 3D Studies must complete 50% of units at level 200 in the chosen stream. Students who choose the Theory Studies stream must do an additional 25% of units at level 200 in Theory Studies. The remaining weighting (50%) is made up of electives, comprising Course details (2001) page 54 level 200/300 units from any of the other schedules, approved complementary TAFE modules or units from other courses in the University. Year 3 Students in the Theatre Studies stream complete the units Theatre Project 1 and 2 (50%). Students in the streams for 2D Studies or 3D Studies complete the units Studio Project 1 and 2 (50%). Students in the Theory Studies stream choose 50% of Theory units at level 300. The remaining weighting (50%) for all students is made up of electives, comprising level 200/300 units from any of the other schedules, approved complementary TAFE modules or units from other courses in the University. Students who intend to apply for an honours course must complete a total of 75% of Theory Studies units, including the core Year 1 theory units Introduction to Cultural Practices 1 and 2. Sample Course 1 – Major in 2D Studies INSERT BCA1.PICT HERE Sample Course 2 – Major in Theatre Studies INSERT BCA2.PICT HERE Sample Course 3 – Major in Theory Studies INSERT BCA3.PICT HERE Articulation Applicants who are accepted for admission, and who have satisfactorily completed a related TAFE diploma, will be awarded status for up to one year or one-third of the degree requirement (100% total). Students commencing study in the BCA will normally be granted a minimum of 25% credit towards the BCA if they have completed another previous degree. Credit for another incomplete degree will be given on a case by case basis. Continuing University students will be able to articulate from the BFA at Launceston and from the BPA (Theatre). On completion of the BCA, graduates will be able apply for entry into honours programs in Fine Arts and in Performing Arts. Articulation with TAFE Course details (2001) page 55 All students in the degree program can count up to an equivalent of 50% of approved complementary TAFE modules, of which no more than 25% may count towards the nominated major stream. For the purposes of credit transfer, each TAFE module has an equivalent weighting of 12.5%. The approved complementary TAFE modules are as follows: 11-449 Jewellery Introduction 11-455 Jewellery – Fabrication Techniques 11-456 Jewellery Casting 11-457 Jewellery Production Casting 11-443 Printmaking Introduction 11-589 Etching Techniques 11-591 Intaglio Drypoint 11-594 Stone Lithography 11-610 Colour Etching 11-690 Two Shaft Weave 11-684 Introduction to Tapestry 11-693 Dyeing 11-695 Introduction to Colour 51-139 Intro to Computers for Graphic Arts Units from other courses Students are permitted to enrol in units from another degree course to count towards the BCA, provided that the weighting of these units totals no more than 25% at level 200 and 25% at level 300. Students enrolled in other courses The School of Visual & Performing Arts offers students a sequence of 12.5% elective units. Students must obtain formal School approval from the lecturer-in-charge prior to enrolment. Schedule A – Theatre Studies stream Course details (2001) page 56 Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Principles and Practice of Theatre 1: Australian Drama L1 12.5% FPB101 Theatre Skills 1 L1 12.5% FPB103 Technical Theatre L1 12.5% FPB105 Introduction to Cultural Practices 1 L1 12.5% FFA102 Principles and Practice of Theatre 2: The Development of Western Drama L2 12.5% FPB102 Theatre Skills 2 L2 12.5% FPB104 Performance and Production L2 12.5% FPB106 Introduction to Cultural Practices 2 L2 12.5% FFA103 Year 2 Classical Production [na] 12.5% FPB201 Classical Performance [na] 12.5% FPB202 Devised Performance [na] 12.5% FPB203 Theatre Skills 3 [na] 12.5% FPB204 Plus 25% from level 200/300 units listed in the Theory Studies Schedule plus 25% elective units from any of the following: Advanced Technical Theatre [na] 12.5% FPB251/351 Professional Presentation Skills [na] 12.5% FPB252/352 Stage Design [na] 12.5% FPB253/353 Lighting Design for Installations and Performances [na] 12.5% FPB254/354 Scriptwriting [na] 12.5% FPB255/355 Voice and Media [na] 12.5% FPB256/356 Acting for Television and Film [na] 12.5% FPB257/357 Wayang Shadow Puppet Theatre L2 12.5% HMN210/310 or other level 200/300 units listed in the BCA schedule, or approved modules from TAFE, or units from other courses offered in the University Year 3 Theatre Project 1: Student Directed Production [na] 12.5% FPB302 Theatre Project 1: Graduate Production [na] 12.5% FPB303 Plus 50% elective units chosen from level 200/300 units listed in the BCA schedule, or approved modules from TAFE. Student may include 25% of units offered by other courses in the University. Course details (2001) page 57 Schedule B – 2D Studies stream Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Introduction to Drawing 1 L1/2 12.5% FFD100 Introduction to Two Dimensional Studies L1 12.5% FFE102 Introduction to Three Dimensional Studies L1 12.5% FFE103 Introduction to Cultural Practices 1 L1 12.5% FFA102 Introduction to Drawing 2 L1/2 12.5% FFD101 Introduction to Cultural Practices 2 L2 12.5% FFA103 Plus 25% from the following: Introduction to Ceramics L2 12.5% FFC110 Introduction to Textiles L2 12.5% FFX110 Introduction to Sculpture L2 12.5% FFS110 Introduction to Printmedia L2 12.5% FFR110 Introduction to Painting L2 12.5% FFP110 Year 2 Choose 50% from the following, including at least 25% from one of Painting, Photography, Digitial Imaging or Drawing: Contemporary Painting Practices L1 12.5% FFP250/350 Painting: Self-directed Project L1 12.5% FFP201/301 Painting Media, Processes and Approaches L1 12.5% FFP202/302 Painting: Material/Descriptive Exploration L2 12.5% FFP203/303 What are the Limits of Painting? L2 12.5% FFP204/304 The Seduction of Black and White: Advanced Techniques and Concepts for the Photographic Medium L1 12.5% FFR201/301 Printmedia Project [na] 12.5% FFR202/302 Digital Project L2 12.5% FFR203/303 Looking Out/Looking In: Approaches to the Landscape L1 12.5% FFR204/304 Photography as Service L1 12.5% FFR250/350 Computer Imaging L2 12.5% FFR252/352 Web Page Design L1 12.5% FFR205/305 Course details (2001) page 58 Drawing: The Body [na] 12.5% FFD201/301 Drawing: Questioning the Practice [na] 12.5% FFD200/300 Drawing into Print L2 12.5% FFD202/302 Drawing: Approaches to Abstraction L1 12.5% FFD203/303 Drawing in the Landscape [na] 12.5% FFD204/304 Plus 25% from level 200/300 units listed in the Theory Studies schedule plus 25% elective units chosen from level 200/300 units listed in the BCA schedule, or approved complementary modules from TAFE, or units offered by other courses in the University. Year 3 Studio Project 1 L1 25% FFE302 Studio Project 2 L2 25% FFE303 Plus 50% elective units chosen from level 200/300 units listed in the BCA schedule, or approved complementary modules from TAFE. Students may include 25% of units offered by other courses in the University. Schedule C – 3D Studies stream Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Introduction to Drawing 1 L1/2 12.5% FFD100 Introduction to Two Dimensional Studies L1 12.5% FFE102 Introduction to Three Dimensional Studies L1 12.5% FFE103 Introduction to Cultural Practices 1 L1 12.5% FFA102 Introduction to Drawing 2 L1/2 12.5% FFD101 Introduction to Cultural Practices 2 L2 12.5% FFA103 Plus 25% from the following: Introduction to Ceramics L2 12.5% FFC110 Introduction to Textiles L2 12.5% FFX110 Introduction to Sculpture L2 12.5% FFS110 Introduction to Printmedia L2 12.5% FFR110 Introduction to Painting L2 12.5% FFP110 Year 2 Choose 50% from the following, including at least 25% from one of Ceramics, Sculpture or Textiles: Form Follows Function: The Art of the Potters Wheel L1 12.5% FFC201/301 The Object in Contemporary Popular Culture [na] 12.5% FFC202/302 Course details (2001) page 59 Ceramics: Precious and Ephemeral L1 12.5% FFC250/350 The Return of the Figure L2 12.5% FFC203/303 The Pot as Narrative L2 12.5% FFC204/304 Ceramics for the Kitchen Dresser [na] 12.5% FFC251/351 Revisiting the Figure [na] 12.5% FFS201/301 Student Initiated Sculpture Project 1 L1 12.5% FFS202/302 Small Scale Sculpture L1 12.5% FFS251/351 The Art of Adding and Removal [na] 12.5% FFS203/303 Student Initiated Sculpture Project 2 L2 12.5% FFS204/304 Sculpture: Fine Art Metal Casting L2 12.5% FFS250/350 All Dressed Up and Going Places – The Art of Costume 1 L1 12.5% FFX202/302 Dressing up, Dressing Down: The Art of Costume 2 L2 12.5% FFX203/303 Plus 25% from level 200/300 units listed in the Theory Studies schedule plus 25% elective units chosen from other level 200/300 units listed in the BCA schedule, or approved complementary modules from TAFE, or units offered in other courses in the University Year 3 Studio Project 1 L1 25% FFE302 Studio Project 2 L2 25% FFE303 Plus 50% from level 200/300 units listed in the BCA schedule, or approved complementary modules from TAFE. Students may include 25% of units offered by other courses in the University Schedule D – Theory Studies stream Unit Title Level 100 Required units [a] Introduction to Drawing 1 Introduction to Two Dimensional Studies Introduction to Three Dimensional Studies Introduction to Cultural Practices 1 Introduction to Drawing 2 campus-sem weight code L1/2 12.5% FFD100 L1 12.5% FFE102 L1 12.5% FFE103 L1 L1/2 12.5% 12.5% FFA102 FFD101 Course details (2001) page 60 Introduction to Cultural Practices 2 L2 12.5% FFA103 [a] Note: Subject to approval from the Head of School, students may replace studio or drawing units with level 100 Theatre Studies units or level 100 units from other courses. plus 25% [a] from the following: Introduction to Ceramics L2 12.5% FFC110 Introduction to Textiles L2 12.5% FFX110 Introduction to Sculpture L2 12.5% FFS110 Introduction to Printmedia L2 12.5% FFR110 Introduction to Painting L2 12.5% FFP110 Level 200/300 Choose 100% from the following: The Construction of Genius [na] 12.5% FFA250/350 Romance and Realism [na] 12.5% FFA251/351 The Avant-Garde and the Necessity of the New [na] 12.5% FFA252/352 The Arts in Revolt [na] 12.5% FFA254/354 Professional Practice [na] 12.5% FFA233/333 Gallery Studies L4 12.5% FFA234/334 Wilderness and Natural Environment L1 12.5% FFA235/335 Subject to Sub-Dean approval, students may also include up to 25% from the units offered by other Schools: any Humanities & Social Science units listed in the BA Schedule; or the following units in Architecture: History & Theory in Design 3 L1 12.5% KDA212 History and Theory in Design 4 L2 12.5% KDA222 History & Theory in Design 5 L1 12.5% KDA312 History and Theory in Design 6 L2 12.5% KDA322 Theory in Design 1 (BArch) L2 12.5% KDA422 Plus 100% elective units chosen from level 200/300 units listed in the BCA schedule, or approved modules from TAFE. Students may include 50% of units offered by other courses in the University Bachelor of Fine Arts (Abbreviation: BFA) Course details (2001) page 61 Course code: F3E This on-campus 3-year (minimum) full-time course is offered by the Faculty of Arts through the Tasmanian School of Art at Hobart and the School of Visual and Performing Arts at Launceston. Part-time study is also available. There will be no new intake into this course on the Launceston campus in 2001. New students at Launceston enrol in the Bachelor of Contemporary Arts (see page B-xx). Admission & prerequisites All applicants will be required to submit a portfolio of recent art work (which may include slides, photographs or video) and attend an interview. Where there are circumstances which prevent an applicant attending for interview, a brief statement outlining interest in the course, including any relevant experience or qualifications, should also be provided, including a portfolio of recent artwork. It is a distinct advantage for applicants to have completed TCE Art, Craft & Design or have equivalent experience and/or qualifications, since admission is competitive. Course objectives The Bachelor of Fine Arts is designed to give students a broad visual arts education and to offer them a wide range of possible disciplines in which to undertake a major program of study. The course requires a commitment to studio-based study, and also offers a substantial program in Art Theory, which includes studies in art history, theory and film. There are opportunities for specialised study in various disciplines, all of which are informed by a rigorous and challenging ongoing theoretical debate. Majors may be undertaken in a range of Studio practices. Students may also choose to do an Art and Cultural Theory major in which they specialise in units from the Art Theory program and are eligible to enrol in a number of units cross-listed with other disciplines. Career outcomes Graduates from the Bachelor of Fine Arts find employment in a variety of positions within the arts professions, including curatorial work, gallery administration, research and teaching, as well as participating in individual and group-generated projects and studio practice. Course structure Level 100 Course details (2001) page 62 (Hobart) Students enrol in at least two Studio A units (2 x 25% weight), and Introduction to Art and Design Theory 1A and 1B (2x12.5%). Additionally they enrol in a further unit from either the Studio A or Studio B list (25%). Studio major – level 200 (Hobart) Students enrol in one Studio A unit (50% weight) and make up the remaining 50% from the level 200 schedule. This may be a multiple selection of 12.5% or 25% units or a second 50% Studio A unit. [Note: FST200/300 Art and Design Theory 2/3 plus a further 12.5% Art and Design Theory unit (normally taken after FST200/300) must be completed at levels 200 or 300]. (Launceston) Students enrol in two level 200 Art Theory units and a level 200 Studio unit, and make up the remaining 25% with a selection of electives. Studio major – level 300 (Hobart) Students enrol in one Studio A unit (50% weight) and make up the remaining 50% from the level 300 schedule. This may be a multiple selection of 12.5% or 25% units or a second 50% Studio A unit. Note: Students must complete a studio major sequence by enrolling in Studio A units at level 100 (25%), level 200 (50%) and level 300 (50%) normally in the same studio. Students may enrol in a level 300 Studio A unit (50%) having gained a Distinction in that same studio in a 25% unit at level 200. (Launceston) Students enrol in either a level 300 Studio unit or another level 200 Studio unit. The remaining 50% can be made up with either a selection of electives or an additional level 200 Studio unit. Notes: • • Normally students enrol in a level 300 Studio unit in third year. Students intending to proceed beyond level 300, i.e. to honours and postgraduate studies, will need to complete 2 semesters of level 300 Art Theory and a level 300 Studio unit. Art and Cultural Theory major – level 200/300 (Hobart ) Students must complete: • • • a sequence of Art Theory units at levels 200 and 300 to the value of 75–100% in total; 25% of them can be taken in units which are cross-listed from other Schools (see Art and Cultural Theory schedule of units below). At least 25% weighting of units should be from level 300 units: level 200 and/or level 300 studio-based units to the total value of 50%; and level 200/300 electives to the value of 50–75%. Course details (2001) page 63 Dipback Normally students complete 100% at each of levels 100, 200 and 300. Subject to Sub-Dean approval, students are permitted to count towards their degree a 'dipback' of 25% in units at a lower level. Articulation Students who are accepted for transfer from other institutions can be given status for equivalent studies satisfactorily completed in bachelor degree programs in other universities. Applicants who are accepted for admission, and who have satisfactorily completed a related TAFE diploma, can be awarded status for one year or one-third of the degree requirement. Students who have completed another previous degree and are commencing study in the BFA will normally be granted 25% credit towards the BFA. Credit is granted for study completed within the past ten years; but for those seeking credit for qualifications completed more than ten years ago, consideration will be given to evidence of continuing professional practice in the field. Transfer provisions A student successfully completing all level 100 units of the course at one campus will be eligible to transfer to units at level 200 at the other campus with full status for level 100 units. However, they would normally only be able to enrol in studios at level 200 if they have completed the prerequisite level 100 studio (full year level 100 Studio for Hobart students transferring to Launceston; semester 1 Studio Survey, full year Drawing and semester 2 Studio for Launceston students transferring to Hobart). In exceptional circumstances the sub-dean may approve an appropriate set of subjects to serve as a prerequisite where a stated prerequisite is not met. Units from other courses Students are permitted to enrol in units from another degree course to count towards the BFA, provided that the weighting of these units totals no more than 75%, being no more than 25% in each of years 1, 2 and 3. Students enrolled in other courses The School of Visual and Performing Arts at Launceston offers students a selection of elective units. Schedule – Hobart Unit Title campus-sem weight code Course details (2001) page 64 Level 100 Art and Design Theory units – compulsory Introduction to Art and Design Theory 1A H1 12.5% FST101 Introduction to Art and Design Theory 1B H2 12.5% FST102 Choose 2 Studio A units (compulsory) AND either 1 Studio A or Studio B unit(s) or units offered by other Schools to the value of 25% Studio A units E-Media 1 Hf 25% FSE110 Furniture Design 1 Hf 25% FSF110 Graphic Design 1 Hf 25% FSG110 Painting 1 Hf 25% FSP110 Photography 1 Hf 25% FSH110 Printmaking 1 Hf 25% FSR110 Sculpture 1 Hf 25% FSS110 Studio B units Introduction to Mould-Making 1 H1 12.5% FSC101 Introduction to Life Drawing H1/2 12.5% FSD150 Media and Methods in Drawing H1/2 12.5% FSD153 Woodskills 1A Hf 25% FSW150 Level 200 Where there are alternative unit codes (e.g. FST201/301) the unit may be taken either at level 200 or level 300. When students enrol, depending on whether they wish to study a unit as a level 200 unit or a level 300 unit, they should use the appropriate code (e.g. FST201 is the level 200 code, and FST301 is the level 300 code). Students choose one unit from Studio A (compulsory), and other units from Studio A, Studio B or Art and Design Theory units to the value of 50%. Students may take units offered by another School in the University, up to a maximum of 25% in year 2 in place of Studio B units to that value. Note 1: Students must complete FST200 or FST300 plus a further 12.5% Art and Design Theory unit at level 200 or 300 (normally taken after FST200/300) Note 2: Major Study Students must complete a sequence of Studio A units at level 100 (25%), level 200 (50%) and level 300 (50%) normally in the same studio. Students may take a level 300 Studio A unit (50%) having gained a Distinction result in that same studio in a 25% unit at level 200. Art and Design Theory 2/3 H1 12.5% FST200/300 Australian Art of the 1970s and 1980s H2 12.5% FST201/301 Cinema H1 12.5% FST202/302 Postmodernism and Visual Culture H1 12.5% FST203/303 Course details (2001) Performance Picturing the Wilderness Contemporary Craft and Design Fashioning the Body Feminist Aesthetics 'Follow the White Rabbit': Fairy Tale, Fable and Cyber Fiction Fantasy Decor Contemporary Art of the Asia-Pacific Region Studio A units E-Media 2 Furniture Design 2 Graphic Design 2 Painting 2 Photography 2 Printmaking 2 Sculpture 2 Studio B units Design Drawing Digital Imaging B Life Drawing: Personal Project A Life Drawing: Personal Project B Image Development: Personal Project A Image Development: Personal Project B Digital Imaging A Digital Imaging B Desktop Publishing WWW (World Wide Web) Design Time-based Multi-Media Sound A Sound B The Moving Image Interactive Installation Digital 3D Modelling, Scenography and Animation Furniture Design 2A Graphic Design 2A Photography 2A Painting 2A page 65 [na] H3 12.5% 12.5% FST204/304 FST205/305 [na] H2 [na] 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% FST206/306 FST207/307 FST209/309 H2 H2 12.5% 12.5% FST210/310 FST212/312 H2 12.5% FST213/313 Hf Hf Hf Hf Hf Hf Hf 50% 50% 50% 50% 50% 50% 50% FSE210 FSF210 FSG210 FSP210 FSH210 FSR210 FSS210 H2 H2 12.5% 12.5% FSB275 FSE251/351 H1 12.5% FSD255/355 H2 12.5% FSD256/356 H1 12.5% FSD257/357 H2 H1/2 H2 [na] 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% FSD258/358 FSE250/350 FSE251/351 FSE252/352 H2 H1 H1 H2 H2 H2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% FSE253/353 FSE254/354 FSE256/356 FSE257/357 FSE258/358 FSE259/359 H1 Hf Hf Hf Hf 12.5% 25% 25% 25% 25% FSE260/360 FSF250 FSG250 FSH250 FSP250 Course details (2001) page 66 Printmaking 2A Hf 25% FSR250 Sculpture 2A Hf 25% FSS250 Woodskills 2A H1 12.5% FSW250 Art, Natural Environment and History H3 12.5% FSZ250/350 Art, Natural Environment and Wilderness H1 12.5% FSZ251/351 Level 300 Students choose one unit from Studio A (compulsory), and other units from Studio A, Studio B or Art and Design Theory units to the value of 50%. Students may take units offered by another School in the University, up to a maximum of 25% at level 300 in place of Studio B units to that value. See Notes 1 and 2 (Level 200) above. Art and Design Theory units See Art and Design Theory units (year 2) above Studio A units Ceramics 3 Hf 50% FSC310 E-Media 3 Hf 50% FSE310 Furniture Design 3 Hf 50% FSF310 Graphic Design 3 Hf 50% FSG310 Painting 3 Hf 50% FSP310 Photography 3 Hf 50% FSH310 Printmaking 3 Hf 50% FSR310 Sculpture 3 Hf 50% FSS310 Studio B units Drawing units, FSD350-358 (see Level 200 listing) above Furniture Design 3A Hf 25% FSF350 Graphic Design 3A Hf 25% FSG350 Photography 3A Hf 25% FSH350 Painting 3A Hf 25% FSP350 Printmaking 3A Hf 25% FSR350 Sculpture 3A Hf 25% FSS350 E-Media units, FSE350–353 and FSE356–360 (see Level 200 listing) above Natural Environment and Wilderness, FSZ350 and FSZ351 (see Level 200 listing) above Schedule – Launceston Unit Title campus-sem weight code There is no new intake into the BFA on the Launceston campus in 2001. Level 200/300 Over the remaining two years of the course (200%), students choose two level 200 Art Theory units (25%) and two Studio units (100%). The remaining 75% can be made up with either another level 200 Studio unit and/or elective units. Students planning to proceed to Honours and postgraduate Course details (2001) page 67 study will need to complete two level 300 Art Theory units and a level 300 Studio unit. Art Theory units A Brief History of 20th-Century Art L1 12.5% FFA202/302 Professional Practice [na] 12.5% FFA233/333 Gallery Studies L4 12.5% FFA234/334 Wilderness and Natural Environment L1 12.5% FFA235/335 The Body in Art L2 12.5% FFA240/340 Landscape and Issues of Postcolonialism in Australian Art [na] 12.5% FFA241/341 Research Seminar Lf 25% FFA300/301 Studio units Ceramics 2 Lf 50% FFC210 Ceramics 3 Lf 50% FFC310 Painting 2 Lf 50% FFP210 Painting 3 Lf 50% FFP310 Printmedia 2 Lf 50% FFR210 Printmedia 3 Lf 50% FFR310 Sculpture 2 Lf 50% FFS210 Sculpture 3 Lf 50% FFS310 Textiles 2 Lf 50% FFX210 Textiles 3 Lf 50% FFX310 Elective units Students may select elective units from level 200/300 units listed in schedules B, C and D of the Bachelor of Contemporary Arts, as well as Theatre electives listed in Schedule A. (See page B-xx). Art and Cultural Theory – Hobart Students wishing to undertake a major in Art and Cultural Theory select units from the Art and Design Theory schedule and may take up to 25% from the units listed below. Unit Title Critical Theory Cultures and Societies of Southeast Asia Japanese Film 'Just like in Thelma and Louise': Feminism and Film LA Noir: Film Noir and Hollywood campus-sem H2 weight 12.5% code HEA260/360 H2 H2~Lv2 12.5% 12.5% HGA254/354 HMJ334 [na] 12.5% HEA278/378 [na] 12.5% HEA279/379 Course details (2001) Le grand écran: A History of French Cinema Philosophy of Art Popular Culture and the Mass Media Popular Fiction: Texts and Audiences Post-1945 German Film Postmodernism and its Critics Power, Pleasure and Perversion Sociology of Nature page 68 [na] H1 12.5% 12.5% HEF230/330 HPA215/315 H2 12.5% HGA225/325 H1 H2 12.5% 12.5% HEA267/367 HEG212/312 [na] 12.5% HPA206/306 [na] [na] 12.5% 12.5% HEA254/354 HGA261/361 Bachelor of Fine Arts with Honours (Abbreviation: BFA(Hons)) Course code: F4A This on-campus full-time (minimum 1 year), or part-time (minimum 2 years) course is offered by the Faculty of Arts through the Tasmania School of Art at Hobart and the School of Visual and Performing Arts at Launceston. Admission & prerequisites On successful completion of a Fine Arts degree, a candidate may make application to undertake a further honours year. Prerequisites for entry into the honours year apply: a candidate shall normally be expected to have gained at least distinctions in 75% of semester units during undergraduate study, 25% of which must be in the final year of the major unit completed. Candidates are also expected to have completed 75% in units offered in Art and Design Theory at levels 100, 200 and 300. Course objectives The course allows students to concentrate on developing a body of work of a speculative and individual nature. The emphasis is placed on a spirit of excellence and a strong sense of independent enquiry. Experimentation is encouraged and the candidate should have a firm commitment to the articulation of visual art theory in written, verbal and visual form, and its integration into art practice. Candidates work with one or two supervisors in a studio/teaching area, and must be prepared to articulate the line of investigation which they wish to Course details (2001) page 69 pursue. This will take the form of a proposal which establishes the framework for assessment. Candidates also undertake a seminar program. The series will vary slightly each year but is devoted to a study of contemporary theory, methodology and criticism of the visual arts. A short course of lectures and workshops is presented at a weekly Honours Seminar in semester 1. This series of lectures is devoted to a study of contemporary theory, methodology and criticism of visual arts and design. During the latter part of the semester, candidates can expect to present their ideas to a workshop group in a relatively informal and provisional manner. In semester 1 and 2, short summaries of papers are presented formally in day-long seminars. In consultation with their theory supervisors, candidates write their summary in final form as a 3,000-word paper; studio supervisor(s) should also be consulted regarding the theme and structure of their paper. The papers are presented as part of the candidates' examination submission. For studio-based candidates, the Art Theory component makes up approximately one fifth of the course. Candidates will be examined by a panel of academic staff, on a presentation of visual work representing results of study undertaken during the year, along with the two seminar papers, and any other written documentation, such as diaries, notebooks and other relevant material. Candidates must satisfy the examiners as to the quality of their submissions in both studio and theory. Course structure The candidate will submit a proposal for a course of study within one of the following studio areas, although this program is not necessarily media-specific: • • • • • • • • • • • Art Theory Ceramics (Ltn only) Drawing E-Media (Hbt only) Furniture Design (Hbt only) Graphic Design (Hbt only) Painting Photography (Hbt only) Printmedia (Ltn only) Printmaking (Hbt only) Sculpture Enrolment Hobart students enrol as follows: Course details (2001) FSA400 page 70 Bachelor of Fine Arts with Honours (Full time) 100% or FSA401 Bachelor of Fine Arts with Honours (Part time) 50% Launceston students enrol as follows: FFA400 Bachelor of Fine Arts with Honours (Full time) 100% or FFA401 Bachelor of Fine Arts with Honours (Part time) 50% Bachelor of Music (Abbreviation: BMus) Course code: F3H This 3-year full-time degree is offered by the Faculty of Arts through the Conservatorium of Music in Hobart. Part time study is also available. Admission & prerequisites Minimum University entrance requirements are normally expected. Pre-tertiary TCE Music is desirable but not essential. Anyone possessing other qualifications and experience deemed by the Faculty to provide an adequate preparation for study equivalent to the successful completion of year 12 in an Australian school system, may be admitted to the course. Applicants are required to attend an audition and interview and to undertake a theory and aural test. Overseas/interstate applicants may submit a certified audio or video tape of a recent performance. Instrumental and vocal applicants should prepare a program comprising three works of contrasting style and period; some technical work may also be required. Composition applicants should present a folio of at least three compositions. Course objectives The course aims to provide students with: Course details (2001) • • • • • • page 71 a broadly-based music education, employing a strong and fundamental aural approach to music learning; a high level of professional vocational training; the necessary communication skills and flexibility to interact with the wider community; appropriate support studies to enable the development of research skills; awareness and experience of recent technological developments in music; knowledge and understanding of recent developments in contemporary and Australian music. Career outcomes Graduates of the Bachelor of Music are engaged at all levels of the music profession, both in Australia and overseas. They enjoy successful careers as performers, teachers and administrators, or may be involved in broadcasting, journalism or as music critics. Course structure The content of each of the first 3 years is notionally divided into 3 categories: Core Studies and Ensemble (compulsory for all students) Principal Study and Related Studies, selected according to the strand of initial specialisation: • • • • • • Keyboard Voice Orchestral Instruments Contemporary Music Composition Guitar Complementary Studies Elective units may be selected according to need or interest. Articulation The course design allows the possibility of articulation with related TAFE courses. Schedule Unit Title Level 100 campus-sem weight code Course details (2001) page 72 Core Studies & Ensemble (all students) Music Theory 1 Hf 12.5% FCT100 Performance and Communications 1 Hf 12.5% FCP100 Aural and Listening 1 Hf 12.5% FCL100 Ensemble 1 Hf 12.5% FCE100 Principal Study and Related Studies Choose one: Keyboard Principal Study Keyboard 1 Hf 25% FCY100 Accompaniment 1 Hf 12.5% FCY150 Voice Principal Study Voice 1 Hf 25% FCV100 French for Singers 1 Hf 25% FCV150 Orchestral Instruments Principal Study Orchestral Instruments 1 Hf 25% FCO100 Orchestra & Repertoire 1 Hf 12.5% FCO150 Contemporary Music Principal Study Contemporary Music 1 Hf 25% FCN100 Style and Analysis 1 Hf 12.5% FCN150 Guitar Principal Study Guitar 1 Hf 25% FCG100 Guitar Repertoire 1 Hf 12.5% FCG150 Composition Principal Study Composition 1 Hf 25% FCC100 Performance for Composers 1 Hf 12.5% FCC150 Complementary Studies Choose one of the following (except Voice students): Musicianship Extension 1 [na] 12.5% FCB110 Improvisation 1 [na] 12.5% FCB120 Keyboard Skills 1 Hf 12.5% FCB130 Principal Study Extension 1 Hf 12.5% FCB100 Orchestration and Arranging 1 [na] 12.5% FCB160 Music Technology 1 Hf 12.5% FCB190 NOTES: Subject to Sub-Dean approval, students may take units offered by another School in the University up to a maximum of 12.5% at level 100 in place of Complementary Studies unit(s). Complementary Studies units are offered subject to sufficient enrolments. Voice students do not take a Complementary Studies unit. Course details (2001) page 73 Level 200 Core Studies & Ensemble (all students) Music Theory 2 Hf 12.5% FCT200 Performance and Communications 2 Hf 12.5% FCP200 Aural and Listening 2 Hf 12.5% FCL200 Ensemble 2 Hf 12.5% FCE200 Principal Study and Related Studies Choose one: Keyboard Principal Study Keyboard 2 Hf 25% FCY200 Accompaniment 2 Hf 12.5% FCY250 Voice Principal Study Voice 2 Hf 25% FCV200 French for Singers 2 Hf 25% FCV250 Orchestral Instruments Principal Study Orchestral Instruments 2 Hf 25% FCO200 Orchestra & Repertoire 2 Hf 12.5% FCO250 Contemporary Music Principal Study Contemporary Music 2 Hf 25% FCN200 Style and Analysis 2 Hf 12.5% FCN250 Guitar Principal Study Guitar 2 Hf 25% FCG200 Guitar Repertoire 2 Hf 12.5% FCG250 Composition Principal Study Composition 2 Hf 25% FCC200 Performance for Composers 2 Hf 12.5% FCC250 Complementary Studies Choose one of the following (except Voice): FCB100. 120, 130, 160, 190 (see Level 100 above) Conducting 1 [na] 12.5% FCB150 Music Teaching and Learning Hf 12.5% FCB205 Improvisation 2 [na] 12.5% FCB220 Keyboard Skills 2 Hf 12.5% FCB230 Music Technology 2 Hf 12.5% FCB290 Principal Study Extension 2 Hf 12.5% FCB200 NOTES: Subject to Sub-Dean approval, students may take units offered by another School in the University up to a maximum of 12.5% at level 200 in place of Complementary Studies unit(s). Course details (2001) page 74 Complementary Studies units are offered subject to sufficient enrolments. Voice students do not take Complementary Studies unit. Level 300 Core Studies & Ensemble (all students) Music Theory 3 Hf 12.5% FCT300 Performance and Communications 3 Hf 12.5% FCP300 Ensemble 3 Hf 12.5% FCE300 Principal Study and Related Studies Choose one: Keyboard Principal Study Keyboard 3 Hf 25% FCY300 Accompaniment 3 Hf 12.5% FCY350 Voice Principal Study Voice 3 Hf 25% FCV300 French for Singers 3 Hf 25% FCV350 Orchestral Instruments Principal Study Orchestral Instruments 3 Hf 25% FCO300 Orchestra & Repertoire 3 Hf 12.5% FCO350 Contemporary Music Principal Study Contemporary Music 3 Hf 25% FCN300 Style and Analysis 3 Hf 12.5% FCN350 Guitar Principal Study Guitar 3 Hf 25% FCG300 Guitar Repertoire 3 Hf 12.5% FCG350 Composition Principal Study Composition 3 Hf 25% FCC300 Performance for Composers 3 Hf 12.5% FCC350 Complementary Studies Choose two [a] of the following: FCB100, 120, 130, 160, 190 (see Level 100 above) FCB150, 205, 200, 260, 290 (see Level 200 above) Aural and Listening 3 Hf 12.5% FCL300 Conducting 2 [na] 12.5% FCB250 Principal Study Extension 3 Hf 12.5% FCB300 NOTES: Subject to Sub-Dean approval, students may take units offered by another School in the University up to a maximum of 12.5% at level 300 in place of Complementary Studies unit(s). Complementary Studies units are offered subject to sufficient enrolments. Course details (2001) [a] page 75 Voice students take one Complementary Studies unit. Music Cross-course enrolments Students enrolled in the BMus may, with the approval of the Dean or the Dean's representative, enrol in units from another course to count towards the BMus degree, entailing no more than 12.5% in years 1 and 2, and 25% in year 3. Voice students are restricted to 12.5% in year 3 as a cross-course enrolment. Subjects replaced by the cross-course enrolment will be the Complementary Studies electives. Students from other courses Students other than Music students from the Faculty of Arts, or the Faculties of Science and Engineering, Health Science or Commerce and Law are currently offered music subjects as a major or minor towards their respective degrees. Students may also undertake a range of individual electives within the BMus course, subject to the approval of the relevant faculty. A list of electives is available from the Conservatorium on request. Students from other faculties are subject to the same entrance tests as BMus students; they participate in the same classes, and are assessed by the same criteria. A major in Music Students from other courses may study for a major in Music, consisting of 25% at level 100, 37.5% at level 200 and 37.5% at level 300 (total 100%). Unit Title campus-sem weight code Music 1 (Level 100) Course weight 25% (all individual units are weighted at 12.5%) Aural and Listening 1 Hf 12.5% FCL100 choose one of the following: Music Theory 1 Hf 12.5% FCT100 Instrumental/Vocal Study 1 Hf 12.5% FCI150 Ensemble 1 Hf 12.5% FCE100 N.B. Students who intend to enrol in Music 2 Major must enrol in FCL100 and FCT100. Units to a combined value of more than 25% may be taken in Music 1, subject to approval from the Head of School and the relevant faculty. Music 2 (level 200) Course weight 37.5% (all individual units are weighted at 12.5%) Aural and Listening 2 Hf 12.5% FCL200 Music Theory 2 Hf 12.5% FCT200 Course details (2001) page 76 choose 12.5% from: Instrumental/Vocal Study 1 Hf 12.5% FCI150 Instrumental/Vocal Study 2 Hf 12.5% FCI250 Orchestration and Arranging 1 [na] 12.5% FCB160 Conducting 1 [na] 12.5% FCB150 Improvisation 1 [na] 12.5% FCB120 Music Technology 1 Hf 12.5% FCB190 Ensemble 2 Hf 12.5% FCE200 Music Theory 1 Hf 12.5% FCT100 N.B. some of these units may carry entry conditions or prerequisites; check individual unit descriptions. Music 3 (Level 300) Course weight 37.5% (all individual units are weighted at 12.5%) choose 25% from: FCB150 or FCB250 FCB120 or FCB220 FCB190 or FCB290 N.B. some of these units may carry entry conditions or prerequisites; check individual unit descriptions. Honours Students who have completed the Major and have gained at least a Distinction in Music 3 may apply to enrol in BMus(Hons). Bachelor of Music (Honours) (Abbreviation: Mus(Hons)) Course code: F4D This on-campus, 1-year (minimum) full-time course is offered by the Faculty of Arts through the Tasmanian Conservatorium of Music at Hobart with specialisation in either Performance or Composition. Course details (2001) page 77 Admission & prerequisites Admission to the honours program is by invitation. Candidates are expected to have a good academic record, and to have satisfied minimum criteria; either – • • successful completion of a Pass degree in Music with High Achievement in performance or composition and at least grades of Credit or higher in other year-3 units; or demonstrate equivalent professional attainment. Course objectives The program emphasises the need for a spirit of excellence and a strong sense of independent inquiry. Experimentation is encouraged and candidates should have a strong commitment to the implications of their research for music practice. Career outcomes Graduates of the Bachelor of Music with Honours are engaged at all levels of the music profession, both in Australia and overseas. They enjoy successful careers as performers, teachers and administrators, or may be involved in broadcasting, journalism or as music critics. Course structure Candidates work with one or two supervisors in a specialist/teaching area, and are expected to submit an honours proposal by mid-March, for approval by a special School meeting chaired by the Director. This proposal will form the basis of the work to be undertaken during the year, and will establish a potential framework for assessment. Candidates are expected to attend a regular Research Seminar program. As an integral part of the Research Seminar, it is expected that candidates will make at least one formal seminar presentation (supported by appropriate documentation), which will then form part of the final assessment process.Students enrol as follows: FCZ400 Bachelor of Music with Honours (Full time) [f] FCZ401 Bachelor of Music with Honours (Part time) [f] 100% 50% Bachelor of Performing Arts (Abbreviation: BPA) Course code: F3B Course details (2001) page 78 This on-campus 3-year full-time course is offered by the Faculty of Arts through the School of Visual and Performing Arts at Launceston and the Conservatorium of Music at Hobart. Part-time study is also available. Note: this course is currently being taught out, and students wishing to pursue theatre training should seek enrolment in the Bachelor of Contemporary Arts. Students will be able to enrol in first-year of the Bachelor of Performing Arts (Music) stream in 2001. However, they need to confirm with the School exactly what will be offered. Admission & prerequisites Applicants (BPA Music stream only) are normally expected to have satisfied the University's admission requirements. Possession of TCE Music is desirable but not essential. Applicants are required to attend an audition and interview (where practicable). Overseas and interstate applicants may submit a certified video tape of the audition performance. The School will advise applicants of specific audition requirements. Course objectives The course aims to satisfy the demand for skilled professionals in the performing arts industry, by producing students who have an awareness of and real insight into related disciplines. It provides students with an appropriate balance between the study of theory and principles, and practical performance in the performing arts. Career outcomes May include professional theatre as actors, stage managers, technicians; film and television; public relations; theatre in education; the music industry. Professional recognition On entering the industry, students are eligible for membership of the Media, Entertainment and Arts Alliance (MEAA). Course structure Course details (2001) page 79 All candidates undertake theoretical and performance studies in one of two strands: Theatre or Contemporary Music, as outlined in the schedule which follows. (Theatre or Music) – Schedule Students enrolling in first-year Theatre do so in the Bachelor of Contemporary Arts degree course, not the Bachelor of Performing Arts, which is to be taught out. Students enrolling in first-year Music units for the BPA at Launceston should confirm with the School which units are available. Unit Title campus-sem weight Music only Year 1 Performance Study 1 (Music) Lf 50% The Arts & Cultural Context 1 Lf 12.5% Theory Composition and Arranging 1 Lf 25% [a] Unspecified Elective 1 Theatre and Music Year 2 Either FPB250 or FPF250 Performance Study 2 (Theatre) Lf 50% Performance Study 2 (Music) Lf 50% FPB215 or FPF200 AND FPC200 or Unspecified Elective 2 Drama 2 Lf 25% Theory Composition and Arranging 2 Lf 25% Vocationally Oriented Study 1 Lf 25% [a] Unspecified Elective 2 Year 3 Either FPB350 or FPF350 Performance Study 3 (Theatre) Lf 50% Performance Study 3 (Music) Lf 50% AND 50% from the following: Drama 3 Lf 25% Vocationally Oriented Study 2 Lf 25% code FPF150 FPC100 FPF100 FPB250 FPF250 FPB215 FPF200 FPC200 FPB350 FPF350 FPB315 FPC300 Course details (2001) page 80 Vocationally Oriented Study 3 Lf 25% FPC350 [a] Unspecified Elective 3 [a] Students may choose up to 25% from units offered by another degree course (e.g. English, Computing, Art) Note: FPB units are Theatre units; FPF are Music units; FPC are combined Music and Drama units. Students taking other courses The School of Visual and Performing Arts offers students a variety of visual and performing arts electives. The following units are also offered to Study Abroad Students or students who are taking other courses in the University who require an elective weighted at 12.5%: Unit Title Performing Arts Elective 1 Performing Arts Elective 2 Performing Arts Elective 3 campus-sem weight code L1/2 12.5% FPS200 L1/2 12.5% FPS201 L1/2f 12.5% FPS300 Visual & Performing Arts Liberal Studies courses Unit Title Year 1 Musicianship Class Instrument Year 2 Musicology Conducting campus-sem weight code Lf Lf 12.5% 12.5% FPH101 FPH102 Lf Lf 12.5% 12.5% FPH201 FPH202 Bachelor of Performing Arts with Honours (Abbreviation: BPA(Hons)) Course code: F4B Course details (2001) page 81 This on-campus one year full-time (or at the discretion of the School, 2 consecutive years part-time) course is offered by the Faculty of Arts through the School of Visual and Performing Arts in Launceston. Admission & prerequisites On successful completion of a Bachelor of Performing Arts degree, a candidate may make application to undertake a further Honours year. Prerequisites for entry into the Honours year apply: a candidate will normally be expected to have gained at least two distinctions or above during the second and third year of undergraduate study, one of which should be in the final year of the relevant specialisation. Course objectives The course allows students to concentrate on developing a body of work in which the emphasis will be placed on a spirit of excellence and a strong sense of independent enquiry. This will involve identification of an issue or hypothesis, an evaluative literature survey plus a study of the selected problem. Experimentation will be encouraged and the candidates will have a strong commitment to the articulation of performing arts theory in written, verbal and theatrical form, and its integration into performance. Career outcomes May lead to postgraduate study or employment in the professional theatre, film and television; public relations; theatre in education. Course structure Candidates work with one or two supervisors in a specialisation and must be prepared to articulate the line of investigation which they wish to pursue. This will take the form of a proposal which establishes the framework for assessment. Candidates undertake a research training seminar program which is devoted to a study of contemporary performance theory, methodology and criticism within the performing arts. Candidates can normally expect to present one research paper of approximately 4,000 words. A seminar paper of approximately 2,500 words which considers the candidate's current work and its theoretical context will also be presented. This will be written in consultation with the candidate's supervisor. These papers will then be presented as part of a candidate's examination submission. Course details (2001) page 82 In addition to the research seminar program, candidates will present either a dissertation of approximately 12,000 words or equivalent performance program within their research specialisation. Candidates will be examined by a panel of academic staff (including one external assessor) on a presentation of work representing results of study undertaken during the year, along with the two seminar papers, and any other written documentation, such as diaries, notebooks and other relevant material. Candidates must satisfy the examiners as to the quality of their submissions. General provisions The Dean may, on the recommendation of the Head of School, grant a candidate an extension of time for the completion of either the dissertation or performance program. Except by special permission of the Faculty there is no re-examination for honours. The classes of honours are First Class, Second Class, and Third Class. There is an upper and lower division in the second class. Enrolment Students enrol as follows: FPA400 FPA401 Bachelor of Performing Arts with Honours (Full time) 100% Bachelor of Performing Arts with Honours (Part time) 50% (see page xx) Bachelor of Social Science (Abbreviation: BSocSc) Course code: R3C (Launceston only) Students are advised to confirm details listed below prior to enrolling in the BSocSci. The Bachelor of Social Science (BSocSc) is a 3-year course which provides a focused course of study for students wanting to gain expertise in social science Course details (2001) page 83 applied to practical real-world issues. It links the disciplinary bases of human resource management, applied sociology, public policy and social ecology to their practical applications. It combines units from the Faculty of Arts with units from the Faculty of Commerce and Law. It teaches valuable skills in the methodology of social research and prepares graduates particularly for careers in the post-industrial service and information sector. Students may study full time or part time and have nine enrolment years, including the year of passing the first unit for the degree, in which to complete course requirements. Students currently enrolled in other degree courses at the University may apply for entry to the BSocSc. Credit may be granted for some or all of their previous study. Prospective students wishing to transfer at a later date to the Bachelor of Social Work degree should discuss their program with a Faculty Officer. Limited mid-year entry is available to this course. Admission & prerequisites Applicants will be expected to meet the minimum entry requirements, which include several categories of special admission, set by the University for entry to degree courses. No specific Faculty or subject prerequisites apply. Course objectives The Bachelor of Social Science aims to give undergraduates a broad exposure to applied social science, while allowing them to study social science and management issues within a non-professional educational context. Students will be able to link the disciplinary bases of management and administrative studies to their practical applications. The program will develop a student's general abilities in the areas of: • • • • • • • • • written expression linguistic skills creative self-expression capacity to analyse and interpret in a dispassionate and objective manner capacity for reasoned criticism data acquisition and analysis research techniques marshalling facts in support of arguments, and evaluating the possible outcomes of alternative courses of action, with the emphasis varying according to the particular program chosen. Students will be able to prepare themselves for careers in the post-industrial service sector whilst acquiring a qualification that will certify them in the specific knowledge and skills that social science can offer. Students may obtain professional recognition from the Australian Human Resources Institute if they have completed a Human Resource Management major. Course details (2001) page 84 Career outcomes Graduates of the Bachelor of Social Science will be strong applicants for positions in a wide range of fields such as social and market research, human resource management, public administration and management in commonwealth, state and local government, policy analysis, social welfare administration, journalism and the media, and industrial relations. Course structure At level 100, students must complete units from a minimum of three disciplines (weighted at a maximum of 25% for each discipline). These can be chosen from Applied Sociology, Human Resource Management, Public Policy or Social Ecology. The remaining 25% can be the remaining unit from those mentioned above, or can be taken from units such as English, Geography, History, Indonesian, Philosophy, Psychology or units from the Faculty of Commerce and Law. At level 200, students select two major subjects which they study over the remaining two years of the award. Each consists of eight 12.5% units, some of which may be compulsory for each major. Currently students have a choice among four majors: Applied Sociology, Human Resource Management , Public Policy and Social Ecology. Units to be included in the degree are listed in the attached schedule. The following conditions apply to enrolment in the Bachelor of Social Science course: • • • • • Students must pass in units totalling 100% weight at each level of the three year course (a total of 300%). Students must select units to meet the requirements for two majors from the following fields of study: Applied Sociology, Human Resource Management, Public Policy and Social Ecology. At least one major must be from a School in the Faculty of Arts A major sequence is defined as sequential studies in one discipline as follows: 25% at level 100 and 100% at levels 200/300. The maximum percentage at level 100 in any given discipline which may be counted towards the degree is 25%. Full-time students may not normally enrol in units totalling more than 100% and part-time students in units totalling more than 74%. Units may be counted towards the degree only if they have been taken in accordance with prerequisites determined by the Faculty. Students may not count towards the degree any unit whose content substantially repeats the content of a unit already counted. Course details (2001) page 85 Sample course 1 Level 100 Indonesian 25% Human Resource Management Public Policy 25% Applied Sociology 25% 25% Level 200 Human Resource Management Public Policy 50% 50% Level 300 Human Resource Management Public Policy 50% 50% A student wishing to cover the option of transferring to a Bachelor of Social Work after the second year could take a course like the one which follows: Sample course 2 Level 100 Public Policy 25% Human Resource Management Applied Sociology 25% Psychology 25% 25% Level 200 Human Resource Management Psychology 25% Applied Sociology 25% 50% If unsuccessful in obtaining entry into the Bachelor of Social Work, the student would continue with a third year enrolment as shown below: Level 300 Human Resource Management Applied Sociology 50% 50% In such a case a student would be granted permission to graduate with a 25% shortfall in either major. Course details (2001) page 86 Relevant units for the course are shown in the Schedule which follows. Students should also consult the discipline entries in the Handbook for details of prescribed units, prerequisites and other requirements relevant to the major in the disciplines chosen. Articulation A student who has completed or partly completed another degree from this University or another approved institution can apply for credit for their previous study towards the BSocSc degree. Units from courses offered by other faculties of the University may be included provided they do not exceed the permissible weighting. Enrolment restrictions – quotas All prospective BSocSc students, including those currently enrolled in other courses in the University, should be aware that admission will be subject to quotas and formal selection procedures. Students interested in studying the BSocSc degree must complete an Application for Admission form available from Student Administration (phone: Launceston (03) 6324 3106; Hobart (03) 6226 2812). Tasmanian Year 12 students will automatically have Admission forms for the following year sent to their home address during August. Schedule A Unit Title campus-sem Year 1 – Group 1 (Level 100) At least three of the following pairs of units: Human Resource Management Introduction to Management H1/2~L1/2~B1 Management of Human Resources [a] H3/2~L3/2 Government Introduction to Government A H1~L1~B1 Introduction to Government B H2~L2~B2 Sociology Sociology A H1~L1~B1~D1 Sociology B H2~L2~B2~D2 Social Ecology Sociology A H1~L1~B1~D1 Sociology B H2~L2~B2~D2 OR weight code 12.5% BMA101 12.5% BMA121/221 12.5% HSG101 12.5% HSG102 12.5% 12.5% HGA101 HGA102 12.5% 12.5% HGA101 HGA102 Course details (2001) page 87 Society, Culture and Health 1 L1 12.5% HGA138 Society, Culture and Health 2 L2 12.5% HGA139 Health Care Where People Live and Work 1 L1 12.5% CNA126 Population and Urbanisation L1~B1~D1 12.5% KJG101 Elective units Further elective units to make 100%. No more than 25% of units at level 100 may be taken from Schools outside the Faculties of Arts and Commerce and Law. Years 2 and 3 – Groups 2 and 3 (Levels 200 and 300) Two of the following four majors. At least one major must be from a school in the Faculty of Arts. 1. Applied Sociology Prerequisite of 25% of HGA101 Sociology A and HGA102 Sociology B at the 100 level. To complete a major in this subject, students must complete 50% in units at the 200 level and 50% of units at the 300 level including the following units: Sociological Analysis of Modern Society H2~L2~D2 12.5% HGA202 Social and Political Research L1~H1 12.5% HGA203/303 And a further 75% of units chosen from Sociology units in the BA. 2. Public Policy Prerequisite of 25% of HSG101 Introduction to Government A and HSG102 Introduction to Government B at the 100 level. To complete a major in this subject, students must complete 50% in units at the 200 level and 50% of units at the 300 level including the following unit: Social and Political Research L1~H1 12.5% HGA203/303 (If not taken as part of another major) And further units chosen from Public Policy units in the BA Schedule to achieve a major of 125% in total. 3. Human Resource Management Prerequisites of 25% in BMA101 Introduction to Management and BMA121 Management of Human Resources. To complete a major in this subject, students must complete 50% in units at the 200 level and 50% of units at the 300 level from the following schedule: Contract of Employment H1~L1 12.5% BMA241 Employee Relations H2~L2 12.5% BMA321 Human Resource Development H2~L2 12.5% BMA224 International Human Resource Management H1~L1 12.5% BMA381 Course details (2001) page 88 Strategic Issues in Human Resource Management H1~L1 12.5% BMA330 Organisational Behaviour H1~L1 12.5% BMA201 Strategic Management H2~L2 12.5% BMA302 Plus one elective from the following list: Method for Management Studies H2~L2 12.5% BMA260 Managerial Social Responsibility H2~L2 12.5% BMA291/391 Special Topics in Management H1/2~L1/2 12.5% BMA371 Understanding Organisations H1 12.5% HGA236/336 [b] Financial Management H2~L2 12.5% BFA181/281 Management and the Natural Environment [na] 12.5% BMA272/372 Method for Management Studies H2~L2 12.5% BMA260 4. Social Ecology Prerequisite of 25% of Social Ecology units at 100 level. To complete a major in this subject, students must complete 50% in units at the 200 level and 50% in units at the 300 level, including the following units: Social Ecology H2~L2 12.5% HGE203/303 Population and Society H1~L1 12.5% HGE204/304 Social and Political Research L1~H1 12.5% HGA203/303 (If not taken as part of another major) And further units chosen from Social Ecology units in the BA Schedule to achieve a major of 125% in total. [a] use level 100 enrolment code (eg BMA121) [b] use level 200 enrolment code (eg BFA281) Bachelor of Social Science (Police Studies) (Abbreviation: BSocSc(PoliceStudies)) Course code: R3K The Bachelor of Social Science (Police Studies) is a vocationally-oriented course offered by the Faculty of Arts at both the Hobart and Launceston campuses. Students may study full-time or part-time and have nine enrolment years, including the year of passing the first unit for the degree, in which to complete course requirements. Course details (2001) page 89 Admission & prerequisites Applicants are expected to meet the normal requirements set by the University for entry to degree courses. These include several categories of special admission, such as mature age. No subject prerequisites apply to this degree. In addition, applicants who have completed the Tasmania Police Recruitment Course (TPRC) are eligible for admission. Entry to the course occurs normally in February, and there may be limited entry in July. Course objectives The Bachelor of Social Science (Police Studies) is designed to provide students with high quality social science training together with specific knowledge and skills of policing. Graduates with this degree will have learned the following: to understand and analyse complex issues concerning policy practice in contemporary society; to understand the changing roles and expectations of police in the context of a changing society; to articulate the interaction between theory and practice in police studies; to develop a broad array of intellectual, practical and professional capabilities; to develop critical, analytical and communication skills; and to organise and conduct research projects. Career outcomes The degree provides a sound academic base for those considering careers in policing. For serving police officers, the acquisition of tertiary qualifications is clearly becoming advantageous for career advancement. Course structure To qualify for the degree, students must complete successfully a number of units weighted at 100% at level 100, 100% at level 200, and 100% at level 300 (ie a total of 300%). At level 100 (first year), students must complete units from four disciplines (weighted at a maximum of 25% for each discipline). These can be chosen from Introduction to Government A and B (level 100 units that constitute part of either the Public Policy or Political Science majors), Sociology, Psychology, Social Ecology, History or Human Resource Management. Introduction to Law (weighted at 25%) may also be taken as a level 100 unit, but students who include this in their program of study are not permitted to undertake a Law major as part of this particular degree in subsequent years. At level 200 (second year), students must complete 50% in units from the Police Studies major and 50% from one of the the disciplines chosen at level 100 (apart from Law). Course details (2001) page 90 At level 300 (third year), students must complete 50% in units for the Police Studies major and 50% from the discipline chosen to continue at level 200 (which then becomes the second major). Note too, that students must include three compulsory 'core' units in their Police Studies major program: Policing and Governance (taught in Hobart and Launceston), Social and Political Research (taught in Hobart and Launceston), and either Criminology (taught in Hobart only) or Crime and Criminal Justice (taught in Launceston and by distance education in 2001) or Sociology of Deviance (taught in Hobart in 2001). Information about units offered in these disciplines and the Police Studies major can be found in the Unit Details section of this Handbook. Sample course structure 1 Year 1 (100%) Introduction to Law 25% Introduction to Government A and B Human Resource Management 25% Sociology 25% Year 2 (100%) Police Studies 50% Sociology 50% Year 3 (100%) Police Studies 50% Sociology 50% Total 300% Police Studies major 100% Sociology major 125% 25% Sample course structure 2 With credit for Tasmania Police Recruitment Course (TPRC) Year 1 (100%) Introduction to Government A & B TPRC credit 25% Sociology 25% History 25% Year 2 (100%) Police Studies 25% TPRC credit 25% Public Policy 50% Year 3 (100%) Police Studies 50% Public Policy 50% 25% Course details (2001) page 91 Totals 300% Police Studies major 100% Public Policy major 125% Articulation Credit for previous study Tasmania Police Recruitment Course graduates are granted a total of 50% credit – unspecified 25% credit at level 100 and 25% credit at level 200 towards the Police Studies major. They are required to take only three elective level 100 disciplines instead of four. A student who has completed or partly completed another degree from this University or another approved institution can apply for credit for their previous study towards the BSocSc(PoliceStudies) degree. Location and notices The BSocSc(PoliceStudies) degree course and the Police Studies major are coordinated from the School of Government. The School is located on the top floor (or Level 5) of the Arts Building in Hobart. Inquiries should be directed to Dr Robert Hall (Room 503, phone (03) 6226 2319) or to the Secretary of the School (Room 504, phone (03) 6226 2329). The BSocSc(PoliceStudies) notice-board for up-to-date information about the degree and the major is next to Dr Hall's office. Students attending the Launceston campus may consult Dr Hans Lofgren (School of Government, Room L220, phone (03) 6324 3262) for immediate advice about the course if for any reason they cannot contact Dr Hall. Schedule A Unit Title campus-sem weight code Level 100 Students are required to complete 100% in units at this level in four elective first-year subjects that are normally taught as two 12.5% units per subject [a] 25% from level 100 History: History 1 Hf 25% HTA100 The Impact of Europe c. 1640–1780 H1~D1 12.5% HTA103 (a) Age of Revolution and Empire c. 1780–1815 (b) The Modern World in Australia to 1860 H2 12.5% HTA104 History 1 Lf~Bf 25% HTA101 The History of Europe from c. 1620 to 1789 L1~B1 12.5% HTA105 Course details (2001) page 92 (a) The Impact of Europe from the French Revolution to the American Civil War; (b) The Modern World in Australia to 1860L2~B2~D2 12.5% HTA106 The Impact of Europe c. 1640–1780 H1~D1 12.5% HTA103 from the Human Resource Management discipline Introduction to Management H1/2~L1/2~B1 12.5% BMA101 Management of Human Resources H3/2~L3/2 12.5% BMA121/221 from the Political Science discipline Introduction to Government A H1~L1~B1 12.5% HSG101 Introduction to Government B H2~L2~B2 12.5% HSG102 from the Psychology discipline Psychology 1A H1~L1~B1 12.5% KHA101 Psychology 1B H2~L2~B2 12.5% KHA102 from the Public Policy discipline Introduction to Government A H1~L1~B1 12.5% HSG101 Introduction to Government B H2~L2~B2 12.5% HSG102 from the Social Ecology discipline Sociology A H1~L1~B1~D1 12.5% HGA101 Sociology B H2~L2~B2~D2 12.5% HGA102 Students already enrolled in either of the two units listed above may select substitutes from the following: Population and Urbanisation L1~B1~D1 12.5% KJG101 Health Care Where People Live and Work 1 L1 12.5% CNA126 Society, Culture and Health 1 L1 12.5% HGA138 Society, Culture and Health 2 L2 12.5% HGA139 Geography and Environmental Studies 1A Hf 25% KGA101 Community Health and Medicine I H1 12.5% CAM105 from the Sociology discipline Sociology A H1~L1~B1~D1 12.5% HGA101 Sociology B H2~L2~B2~D2 12.5% HGA102 or the unit Course details (2001) page 93 Introduction to Law Hf~Lf 25% BLA101 [a] Students who have completed the Tasmania Police Recruitment Course (TPRC) are granted 25% at level 100, which means they are required to complete only three of the 25% elective level 100 subjects, not four. 1 Police Studies major (compulsory) To achieve a major in Police Studies students must complete 50% in level 200 units and 50% in level 300 units taken from the following Schedule: Unit Title campus-sem weight code Level 200 and level 300 Three core units (with a total weight of 37.5%): Policing and Governance H1~L1 12.5% HSD205/305 Social and Political Research L1~H1 12.5% HGA203/303 and either BLA615 or HGA206/306 or HGA259/359 Criminology H1 12.5% BLA615 Crime and Criminal Justice L1~D1 12.5% HGA206/306 Sociology of Deviance H1 12.5% HGA259/359 [a] Plus electives units (weighted at a total of 62.5%) from the following: Contemporary Indigenous Tasmania [na] 12.5% HAB206/306 Crime and Criminal Justice [b] L1~D1 12.5% HGA206/306 Crime and the Law in Historical Perspective H2 12.5% HTA218/318 [c] Criminal Law Hf 25% BLA202 Criminology [b][c] H1 12.5% BLA615 Espionage, Terror and Global Disorder H1 12.5% HSA270/370 Indigenous Justice Issues L2~D2 12.5% HAB208/308 Law, Society and Morality [na] 12.5% HPA242/342 Population and Society H1~L1 12.5% HGE204/304 Professional Ethics H2~Lv2 12.5% HPA212/312 Race and Ethnic Politics [na] 12.5% HSA201/301 Sex, Drugs and Toxic Waste: The Politics of Regulation [na] 12.5% HSD207/307 Social Policy in Welfare States H2~L2 12.5% HSD231/331 [b] Sociology of Deviance H1 12.5% HGA259/359 Sociology of Law [c] H2 12.5% BLA616 [c] Sociology of Youth [na] 12.5% HGA277/377 Course details (2001) [a] [b] [c] page 94 Students who have completed the Tasmania Police Recruitment Course (TPRC) are granted 25% at level 200 towards the Police Studies major. Thus they are required to complete only 25% of level 200 subjects instead of 50%. if not taken as a core unit Criminology, Criminal Law and Sociology of Law may count at either level 200 or 300. Students should note that BLA101 Introduction to Law is a prerequisite for BLA202 Criminal Law. 2 History major Prerequisite: 25% of History units at level 100. To achieve a major in History students must complete 50% in units at level 200 and 50% in units at level 300 as listed in the Bachelor of Arts Schedule on page B-xx 3 Human Resource Management major Prerequisite: 25% in BMA101 Introduction to Management and BMA121 Management of Human Resources. To achieve a major in Human Resource Management students must complete 100% in units at level 200 and level 300 from the following schedule: Unit Title campus-sem Core units: Organisational Behaviour H1~L1 Contract of Employment H1~L1 Strategic Management H2~L2 Employee Relations H2~L2 Method for Management Studies H2~L2 Strategic Issues in Human Resource Management H1~L1 Human Resource Development H2~L2 Elective units: Managerial Social Responsibility H2~L2 Special Topics in Management H1/2~L1/2 Financial Management [a] H2~L2 Principles of Marketing [a] H3/2~L3/2 [a] use the level 200 enrolment code (eg BFA281) weight code 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BMA201 BMA241 BMA302 BMA321 12.5% BMA260 12.5% BMA330 12.5% BMA224 12.5% BMA291/391 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BMA371 BFA181/281 BMA151/251 4 Political Science major (Hobart campus) Course details (2001) page 95 Prerequisite: 25% level 100 Political Science. To achieve a major in Political Science students must complete 50% in units at level 200 and 50% in units at level 300 from the Bachelor of Arts Schedule listed on page B-xx). 5 Psychology major (Hobart campus) Prerequisite: 25% level 100 Psychology. To achieve a major in Psychology students must complete 50% in units at level 200 and 50% in units at level 300 from the following schedule: Unit Title campus-sem weight code Core units: Research Methods in Psychology H1~L1 12.5% KHA201 Assessment and Research Methods H1 12.5% KHA301 Plus a further 37.5% of electives at level 200 and a further 37.5% at level 300 from: Developmental Psychology H2~L2 12.5% KHA202 Health & Rehabilitation Psychology H1 12.5% KHA209/309 Peace, Conflict & Law H2 12.5% KHA212/312 Psychology of Health & Stress L2 12.5% KHA213/313 Organisational Psychology L1 12.5% KHA215/315 Human Neuroscience H1 12.5% KHA303 Psychophysiology & Emotion H1 12.5% KHA304 Clinical Psychology H1 12.5% KHA305 Cognition and Memory H2 12.5% KHA306 Advanced Research Methods H2 12.5% KHA308 Learning & Skilled Performance H2 12.5% KHA314 Individual Differences H1 12.5% KHA318 Educational Psychology H1 12.5% KHA319 6 Public Policy major Prerequisites: 25% in level 100 Public Policy. To achieve a major in Public Policy students must complete 50% of level 200 units and 50% of level 300 chosen from the Bachelor of Arts schedule on page B-xx. 7 Social Ecology major Course details (2001) page 96 Prerequisites: 25% in level 100 Social Ecology. To achieve a major in Social Ecology students must complete 50% of level 200 units and 50% of level 300, including the following: Unit Title campus-sem weight code Social Ecology H2~L2 12.5% HGE203/303 Population and Society H1~L1 12.5% HGE204/304 And a further 75% of units chosen from the Social Ecology units listed in the Bachelor of Arts Schedule (on page B-xx); but excluding HGA203/303. 8 Sociology major Prerequisites: 25% in level 100 Sociology. To achieve a major in Sociology students must complete 50% of level 200 units and 50% of level 300 including the following unit: Unit Title Sociological Analysis of Modern Society campus-sem weight code H2~L2~D2 12.5% HGA202 and a further 87.5% of units chosen from the Sociology units listed in the Bachelor of Arts schedule on page xx but excluding HGA203/303. NOTE: no unit may be counted twice as part of the Police Studies Major and the second major. Bachelor of Social Work (Abbreviation: BSW) Course code: R3B The Bachelor of Social Work is a 2 year end-on degree program that follows 2 years of successful study in a relevant degree from a recognised tertiary institution. It is offered by the School of Sociology and Social Work within the Faculty of Arts on the Launceston campus. The course consists of eight academic units plus two fieldwork placements (Practicum 1 & 2). The academic units are available only on the Launceston campus. Placements are offered in a range of social work agencies throughout Tasmania and applicants should be aware that they may be required to travel away from Launceston for at least one practicum. All travel and accommodation costs incurred during placement are to be met by students. Course details (2001) page 97 Academic units may be studied on a full-time or part-time basis. The Practicum units are normally full time although applications for part time practicum will be considered by the Head of Discipline on a case-by-case basis. The maximum period of time allowed to complete the BSW degree is 5 years. Admission & prerequisites In order to be eligible for entry to the course applicants must either: • • have completed the equivalent of at least two years full-time study in a degree program; with a substantial amount of that study in both sociology and psychology at levels 100 and 200. Students are invited to check with the course coordinator whether they have sufficient and appropriate prerequisite subjects. OR • • have successfully completed the Associate Diploma of Social Science (Community Welfare), or its equivalent, in the TAFE sector; and, have completed one full year of the BA or BSocSc with level 100 units in both psychology and sociology. If applicants believe they meet either of these requirements they may apply for admission to the course. They will be assessed against the following criteria: • • • • • academic achievement relevance of previous study to social work demonstrated interest in the course and the career relevance of previous work experience to the course and career equity and special considerations. Course objectives The course is designed to meet the educational requirements of the Australian Association of Social Workers (AASW). It provides the opportunity for students to gain knowledge and understanding of social functioning, social problems and social services. It emphasises the application of professional social work methods in the workplace and aims to produce graduates who have achieved the level of competency expected of those who are beginning a career in social work. As a student you will be expected to develop: • the ability to think critically and constructively about different approaches to social work; Course details (2001) • • • • page 98 the necessary analytical and interactional skills for a wide range of situations involving individuals, families, groups, organisations and communities; personal insight and awareness in order to develop the potential for continued professional growth; the ability to contribute to the improvement and development of social welfare policy and services; and the ability to conduct research for the development of social work knowledge. Career outcomes Graduates are qualified to work in a variety of positions and may find employment as social workers, community workers, crisis intervention workers, counsellors, managers of human services and outreach workers. Professional recognition The degree course is the only course in Tasmania which leads to accreditation with the Australian Association of Social Workers. Course structure The program of units for the course is set out in the schedule below. The course comprises 2 years full-time study (or its part time equivalent) in compulsory academic and practicum units. Full-time students are required to enrol in units with a combined weighting of not more than 100%. Students will not be permitted any more than two attempts at any academic unit and must complete the two practicum units in not more than three attempts (including withdrawals) for the two units. Where students fail a field practicum they may be required to complete additional work specified by the Head of Discipline before being permitted to re-enrol in that field practicum. If students cannot complete the practicum units in three attempts (due to failure or withdrawal) they will not be eligible for the degree unless they receive the specific permission of the Head of Discipline to re-enrol. Articulation This course articulates with other degrees and units from recognised tertiary institutions as well as with the Associate Diploma in Social Sciences (Community Welfare) (or equivalent) from TAFE institutions in Australia. Specific details are given under the heading 'Admission requirements and prerequisites'. Course details (2001) page 99 Schedule A (Unit) weight represents the proportion (%) of a normal full-time study load, and is used for calculating the services and amenities fee and HECS liability. Full-time students are required to complete a 100% study load in both Year 1 and Year 2. This load includes the three compulsory units in Year 1 and Year 2, plus two of the alternate units in each year. For detailed information on the units, refer to the 'Unit details' section of this handbook. Note also that the Faculty reserves the right to correct errors or inconsistencies, with or without notice, and to make changes to this schedule and its appendices. Unit Title Year 1 Interpersonal Theory and Practice 1 Social Work Practice and Theory Social Work Practicum 1 Year 2 Interpersonal Theory and Practice 2 Community Work Practice Social Work Practicum 2 Rotating units Social Policy Research Processes in Social Work Organisational Context and Administrative Practice Social Work Practice and the Law campus-sem weight code L1 12.5% HGW301 L1 L2 12.5% 50% HGW302 HGW303 L1 L1 L2 12.5% 12.5% 50% HGW401 HGW402 HGW403 L1 12.5% HGW304/404 L1 12.5% HGW305/405 [na] 12.5% HGW306/406 [na] 12.5% HGW307/407 Bachelor of Social Work with Honours (Abbreviation: BSW(Hons)) Course code: R4B A candidate who has completed level 300 of the degree of Bachelor of Social Work with sufficient merit may be accepted by the Faculty of Arts as a candidate for the degree of Bachelor of Social Work with Honours. Course details (2001) page 100 Potential students should discuss their application with the Head of Discipline who should also approve enrolment in the course. Admission & prerequisites The candidate's acceptance for honours is based on the achievement of a minimum Credit average in the academic units of the Bachelor of Social Work and Bachelor of Arts or Bachelor of Social Science or equivalent degree taken at level 200. The Faculty will consider applicants who do not meet these requirements on a case-by-case basis. Course objectives The honours course is concurrent with the final year of the Bachelor of Social Work degree course. Course structure In addition to the normal academic units of the fourth year, candidates for honours undertake two practicums – one in an agency (Social Work Practicum 2 – weighting 25%), and the other in a research unit on campus (Social Work Practicum 3 – weighting 12.5%). Additionally candidates must undertake a supervised research project on a topic relevant to social work and submit a dissertation – weighting 12.5%. The levels of honours are First Class, Second Class, and Third Class. There is an upper and lower division in the second class. To gain first class honours you are required to complete all units with a minimum Grade-Point Average of 7.0 in academic units, including an award of HD in the honours dissertation. To gain upper second class honours you are required to complete all units with a minimum Grade-Point Average of 6.5 in academic units, including an award of DN in the honours dissertation. To gain lower second class honours you are required to complete all units with a minimum Grade-Point Average of 6.0 in academic units, including an award of CR in the honours dissertation. To gain third class honours you are required to complete all units with a minimum Grade-Point Average of 5.0 in academic units, and gain an award of PP in the honours dissertation. Except by special permission of Faculty there is no re-examination for honours. Note: The Grade-Point Average for entry is computed as follows: HD=9, DN=7, CR=6, PP=5, TP=4.5, NN= 4. Schedule A Unit Title Interpersonal Theory and Practice 2 campus-sem weight code L1 12.5% HGW401 Course details (2001) page 101 Community Work Practice Social Work Practicum 2 (Honours) Social Work Practicum 3 (Honours) Social Work Honours Dissertation Plus two of the following rotating units Social Policy Research Processes in Social Work Organisational Context and Administrative Practice Social Work Practice and the Law L1 12.5% HGW402 L2 25% HGW408 L2 12.5% HGW409 Lf 12.5% HGW410 L1 12.5% HGW304/404 L1 12.5% HGW305/405 [na] 12.5% HGW306/406 [na] 12.5% HGW307/407 Bachelor of Tourism (Abbreviation: BTourism) Course code: R3J Students who commenced the Bachelor of Tourism in 2000 should note that from 2001 there will be no new intake into the Bachelor of Tourism at the Hobart campus and that it will be taught out on this campus. Starting in 2001, the Bachelor of Tourism (BTourism), a three-year course offered by the Faculty of Arts, will be offered at the Launceston campus only. Students may study full time or part time and have nine enrolment years, including the year of passing the first unit for the degree, in which to complete the course requirements. Admission & prerequisites To gain entry to the BTourism, students must meet the normal minimum University entry requirements which include several categories of special admission, such as mature age. No particular subject prerequisites apply for this course. Students normally enter in February. There is limited entry in July. Course objectives The BTourism provides a general course of study for students considering a career in the tourism industry. The degree comprises an overview of tourism as a field of human activity, introduces students to the key areas of academic knowledge and provides skills with vocational relevance. Students will receive Course details (2001) page 102 a solid grounding in the areas of wilderness and heritage tourism as well as marketing or management. The degree links the disciplinary bases of Management and Commerce, Geography, Sociology, History, Administration, Antarctic Studies and Aboriginal Studies. It combines units from the Faculty of Arts with units from the Faculty of Commerce and Law, and the Faculty of Science and Engineering. Career outcomes Graduates of the Bachelor of Tourism degree will be strong applicants for jobs in a wide range of fields, for example: • • • • • Tourism and the travel industries; heritage tourism, museums and historic sites; wilderness, antarctic and nature tourism; tourism research; tourism marketing; tourism administration; tourism journalism and the media. Course structure In their first year, students must study five subjects, Foundations of Tourism, Introduction to Management, History, Geography plus a further 25% from a range of subjects as detailed in the Schedule. In their second and third years students study three core areas: Interpretation and Heritage, Wilderness and Antarctic, and Management and Policy. In addition, they must choose four electives, one will be chosen from research methods units, and three from a list of electives. Sample course Year 1 Foundations of Tourism A and B 25% Introduction to Management 12.5% History 12.5% Geography 25% Indonesian 25% Year 2 Interpretation and Heritage Wilderness and Antarctic 25% Management and Policy 25% 25% Course details (2001) Indonesian 12.5% Services Marketing page 103 12.5% Year 3 Interpretation and Heritage 25% Wilderness and Antarctic 25% Management and Policy 25% Marketing Research 12.5% Sport and Leisure 12.5% <tbz> Articulation Students who have completed a TAFE Associate Diploma or a Diploma in tourism-related subjects may apply for credit towards the BTourism degree course. Students who have studied in another degree such as the Bachelor of Arts (BA) and want to transfer to the BTourism may also apply for credit. Students who are currently studying for another degree can transfer to the BTourism course. Schedule of units Students qualify for the Bachelor of Tourism by successfully completing 24 units (each 25%) of core and elective units (total 300%). Launceston schedule Unit Title campus-sem Level 100 Foundations of Tourism A L1~H1 Economics for Business H1~L1~B1 Foundations of Tourism B L2~H2 (b) The Modern World in Australia to 1860 L2~B2~D2 Introduction to Management H1/2~L1/2~B1 Population and Urbanisation L1~B1~D1 Plus 25% from the following list: Introductory Indonesian [a] Hf~Lf [a] Chinese 1 Hf~Lf Contemporary Indigenous Australia L1~H1~D1 weight code 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HTM101 BEA110 HTM102 12.5% HTA106 12.5% BMA101 12.5% KJG101 25% 25% HMN100 HMC100 12.5% HAB102 Course details (2001) page 104 Introduction to International Business H2~L2 12.5% BMA181/281 The Physical Environment L2~B2~D2 12.5% KJG102 Organisational Behaviour H1~L1 12.5% BMA201 Level 200/300 Students must complete all units in the three core areas Interpretation and Heritage Core Tourism Theory H1~L1 12.5% HTM200/300 Australian History 1788–1990s D1 12.5% HTA240/340 History and Heritage L2~H2~D2 12.5% HTA290/390 Indigenous Tourism H2 12.5% HAB210/310 Wilderness and Antarctic Core Natural Resources Management L2~D2 12.5% KJG202 Australian Natural Environments L1~D1 12.5% KJG201 plus two 12.5% units to be advised Management, Marketing and Policy Core Principles of Marketing H3/2~L3/2 12.5% BMA151/251 Sport and Tourism: Policy and Politics H2~L2 12.5% HSD210/310 Placement in the Tourism Industry, not offered in 2001 Human Resource Management in Tourism and Hospitality H2~L2 12.5% BMA225/325 Electives Students choose four electives. One of BMA253 or HGA203/303 Marketing Research H2 12.5% BMA253 Social and Political Research L1~H1 12.5% HGA203/303 Plus three electives (37.5%) from: One 12.5% unit from elective spoken language courses Accounting and Financial Decision Making [b] H1~L1~B1 12.5% BFA103 Buyer Behaviour H2 12.5% BMA252 Marketing Communications H1 12.5% BMA255 [a] Strongly recommended units [b] Students undertaking this unit are permitted to count the unit as a 200/300 level elective Hobart schedule Unit Title Level 100 Foundations of Tourism A campus-sem weight code L1~H1 12.5% HTM101 Course details (2001) page 105 Foundations of Tourism B L2~H2 12.5% HTM102 Introduction to Management H1/2~L1/2~B1 12.5% BMA101 Plus one of the following: Chinese 1 Hf~Lf 25% HMC100 French 1 Hf 25% HEF100 German 1 Hf 25% HEG100 Introductory Indonesian Hf~Lf 25% HMN100 Japanese 1 Hf 25% HMJ100 (b) The Modern World in Australia to 1860 H2 12.5% HTA104 Plus one of: Geography and Environmental Studies 1 Hf 25% KGA100 Geography and Environmental Studies 1A Hf 25% KGA101 Level 200/300 Students must complete all units in the three core areas. The following level 200/300 units will be offered in Hobart in 2001: Interpretation and Heritage Core Tourism Theory H1~L1 12.5% HTM200/300 Van Diemen's Land 1642–1850 H1 12.5% HTA229/329 Indigenous Tourism H2 12.5% HAB210/310 Wilderness and Antarctic Core Environmental Impact Assessment and Decision Making H2 12.5% KGA381 Wilderness and Natural Area Management: Natural and Cultural Values H2 12.5% KGA278/378 Management, Marketing and Policy Core Principles of Marketing [c] H3/2~L3/2 12.5% BMA151/251 Sport and Tourism: Policy and Politics H2~L2 12.5% HSD210/310 Elective units One of: Marketing Research H2 12.5% BMA253 Social and Political Research L1~H1 12.5% HGA203/303 Qualitative Research Methods H1~L2 12.5% HGA230/330 Survey Research H3 12.5% HGA204/304 Plus three (37.5%) from the following: Chinese for Tourism H1 12.5% HMC205 Japanese for Tourism H1 12.5% HMJ203 French for Tourism and Business H1 12.5% HEF203/303 Course details (2001) German for Tourism and Business Accounting and Financial Decision Making Buyer Behaviour Cultures and Societies of Southeast Asia Art, Natural Environment and History Environmental Ethics Fauna Conservation Management Geography of Asia Marketing Communications Services Marketing Social & Environmental Accounting [d] Tourism, Sport and Leisure Art, Natural Environment and Wilderness Natural Vegetation of Tasmania Vegetation Management History and Heritage Uncovering the Past [c] use enrolment code BMA251. [d] use enrolment code BFA307. page 106 H1 12.5% HEG203 H1~L1~B1 H2 12.5% 12.5% BFA103 BMA252 H2 12.5% HGA254/354 H3 H1 12.5% 12.5% FSZ250/350 HPA277/377 H1 H1 H1 H1 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KGA332 KGA202/302 BMA255 BMA353 H2 12.5% BFA207/307 H1 12.5% HGA251/351 H1 12.5% FSZ251/351 H2 H1 L2~H2~D2 H2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KPA152 KGA331 HTA290/390 HTC204/304 BA Combined degreesBachelor of Arts and Bachelor of Laws (Abbreviation: BA–LLB) Course code: L3D This is a five-year full-time degree course. The first year is studied in the Bachelor of Arts degree, taking the subject BLA101 Introduction to Law (25%), plus three further subjects from the BA schedule (75%). At the end of the first year, students apply for entry to the combined Bachelor of Arts–Bachelor of Laws degree course or the Bachelor of Laws. Entry is based on first-year results. If students are unsuccessful, they continue with the BA degree course. Course details (2001) page 107 If successful in gaining entry to combined degree course, students complete a major in the BA, plus the required and elective Law units specified below. In the second year, students study BLA200 Contract (20%), BLA201 Torts (20%), level 200 units to the value of 62.5% from the BA schedule (a 2.5% overload). In the third year, students study BLA202 Criminal Law (25%), BLA203 Principles of Public Law (25%), and 50% of level 300 units from the BA schedule. By the end of the first three years of the degree, students normally have completed a major from within the BA. In the fourth and fifth years, students study prescribed Law units. See page xx. Course objectives Course structure Sample course Year 1 Introduction to Law 25% English 25% Political Science 25% History 25% Year 2 Contract 20% Torts 20% English 37.5% Political Science 25% Year 3 Criminal Law 25% Principles of Public Law 25% English 12.5% Political Science 37.5% Year 4 Required Law units 100% Course details (2001) page 108 Year 5 Required Law units 100% <tbz> Schedule Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Introduction to Law Hf~Lf 25% BLA101 plus 75% units from BA ( course code R3A) on page xx Year 2 Contract Law [a] Hf 25% BLA200 Torts [a] Hf 25% BLA201 plus 62.5% units from BA (course code R3A) on page xx Year 3 Criminal Law Hf 25% BLA202 Principles of Public Law Hf 25% BLA203 plus 50% units from BA ( course code R3A) on page xx Year 4 Property Law Hf 25% BLA303 Law of Groups H1 12.5% BLA304 plus 5 electives from Schedule of Electives on page xx Year 5 Litigation Hf 25% BLA402 Equity and Trusts H1 12.5% BLA401 plus 5 electives from Schedule of Electives on page xx [a] the weighting of these units is 20% for students enrolled in this combined degree Bachelor of Arts and Bachelor of Computing (Abbreviation: BA–BComp) Course code: R3L This four year (minimum) combined degree of Bachelor of Arts–Bachelor of Computing is offered on the Launceston campus by the Faculty of Arts and Faculty of Science and Engineering. A fuller description of the course may be found on page B-xx. Course details (2001) page 109 Course objectives Bachelor of Arts and Bachelor of Fine Arts (Abbreviation: BA–BFA) Course code: R3F This is a five-year full-time degree course which may also be studied part time. In the first year students study two first-year subjects from the BA schedule and two first-year subjects from the BFA degree course. Over the five years of the degree, students complete the requirements for both the BA and the BFA, by completing either two majors or a double major in the BA degree and either a studio major and a minor in Art and Design Theory in the BFA or a major in Art History and Cultural Theory along with studio-based and elective units to make up the remaining percentage. The full structure of the degree is shown on page B-xx. Course objectives Course structure Sample course Year 1 (100%–125%) Journalism and Media Studies Philosophy 25% E-Media 25% Art and Design Theory 25% 25% Year 2 (100%) Journalism and Media Studies Philosophy 25% E-Media 50% Year 3 (100%) 25% Course details (2001) Journalism and Media Studies E-Media 50% Art and Design Theory 25% page 110 25% Year 4 (100%) Journalism and Media Studies Philosophy 25% Drawing 25% Art and Design Theory 3 25% 25% Year 5 (100%) Journalism and Media Studies Philosophy 25% Women's Studies 25% Fine Arts electives 25% 25% Major totals Journalism and Media Studies major (125%)(100% min) Philosophy major 100% min Art and Design Theory 75% (50% min) E-Media major 125% <tbz> Bachelor of Arts and Bachelor of Applied Science (Abbreviation: BA–BAppSc) Course code: R3G The last intake of students into the combined BA–BAppSc degree was 2000. The BAppSc is being taught out over the period 2001 to 2003. Students should refer to the BA and BAppSc schedules as listed in this handbook; but for other details may refer to the Course and Unit Handbook 2000. Current students should contact Mrs Michelle Horder on (03) 6324 3863 if advice is needed. Bachelor of Arts and Bachelor of Science (Abbreviation: BA–BSc) Course details (2001) page 111 Course code: R3H This is a five-year full-time degree course which may also be studied part time. In the first year students study two first-year subjects from the BA schedule and two first-year subjects from the BSc degree course. Over the five years of the degree, students complete the requirements for both the BA and the BSc, by completing either two majors or a double major in the BA degree and a major in the BSc. The full structure of the degree is shown on page xx. Course objectives Graduate Diploma in Languages (Abbreviation: GradDipLang) Course code: R6J The Graduate Diploma in Languages is offered on the Hobart campus. The course may be completed in a minimum of one calendar year and a maximum of three consecutive calendar years of study. Candidates whose work has been interrupted by illness or other unavoidable cause may be given additional time to complete the course. Candidates may currently study one of the following languages: • • • • • French German Japanese Chinese Indonesian The approved abbreviation for the award is GradDipLang with the name of the language studied following in parentheses. Some HECS-based places may be offered. Admission & prerequisites Applicants must consult the head of the School of English and European Languages and Literatures or the Head of the School of Asian Languages and Studies before enrolling. To be admitted to the course applicants must have qualified for admission to the degree of Bachelor of Arts, or another approved bachelor degree, of the Course details (2001) page 112 University of Tasmania. They should also have obtained a pass at Credit level or better in units totalling at least 37.5% at the 200 level of the language which they propose to study. Applicants who hold an approved degree or diploma from another university or tertiary institution may be considered for admission provided they have met the standard indicated above in the language they propose to study. In special cases applicants who have completed an approved three-year course at a lower standard may be admitted to the course. Course objectives The Graduate Diploma in Languages course is designed to enable candidates, who may not have qualified for admission to an Honours program, to pursue studies at a postgraduate level and achieve a high level of spoken and written competence in the language of their choice. Course structure To qualify for the award candidates must pass units in one of French, German, Japanese Chinese or Indonesian, as approved by the Head of the School of English and European Languages and Literatures or the Head of the School of Asian Languages and Studies, at level 300 and/or 400 with a combined weight of 100%. General provisions Candidates may not, without the consent of the Faculty, submit for examination for the Graduate Diploma any work which has previously been submitted for any degree or diploma. Candidates who fail to make satisfactory progress may be required by the Faculty to withdraw from the course or to repeat some or all of the work prescribed. Enrolment codes French HEF500 Full time HEF501 Part time German HEG500 Full time HEG501 Part time Japanese HMJ500 Full time HMJ501 Part time Chinese HMC500 Full time HMC501 Part time Indonesian HMN500 Full time HMN501 Part time Course details (2001) page 113 Graduate Diploma of Music (Abbreviation: GradDipMus) Course code: F6D The Graduate Diploma of Music is a one-year coursework award designed to suit the needs of practising professional musicians. Course objectives The course is designed to support advanced studies in instrumental/vocal performance, composition and music technology. Primary concentration will be given to the development of high level technical and music skills within the specialist area. On completion of this course students should have: • • • developed advanced skills as performers and/or composers acquired increased skills in their particular area developed a comprehensive understanding of a wide range of repertoire and concepts. Articulation Students who wish to proceed to the Master of Music (coursework) cannot take out the GradDipMus but transfer to the MMus with full credit. Schedule The Graduate Diploma of Music consists of the completion of a total load of 100% which may comprise any four of the following units. Note: all units are one semester long Unit Title Performance 1 Performance 2 Composition 1 Composition 2 Music Technology Music Publishing Multimedia Authoring 1 Multimedia Authoring 2 Ensemble 1 Ensemble 2 Music Research Project campus-sem H1/2 H1/2 H1/2 H1/2 H1/2 H2 [na] [na] H1/2 H1/2 H1 weight 25% 25% 25% 25% 25% 25% 25% 25% 25% 25% 25% code FCA501/701 FCA502/702 FCA511/711 FCA512/712 FCA521/721 FCA522/722 FCA523/723 FCA524/724 FCA531/731 FCA532/732 FCA540/740 Course details (2001) page 114 Admission to the Graduate Diploma of Music is by application and audition. Performers are expected to prepare at least 30–40 mins of music that demonstrate their musical skills. Composers are to submit a folio of recent work either as scores, sound recording, video or a combination of these. The Graduate Diploma of Music is fully articulated with the Master of Music (coursework). Current students who have completed 100% of the Graduate Diploma may apply to enter the Master of Music (coursework) and be given credit for units completed in the Graduate Diploma. Master of Fine Art and Design (Abbreviation: MFAD) Course code: F7D The Master of Fine Art and Design is offered on a full fee-paying basis only. The Master of Fine Art and Design is a 3-semester full-time or equivalent half-time or equivalent summer school/evening study/weekend study program. Students may enrol for semester 1 or semester 2 entry. Admission & prerequisites To qualify for admission, applicants must demonstrate, during an interview process, the potential to undertake the MFAD. Normally applicants should have a degree or degree-equivalent qualifications in Fine Art, Design, or in an accepted cognate discipline. A person who possesses such other qualifications and professional experience deemed by the Faculty to provide an adequate preparation for study equivalent to that provided for by an undergraduate degree, may be admitted to the course. Upon admission into the course students may apply for status. Normally, students who have graduated in the Graduate Diploma or Honours degree may, at the discretion of the Faculty, be awarded up to 33.33% credit of the course or credit of up to 33.33% may be given, at the discretion of the Faculty, for achievements by candidates in other awards and professional practice areas. Course objectives Course details (2001) page 115 The MFAD aims to provide a high quality recognised qualification at postgraduate level in a professional practice-oriented coursework program. The course provides a flexibly structured program with the capability of cross-disciplinary, cross-faculty and cross-campus study which allows students, in conjunction with the School, to design a course which best serves their professional needs. Students complete a professional practice project or a series of such projects agreed upon in consultation with the Postgraduate Awards Committee, with the option of undertaking a research component in the final semester. This course allows a great deal of flexibility for students and involves a substantial amount of independent study. Students enrolling at the School of Art at Hobart may undertake projects in art theory, ceramics, drawing, e-media, furniture design, graphic design, painting, photography, printmaking or sculpture. Students enrolling at the School of Visual and Performing Arts at Launceston may undertake projects in art theory, ceramics, painting, printmedia, sculpture or textiles. Career outcomes Graduates of the Master of Fine Art and Design find employment in a variety of positions within the arts professions including curatorial work, gallery administration, research and teaching, as well as participating in individual and group-generated projects and studio practice. Course structure Students have the option of undertaking a straight coursework program over three semesters or may include a research component in the third semester. Students completing the coursework program must complete a professional practice project, or a series of projects over a three-semester period. Students enrolling in the research component must complete a professional practice project or a series of projects over a two-semester period and then a dissertation by exhibition and documentation or an 8,000 word thesis. All projects and dissertations undertaken must be approved by the Postgraduate Awards Committee. Students may complete the three-semester course over a twelve-month period by completing the third unit in the program by summer school, or evening or weekend study programs at the approval of the School. Students are also given the option of enrolling in an approved postgraduate coursework unit from another School with a total weight of 50%. Schedule of Units Course details (2001) page 116 Note: students enrolling at Launceston enrol in unit code FFA-, and students enrolling at Hobart enrol in the unit code FSA–.• Students must complete a total of 150% of units to qualify for the award; • Students wishing to include a research component take FFA/FSA753 Research Project as one of their units; • Students may undertake approved postgraduate coursework units from other faculties with a total weight of 50%, and MFAD units to give a combined weight of 150% in one year of full-time study. Schedule for Hobart students Unit Title campus-sem weight Full-time study Choose three of the following: Professional Practices 1 H1/2 50% Professional Practices 2 H1/2 50% Professional Practices 3 H1/2 50% Research Project H1/2 50% Part-time study As above, except that unit enrolment codes are FSA760/761/762/763 respectively and each unit is taken over 2 semesters. code FSA750 FSA751 FSA752 FSA753 Schedule for Launceston students Unit Title campus-sem weight Full-time study Professional Practices 1 L1/2 50% Professional Practices 2 L1/2 50% Professional Practices 3 L1/2 50% Research Project L1/2 50% Part-time study As above, except that unit enrolment codes are FFA760/761/762/763 respectively and each unit is taken over 2 semesters. code FFA750 FFA751 FFA752 FFA753 Master of Music (Abbreviation: MMus) Course code: F7E The Master of Music (coursework) is a two-year coursework award designed to suit the needs of practising professional musicians. Course objectives Course details (2001) page 117 The course is designed to support advanced studies in instrumental/vocal performance, composition and music technology. Primary concentration will be given to the development of high level technical and music skills within the specialist area. On completion of this course students should have: • • • developed advanced skills as performers and/or composers acquired increased skills in their particular area developed a comprehensive understanding of a wide range of repertoire and concepts. Career outcomes Graduates of the Master of Music are engaged at all levels of the music profession, both in Australia and overseas. They enjoy successful careers as performers, teachers and administrators, or may be involved in broadcasting, journalism or as music critics. Articulation Students who have completed, but not graduated in, the Graduate Diploma of Music, may apply for entry to the Master of Music and receive full credit for all GradDipMus units completed. Schedule The Master of Music consists of the completion of a total load of 200% comprising the following units: Unit Title campus-sem Compulsory unit Music Research Project H1 Plus a further 7 units from the following: Performance 1 H1/2 Performance 2 H1/2 Performance 3 H1/2 Performance 4 H1/2 Composition 1 H1/2 Composition 2 H1/2 Composition 3 H1/2 Composition 4 H1/2 Music Technology H1/2 Music Publishing H2 Multimedia Authoring 1 [na] Multimedia Authoring 2 [na] weight code 25% FCA540/740 25% 25% 25% 25% 25% 25% 25% 25% 25% 25% 25% 25% FCA501/701 FCA502/702 FCA703 FCA704 FCA511/711 FCA512/712 FCA713 FCA714 FCA521/721 FCA522/722 FCA523/723 FCA524/724 Course details (2001) page 118 Ensemble 1 H1/2 25% FCA531/731 Ensemble 2 H1/2 25% FCA532/732 Ensemble 3 H1/2 25% FCA733 Ensemble 4 H1/2 25% FCA734 Up to 75% of the total load may be taken from other Schools with the prior approval of the Coordinator of Postgraduate studies. Admission to the Master of Music (coursework) is by application and audition. Performers are expected to prepare at least 30–40 mins of music that demonstrates their musical skills. Composers are to submit a folio of recent work either as scores, sound recording, video or a combination of these. Master of Public Administration (Abbreviation: MPA) Course code: R7D The Master of Public Administration course is being discontinued and there will be no further intake in 2001. Students already enrolled in the course should consult the Course and Unit Handbook 2000 for details of the course structure. Course specifications are given in the Calendar. Bachelor of Business Administration (Enterprise Development) (Abbreviation: BBA(EntDev)) Course code: C3W This on-campus, 3-year full-time or 6-year part-time course is offered by the Faculty of Commerce and Law at Launceston. Admission & prerequisites Categories of students will be considered for admission, either as: (a) applicants who possess the University's basic requirements for admission to undergraduate courses; or alternative entry application as: Course details (2001) (b) (c) page 119 mature age people with business experience but limited formal academic achievements. In ranking for entry, practical business experience will provide substantial points towards entry; secondary school (or college), TAFE, and State Enterprise Workshop students undertaking specific certificate and diploma courses in enterprise education. Applicants in this category will be interviewed to assess their potential to undertake this course. Course objectives The course provides a 'whole-of-business' strategic focus to the operation of business enterprises, with ability to clearly identify structural change and its impacts, and then develop skills in how to innovate and redesign business activity. Students learn how to • • • • • • • • identify and analyse business opportunities within such changing structures that add value to society; use core business and economics-based skills in strategic enterprise developments; generate support through all forms of communication and negotiation, to share with others the value of innovative opportunities; think divergently and creatively through synthesis of many economics and business concepts; develop business strategies and plan them out from inception, growth and redesign; undertake varied simulation and on-the-job experiences of enterprise development practices; cultivate recognition of frontier technologies and path-dependent business developments that provide the basis for strategic activities; work co-operatively in teams and business alliances with appropriate entrepreneurial role models. Professional recognition There is currently no appropriate professional body in this area. Course structure The course structure is outlined in the schedule. All units are weighted at 12.5%, with the exception of the core unit, Foundations of Enterprise Development which is a full-year unit of 25%. This unit establishes the basic principles and fundamental issues in the strategically focused area of developing new or redesigning extant enterprises. Schedule Course details (2001) Unit Title campus-sem Year 1 Accounting and Financial Decision Making H1~L1~B1 Business Information Systems H1/2~L1/2~B1 Introduction to Management H1/2~L1/2~B1 One elective unit (12.5%) Foundations of Enterprise Development Lf Data Handling and Statistics 1 H1/2~L1/2~B2 Principles of Marketing H3/2~L3/2 Year 2 Economics for Business H1~L1~B1 Business Logistics L1 Organisational Behaviour H1~L1 One elective unit (12.5%) Commercial Transactions H2~L2~B2 Project Financing L2 Two elective units (totalling 25%) Year 3 Entrepreneurship and Innovation H?~L? Electronic Marketing H2 Two elective units (totalling 25%) Economics, Management and Organisation H1 Field Operation L2 Strategic Management H2~L2 One elective unit (12.5%) page 120 weight code 12.5% BFA103 12.5% BSA101 12.5% BMA101 25% BEA103 12.5% 12.5% KMA153 BMA151/251 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BEA110 BSA204 BMA201 12.5% 12.5% BFA141 BFA203 12.5% 12.5% BEA326 BMA308 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BEA302 BEA336 BMA302 Bachelor of Business Administration (Hospitality Management) (Abbreviation: BBA(HospMgmt)) Course code: C3T This on-campus, 3-year full-time or 6-year part-time course is offered by the Faculty of Commerce and Law at Hobart and Launceston. Course details (2001) page 121 Admission & prerequisites Possession of the University's basic admission requirements. The Drysdale Institute of TAFE Advanced Diploma of Hospitality or an equivalent award is also required. Those without the latter and those wishing to transfer from another degree course will be counselled as to the program of study that they would need to follow in order to undertake the Bachelor of Business Adminstration (HospMgmt). Course objectives The course is designed to produce graduates with a sound knowledge of the fundamental principles and concepts of management, a familiarity with significant literature in the field and the ability to review, consolidate, extend and apply the knowledge and techniques to the hospitality management sector. It seeks to produce graduates with knowledge, skills and understanding of best practice in hospitality management, and the value of research, critical thinking and effective communication. Graduates develop professional skills in such areas as interpersonal communication, services management, working in teams, report writing and problems-solving techniques. They are given the opportunity to gain a professional degree in hospitality management. The course also provides holders of a Drysdale Institute of TAFE Advanced Diploma of Hospitality with the opportunity to gain a university qualification in hospitality management. Course structure The Bachelor of Business Administration in Hospitality Management consists of 16 specified core units and 8 specialised hospitality units. Because of the specialised nature of the course, it is not possible to include elective units. For specific details, see the Schedule. Articulation Applicants who have completed the Drysdale Institute of TAFE Advanced Diploma of Hospitality will be granted credit for fourteen units towards the Bachelor of Business Administration (HospMgmt) degree course. Candidates with an equivalent award will also be considered on an individual basis and following the advice from the course advisory committee, may be granted credit. Schedule The course is designed for articulation with the Advanced Diploma of Hospitality offered by the Drysdale Institute of TAFE and equivalent Australian and International awards. Course details (2001) page 122 Prospective students will therefore enter the course in the summer semester of year 2 of the course and the structure of the course will be as follows: Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Semester 1 and 2: studies undertaken at Drysdale Institute of TAFE or equiv Year 2 Semester 1 and 2: studies undertaken at Drysdale Institute of TAFE or equiv Summer semester Principles of Marketing [a] H3/2~L3/2 12.5% BMA151/251 Management of Human Resources [a] H3/2~L3/2 12.5% BMA121/221 Year 3 Semester 1 Organisational Behaviour H1~L1 12.5% BMA201 Contract of Employment H1~L1 12.5% BMA241 * contact school for details of HGA214 Electronic Commerce H1~L1 12.5% BSA306 Semester 2 Human Resource Management in Tourism and Hospitality H2~L2 12.5% BMA225/325 Strategic Management H2~L2 12.5% BMA302 Employee Relations H2~L2 12.5% BMA321 Introduction to International Business [a] H2~L2 12.5% BMA181/281 [a] Students should use appropriate level 200 enrolment code BMA251, BMA221, BMA281 Bachelor of Business Administration (Human Resource Management) (Abbreviation: BBA(HRM)) Course code: C3U This on-campus, 3-year full-time or 6-year part-time course is offered by the Faculty of Commerce and Law at Hobart and Launceston. Admission & prerequisites Possession of the University's basic admission requirements. Course objectives Course details (2001) page 123 The course provides the opportunity for students to combine the core of a business administration degree with a focused study of the foundations of Human Resource Management (HRM). It is a professional course that will enable graduates to fulfil key roles in the human resource management area. Such graduates will have a good understanding of the role of HRM in both private and public sector enterprises, and will have knowledge, skills and understanding of best practice in HRM, and value research, critical thinking and effective communication in HRM. Graduates will have developed professional skills in such areas as interpersonal communication, working in teams, report writing and problem-solving techniques. Course structure The Bachelor of Business Administration in Human Resource Management consists of 19 specified core units, one BCom core elective and 4 elective units. The electives may be chosen from any other discipline area in the University. Articulation Applicants who have completed the TAFE associate diplomas or diplomas or an equivalent qualification will be granted credit for eight units towards the BBA(HRM). Applications for such credit, however, will be considered on an individual basis. Schedule Unit Title Year 1 Semester 1 Business Information Systems Introduction to Management Economics for Business Accounting and Financial Decision Making Semester 2 Data Handling and Statistics 1 Management of Human Resources [a] Commercial Transactions Principles of Marketing [a] Year 2 Semester 1 Organisational Behaviour campus-sem weight code H1/2~L1/2~B1 12.5% BSA101 H1/2~L1/2~B1 H1~L1~B1 12.5% 12.5% BMA101 BEA110 H1~L1~B1 12.5% BFA103 H1/2~L1/2~B2 12.5% KMA153 H3/2~L3/2 H2~L2~B2 H3/2~L3/2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BMA121/221 BFA141 BMA151/251 H1~L1 12.5% BMA201 Course details (2001) page 124 Contract of Employment H1~L1 12.5% BMA241 Elective unit 12.5% Elective unit 12.5% Semester 2 Employee Relations H2~L2 12.5% BMA321 Human Resource Development H2~L2 12.5% BMA224 Method for Management Studies H2~L2 12.5% BMA260 one BCom core elective unit 12.5% Year 3 Semester 1 Strategic Issues in Human Resource Management H1~L1 12.5% BMA330 International Human Resource Management H1~L1 12.5% BMA381 Electronic Commerce H1~L1 12.5% BSA306 Elective unit 12.5% Semester 2 Managerial Social Responsibility H2~L2 12.5% BMA291/391 Strategic Management H2~L2 12.5% BMA302 Human Resource Management in Tourism and Hospitality H2~L2 12.5% BMA225/325 Elective unit 12.5% [a] Students should use appropriate level 100 unit code: BMA121, BMA151 Bachelor of Business Administration (Tourism Management) (Abbreviation: BBA(Tourism Mgmt)) Course code: C3V This on-campus, 3-year full-time or 6-year part-time course is offered by the Faculty of Commerce and Law at Hobart. Admission & prerequisites Possession of the University's basic admission requirements. The Drysdale Institute of TAFE Advanced Diploma of Tourism or an equivalent award is also required. Those without the latter and those wishing to transfer from another degree course will be counselled as to the program of study that they would Course details (2001) page 125 need to follow in order to undertake the Bachelor of Business Administration (TourismMgmt). Course objectives The course is designed to produce graduates with a sound knowledge of the fundamental principles and concepts of management, a familiarity with significant literature in the field and the ability to review, consolidate, extend and apply the knowledge and techniques to the tourism management sector. It seeks to produce graduates with knowledge, skills and understanding of best practice in tourism management, and the value of research, critical thinking and effective communication. Graduates develop professional skills in such areas as interpersonal communication, services management, working in teams, report writing and problems-solving techniques. They are given the opportunity to gain a professional degree in tourism management. The course also provides holders of a Drysdale Institute of TAFE Advanced Diploma of Tourism with the opportunity to gain a university qualification in tourism management. Course structure The Bachelor of Business Administration in Tourism Management consists of 16 specified core units and 8 specialised hospitality units. Because of the specialised nature of the course, it is not possible to include elective units. For specific details, see the Schedule. Articulation Applicants who have completed the Drysdale Institute of TAFE Advanced Diploma of Tourism will be granted credit for fourteen units towards the Bachelor of Business Administration (TourismMgmt) degree course. Candidates with an equivalent award will also be considered on an individual basis and following the advice from the course advisory committee, may be granted credit. Schedule The course is designed for articulation with the Advanced Diploma of Tourism offered by the Drysdale Institute of TAFE and equivalent Australian and International awards. Prospective students will therefore enter the course in the summer semester of year 2 of the course and the structure of the course will be as follows: Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Semester 1 and 2: studies undertaken at Drysdale Institute of TAFE or equiv Year 2 Course details (2001) page 126 Semester 1 and 2: studies undertaken at Drysdale Institute of TAFE or equiv Summer semester Principles of Marketing [a] H3/2~L3/2 12.5% BMA151/251 Management of Human Resources [a] H3/2~L3/2 12.5% BMA121/221 Year 3 Semester 1 Marketing Communications H1 12.5% BMA255 Organisational Behaviour H1~L1 12.5% BMA201 Services Marketing H1 12.5% BMA353 Contract of Employment H1~L1 12.5% BMA241 Semester 2 Strategic Management H2~L2 12.5% BMA302 Buyer Behaviour H2 12.5% BMA252 Management and the Natural Environment [na] 12.5% BMA272/372 Human Resource Management in Tourism and Hospitality H2~L2 12.5% BMA225/325 [a] Students should use the appropriate level 200 enrolment code BMA251, BMA221 Bachelor of Commerce (Abbreviation: BCom) Course code: C3C New majors in Business Management, Business Economics, Corporate Accountability and The Information Economy are being introduced. This on-campus, 3-year full-time or 6-year part-time course is offered at Hobart and Launceston. Majors in Accounting, Business Management, Corporate Accountability, Information Systems and Human Resource Management are available in Hobart and Launceston. Majors in Business Economics, Finance, Marketing and International Business are available only in Hobart. A major in The Information Economy is available in Launceston only. The major in Accounting and some second year Information Systems units are available at the North-West Centre. Admission & prerequisites Possession of the University's basic admission requirements. In addition, applicants must have passed TCE *MT730 Mathematics Applied or a higher level Mathematics subject. Candidates should note, however, that admission to the Faculty is subject to quota selection. Selection is based on a score calculated Course details (2001) page 127 on an applicant's five best TCE subjects – three of which must be taken in Year 12 – chosen from the list of subjects approved by the University for admission purposes. The mathematics subject referred to above does not have to be one of the five counted for the purposes of the calculation of the TE score. Course objectives The course is designed to produce well educated and adaptable graduates, with appropriate professional skills to meet the existing needs and demands of business and related professions. The course specifically prepares students to work in accounting, economics, finance, management, marketing, information systems, international business and in human resource management. Career outcomes Graduates of the Bachelor of Commerce can expect to obtain employment in accounting, economics, finance, international business, human resource or personnel management, marketing, journalism and public relations, government and teaching. Professional recognition If students wish to be eligible for membership of a professional body they will need to select units endorsed by that body. The Faculty of Commerce and Law offers units to enable students to join the following professional bodies: • • • • • • • • Institute of Chartered Accountants in Australia Australian Society of Certified Practising Accountants Australian Human Resources Institute Australian Institute of Management Australian Marketing Institute Chartered Institute of Company Secretaries in Australia Australian Institute of Banking and Finance Australian Computer Society Membership details may be obtained from the relevant Schools or the appropriate professional body. Course structure The Bachelor of Commerce consists of 24 units of study. To qualify, students must complete a compulsory core of six units, two other first-year approved electives, a major of eight units offered within the Faculty and eight elective units which may be in the form of another major or in a grouping of units approved by the Dean (See Schedule of common first year units, below). Course details (2001) page 128 The first year is common to all students (except that students have a choice of two core electives). Students then elect to specialise in one of the following majors offered by the Faculty. Each major consists of eight units which are listed in the following section, Bachelor of Commerce: Course Structure, Majors. • • • • • • • • • • Accounting (Hobart, Launceston, NWC) Business Economics (Hobart only) Business Management (Hobart , Launceston) Corporate Accountability (Hobart, Launceston, NW Centre) Finance (Hobart only) Human Resource Management (Hobart, Launceston) Information Systems (Hobart, Launceston) International Business (Hobart only) Marketing (Hobart only) The Information Economy (Launceston only) The remaining eight elective units may be studied as another major or in a form approved by the Dean. Details of the units offered are outlined in Schedule A while the Bachelor of Commerce: course structure shows specimen courses. Students should also refer to the BCom degree specifications which are printed in full in the Calendar. Articulation Students who have completed approved courses in the Diploma of Business from a Tasmanian Institute of TAFE (or equivalent), and have been admitted to the course, will receive credit for eight first-year units. In the case of international students, English language skills will also need to be verified. Direct credit is offered for all University Commerce & Economics undergraduate awards. For example, a BEc student wishing to transfer to either the BIS or the BCom with credit and vice versa. Applicants wishing to obtain credit for study already undertaken at another faculty, or Australian or overseas tertiary institution should consult the Admission Guide for information on procedure. Alternative enrolment Students entering the Bachelor of Commerce course in 2001 and intending to study a combined degree in Commerce and Law or to study a Major in another faculty should see 'Combined degrees' (below). Combined degree with Law Course details (2001) page 129 Students enrolled for the BCom must applyat the end of Year 1 to enter combined studies with the Bachelor of Laws (LLB) degree. The combined degree takes five years full time. Quotas apply. The first year of the combined degree is available at Launceston. Students must complete the combined degree at the Hobart campus. The BCom-LLB provides a strong basis for a subsequent career in business or public administration, with specialisation in the relationships between economic decisions and legal constraints and requirements. The unit BLA101 Introduction to Law is compulsory in Year 1 for those intending to transfer to the combined degrees. A full-time student will complete BEA110, BSA101, BFA103, BMA101, BEA140 plus one core elective unit and BLA101 in Year 1 (total of 100%). Should the student not progress with Law after the completion of Year 1, the outstanding core unit, BFA141 Commercial Transactions, must be completed. This can be taken in Year 2. Students progressing with Law will be exempt from taking BFA141 as the Law units BLA200 Contract and BLA201 Torts will be its substitute. Combined degrees with Arts, Information Systems and Science and Engineering Four-year combined degree programs are available based on the Bachelor of Commerce and the Bachelor of Arts/Bachelor of Computing/Bachelor of Information Systems. Honours degree The Honours degree in the fields of Accounting & Finance or Management (incorporating Business Management, Human Resource Management, Marketing, Information Systems and International Business) requires one year of full-time study in addition to the requirements for the BCom pass degree. Students with a major in Information Systems in the BCom degree may complete an honours degree program in the BIS honours program. See Bachelor of Commerce with Honours on page xx, and Bachelor of Information systems on page xx. Schedule of common first year units Unit Title campus-sem weight code All students are required to complete the following first-year core units: Economics for Business H1~L1~B1 12.5% BEA110 Business Information Systems H1/2~L1/2~B1 12.5% BSA101 Accounting and Financial Decision Making H1~L1~B1 12.5% BFA103 Introduction to Management H1/2~L1/2~B1 12.5% BMA101 Course details (2001) page 130 Quantitative Methods 1 H2~L2~B2 12.5% Commercial Transactions H2~L2~B2 12.5% Two core elective units are to be selected from the following: Accounting Context and Method H2~L2~B2 12.5% Foundations of Economic Policy H2~L2~B2 12.5% Financial Management [a] H2~L2 12.5% Management of Human Resources [a] H3/2~L3/2 12.5% Information Modelling H2~L2~B2 12.5% Introduction to International Business [a] H2~L2 12.5% [a] Principles of Marketing H3/2~L3/2 12.5% Information Industries L2 12.5% [a] use level 100 enrolment code (eg BFA181) BEA140 BFA141 BFA104 BEA130 BFA181/281 BMA121/221 BSA102 BMA181/281 BMA151/251 BSA103 Schedule A Unit Title campus-sem weight code Students who enrolled before 1999 should refer to the schedule in the Course and Unit Handbook 1998 Year 1 Accounting & Finance Accounting and Financial Decision Making H1~L1~B1 12.5% BFA103 Commercial Transactions H2~L2~B2 12.5% BFA141 Economics Economics for Business H1~L1~B1 12.5% BEA110 Quantitative Methods 1 H2~L2~B2 12.5% BEA140 Information Systems Business Information Systems H1/2~L1/2~B1 12.5% BSA101 Management Introduction to Management H1/2~L1/2~B1 12.5% BMA101 Plus two elective core units from the following Leading to an Accounting or Corporate Accountability major: Accounting Context and Method H2~L2~B2 12.5% BFA104 Leading to a Business Economics major: Foundations of Economic Policy H2~L2~B2 12.5% BEA130 Leading to a Finance major: Financial Management [a] H2~L2 12.5% BFA181/281 Leading to a Human Resource Management or Business Management major: Course details (2001) page 131 Management of Human Resources [a] H3/2~L3/2 12.5% BMA121/221 Leading to an Information Systems major: Information Modelling H2~L2~B2 12.5% BSA102 Leading to an International Business major: Introduction to International Business [a] H2~L2 12.5% BMA181/281 Leading to a Information Economy major: Information Industries L2 12.5% BSA103 Leading to a Marketing major: Principles of Marketing [a] H3/2~L3/2 12.5% BMA151/251 Years 2 and 3 Students complete EITHER a major (eight units) and eight approved units OR two majors (16 units) from the following schedules [a] use level 100 enrolment code (eg BFA181) Major in Accounting Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 First year foundation core units and electives including [b] Accounting Context and Method H2~L2~B2 12.5% BFA104 [a] Financial Management H2~L2 12.5% BFA181/281 Years 2 and 3 Financial Accounting H1~L1~B1 12.5% BFA201 Accounting Information Systems H2~L2~B2 12.5% BFA221 Corporate Regulation and Accountability H1~L1 12.5% BFA241 Management Accounting H2~L2 12.5% BFA261 Advanced Financial Accounting H1~L1~Bv1 12.5% BFA301 Accounting Theory H2~L2~B2 12.5% BFA302 Auditing H1~L1 12.5% BFA303 Taxation H2~L2 12.5% BFA391 [a] use level 100 enrolment code (eg BFA181) [b] Completion of the above units ( including BFA181 Financial Management and the required first year foundation and elective core units) should permit a student to seek entry to professional accounting programs leading to membership of the Institute of Chartered Accountants in Australia and CPA Australia. The units BFA103 and BFA104 are together the equivalent of BFA101 and BFA102. Students will not be admitted to the Accounting major unless they have completed BFA101 and BFA102 or BFA101 and BFA104 or BFA103 and BFA104 or BFA101 and BFA103. Course details (2001) page 132 If units are taken out of the prescribed sequence, students will need to ensure that they have completed the necessary prerequisite units, which are listed in the unit details. Major in Business Economics Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 First year foundation core units and electives including BEA130 Foundations of Economic Policy H2~L2~B2 12.5% BEA130 Year 2 Two of BEA235, BEA306 and BEA326 Economics of Human Resources H1 12.5% BEA306 Thinking Strategically: The Competitive Edge H2 12.5% BEA235 Entrepreneurship and Innovation H?~L? 12.5% BEA326 Two of BEA200, BEA302 and BEA305 Intermediate Microeconomics H2 12.5% BEA200 Economics, Management and Organisation H1 12.5% BEA302 Industrial Organisation [na] 12.5% BEA305 Year 3 Prices and Profits [na] 12.5% BEA325 One nominated elective chosen from the level 200 or level 300 BEA units or BFA181/281. If a BEA unit is chosen it must be one not already completed. Financial Management H2~L2 12.5% BFA181/281 If units are taken out of the prescribed sequence, students will need to ensure that they have completed the necessary prerequisite units, which are listed in the unit details. Major in Business Management Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 First year foundation core units and electives including BMA121: Management of Human Resources [a] H3/2~L3/2 12.5% BMA121/221 Years 2 and 3 Organisational Behaviour H1~L1 12.5% BMA201 Contract of Employment H1~L1 12.5% BMA241 Principles of Marketing H3/2~L3/2 12.5% BMA151/251 Course details (2001) page 133 Financial Management H2~L2 12.5% BFA181/281 Corporate Regulation and Accountability H1~L1 12.5% BFA241 Electronic Commerce H1~L1 12.5% BSA306 Strategic Management H2~L2 12.5% BMA302 Plus one nominated elective to make up 100% for the year chosen from the list below: Nominated electives Managerial Social Responsibility H2~L2 12.5% BMA291/391 Employee Relations H2~L2 12.5% BMA321 Human Resource Management in Tourism and Hospitality H2~L2 12.5% BMA225/325 Human Resource Development H2~L2 12.5% BMA224 In special cases, another relevant unit may be approved by the Head of School as a nominated elective. [a] use level 100 enrolment code (eg BFA181) Major in Corporate Accountability Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Accounting Context and Method H2~L2~B2 12.5% BFA104 Years 2 and 3 Financial Management H2~L2 12.5% BFA181/281 Accounting Information Systems H2~L2~B2 12.5% BFA221 Corporate Regulation and Accountability H1~L1 12.5% BFA241 Plus nominated elective to make up 100% for the year chosen from the following: Nominated electives Environmental and Resource Economics H1 12.5% BEA301 Financial Accounting H1~L1~B1 12.5% BFA201 Personal Financial Management H2 12.5% BFA205/305 Social & Environmental Accounting H2 12.5% BFA207/307 Management Accounting H2~L2 12.5% BFA261 Investment Analysis H1 12.5% BFA285 Accounting Theory H2~L2~B2 12.5% BFA302 Financial Risk Management H2 12.5% BFA385 Taxation H2~L2 12.5% BFA391 Course details (2001) page 134 Managerial Social Responsibility Management and the Natural Environment Environmental Ethics H2~L2 12.5% BMA291/391 [na] H1 12.5% 12.5% BMA272/372 HPA277/377 Major in Finance Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 First year foundation core units and electives including BFA181 Financial Management [a] H2~L2 12.5% BFA181/281 Years 2 and 3 Banking and Financial Institutions H2 12.5% BEA321 Investment Analysis H1 12.5% BFA285 Financial Services H2 12.5% BFA347 International Finance H1 12.5% BFA384 plus four nominated electives to make up 100% for the year chosen from the following list Nominated electives Personal Financial Management H2 12.5% BFA205/305 Services Marketing H1 12.5% BMA353 Intermediate Microeconomics H2 12.5% BEA200 Research Methods for Finance H2 12.5% BEA241 Introduction to Econometrics H1 12.5% BEA242 Financial Economics H2 12.5% BEA304 Financial Risk Management H2 12.5% BFA385 Taxation H2~L2 12.5% BFA391 Completion of this major permits a student to seek membership of the Australian Institute of Banking and Finance. If units are taken out of the prescribed sequence, students will need to ensure that they have completed the necessary prerequisite units, which are listed in the unit details. [a] use level 100 enrolment code (eg BFA181) Major in Human Resource Management Unit Title campus-sem weight Year 1 First year foundation core units and electives including BMA121 code Course details (2001) page 135 Management of Human Resources [a] H3/2~L3/2 12.5% BMA121/221 Years 2 and 3 Organisational Behaviour H1~L1 12.5% BMA201 Contract of Employment H1~L1 12.5% BMA241 Method for Management Studies H2~L2 12.5% BMA260 Human Resource Development H2~L2 12.5% BMA224 International Human Resource Management H1~L1 12.5% BMA381 Strategic Management H2~L2 12.5% BMA302 Strategic Issues in Human Resource Management H1~L1 12.5% BMA330 Plus one nominated elective to make up 100% for the year chosen from the list below Nominated electives Managerial Social Responsibility H2~L2 12.5% BMA291/391 Financial Management H2~L2 12.5% BFA181/281 Employee Relations H2~L2 12.5% BMA321 Human Resource Management in Tourism and Hospitality H2~L2 12.5% BMA225/325 In special cases, another relevant unit may be approved by the Head of School as a nominated elective. Completion of this major permits a student to seek membership of the Australian Human Resources Institute. [a] use level 100 enrolment code (eg BFA181) Major in Information Systems Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 First year foundation core units and electives including BSA102 Information Modelling H2~L2~B2 12.5% BSA102 Years 2 and 3 Principles of Systems H1~L1~B1 12.5% BSA201 Programming and Problem Solving H1~L1/2~B1 12.5% KXA151 Information Management H2~L2~B2 12.5% BSA203 Management of Information Systems H1~L1 12.5% BSA303 Plus four nominated electives to make up 100% for the year chosen from the list given below Nominated electives Systems Development H2~L2~B2 12.5% BSA202 Course details (2001) page 136 IS Project Management H1~L1 12.5% BSA301 IS Project H2~L2 12.5% BSA302 Decision Support Systems H2 12.5% BSA304 Current Trends in IS H2~L2 12.5% BSA305 Electronic Commerce H1~L1 12.5% BSA306 Electronic Commerce Project H2~L2 12.5% BSA307 Accounting Information Systems H2~L2~B2 12.5% BFA221 Information Technology Law H1~L1 12.5% BLA670 Organisational Behaviour H1~L1 12.5% BMA201 Electronic Marketing H2 12.5% BMA308 Completion of this major (including at least 7 BSA units plus KCA151) permits a student to seek membership of the Australian Computer Society. If units are taken out of sequence students will need to ensure that they have completed the necessary prerequisite units, which are listed in the unit details. Major in International Business Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 First year foundation core units and electives including BMA181 Introduction to International Business [a] H2~L2 12.5% BMA181/281 Years 2 and 3 Managing Business in the Asia Pacific H1 12.5% BMA285 International Business Theories H1 12.5% BMA284/384 Method for Management Studies H2~L2 12.5% BMA260 A combination of either BMA151 and BMA281 or BMA121/221 and BMA381 or (only for students taking a double-major in Accounting/Finance) BFA281 and BFA384: Principles of Marketing H3/2~L3/2 12.5% BMA151/251 International Marketing H2 12.5% BMA282 Management of Human Resources H3/2~L3/2 12.5% BMA121/221 International Human Resource Management H1~L1 12.5% BMA381 Financial Management H2~L2 12.5% BFA181/281 International Finance H1 12.5% BFA384 International Business Strategies H1 12.5% BMA386 Course details (2001) page 137 Strategic Management H2~L2 12.5% BMA302 Plus one nominated elective to make up 100% for the year chosen from the following list: Managerial Social Responsibility H2~L2 12.5% BMA291/391 Australia and the Asia-Pacific Economies: Trade Principles and Policy [na] 12.5% BEA303 In special cases, another relevant unit may be approved by the Head of School as a nominated elective. [a] use level 100 enrolment code (eg BFA181) Major in Marketing Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 First year foundation core units and electives including BMA151 Principles of Marketing [a] H3/2~L3/2 12.5% BMA151/251 Years 2 and 3 Marketing Research H2 12.5% BMA253 Marketing Communications H1 12.5% BMA255 Buyer Behaviour H2 12.5% BMA252 Organisational Behaviour H1~L1 12.5% BMA201 Marketing Management H1 12.5% BMA351 Services Marketing H1 12.5% BMA353 Strategic Management H2~L2 12.5% BMA302 Plus one nominated elective chosen from: Nominated electives International Marketing H2 12.5% BMA282 Managerial Social Responsibility H2~L2 12.5% BMA291/391 Financial Management H2~L2 12.5% BFA181/281 Electronic Marketing H2 12.5% BMA308 In special cases, another relevant unit may be approved by the Head of School as a nominated elective. [a] use level 100 enrolment code (eg BFA181) Major in The Information Economy Unit Title campus-sem weight Year 1 First year fundation core units and electives including BSA103 Information Industries L2 12.5% Years 2 and 3 Business Logistics L1 12.5% code BSA103 BSA204 Course details (2001) page 138 The Information Economy L? 12.5% BEA212 Entrepreneurship and Innovation H?~L? 12.5% BEA326 Globalisation and the Information Economy L2 12.5% BEA310 Electronic Commerce H1~L1 12.5% BSA306 Information Technology Law H1~L1 12.5% BLA670 Plus two nominated electives to make up 100% for the year chosen from the list below: Policy Frameworks for the Information Economy L2 12.5% BSA205 Management of Information Systems H1~L1 12.5% BSA303 If units are taken out of sequence students will need to ensure that they have completed the necessary prerequisite units, which are listed in the unit details. A Second Major Students wishing to enhance their degree may take a second major. A major offered by the Faculty of Commerce and Law is eight units (total weight of 100%). A student may select a second major from the ten set out in the previous section. Bachelor of Commerce with Honours (Abbreviation: BCom(Hons)) Course code: C4C This on-campus, 1-year full-time or 2-year part-time honours degree course is offered in the fields of Accounting, Finance and Corporate Governance at Hobart and Management (incorporating Human Resource Management, Marketing, International Business and Business Management) at Hobart. Admission & prerequisites Bachelor of Commerce (or equivalent approved qualification) with an average of distinction or higher in at least 50% of the final year units of the pass degree. Candidates for the BCom with Honours in Management require a grade point average (GPA) of 6.5 or better for the 200 and 300 level units forming the relevant major in their degree. Currently, the GPA is calculated on the basis of HD=9, DN=7.5, CR=6.5, PP=5.5, TP=5.0, NN=4.0. Course details (2001) page 139 Course objectives The aim of the honours year is to enable students to develop their interests and research skills further and to provide a foundation for postgraduate study in Commerce. Course structure Students may elect to pursue one of the fields of study identified in accordance with the requirements for that field of study as outlined in Schedule A. The award of honours is given in relation to the whole of the year's work. The award is graded First Class; Second Class, upper division; Second Class, lower division; or Third Class. See Schedule A for details of the course. Students should also refer to the BCom with Honours degree specifications which are printed in full in the Calendar. Full details of units may be obtained from both the School of Accounting and Finance and the School of Management. Articulation Graduates of BCom, BEc, BCom–LLB may seek enrolment in BCom(Hons) The BCom(Hons) can lead to MCom and PhD. Schedule A Unit Title campus-sem weight code Accounting and Finance Bachelor of Commerce Honours BFA498/499 Candidates are required to undertake training in research methodology and to complete four units of coursework plus a dissertation. four elective units chosen from: Advanced Financial Accounting H2 12.5% BFA401 Advanced Auditing H? 12.5% BFA408 Advanced Taxation Accounting [na] 12.5% BFA409 Advanced Accounting Theory H1 12.5% BFA420 Advanced Finance H? 12.5% BFA424 Advanced Accounting Information Systems H1 12.5% BFA425 Course details (2001) page 140 Government Financial Management [na] 12.5% BFA427 Corporate Governance and Accountability H2 12.5% BFA429 Advanced Management Accounting [na] 12.5% BFA435 or: two units chosen from above plus two units from another subject area approved by the HoS, AND in either case: Dissertation H BFA441 Management Candidates are required to complete four units consisting of: Research Methods in Management H1 12.5% BMA401 Management Honours Seminar Hf 12.5% BMA402 Dissertation Hf 62.5% BMA404 PLUS either one elective chosen from: Special Topics in Management H1 12.5% BMA403 Human Resource Theory and Practice H1 12.5% BMA421 Marketing Theory and Research H1 12.5% BMA451 or one unit from another subject area approved by the HoS. Bachelor of Economics (Abbreviation: BEc) Course code: C3E This on-campus, 3-year full-time or 6-year part-time course is offered at Hobart. The first year of the degree is offered at Launceston. Students must transfer to the Hobart campus to complete the degree. Admission & prerequisites In addition to meeting the University's basic admission requirements, applicants must have passed TCE *MT730 Mathematics Applied or a higher level Mathematics subject. Candidates should note, however, that admission to the Faculty is subject to quota selection. Selection will be based on a score calculated on an applicant's five best TCE subjects – three of which must be taken in Year 12 – chosen from Course details (2001) page 141 the list of subjects approved by the University for admission purposes. The mathematics subject referred to above does not have to be one of the five counted for the purposes of the calculation of the TE score. Course objectives The general aims and objectives of the Bachelor of Economics are to produce well educated and adaptable graduates with appropriate knowledge and professional skills to meet the existing needs and demands of employment in industry, commerce, banking, public administration or the more specialised fields of professional or research economics. Course structure The Bachelor of Economics is described in terms of 12.5% units. To complete the Bachelor of Economics, units to a value of 300% must be passed, including a maximum of 125% from 100-level units, a maximum of 100% from 200-level units, and a minimum of 75% from 300-level units. In the Schedule which follows, Groups 1, 2 and 3 mean Year 1, Year 2 and Year 3 units from units offered by the Faculty of Commerce and Law and Groups 1A, 2A and 3A refer to 1st, 2nd and 3rd year units offered by departments in other Faculties. It is possible to count a number of units from other departments, for example: Administration, Information Systems, Languages, Mathematics, Government, Psychology, etc. (See 'Outline of course' below.) Articulation Students who have completed the Associate Diploma of Business from a Tasmanian Institute of TAFE, and have been admitted to the course, will receive credit for up to eight units towards the degree. The status of individual units is determined at the time of offer. Faculty also offers direct credit for its awards. For example, a BCom student wishing to transfer to the BEc with credit and vice versa. Applicants wishing to obtain credit for study already undertaken with another faculty, or an Australian or overseas tertiary institution should consult the Admission Guide and the Student Information Handbook for information on procedure. Combined degree with Law Students enrolled for the BEc may, starting in Year 2, combine studies with the Bachelor of Laws (LLB) degree, in a course taking five years full time. Quotas apply. Course details (2001) page 142 The BEc-LLB provides a strong basis for a subsequent career in business or public administration, where there is a need for an understanding of the relationships between economic decisions and legal constraints and requirements. The subject BLA101 Introduction to Law is compulsory in first year for those intending to transfer to the combined degrees. The first year unit of law is offered also in Launceston. Students must transfer to Hobart to complete the degree. (See School of Law section, p B-xx, for further information). Combined degrees with Arts A four-year combined degree program is available based on the Bachelor of Arts and the Bachelor of Economics. Please refer to the combined degrees section further on in this faculty entry. Honours degree The Honours degree requires one year of full-time study in addition to the requirements for the BEc pass degree. Please see Bachelor of Economics with Honours on page xx. Common first year units Unit Title campus-sem weight code In first year, 37.5% must be taken from the following compulsory units: Economics for Business H1~L1~B1 12.5% BEA110 Foundations of Economic Policy H2~L2~B2 12.5% BEA130 Quantitative Methods 1 H2~L2~B2 12.5% BEA140 In the second year, 37.5% must be taken from the following compulsory units: Intermediate Microeconomics H2 12.5% BEA200 Intermediate Macroeconomics H1 12.5% BEA220 BEA242 or BEA241 Introduction to Econometrics H1 12.5% BEA242 Research Methods for Finance H2 12.5% BEA241 plus not less than 12.5% selected from the second and third year options listed below: In the third year, 50% must be selected from the following list of second and third year options: Quantitative Methods 2 H1 12.5% BEA240 Course details (2001) Australian Political Economy Thinking Strategically: The Competitive Edge The Asia-Pacific Economies: Tigers Macroeconomic Theory and Policy Australia and the Asia-Pacific Economies: Trade Principles and Policy Industrial Organisation Economics of Human Resources Econometrics Financial Economics Environmental and Resource Economics Microeconomic Theory and Policy Economics, Management and Organisation Banking and Financial Institutions Prices and Profits Entrepreneurship and Innovation page 143 [na] 12.5% BEA210 H2 12.5% BEA235 H1 12.5% BEA211 H2 12.5% BEA320 [na] [na] 12.5% 12.5% BEA303 BEA305 H1 H2 H2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BEA306 BEA342 BEA304 H1 12.5% BEA301 H1 12.5% BEA300 H1 12.5% BEA302 H2 [na] 12.5% 12.5% BEA321 BEA325 H?~L? 12.5% BEA326 Details of the units offered are outlined in Schedules A, B and C and illustrated by the accompanying sample of BEc degree options. Students should also refer to the BEc degree specifications which are printed in full in the Calendar. Schedule A Unit Title Year 1 Group 1 Economics Economics for Business Foundations of Economic Policy Quantitative Methods 1 Accounting & Finance Accounting and Financial Decision Making Accounting Context and Method campus-sem weight code H1~L1~B1 12.5% BEA110 H2~L2~B2 H2~L2~B2 12.5% 12.5% BEA130 BEA140 H1~L1~B1 12.5% BFA103 H2~L2~B2 12.5% BFA104 Course details (2001) page 144 Commercial Transactions [a] H2~L2~B2 12.5% BFA141 [e] Financial Management H2~L2 12.5% BFA181/281 Information Systems Business Information Systems H1/2~L1/2~B1 12.5% BSA101 Information Modelling H2~L2~B2 12.5% BSA102 Management Introduction to Management H1/2~L1/2~B1 12.5% BMA101 Management of Human Resources [e] H3/2~L3/2 12.5% BMA121/221 [e] Principles of Marketing H3/2~L3/2 12.5% BMA151/251 Introduction to International Business [e] H2~L2 12.5% BMA181/281 Year 1 Group 1A Any first-year subjects and/or units offered by other Schools in the University at Hobart. Interested students should consult other faculty sections for course descriptions, details of prerequisite requirements and so on. Year 2 Group 2 [b] Economics Hbt or as otherwise advised Intermediate Microeconomics H2 12.5% BEA200 Australian Political Economy [c] [na] 12.5% BEA210 The Asia-Pacific Economies: Tigers H1 12.5% BEA211 Intermediate Macroeconomics H1 12.5% BEA220 Thinking Strategically: The Competitive Edge H2 12.5% BEA235 Quantitative Methods 2 H1 12.5% BEA240 Research Methods for Finance H2 12.5% BEA241 Introduction to Econometrics H1 12.5% BEA242 Accounting & Finance Financial Accounting H1~L1~B1 12.5% BFA201 Accounting Information Systems H2~L2~B2 12.5% BFA221 Corporate Regulation and Accountability H1~L1 12.5% BFA241 Management Accounting H2~L2 12.5% BFA261 Investment Analysis H1 12.5% BFA285 Management Organisational Behaviour H1~L1 12.5% BMA201 Contract of Employment H1~L1 12.5% BMA241 Buyer Behaviour H2 12.5% BMA252 Course details (2001) page 145 Marketing Research H2 12.5% BMA253 Marketing Communications H1 12.5% BMA255 International Marketing H2 12.5% BMA282 International Business Theories H1 12.5% BMA284/384 Year 2 Group 2A Any second-year subjects and/or units offered by other Schools in the University at Hobart. Interested students should consult other faculty sections for course descriptions, details of prerequisite requirements and so on. Year 3 Group 3 Economics Microeconomic Theory and Policy H1 12.5% BEA300 Environmental and Resource Economics [d] H1 12.5% BEA301 Economics, Management and Organisation [d] H1 12.5% BEA302 Australia and the Asia-Pacific Economies: Trade Principles and Policy [na] 12.5% BEA303 Financial Economics H2 12.5% BEA304 Industrial Organisation [na] 12.5% BEA305 Economics of Human Resources H1 12.5% BEA306 Macroeconomic Theory and Policy H2 12.5% BEA320 Banking and Financial Institutions [d] H2 12.5% BEA321 Prices and Profits [na] 12.5% BEA325 Entrepreneurship and Innovation H?~L? 12.5% BEA326 Econometrics H2 12.5% BEA342 Accounting & Finance Advanced Financial Accounting H1~L1~Bv1 12.5% BFA301 Accounting Theory H2~L2~B2 12.5% BFA302 Auditing H1~L1 12.5% BFA303 Governmental Financial Management & Accounting [na] 12.5% BFA306 unit (BFA307) to be advised Financial Services H2 12.5% BFA347 Advanced Management Accounting [na] 12.5% BFA366 International Finance H1 12.5% BFA384 Financial Risk Management H2 12.5% BFA385 Taxation H2~L2 12.5% BFA391 Course details (2001) page 146 Information Systems Decision Support Systems H2 12.5% BSA304 Management Managerial Social Responsibility H2~L2 12.5% BMA291/391 Strategic Management H2~L2 12.5% BMA302 Employee Relations H2~L2 12.5% BMA321 Human Resource Development H2~L2 12.5% BMA224 Marketing Management H1 12.5% BMA351 Services Marketing H1 12.5% BMA353 Special Topics in Management H1/2~L1/2 12.5% BMA371 International Human Resource Management H1~L1 12.5% BMA381 Further units may be available with approval from the relevant sub-deans. Please contact the School of Economics for further details. Year 3 Group 3A Any third-year subjects and/or units offered by other Schools in the University at Hobart. Interested students should consult other faculty sections for course descriptions, details of prerequisite requirements and so on. [a] Combined BCom-LLB degree students should refer to Calendar for combined degree rules restrictions [b] For combined BEc-LLB degree candidates, Group 2 unit weights for both combined degree and HECS purposes will be 12% instead of 12.5% as listed in this schedule [c] May be approved as a Group 1 unit [d] May be approved as a Group 2 unit [e] These units are available at both level 100 and level 200 BFA181/281, BMA121/221, BMA151/251, BMA181/281, etc Note: all units offered by the Faculty are valued at 12.5%. Single semester units of comparable rigour taken in other faculties will be weighted at 12.5% and full-year units at 25% for the purposes of the BEc. Sample degree options It is possible to complete a BEc degree by undertaking a general program of studies, combining, say, economics with other disciplines such as accounting, social science or humanities. It is also possible to complete a BEc by undertaking one of the following majors. Students should ensure that they take, in addition to the prescribed units below, sufficient elective units to fulfil the requirements of the degree. See rules of the degree. Students who wish to undertake more than one major from the School of Economics will be required to present alternative units as directed by the School Student Adviser. Course details (2001) page 147 The five majors, which are available to students enrolled for the BEc degree, are under review. The compulsory units required for each major are as follows: Analytical Economics Major Unit Title Year 1 Economics for Business Foundations of Economic Policy Quantitative Methods 1 Year 2 Intermediate Microeconomics Intermediate Macroeconomics Introduction to Econometrics Quantitative Methods 2 Year 3 Microeconomic Theory and Policy Macroeconomic Theory and Policy Either BEA303 or BEA304 Australia and the Asia-Pacific Economies: Trade Principles and Policy Financial Economics campus-sem weight code H1~L1~B1 12.5% BEA110 H2~L2~B2 H2~L2~B2 12.5% 12.5% BEA130 BEA140 H2 12.5% BEA200 H1 12.5% BEA220 H1 H1 12.5% 12.5% BEA242 BEA240 H1 12.5% BEA300 H2 12.5% BEA320 [na] H2 12.5% 12.5% BEA303 BEA304 Australian Economy and the Asia Pacific Unit Title Year 1 Economics for Business Foundations of Economic Policy Quantitative Methods 1 Year 2 Intermediate Microeconomics Intermediate Macroeconomics Either BEA242 or BEA241 Introduction to Econometrics campus-sem weight code H1~L1~B1 12.5% BEA110 H2~L2~B2 H2~L2~B2 12.5% 12.5% BEA130 BEA140 H2 12.5% BEA200 H1 12.5% BEA220 H1 12.5% BEA242 Course details (2001) Research Methods for Finance Australian Political Economy The Asia-Pacific Economies: Tigers Year 3 Industrial Organisation Economics of Human Resources Australia and the Asia-Pacific Economies: Trade Principles and Policy page 148 H2 12.5% BEA241 [na] 12.5% BEA210 H1 12.5% BEA211 [na] 12.5% BEA305 H1 12.5% BEA306 [na] 12.5% BEA303 Economics, Organisations and Industrial Relations Unit Title Year 1 Economics for Business Foundations of Economic Policy Quantitative Methods 1 Introduction to Management Commercial Transactions Year 2 Intermediate Microeconomics Research Methods for Finance Intermediate Macroeconomics Management of Human Resources [a] Contract of Employment Organisational Behaviour Thinking Strategically: The Competitive Edge Year 3 Economics of Human Resources Economics, Management and Organisation Employee Relations Managerial Social Responsibility [b] campus-sem weight code H1~L1~B1 12.5% BEA110 H2~L2~B2 H2~L2~B2 12.5% 12.5% BEA130 BEA140 H1/2~L1/2~B1 H2~L2~B2 12.5% 12.5% BMA101 BFA141 H2 12.5% BEA200 H2 12.5% BEA241 H1 12.5% BEA220 H3/2~L3/2 H1~L1 H1~L1 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BMA121/221 BMA241 BMA201 H2 12.5% BEA235 H1 12.5% BEA306 H1 H2~L2 12.5% 12.5% BEA302 BMA321 H2~L2 12.5% BMA291/391 Course details (2001) page 149 Prices and Profits [na] 12.5% BEA325 Entrepreneurship and Innovation H?~L? 12.5% BEA326 Further units may be available with approval from the relevant sub-deans. Please contact the School of Economics for further details. [a] Students use appropriate level 200 enrolment code [b] Students use appropriate level 300 enrolment code Economic Policy Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Quantitative Methods 1 [a] H2~L2~B2 12.5% BEA140 Economics for Business H1~L1~B1 12.5% BEA110 Foundations of Economic Policy H2~L2~B2 12.5% BEA130 Plus a further 37.5% Group 1 or Group 1A units from Schedule A Years 2 and 3 Intermediate Microeconomics H2 12.5% BEA200 Intermediate Macroeconomics H1 12.5% BEA220 Australian Political Economy [na] 12.5% BEA210 Environmental and Resource Economics H1 12.5% BEA301 Australia and the Asia-Pacific Economies: Trade Principles and Policy [na] 12.5% BEA303 Banking and Financial Institutions H2 12.5% BEA321 Industrial Organisation [na] 12.5% BEA305 The Asia-Pacific Economies: Tigers H1 12.5% BEA211 Plus a further 50% taken from Group 2 and 2A units and 50% taken from Group 3 and 3A units from Schedule A. [a] May be taken in the second year if preferred. Financial Markets and Institutions Unit Title Year 1 Economics for Business Foundations of Economic Policy Quantitative Methods 1 campus-sem weight code H1~L1~B1 12.5% BEA110 H2~L2~B2 H2~L2~B2 12.5% 12.5% BEA130 BEA140 Course details (2001) page 150 Accounting and Financial Decision Making Accounting Context and Method Business Information Systems Year 2 Intermediate Microeconomics The Asia-Pacific Economies: Tigers Research Methods for Finance Introduction to Econometrics Financial Management [a] Investment Analysis Year 3 Financial Economics Banking and Financial Institutions Econometrics Financial Risk Management plus 1 elective [a] H1~L1~B1 12.5% BFA103 H2~L2~B2 12.5% BFA104 H1/2~L1/2~B1 12.5% BSA101 H2 12.5% BEA200 H1 12.5% BEA211 H2 12.5% BEA241 H1 H2~L2 H1 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BEA242 BFA181/281 BFA285 H2 12.5% BEA304 H2 H2 H2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BEA321 BEA342 BFA385 Students use appropriate level 200 enrolment code BFA281 Business Economics and Market Strategies Unit Title Year 1 Economics for Business Foundations of Economic Policy Quantitative Methods 1 Introduction to Management Year 2 Intermediate Microeconomics Australian Political Economy The Asia-Pacific Economies: Tigers Research Methods for Finance campus-sem weight code H1~L1~B1 12.5% BEA110 H2~L2~B2 H2~L2~B2 12.5% 12.5% BEA130 BEA140 H1/2~L1/2~B1 12.5% BMA101 H2 12.5% BEA200 [na] 12.5% BEA210 H1 12.5% BEA211 H2 12.5% BEA241 Course details (2001) page 151 Principles of Marketing H3/2~L3/2 12.5% BMA151/251 Marketing Research H2 12.5% BMA253 Introduction to International Business [a] H2~L2 12.5% BMA181/281 Thinking Strategically: The Competitive Edge H2 12.5% BEA235 Year 3 Economics, Management and Organisation H1 12.5% BEA302 Financial Economics H2 12.5% BEA304 Industrial Organisation [na] 12.5% BEA305 Banking and Financial Institutions H2 12.5% BEA321 Entrepreneurship and Innovation H?~L? 12.5% BEA326 Strategic Management H2~L2 12.5% BMA302 Marketing Management H1 12.5% BMA351 International Business Theories H1 12.5% BMA284/384 [a] Students use appropriate level 200 enrolment code BMA281. Bachelor of Economics with Honours (Abbreviation: BEc(Hons)) Course code: C4E This on-campus, 1-year full-time or 2-year part-time honours degree course is offered through the School of Economics at Hobart. Admission & prerequisites Bachelor of Economics (or equivalent approved qualification) with a minimum of 65 average in four level 300 Economics units including BEA300 and BEA320. Students are also expected normally to have passed BEA342. Course objectives The aim of the honours year is to enable students to develop their interests further and to provide a foundation for postgraduate study in Economics. Course structure Candidates are required to complete four units of coursework and to write a dissertation under individual supervision. Course details (2001) page 152 They may pursue either a single course of study in Economics or a joint course in Economics and a subject area from another department approved by the Faculty. They may therefore choose all four units from the School of Economics (as outlined in Schedule B, below) or two from Schedule B and two from the other department. The award of honours is given in relation to the whole of the year's work. Grades of award are First Class; Second Class, upper division; Second Class, lower division; or Third Class. See the following Schedule for details of the course. Candidates should also refer to the BEc with Honours degree specifications which appear in full in the Calendar. Full details of units may be obtained from the School of Economics. Schedules Unit Title campus-sem weight code Schedule A Microeconomic Theory and Policy H1 12.5% BEA300 Australia and the Asia-Pacific Economies: Trade Principles and Policy [na] 12.5% BEA303 Macroeconomic Theory and Policy H2 12.5% BEA320 Econometrics H2 12.5% BEA342 Schedule B Master course codes Bachelor of Economics (Honours) H1/2 50%/100% BEA498/499 Note: for descriptions of the following Honours units, contact HoS The course includes the following compulsory units: Microeconomics 12.5% BEA400 Macroeconomics 12.5% BEA420 Dissertation 50% BEA460 and two units from: Economics of Natural Resources 12.5% BEA401 Regional Economics Modelling 12.5% BEA402 International Economics 12.5% BEA403 Course details (2001) page 153 Public Economics 12.5% BEA404 Industrial Economics 12.5% BEA405 Labour Economics 12.5% BEA406 Microeconomic Reform 12.5% BEA407 Economics Thought 12.5% BEA410 Methods of Enquiry 12.5% BEA411 Econometrics 12.5% BEA442 Special Option 12.5% BEA450 Bachelor of Information Systems (Abbreviation: BIS) Course code: C3S This on-campus, 3-year (minimum) full-time or 6-year part-time course is offered at the Hobart and Launceston campuses. The first year of the course and selected later year units are offered at the North-West Centre in Burnie. Admission & prerequisites Possession of the University's basic admission requirements. A completed TAFE Diploma in Information Technology or Business is also acceptable and will attract up to 8 units credit. Other TAFE Diplomas or Associate Diplomas will be considered on an individual basis. Studying TCE *MT730 Mathematics Applied or a higher level Mathematics subject is recommended for students seeking admission to the Bachelor of Information Systems. TCE Information Systems and Computer Science or their equivalent are useful background, but are not prerequisites for admission to the degree. Course objectives The course aims to – Course details (2001) • • • • • page 154 provide a professional degree that will graduate people able to fulfil key roles in the IT and related industries, and who will liaise between IT personnel and other professional and industrial personnel; produce graduates who have a good understanding of roles of IT in society, in organisations, and for individuals, that IT is a powerful factor for change in modern society; provide the community, particularly Tasmania, with graduates who are well equipped to deal with information technology and develop information infrastructures, both in the public and private spheres; produce graduates with knowledge, skills and understanding of: (a) the relationships of information and information technology to organisational needs; (b) current management practice in the development of information systems, their use and associated policy formulation and analysis; (c) the value of research, critical thinking and effective communication in the management of information systems. produce graduates who have well developed professional skills in such areas as interpersonal communication, working in teams, and technical report writing. Career outcomes Associate membership of the Australian Computer Society. Graduates of the Bachelor of Information Systems could expect to find employment as a business analyst, database analyst, systems analyst, IT project manager, IT manager, Information manager, database administrator, IT administrator or manager, telecommunications manager, IT consultant, electronic commerce or electronic business consultant, web developer, webmaster. Course structure The Bachelor of Information Systems degree consists of twenty-four units of study. There are 15 specified core units in Information Systems and 9 elective units which may be chosen from any other discipline area within the University. Students are encouraged to seek combinations of units from other schools which will complement their studies in Information Systems. They are strongly encouraged to seek a complementary major in professional areas, such as Journalism and Media Studies, Computing, Economics, Government, Sociology or Psychology. In order to achieve a recognised major in the elective component of the Bachelor of Information Systems degree a student will be required to pass units in a single field of study that: (a) (c) can be completed within the elective units of the Bachelor of Information Systems, and are recognised as a major by a faculty of the University. Course details (2001) page 155 Articulation The Bachelor of Information Systems may articulate with other courses and degrees, such as those offered through TAFE, and by other tertiary institutions. The transfer arrangements will be determined on an individual student basis and will depend on the standing of the student and the relationship between units completed elsewhere and the units required in this degree. Combined degree with Commerce Students entering the Bachelor of Information Systems course in 2001 and intending to study a Commerce major should see the section on the Bachelor of Commerce–Bachelor of Information Systems combined degree on page xx. Combined degree with Law Students who wish to complete the five-year combined degree Bachelor of Information Systems–Bachelor of Laws must enrol in the unit BLA101 Introduction to Law in the first year of their Bachelor of Information Systems course, and must then apply for admission to the combined BIS–LLB degree at the end of their first year. The first year of the combined degree is available in Launceston, but students must complete the combined degree at the Hobart campus. Schedule A Unit Title Year 1 Core units Accounting & Finance Accounting and Financial Decision Making Management Introduction to Management Information Systems Business Information Systems Information Modelling Philosophy Introduction to Logic Computing Programming and Problem Solving Software Process Year 2 Management campus-sem weight code H1~L1~B1 12.5% BFA103 H1/2~L1/2~B1 12.5% BMA101 H1/2~L1/2~B1 H2~L2~B2 12.5% 12.5% BSA101 BSA102 H1~D1~Lw1~Bw1 12.5% HPA291/391 H1~L1/2~B1 H2~L2~B2 12.5% 12.5% KXA151 KXA154 Course details (2001) Organisational Behaviour Principles of Marketing Information Systems Principles of Systems Systems Development Information Management Computing Algorithms and Metrics Year 3 Accounting & Finance Accounting Information Systems Information Systems IS Project Management IS Project Management of Information Systems Decision Support Systems Current Trends in IS Electronic Commerce Law Information Technology Law Management Electronic Marketing page 156 H1~L1 H3/2~L3/2 12.5% 12.5% BMA201 BMA151/251 H1~L1~B1 H2~L2~B2 H2~L2~B2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BSA201 BSA202 BSA203 H1~L1 12.5% KXA251 H2~L2~B2 12.5% BFA221 H1~L1 H2~L2 12.5% 12.5% BSA301 BSA302 H1~L1 H2 H2~L2 H1~L1 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BSA303 BSA304 BSA305 BSA306 H1~L1 12.5% BLA670 H2 12.5% BMA308 Management of Information Systems Program Schedule of units Unit Title Year 1 Business Information Systems Programming and Problem Solving Accounting and Financial Decision Making Elective H1/2:L1/2 Information Modelling Introduction to Management Introduction to Logic Elective H1/2:L1/2 Year 2 Principles of Systems Organisational Behaviour Either KXA154 or KXA231 campus-sem weight code H1/2~L1/2~B1 12.5% BSA101 H1~L1/2~B1 12.5% KXA151 H1~L1~B1 12.5% H2~L2~B2 12.5% BFA103 12.5% BSA102 H1/2~L1/2~B1 H1~D1~Lw1~Bw1 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BMA101 HPA291/391 H1~L1~B1 H1~L1 12.5% 12.5% BSA201 BMA201 Course details (2001) page 157 Software Process H2~L2~B2 Algorithms and Metrics H1~L1 Elective H1/2:L1/2 12.5% Systems Development H2~L2~B2 Information Management H2~L2~B2 Elective H2:L2 12.5% Elective H2:L2 12.5% Year 3 IS Project Management H1~L1 Management of Information Systems H1~L1 Elective H1:L1 12.5% Elective H1:L1 12.5% IS Project H2~L2 12.5% One of BSA304, BSA305, BSA306 or BFA221 Decision Support Systems H2 Current Trends in IS H2~L2 Electronic Commerce H1~L1 Accounting Information Systems H2~L2~B2 Elective H2:L2 12.5% Elective H2:L2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KXA154 KXA251 12.5% 12.5% BSA202 BSA203 12.5% BSA301 12.5% BSA303 BSA302 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BSA304 BSA305 BSA306 12.5% BFA221 Electronic Commerce Program Schedule of units Unit Title Year 1 Business Information Systems Programming and Problem Solving Accounting and Financial Decision Making Elective H1/2:L1/2 Information Modelling Introduction to Management Introduction to Logic Elective H1/2:L1/2 Year 2 Principles of Systems Either BMA201 or BSA202 Organisational Behaviour Systems Development Principles of Marketing Elective H1:L1 campus-sem weight code H1/2~L1/2~B1 12.5% BSA101 H1~L1/2~B1 12.5% KXA151 H1~L1~B1 12.5% H2~L2~B2 12.5% BFA103 12.5% BSA102 H1/2~L1/2~B1 H1~D1~Lw1~Bw1 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BMA101 HPA291/391 H1~L1~B1 12.5% BSA201 H1~L1 H2~L2~B2 H3/2~L3/2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BMA201 BSA202 BMA151/251 Course details (2001) Information Management Elective H2:L2 Electronic Marketing Elective H2:L2 Year 3 Management of Information Systems Electronic Commerce Elective H1:L1 Elective H1:L1 Electronic Commerce Project Information Technology Law Elective H2:L2 Elective H2:L2 page 158 H2~L2~B2 12.5% H2 12.5% 12.5% BSA203 12.5% BMA308 H1~L1 H1~L1 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BSA303 BSA306 H2~L2 12.5% BSA307 H1~L1 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BLA670 Bachelor of Information Systems with Honours (Abbreviation: BIS(Hons)) Course code: C4S This on-campus, 1-year (minimum) full-time or 2-year part-time course is offered by the Faculty of Commerce and Law at the Hobart and Launceston campuses. Admission & prerequisites Candidates for the Bachelor of Information Systems with honours degree will be required to satisfy the following: (a) (b) have completed a bachelor degree with a major in Information Systems, or a closely related field; and have achieved at least a Distinction grade in two of the final year units (total weighting of 25%) in their Information Systems major. Course objectives The course aims to provide – Course details (2001) 1 2 3 4 page 159 students with a good understanding of the research methods in Information Systems and provide the training necessary to pursue a research degree in the field; advanced professional education and training in order to fulfil key roles in the IT and related industries; the community, particularly Tasmania, with honours graduates who have the research skills and knowledge that will lead to positions of leadership and management, particularly in the IT profession; and to produce graduates who have well developed professional skills in such areas as negotiation and conflict resolution, team building and leadership. Career outcomes Associate membership of the Australian Computer Society. Graduates of the Bachelor of Information Systems could expect to find employment as a business analyst, database analyst, systems analyst, IT project manager, IT manager, Information manager, database administrator, IT administrator or manager, telecommunications manager, IT consultant, electronic commerce or electronic business consultant. Course structure The Bachelor of Information Systems honours program will consist of– • • • • a major project culminating in the production of a thesis, equivalent in weighting to 4 units or 50%, one required unit on research methods, with a weighting of 12.5%, two elective units, with a total weighting of 25%, and a professional skills unit, with a weighting of 12.5%. Schedule A Unit Title campus-sem Bachelor of Information Systems with Honours Consisting of the following units and dissertation Professional Skills Hf~Lf Information Systems Research Methods H1~L1 Dissertation Hf~Lf Any two of BSA411, BSA412, BSA414 Strategic Information Systems H1~L1 Systems Development Methodologies H2~L2 Advanced Electronic Commerce H2~L2 weight code BSA498/499 12.5% BSA410 12.5% 50% BSA413 BSA420 12.5% BSA411 12.5% BSA412 12.5% BSA414 Course details (2001) page 160 Bachelor of Laws (Abbreviation: LLB) Course code: L3B This on-campus course at Hobart is offered by the Faculty of Commerce and Law and is available full time (a minimum of 3 years) or part time (a maximum of 8 years). Admission & prerequisites Students will need either: (a) (b) a first year in another faculty, which includes the unit BLA101 Introduction to Law (or the academic equivalent); or a bachelor degree. Course objectives The Bachelor of Laws course is the basic academic preparation for persons who wish to enter the legal profession and other careers involving legal work. The course also has wider applicability in developing the attributes and skills inherent in a general university education. Students develop the values and intellectual abilities necessary to marshal facts and to critically assess and evaluate information, theories and doctrines thus preparing themselves for a variety of career roles. A degree in law is the first step towards entering the legal profession. After graduating from the University, a law student wishing to practise in Tasmania is required to undertake a 6 months Legal Practice course. Law students intending to practise law in another State should inquire of the respective Law Society or Bar Council what they must do to qualify for practice in their chosen State. Overseas students should address such enquiries to the relevant authority in their home country. Career outcomes A law degree is a prerequisite to admission as a legal practitioner. Today, however, employers from a widening range of disciplines value the skills that law graduates possess. A range of careers choices lies open to law graduates as Course details (2001) page 161 a solicitor, barrister, industry legal officer or ministerial adviser, as well as in legal aid, community legal centres, the Attorney-General's department, law reform commissions, consumer affairs, environment, foreign affairs, police, legal drafting. politics, banking, finance, journalism, publishing and teaching. Course structure Students who have satisfied the entrance requirements and have been selected for the degree of Bachelor of Laws, are required to pass in sequence, and in the year of study prescribed, the compulsory units set out below and 10 electives chosen from the schedule of electives following. One elective must be chosen from each of Groups A, B, C, D and E over years 2 and 3. Articulation Students who have completed units of similar weight and standing which may be taken as part of a Bachelor of Laws degree course at another tertiary institution may be given credit in units of the Bachelor of Laws degree to the limits prescribed by the Faculty and the University. Skills The components, and the assessment, of the Skills unit have been fully integrated into the core units. Each core unit description outlines the skills covered by that unit. Moot – Students are required to attend and participate in one moot. Satisfactory performance in the moot is a prerequisite to obtaining the degree. Compulsory units Unit Title campus-sem Year 1 Contract Law Hf Torts Hf Criminal Law Hf Principles of Public Law Hf Year 2 Property Law Hf Law of Groups H1 and five electives from Schedule of Electives Year 3 Equity and Trusts H1 Litigation Hf and five electives from Schedule of Electives weight code 25% 25% 25% 25% BLA200 BLA201 BLA202 BLA203 25% 12.5% BLA303 BLA304 12.5% 25% BLA401 BLA402 Course details (2001) page 162 Schedule of Electives Students are required to take one elective from each of Groups A, B, C, D and E during their course of study All units are of one semester length with a weighting of 12.5% with the exception of BLA699 Elective 3 which has a weighting of 25% and is a full-year unit, equivalent to 2 one-semester units for the purposes of the number of electives required for the degree. Unit Title Group A Jurisprudence 1 Jurisprudence 2 Jurisprudence 3 Jurisprudence 4 Criminology Sociology of Law Comparative Law Legal History Group B International Law Law of the Sea Antarctic and Southern Ocean Law Human Rights Advanced International Law Law of the European Union Maritime Law Group C Planning Law Advanced Administrative Law Conciliation and Arbitration Law Advanced Constitutional Law Environmental Law Employment Law Trade Union Law Advanced Criminal Law Welfare Law Anti-discrimination Law Media Law Group D Commercial Law campus-sem weight code [na] H1 [na] [na] H1 H2 [na] H2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BLA611 BLA612 BLA613 BLA614 BLA615 BLA616 BLA617 BLA618 H1 H2 12.5% 12.5% BLA631 BLA632 H1 H2 12.5% 12.5% BLA633 BLA634 H3 H3 [na] 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BLA635 BLA636 BLA638 [na] 12.5% BLA641 H2 12.5% BLA642 [na] 12.5% BLA643 [na] H2 [na] [na] [na] [na] [na] H1 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BLA644 BLA645 BLA646 BLA647 BLA648 BLA649 BLA651 BLA652 H2 12.5% BLA661 Course details (2001) page 163 Tax 1 International Trade Intellectual Property Internal Company Structure Trade Practices Law Law and Finance Personal and Corporate Solvency Consumer Protection Information Technology Law Tax 2 Regulation of Securities Financial Institutions Law Group E Family 1 – the Family and the Child Family 2 – Financial Aspects of Family Law Succession Conflicts (Private International Law) Information Law Landlord and Tenant Sentencing Compensation Law Restitution Elective 1 (Jessup Moot) Elective 2 (Supervised Research) Clinical Legal Education Law and Ethics of Health Care Professional Conduct Remedies Heritage Law Elective 3 (Supervised Research) H1 H3 H2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BLA662 BLA663 BLA664 H2 H1 [na] 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BLA665 BLA666 BLA667 [na] [na] 12.5% 12.5% BLA668 BLA669 H1~L1 [na] [na] 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BLA670 BLA671 BLA672 H3 12.5% BLA673 H1 12.5% BLA681 [na] H2 12.5% 12.5% BLA682 BLA683 H1 [na] [na] [na] [na] [na] H3 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BLA684 BLA685 BLA687 BLA688 BLA689 BLA691 BLA692 H1/2 [na] 12.5% 12.5% BLA693 BLA694 H1 H2 [na] [na] 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BLA695 BLA696 BLA697 BLA698 Hf 25% BLA699 Honours in Law (Abbreviation: LLB(Hons)) Course details (2001) page 164 Course code: L4B Candidates may be awarded a Law degree with Honours if they accumulate sufficient honours points in Law units passed. Honours points are awarded for performance at the Distinction and High Distinction level in accordance with the Specifications of Bachelor of Laws and Combined Degrees with Honours. The degree may be awarded with either First or Second Class Honours. Course objectives Degrees combining with LawBachelor of Arts and Bachelor of Laws (Abbreviation: BA–LLB) Course code: L3D (See also BA–LLB under Faculty of Arts entry on page xx, L3F (BCom–LLB), L3E (BEc–LLB), L3K (BIS–LLB), L3G (BSc–LLB) following.) These on-campus courses at Hobart are offered by the Faculties of Arts, Commerce & Law, and Science & Engineering. They are available full time (a minimum of 5 years) or part time (a maximum of 10 years). Admission & prerequisites Students must pass the first year of their BA, BCom, BEc, BIS or BSc degree, including the subject BLA101 Introduction to Law, available at Hobart and Launceston, or its academic equivalent. Students who have a different academic background, either from this University or another approved tertiary institution, may be considered for admission. Course objectives The objectives of the combined degree courses are those of the component degrees. Reference should be made to the Bachelor of Laws course entry and to the course entry for the other relevant degree. Career outcomes Graduates of combined degrees could expect to find open to them all the career paths that are open to graduates of the component degree courses. Course details (2001) page 165 Course structure The courses are arranged so that the BA, BCom, BEc, BIS, or BSc requirement is completed in the first three years. The remaining two years are devoted to Law studies. Students who have satisfied the entrance requirements and have been selected for a degree combining with Law, are required to pass in sequence, and in the year of study prescribed, the compulsory units set out below and 10 electives chosen from the schedule of electives on the previous page. One elective must be chosen from each of Groups A, B, C, D and E over years 4 and 5. Skills The components, and the assessment, of the Skills unit have been fully integrated into the core units. Each core unit description outlines the skills covered by that unit. Moots– Students are required to attend and participate in one moot. Satisfactory performance in the moot is a prerequisite to obtaining the degree. Schedule Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Introduction to Law Hf~Lf 25% BLA101 plus 75% units from BA ( course code R3A) on page xx Year 2 Contract Law [a] Hf 25% BLA200 [a] Torts Hf 25% BLA201 plus 62.5% units from BA (course code R3A) on page xx Year 3 Criminal Law Hf 25% BLA202 Principles of Public Law Hf 25% BLA203 plus 50% units from BA ( course code R3A) on page xx Year 4 Property Law Hf 25% BLA303 Law of Groups H1 12.5% BLA304 plus 5 electives from Schedule of Electives on page xx Year 5 Litigation Hf 25% BLA402 Equity and Trusts H1 12.5% BLA401 plus 5 electives from Schedule of Electives on page xx [a] the weighting of these units is 20% for students enrolled in this combined degree Course details (2001) page 166 Bachelor of Commerce and Bachelor of Laws (Abbreviation: BCom–LLB) Course code: L3F See introductory details of Bachelor of Arts–Bachelor of Laws (above). Course objectives Schedule Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Introduction to Law Hf~Lf 25% BLA101 plus 75% units from BCom (course code C3C) on page xx Year 2 Contract Law [a] Hf 25% BLA200 [a] Torts Hf 25% BLA201 plus 62.5% units from BCom (course code C3C) on page xx Year 3 Criminal Law Hf 25% BLA202 Principles of Public Law Hf 25% BLA203 plus 50% units from BCom (course code C3C) on page xx Year 4 Property Law Hf 25% BLA303 Law of Groups H1 12.5% BLA304 plus 5 electives from Schedule of Electives on page xx Year 5 Litigation Hf 25% BLA402 Equity and Trusts H1 12.5% BLA401 plus 5 electives from Schedule of Electives on page xx [a] the weighting of these units is 20% for students enrolled in this combined degree Bachelor of Economics and Bachelor of Laws (Abbreviation: BEc–LLB) Course details (2001) page 167 Course code: L3E See introductory details of Bachelor of Arts–Bachelor of Laws (above). Course objectives Schedule Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Introduction to Law Hf~Lf 25% BLA101 plus 75% units from BEc (course code C3E) on page xx Year 2 Contract Law [a] Hf 25% BLA200 [a] Torts Hf 25% BLA201 plus 62.5% units from BEc (course code C3E) on page xx Year 3 Criminal Law Hf 25% BLA202 Principles of Public Law Hf 25% BLA203 plus 50% units from BEc (course code C3E) on page xx Year 4 Property Law Hf 25% BLA303 Law of Groups H1 12.5% BLA304 plus 5 electives from Schedule of Electives on page xx Year 5 Litigation Hf 25% BLA402 Equity and Trusts H1 12.5% BLA401 plus 5 electives from Schedule of Electives on page xx [a] the weighting of these units is 20% for students enrolled in this combined degree Bachelor of Information Systems and Bachelor of Laws (Abbreviation: BIS–LLB) Course code: L3K See introductory details of Bachelor of Arts–Bachelor of Laws (above). Course objectives Course details (2001) page 168 Schedule Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Introduction to Law Hf~Lf 25% BLA101 plus 75% units from BIS (course code C3S) on page xx Year 2 Contract Law [a] Hf 25% BLA200 Torts [a] Hf 25% BLA201 plus 62.5% units from BIS (course code C3S) on page xx Year 3 Criminal Law Hf 25% BLA202 Principles of Public Law Hf 25% BLA203 plus 50% units from BIS (course code C3S) on page xx Year 4 Property Law Hf 25% BLA303 Law of Groups H1 12.5% BLA304 plus 5 electives from Schedule of Electives on page xx Year 5 Litigation Hf 25% BLA402 Equity and Trusts H1 12.5% BLA401 plus 5 electives from Schedule of Electives on page xx [a] the weighting of these units is 20% for students enrolled in this combined degree Bachelor of Science and Bachelor of Laws (Abbreviation: BSc–LLB) Course code: L3G See introductory details of Bachelor of Arts–Bachelor of Laws (above). Course objectives Schedule Unit Title Year 1 Introduction to Law campus-sem weight code Hf~Lf 25% BLA101 Course details (2001) page 169 plus 75% Group 1 core units from Schedule A of BSc (25% each from three Schools) on page xx Year 2 Contract Law [a] Hf 25% BLA200 [a] Torts Hf 25% BLA201 plus 66.67% Group 2 core units from Schedule A of the BSc (33.33% each from two Schools) on page xx Year 3 Criminal Law Hf 25% BLA202 Principles of Public Law Hf 25% BLA203 plus 50% Group 3 core units from Schedule A of the BSc (50% from one School representing a major) on page xx Year 4 Property Law Hf 25% BLA303 Law of Groups H1 12.5% BLA304 plus 5 electives from Schedule of Electives on page xx Year 5 Litigation Hf 25% BLA402 Equity and Trusts H1 12.5% BLA401 plus 5 electives from Schedule of Electives on page xx [a] the weighting of these units is 20% for students enrolled in this combined degree Bachelor of Arts and Bachelor of Laws with Honours in Law (Abbreviation: BA–LLB(Hons)) Course code: L4D See introductory details of Bachelor of Arts–Bachelor of Laws and Honours in Laws. Schedule Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Introduction to Law Hf~Lf 25% BLA101 plus 75% Group 1 core units from Schedule A of BSc (25% each from three Schools) on page xx Year 2 Contract Law [a] Hf 25% BLA200 Torts [a] Hf 25% BLA201 Course details (2001) page 170 plus 66.67% Group 2 core units from Schedule A of the BSc (33.33% each from two Schools) on page xx Year 3 Criminal Law Hf 25% BLA202 Principles of Public Law Hf 25% BLA203 plus 50% Group 3 core units from Schedule A of the BSc (50% from one School representing a major) on page xx Year 4 Property Law Hf 25% BLA303 Law of Groups H1 12.5% BLA304 plus 5 electives from Schedule of Electives on page xx Year 5 Litigation Hf 25% BLA402 Equity and Trusts H1 12.5% BLA401 plus 5 electives from Schedule of Electives on page xx [a] the weighting of these units is 20% for students enrolled in this combined degree Bachelor of Commerce and Bachelor of Laws with Honours in Law (Abbreviation: BCom–LLB(Hons)) Course code: L4F See introductory details of Bachelor of Arts–Bachelor of Laws and Honours in Laws. Schedule Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Introduction to Law Hf~Lf 25% BLA101 plus 75% Group 1 core units from Schedule A of BSc (25% each from three Schools) on page xx Year 2 Contract Law [a] Hf 25% BLA200 [a] Torts Hf 25% BLA201 plus 66.67% Group 2 core units from Schedule A of the BSc (33.33% each from two Schools) on page xx Year 3 Criminal Law Hf 25% BLA202 Principles of Public Law Hf 25% BLA203 Course details (2001) page 171 plus 50% Group 3 core units from Schedule A of the BSc (50% from one School representing a major) on page xx Year 4 Property Law Hf 25% BLA303 Law of Groups H1 12.5% BLA304 plus 5 electives from Schedule of Electives on page xx Year 5 Litigation Hf 25% BLA402 Equity and Trusts H1 12.5% BLA401 plus 5 electives from Schedule of Electives on page xx [a] the weighting of these units is 20% for students enrolled in this combined degree Bachelor of Economics and Bachelor of Laws with Honours in Law (Abbreviation: BEc–LLB(Hons)) Course code: L4E See introductory details of Bachelor of Arts–Bachelor of Laws and Honours in Laws. Schedule Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Introduction to Law Hf~Lf 25% BLA101 plus 75% Group 1 core units from Schedule A of BSc (25% each from three Schools) on page xx Year 2 Contract Law [a] Hf 25% BLA200 Torts [a] Hf 25% BLA201 plus 66.67% Group 2 core units from Schedule A of the BSc (33.33% each from two Schools) on page xx Year 3 Criminal Law Hf 25% BLA202 Principles of Public Law Hf 25% BLA203 plus 50% Group 3 core units from Schedule A of the BSc (50% from one School representing a major) on page xx Year 4 Property Law Hf 25% BLA303 Law of Groups H1 12.5% BLA304 plus 5 electives from Schedule of Electives on page xx Course details (2001) page 172 Year 5 Litigation Hf 25% BLA402 Equity and Trusts H1 12.5% BLA401 plus 5 electives from Schedule of Electives on page xx [a] the weighting of these units is 20% for students enrolled in this combined degree Bachelor of Information Systems and Bachelor of Laws with Honours in Law (Abbreviation: BIS–LLB(Hons)) Course code: L4K See introductory details of Bachelor of Arts–Bachelor of Laws and Honours in Laws. Schedule Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Introduction to Law Hf~Lf 25% BLA101 plus 75% Group 1 core units from Schedule A of BSc (25% each from three Schools) on page xx Year 2 Contract Law [a] Hf 25% BLA200 [a] Torts Hf 25% BLA201 plus 66.67% Group 2 core units from Schedule A of the BSc (33.33% each from two Schools) on page xx Year 3 Criminal Law Hf 25% BLA202 Principles of Public Law Hf 25% BLA203 plus 50% Group 3 core units from Schedule A of the BSc (50% from one School representing a major) on page xx Year 4 Property Law Hf 25% BLA303 Law of Groups H1 12.5% BLA304 plus 5 electives from Schedule of Electives on page xx Year 5 Litigation Hf 25% BLA402 Equity and Trusts H1 12.5% BLA401 plus 5 electives from Schedule of Electives on page xx [a] the weighting of these units is 20% for students enrolled in this combined degree Course details (2001) page 173 Bachelor of Science and Bachelor of Laws with Honours in Law (Abbreviation: BSc–LLB(Hons)) Course code: L4G See introductory details of Bachelor of Arts–Bachelor of Laws and Honours in Laws. Schedule Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Introduction to Law Hf~Lf 25% BLA101 plus 75% Group 1 core units from Schedule A of BSc (25% each from three Schools) on page xx Year 2 Contract Law [a] Hf 25% BLA200 [a] Torts Hf 25% BLA201 plus 66.67% Group 2 core units from Schedule A of the BSc (33.33% each from two Schools) on page xx Year 3 Criminal Law Hf 25% BLA202 Principles of Public Law Hf 25% BLA203 plus 50% Group 3 core units from Schedule A of the BSc (50% from one School representing a major) on page xx Year 4 Property Law Hf 25% BLA303 Law of Groups H1 12.5% BLA304 plus 5 electives from Schedule of Electives on page xx Year 5 Litigation Hf 25% BLA402 Equity and Trusts H1 12.5% BLA401 plus 5 electives from Schedule of Electives on page xx [a] the weighting of these units is 20% for students enrolled in this combined degree Bachelor of Computing and Bachelor of Laws with Honours in Law Course details (2001) page 174 (Abbreviation: BComp–LLB(Hons)) Course code: L4H See introductory details of Bachelor of Arts–Bachelor of Laws and Honours in Laws. Schedule Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Introduction to Law Hf~Lf 25% BLA101 plus 75% Group 1 core units from Schedule A of BSc (25% each from three Schools) on page xx Year 2 Contract Law [a] Hf 25% BLA200 [a] Torts Hf 25% BLA201 plus 66.67% Group 2 core units from Schedule A of the BSc (33.33% each from two Schools) on page xx Year 3 Criminal Law Hf 25% BLA202 Principles of Public Law Hf 25% BLA203 plus 50% Group 3 core units from Schedule A of the BSc (50% from one School representing a major) on page xx Year 4 Property Law Hf 25% BLA303 Law of Groups H1 12.5% BLA304 plus 5 electives from Schedule of Electives on page xx Year 5 Litigation Hf 25% BLA402 Equity and Trusts H1 12.5% BLA401 plus 5 electives from Schedule of Electives on page xx [a] the weighting of these units is 20% for students enrolled in this combined degree Bachelor of Commerce and Bachelor of Applied Science (Abbreviation: BCom–BAppSc) Course code: C3A Course details (2001) page 175 No new enrolments will be taken as this course is being taught out. Details of the course outline and study schedules can be found in earlier versions of the Course and Unit Handbook. Bachelor of Arts and Bachelor of Commerce (Abbreviation: BA–BCom) Course code: C3R The 4-year full-time combined degree of Bachelor of Arts–Bachelor of Commerce is offered on the Launceston and Hobart campuses by the Faculty of Arts and the Faculty of Commerce and Law. A restricted program is available at the North-West Centre. For further information, contact the Faculty of Commerce and Law. Admission & prerequisites Possession of the University's minimum entry requirements including in the case of Tasmanian school-leavers TCE *MT730 Mathematics Applied. Course objectives The objectives of the combined degrees are: • • to complement traditional studies in humanities and social sciences with a wide range of management, accounting, marketing and business skills; to broaden the opportunities of commerce students to undertake studies in languages and area studies. Career outcomes Graduates of the Bachelor of Commerce could expect to obtain employment in accounting, finance, international business, human resource or personnel management, marketing, journalism and public relations, government and teaching. Professional recognition If students wish to be eligible for membership of a professional body they will need to select units endorsed by that body. The faculty offers units to enable students to join the following professional bodies: • Institute of Chartered Accountants in Australia Course details (2001) • • • • • • • page 176 Australian Society of Certified Practising Accountants Australian Human Resources Institute Australian Institute of Management Australian Marketing Institute Chartered Institute of Company Secretaries in Australia Australian Institute of Banking and Finance Australian Computer Society Membership details may be obtained from the relevant Schools or the professional body. Course structure To qualify for Bachelor of Arts–Bachelor of Commerce students must successfully complete 32 units (400%) comprising: 16 (12.5%) units (200%) from Commerce and two majors (200%) from Arts. Articulation Students who have completed the Associate Diploma of Business and have been admitted to the course will receive credit for the core compulsory units in Commerce. Sample Course Structure Unit Title Year 1 Bachelor of Commerce Business Information Systems Introduction to Management Commercial Transactions Elective Bachelor of Arts Subject A (level 100) Subject B (level 100) Year 2 Bachelor of Commerce Accounting and Financial Decision Making Economics for Business Quantitative Methods 1 Elective for major Bachelor of Arts Subject A (level 200) Subject A level 200 campus-sem weight code H1/2~L1/2~B1 12.5% BSA101 H1/2~L1/2~B1 H2~L2~B2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BMA101 BFA141 25% 25% H1~L1~B1 H1~L1~B1 H2~L2~B2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 25% 25% BFA103 BEA110 BEA140 Course details (2001) Year 3 Bachelor of Commerce Commerce major unit 1 Commerce major unit 2 Commerce major unit 3 Commerce major unit 4 Bachelor of Arts Subject A (level 200/300) Subject B (level 200/300) Year 4 Bachelor of Commerce Commerce major unit 5 Commerce major unit 6 Commerce major unit 7 Commerce major unit 8 Commerce major = 200% Bachelor of Arts Subject A (level 300 units) Subject B (level 300 units) Major A = 100%; Major B = 100% page 177 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 25% 25% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 25% 25% For choice of Commerce majors see details of Bachelor of Commerce. For the choice of Arts majors see details of Bachelor of Arts. Bachelor of Commerce and Bachelor of Computing (Abbreviation: BCom–BComp) Course code: C3X The 4-year full-time combined degree of Bachelor of Commerce-Bachelor of Computing is offered on the Launceston campus by the Faculty of Commerce & Law and the Faculty of Science & Engineering. Admission & prerequisites Possession of the University's minimum entry requirements including, in the case of Tasmanian school-leavers, TCE *MT730 Mathematics Applied. Course objectives Course details (2001) page 178 To combine professional studies in computing with professional studies in commerce (in areas such as accounting and human resource management). Career outcomes Graduates of the combined degree could expect to find employment in such fields as accounting, human resource management, programming, software construction, multimedia and internet technology. Course structure To qualify for Bachelor of Commerce–Bachelor of Computing students must successfully complete 32 units comprising: 16 (12.5%) units from Computing and 16 (12.5%) units from Commerce. Articulation Students who have completed the TAFE Associate Diploma of Business or the Diploma of Information Technology and have been admitted to the course may receive one year of credit in Commerce or Computing respectively. Sample Course Structure Unit Title Year 1 Bachelor of Commerce Business Information Systems Accounting and Financial Decision Making Commercial Transactions Elective Bachelor of Computing Programming and Problem Solving Professional Computing Multimedia and Web Applications Software Process Year 2 Bachelor of Commerce Economics for Business Introduction to Management Quantitative Methods 1 Elective Bachelor of Computing campus-sem weight code H1/2~L1/2~B1 12.5% BSA101 H1~L1~B1 H2~L2~B2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BFA103 BFA141 H1~L1/2~B1 H2~L2~B2 12.5% 12.5% KXA151 KXA155 H2~L2~B2 H2~L2~B2 12.5% 12.5% KXA156 KXA154 H1~L1~B1 12.5% BEA110 H1/2~L1/2~B1 H2~L2~B2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BMA101 BEA140 Course details (2001) Software Design Artificial Intelligence Computer Organisation and Architecture Operating Systems Year 3 Bachelor of Commerce Commerce major unit 1 Commerce major unit 2 Commerce major unit 3 Commerce major unit 4 Bachelor of Computing Computing elective unit 1 Algorithms and Metrics Computing elective unit 2 Computing elective unit 3 Year 4 Bachelor of Commerce Commerce major unit 5 Commerce major unit 6 Commerce major unit 7 Commerce major unit 8 Bachelor of Computing Computing elective unit 4 Computing elective unit 5 Computing Project A Computing Project B page 179 H2~L2 H1~L1 12.5% 12.5% KXA253 KXA252 H1~L1~B1 H2~L2 12.5% 12.5% KXA152 KXA254 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% H1~L1 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KXA251 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% L1/2 L1/2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KXA331 KXA332 Bachelor of Commerce and Bachelor of Information Systems (Abbreviation: BCom–BIS) Course code: C3L The 4-year full-time combined degree of Bachelor of Commerce-Bachelor of Information Systems is offered on the Launceston and Hobart campuses by the Faculty of Commerce & Law. The first year and some selected later year units are available at the North-West Centre. Admission & prerequisites Applicants need to meet the requirements for entry into the Bachelor of Commerce and Bachelor of Information Systems courses. Course details (2001) page 180 Course objectives The purpose of the course is to combine professional studies in information systems with professional studies in commerce. Career outcomes Graduates of the combined degree could expect to find employment in areas such as those enumerated for the Bachelor of Commerce and Bachelor of Information degrees. Course structure The course structure of the combined degree includes: The core units in the first year of the BCom degree One Commerce major (other than Information Systems), as prescribed within the BCom degree The core program of the BIS degree Five additional elective units, with a total weight of 62.5% The recommended program of study for this combined degree is shown in the 'Schedule of units'. The first year of the combined degree is a standard first year of the BCom, with one of the electives chosen to be BSA102. This allows a student to transfer between this program and a BCom without penalty after first year. A student who has completed the first year of the BIS degree may transfer into this combined degree program, with the only penalty being the requirement to complete the first eight Commerce units. After second year of this combined degree program a student could transfer into either the BCom or BIS without penalty. After third year of this combined degree program a student could graduate with a BCom, including an IS major but not have satisfied the requirements of a BIS. Articulation Course details (2001) page 181 Students who have completed the TAFE Associate Diploma of Business or the Diploma of Information Technology and have been admitted to the course may receive one year of credit in Commerce or Information Systems respectively. Schedule of units Unit Title campus-sem Year 1 Economics for Business H1~L1~B1 Quantitative Methods 1 H2~L2~B2 Commercial Transactions H2~L2~B2 First year Commerce elective for major Business Information Systems H1/2~L1/2~B1 Information Modelling H2~L2~B2 Introduction to Management H1/2~L1/2~B1 Accounting and Financial Decision Making H1~L1~B1 Year 2 Commerce major unit 1 Commerce major unit 2 Commerce major unit 3 Commerce major unit 4 Introduction to Logic H1~D1~Lw1~Bw1 Programming and Problem Solving H1~L1/2~Bv/1 Information Systems core unit 1 Information Systems core unit 2 Year 3 Commerce major unit 5 Commerce major unit 6 Commerce major unit 7 Commerce major unit 8 Information Systems core unit 3 Information Systems core unit 4 Information Systems core unit 5 Information Systems core unit 6 Year 4 Four elective units (12.5%) each Information Systems core unit 7 Information Systems core unit 8 Information Systems core unit 9 Elective unit weight code 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BEA110 BEA140 BFA141 12.5% 12.5% BSA101 BSA102 12.5% BMA101 12.5% BFA103 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HPA291/391 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KXA151 Course details (2001) page 182 Note: The Commerce major units must satisfy the requirements of a Commerce major, other than Information Systems. The IS core units must comprise a specified core program of the Bachelor of Information Systems. Bachelor of Arts and Bachelor of Economics (Abbreviation: BA–BEc) Course code: C3Y The 4-year full-time combined degree of Bachelor of Arts–Bachelor of Economics is offered on the Hobart campus by the Faculty of Commerce and Law and the Faculty of Arts. The first year may be completed at Launceston. Admission & prerequisites Possession of the University's minimum entry requirements including in the case of Tasmanian school-leavers TCE *MT730 Mathematics Applied. Course objectives The objectives of the combined degrees are: • • • • • to complement studies in humanities and social sciences with a solid grounding in modern economics; to broaden the opportunities of economics students to undertake studies in languages and area studies; to prepare students for eventual responsible professional posts in private and public organisation; to produce graduates capable of operating effectively in a rapidly changing environment; to develop students as persons with a life-long interest for learning in their special and related fields. Career outcomes Graduates of the combined degree could expect to find positions in banking, financial management, statistics, market research, stock market, government agencies, teaching. Course structure Course details (2001) page 183 To qualify for Bachelor of Arts–Bachelor of Economics students must successfully complete 32 units comprising: 11 (12.5%) units from Economics; two majors (200%) from Arts and five other approved units. Articulation Students who have completed the TAFE Diploma of Business and have been admitted to the course will receive credit for up to eight units towards the degree. The status of individual units is determined at the time of offer. Sample Course Structure Unit Title Year 1 Bachelor of Economics Economics for Business Foundations of Economic Policy Quantitative Methods 1 Elective Bachelor of Arts Subject A (level 100) Subject B (level 100) Year 2 Bachelor of Economics Intermediate Microeconomics Intermediate Macroeconomics BEA241 or BEA242 Research Methods for Finance Introduction to Econometrics Elective Bachelor of Arts Subject A (level 200) Subject B (level 200) Year 3 Bachelor of Economics Approved Economics elective 1 Approved Economics elective 2 Approved Economics elective 3 Approved Economics elective 4 Bachelor of Arts Subject A (level 200/300) Subject B (level 200/300) campus-sem weight code H1~L1~B1 12.5% BEA110 H2~L2~B2 H2~L2~B2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BEA130 BEA140 25% 25% H2 12.5% BEA200 H1 12.5% BEA220 H2 12.5% BEA241 H1 12.5% 12.5% BEA242 25% 25% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 25% 25% Course details (2001) Year 4 Bachelor of Economics Economics or approved Group 3A elective 1 Economics or approved Group 3A elective 2 Economics or approved Group 3A elective 3 Economics or approved Group 3A elective 4 Approved Economics electives program = 200% Bachelor of Arts Subject A (level 300) Subject B (level 300) Major A = 100%; Major B = 100% For Economics majors, see Bachelor of Economics. For Arts majors, see Bachelor of Arts. page 184 12.5 12.5 12.5 12.5 25% 25% Graduate Certificate in Legal Practice (Abbreviation: GradCertLegPrac) Course code: L5B A 24–26-week full-time course, the GradCertLegPrac runs in Hobart from February to July each year. Admission & prerequisites Applicants need to have successfully completed a degree of Bachelor of Laws or a combined degree course including the Bachelor of Laws at the University of Tasmania or any other approved Australian university. Applicants need to have passed the requirements of the subjects prescribed by the Board of Legal Education pursuant to Section 23(b) of the Legal Profession Act 1993 (Tas). Course objectives Successful completion of the course is normal prerequisite for admission as a Barrister and Solicitor of the Supreme Court of Tasmania. Fees The Graduate Certificate in Legal Studies is a HECS based course for students commencing in 2001. Further details For further details and information, please contact the Law School on (03) 6226 2066 or Course details (2001) page 185 Mr Peter Tree (03) 6226 7570. Graduate Certificate of Management (Abbreviation: GradCertMgt) Course code: C5T A 1-year part-time, on-campus course offered by the Faculty of Commerce and Law at Hobart and Launceston. Faculty's Graduate School of Management is a member of the Consortium of Australian Management and Business Schools Ltd. CAMBS offers a national Graduate Certificate of Management on-campus in Adelaide, Brisbane, Hobart and Launceston, Melbourne, Perth and Sydney, in Penang through the International College/University of Sydney twinning arrangement, and throughout Australia via off-campus education through Deakin University. All course materials have been prepared by Deakin University, drawing on Deakin's acknowledged leadership in the preparation of off-campus materials, plus the expertise of acknowledged specialists within the Consortium. Students in each university will have an identical curriculum, assessment requirements and course materials. As a result, they may attend classes at any of the participating universities whether for short periods if they are required to work interstate intermittently, or can transfer entirely to another member of the Consortium. The course is conducted over 7 weekend sessions per semester. For each unit, seven 3.25-hour (Saturday) sessions are held alternatively between Hobart and Launceston (ie 4/7 at Hobart and 3/7 at Launceston). The course is full fee paying. Fees cover tuition, all study materials (with the exception of textbooks) and costs associated with the study sessions. Admission & prerequisites The Faculty of Commerce and Law may accept as a candidate for the Graduate Certificate of Management any of the following: (i) A person who: (a) (b) has completed an undergraduate degree of an Australian higher education institution or the equivalent standard in any other institution, and has had at least six months work experience; Course details (2001) (ii) page 186 A person who is not a graduate but whose demonstrated managerial competencies and relevant experience of seven years' standing indicate a level of knowledge and skill equivalent to those of graduates in similar situations. Course objectives Career outcomes Graduate studies have an important place in management development. They offer individuals aspiring to either general management or senior functional management roles the opportunity to develop competencies relevant to the effective management of enterprises. Course structure The Graduate Certificate is made up of four units: three core and one elective which form the basis of management education: Articulation May lead to the Graduate Diploma of Business Administration. Unit Title Organisational Behaviour Financial Reporting & Analysis Marketing Management and one elective unit from: Managing Human Resources Law for Managers Management Ethics International Business Management campus-sem H1/2~L1/2 weight 12.5% code BMA581 H1/2~L1/2 H1/2~L1/2 12.5% 12.5% BMA582 BMA584 H1/2~L1/2 H1/2~L1/2 H1/2~L1/2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BMA583 BMA682 BMA773 H1/2~L1/2 12.5% BMA774 The course consists of 156 hours contact made up of 39 hours per unit comprised of 22 hours class contact with the balance being made up of structured learning through a comprehensive distance education package. Participants who successfully complete all four units of the Graduate Certificate, and make application for further study, may be granted admission with advanced standing to the Graduate Diploma of Business Administration. Students should refer to the specifications for the Graduate Certificate of Management which are printed in full in the Calendar. Course details (2001) page 187 Graduate Diploma of Business Administration (Abbreviation: GDBA) Course code: C6Q This 2-year part-time, on-campus course is offered by the Faculty of Commerce and Law at the Hobart and Launceston campuses. The course is conducted over 7 weekend sessions per semester. For each unit seven 3.25-hour (Saturday) sessions are held alternatively between Hobart and Launceston (ie 4/7 at Hobart and 3/7 at Launceston). The course is full fee paying. Fees cover tuition, all study materials (with the exception of text books) and costs associated with the study sessions. All units are subject to formal assessment including, but not limited to, assignments, essays and examinations. Admission & prerequisites The Faculty of Commerce and Law may accept as a candidate for the Graduate Diploma of Business Administration any of the following: (i) A person who: (a) (b) (ii) has completed an undergraduate degree of an Australian higher education institution or the equivalent standard in any other institution, and has had at least six months appropriate work experience; A person who is not a graduate but who has satisfactorily completed the Graduate Certificate of Management of the University of Tasmania or another participating member of the Consortium of Australian Management and Business Schools Ltd, or an equivalent award. Course objectives The broad aims of the course are to assist course participants to become better managers by providing them with a basic understanding of the broad body of knowledge of a number of different management disciplines. Career outcomes Course details (2001) page 188 Graduate studies have an important place in management development. They offer individuals aspiring to either general management or senior functional management roles the opportunity to develop competencies relevant to the effective management of enterprises. Course structure To qualify for the Graduate Diploma, the candidate must complete eight units, as outlined in the following schedule: Articulation Graduates of the Graduate Certificate of Management may receive full credit The course leads on to the Master of Business Administration. Unit Title Compulsory units Organisational Behaviour Financial Reporting & Analysis Marketing Management Quantitative Analysis for Managers Economics for Managers and three electives from: Elective units Managing Human Resources Law for Managers Management Ethics International Business Management campus-sem weight code H1/2~L1/2 12.5% BMA581 H1/2~L1/2 H1/2~L1/2 12.5% 12.5% BMA582 BMA584 H1/2~L1/2 H1/2~L1/2 12.5% 12.5% BMA681 BMA683 H1/2~L1/2 H1/2~L1/2 H1/2~L1/2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BMA583 BMA682 BMA773 H1/2~L1/2 12.5% BMA774 Students who have completed the Graduate Certificate may receive advanced standing amounting to four units of credit towards the GDBA. In turn candidates who successfully complete the Graduate Diploma may be granted admission with advanced standing to the Master of Business Administration. Students should refer to the Specifications for the Graduate Diploma of Business Administration which are printed in full in the Calendar. Master of Business Administration (Abbreviation: MBA) Course code: C7M Course details (2001) page 189 This 3-year part-time, on-campus course is offered by the Faculty of Commerce and Law: at the Hobart and Launceston campuses. Initially the course has been offered in the part-time mode only with the minimum time for completion of the 12 unit course being 3 years. Students will now have the option of completing the course in less than three years by taking summer school units. The course is conducted over 7 weekend sessions per semester. For each unit seven 3.25-hour (Saturday) sessions are held alternatively between Hobart and Launceston (ie 4/7 at Hobart and 3/7 at Launceston). The course is full fee paying. Fees cover tuition, all study materials (with the exception of text books) and costs associated with the study sessions. All units are subject to formal assessment normally including assignments and a final examination. Admission & prerequisites The Faculty of Commerce and Law may accept as a candidate for the Master of Business Administration any of the following: (i) A person who: (a) (b) (ii) has completed an undergraduate degree of an Australian higher education institution or the equivalent standard in any other institution, and has had at least two years' appropriate work experience; A person who has satisfactorily completed the Graduate Diploma of Business Administration of the University of Tasmania or an equivalent award of another Australian higher education institution. Course objectives Faculty believes that significant graduate outcomes will include: • • • • an ability to plan and manage successfully in an increasingly complex and turbulent national and international environment, within the framework of societal values; a high level of analytical, problem solving and communication skills; a creative, innovative and ethical approach in seeking new business opportunities; and an ability to act as an agent of change in organisational transformation. Career outcomes Course details (2001) page 190 Graduate studies have an important place in management development. They offer individuals aspiring to either general management or senior functional management roles the opportunity to develop competencies relevant to the effective management of enterprises. Course structure To qualify for the MBA, the candidate must complete 12 units, as outlined in the following schedule: Articulation Graduates of the Graduate Diploma of Business Administration may receive full credit. Unit Title Compulsory units Organisational Behaviour Financial Reporting & Analysis Managing Human Resources Marketing Management Quantitative Analysis for Managers Law for Managers Economics for Managers Management Ethics International Business Management Strategic Management Two of the following electives: Elective units Managerial Accounting Finance for Managers Management Information Technology Human Resource Development International Human Resource Management Special Topics in Management Research Project campus-sem weight code H1/2~L1/2 12.5% BMA581 H1/2~L1/2 H1/2~L1/2 H1/2~L1/2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BMA582 BMA583 BMA584 H1/2~L1/2 H1/2~L1/2 H1/2~L1/2 H1/2~L1/2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BMA681 BMA682 BMA683 BMA773 H1/2~L1/2 H1/2~L1/2 12.5% 12.5% BMA774 BMA799 H1/2~L1/2 H1/2~L1/2 12.5% 12.5% BMA771 BMA772 H1/2~L1/2 12.5% BMA775 H1/2~L1/2 12.5% BMA776 H1/2~L1/2 12.5% BMA777 H1/2~L1/2 H1/2~L1/2 12.5% 25% BMA790 BMA798 Students who have completed the Graduate Diploma of Business Administration may receive advanced standing amounting to eight units of Course details (2001) page 191 credit towards the MBA. Students should refer to the Specifications for the Master of Business Administration which are printed in full in the Calendar. Graduate Diploma in Information Systems (Abbreviation: GradDipIS) Course code: C6P This on-campus, 1-year (minimum) full-time or 3-year part-time course is offered by the Faculty of Commerce and Law at the Hobart and Launceston campuses. Admission & prerequisites Candidates for the Graduate Diploma in Information Systems will be required to satisfy the following: (a) (b) a bachelor degree from an accredited university; and have a basic knowledge of information technology and information modelling, as may be gained by self study, professional experience or by attending the units BSA101 Business Information Systems and BSA102 Information Modelling. Course objectives The course aims to – • • • • – – – enable graduates to fulfil key roles in the it and related industries, and to liaise between IT personnel and other professional and industrial personnel provide graduates with a strong systems focus, in their ability to conceive of new designs, address business needs and solve problems; give graduates a good understanding of the roles of IT in society, in organisations and for individuals, and an awareness that IT is a powerful factor for change in modern society provide knowledge, skills and understanding of the relationships of information and information technology to organisational needs; current management practice in the development of information systems, their use and associated policy formulation and analysis; the value of research, critical thinking and effective communication in the management of information systems; and to Course details (2001) • page 192 develop professional skills in such areas as interpersonal communication, working in teams, and technical report writing. Career outcomes Associate membership of the Australian Computer Society. Graduates of the Bachelor of Information Systems could expect to find employment as a business analyst, database analyst, systems analyst, IT project manager, IT manager, Information manager, database administrator, IT administrator or manager, telecommunications manager, IT consultant, electronic commerce or electronic business consultant, web developer, webmaster. Course structure Course units with the Graduate Diploma in Information Systems are of 12.5% weighting. There are 5 specified core units and one elective unit in Information Systems as outlined in the Schedule. The project is a full-year unit with a 25% weighting. Schedule Unit Title campus-sem weight code Core units Principles of Systems H1~L1~B1 12.5% BSA201 Management of Information Systems H1~L1 12.5% BSA303 Either BSA305 or BSA306 Current Trends in IS H2~L2 12.5% BSA305 Electronic Commerce H1~L1 12.5% BSA306 Systems Development H2~L2~B2 12.5% BSA202 Information Management H2~L2~B2 12.5% BSA203 Project Hf 25% BSA559 Elective: one unit to make up 12.5% chosen from a range of units offered within the School of Information Systems and elsewhere, by negotiation with the course coordinator. Master of Commerce (Abbreviation: MCom) Course code: C7C The aim of the course is to provide a master degree for candidates who wish to undertake initial training at postgraduate level in research in accounting or accounting combined with another subject area. The course requirement Course details (2001) page 193 consists of six units of coursework including a compulsory unit Research Methodology followed by the dissertation. The course requirements can be completed in a minimum of three semesters of full-time (or part-time equivalent) study. The course is offered in Hobart through the School of Accounting and Finance. Admission & prerequisites The Faculty of Commerce and Law may accept as a candidate for the Master of Commerce [by coursework] any of the following: • • • • [a] a person who has completed the degree of Bachelor of Commerce with Honours at the University of Tasmania or a qualification of equivalent standard in another tertiary institution; a person who has completed the degree of Bachelor of Commerce, Bachelor of Business or Bachelor of Economics at the University of Tasmania (or a qualification of equivalent standard in another tertiary institution), provided that the applicant's standard of achievement in that degree course is acceptable to the Faculty [a]; a person who has completed four units of the Bachelor of Commerce with Honours at the University of Tasmania provided that the applicant has achieved a grade of second class upper division in each unit; a person who possesses such other qualification and experience deemed by the Faculty to provide a preparation for study equivalent to that provided for by the prescriptions given in the first two categories above. Candidates in this category shall be required to have achieved a standard of Distinction or higher in at least 50% of the final year degree units or in equivalent postgraduate coursework/experience. Such candidates will be admitted provisionally and the continuation of candidature will depend on satisfactory progress. Course objectives Course structure Candidates are required to present for examination in Research Methodology plus five other units approved by the Head of the School of Accounting and Finance. At least three elective units must be from a list of units offered by the School of Accounting and Finance. Candidates may present for examination in up to two units (or equivalent) offered by another School in the University subject to the permission of the Head of the School of Accounting and Finance. Course details (2001) page 194 Candidates are required to achieve a second class upper division grade in each unit to satisfy the requirements of the degree. Course Structure Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Compulsory unit Research Methodology H1 BFA710 [a] Elective units Advanced Financial Accounting H2 BFA701 Advanced Auditing H? BFA708 Advanced Taxation Accounting [na] BFA709 Advanced Accounting Theory H1 BFA711 Advanced Finance [na] BFA724 Advanced Accounting Information Systems H1 BFA725 Corporate Governance and Accountability H2 12.5% BFA729 Advanced Management Accounting [na] BFA735 Year 2 Dissertation [b] H BFA741 [a] Elective units offered by the School of Accounting & Finance, subject to student demand and staff resources. Candidates with a first class or second class (upper division) honours degree may be given up to 3 units credit towards the Master of Commerce. [b] Candidates are required to present a dissertation of approximately 30,000 words. During the first year, candidates are required to present a satisfactory proposal for the Dissertation before enrolling in Year 2 (Dissertation). Students should also refer to the specifications for the Master of Commerce which are printed in full in the Calendar. Master of Information Systems (Abbreviation: MIS) Course code: C7A Course coordinator: Professor CD Keen Course details (2001) page 195 The Master of Information Systems is offered on the Hobart campus by the School of Information Systems. The course may be completed on a full-time basis in 3 semesters of study. Coursework is completed in semesters 1 and 2, and the MIS Project is completed during a third semester. Part-time enrolment in the degree can be completed in a maximum of 8 semesters or 4 years. The Master of Information Systems is a professional, applied degree which specialises in topics related to the management of information systems. Project work within the degree will equip the students with appropriate methodological and analytical skills, as well as requiring students to apply information systems management theory to practical problem solving and case work. It is expected that the majority of students taking the course will undertake project work closely related to their current or proposed area of employment. Admission & prerequisites Candidates for the Master of Information Systems program will be required to satisfy one of the following: (a) (b) (c) a four-year degree, or combination of degrees and diplomas, from an accredited university, which include major or submajor studies in a relevant discipline, such as Information Systems, Computer Science, Business Information Technology, Business Computing, Information Management, Information Science or Library Science; a three year degree from an accredited university, and at least three years of relevant professional experience; or have significant relevant professional experience in the areas of management and information systems, but fail to meet criteria (a) or (b). Under exceptional circumstances provisional entry status may be granted to such candidates. Such provisional entry status will be dependent on the candidate's successful completion of the equivalent of one semester of full-time study. Course objectives The course aims to provide – • • • – professional, postgraduate level education to existing managers, and those seeking to move into positions of information systems managers; management of information systems education which is at the level of world best practice in its currency, applicability and relevance to the IS profession; graduates of the course with knowledge, skills and understanding about: the relationships of information and information technology to organisational needs; Course details (2001) – – page 196 current management practice in the development of information systems, their use and associated policy formulation and analysis; the value of research, critical thinking and effective communication in the management of information systems. Career outcomes Associate membership of the Australian Computer Society. Graduates of the Bachelor of Information Systems could expect to find employment as a business analyst, database analyst, systems analyst, IT project manager, IT manager, Information manager, database administrator, IT administrator or manager, telecommunications manager, IT consultant, electronic commerce or electronic business consultant. Course structure Course units within the Master of Information Systems are of 12.5% weighting and comprise 26 contact hours over the period of one semester. The degree consists of 2 semesters of coursework with a total weighting of 100%; and a MIS Project, including the production of a thesis, weighted at 50% and completed over a single semester. The coursework consists of seven compulsory core units and one elective unit as outlined in the Schedule. Articulation Up to four units credit may be given for appropriate previous study. Schedule Unit Title Core units Management of Information Systems Information Management Information Systems Strategy Formulation Managing Organisational Change System Development Methodologies Information Systems Modelling Techniques Information Systems Research Methods campus-sem weight code H1 H1 12.5% 12.5% BSA751 BSA752 H1 12.5% BSA753 H2 12.5% BSA754 H2 12.5% BSA755 H2 12.5% BSA756 H1 12.5% BSA757 Course details (2001) page 197 MIS Project H1/2 50% BSA759 Elective: One 12.5% elective may be drawn from a range of electives offered within the School of Information Systems and elsewhere, by negotiation with the course coordinator – including: Decision Support and Executive Information Systems H2 12.5% BSA758 Bachelor of Adult and Vocational Education (Abbreviation: BAdVocEd) Course code: E3G The BAdVocEd is a 3-year award in adult and vocational education, offered in a fully external mode by a flexible delivery format. The distance materials are supplemented by a variety of flexible alternatives, including optional face-to-face tutorials and seminars, computer-web sites, tele- and video-seminars, email, fax and phone. Practical work is an essential element of this course. Admission & prerequisites Candidates for the degree of Bachelor of Adult and Vocational Education shall be qualified for entry in accordance with the provisions of the University's Rules of Admission. All candidates will complete the first year of the course in another faculty. (See also 'Profile of mature-aged entry applicants' below.) To qualify for admission to Year 2 candidates will meet the following criteria: 1 2 3 Candidates must have successfully completed one full year of degree level study in another faculty and at least three years of work experience relevant to the intended area of practice. (See also 'Articulation from' below); AND Candidates must have access to, or be prepared to negotiate access to a site where their prescribed practical work can be carried out and assessed. (The university lecturer who coordinates the practical work will help students in this task, but the primary responsibility rests with the student.); AND Candidates must provide sufficient documentation to support their application. (It is in their interest to ensure that the copies of degree, diploma, certificate and other course records are provided in a clearly Course details (2001) page 198 presented manner, with a clear covering statement which summarises the full-time equivalence of each course claimed, and totals these into a claim against one year of credit.) Course objectives The course provides an initial training for people entering the field of Adult and Vocational Education. The course prepares educators, teachers and trainers to work in a variety of modern educational situations in a range of contexts, including technical and further education, industry and workplace training (eg human resource development), community and public education, language, literacy and numeracy education and instructional design. Career outcomes Students in the field of adult and vocational education typically work in, or wish to work in, the following capacities: • • • • • educators of adults in TAFE institutes trainers and educators in industry, such as human resource developers teachers in adult and community education adult English language, literacy and numeracy educators instructional designers. It is envisaged that graduate students of this degree will soon be recognised as suitably qualified to teach vocational, education and training subjects in High School and Secondary Colleges. Course structure There are four areas of elective study possible in the final year of the course: • • • • Workplace Learning and Training Community and Public Education Instructional Design in AdVocEd Language, Literacy and Numeracy in AdVocEd This choice represents leading current trends in Adult and Vocational Education and will provide relevant and practical skills and knowledge for application in these areas. Articulation The Faculty may grant equivalence for the first year on the basis of advanced diploma or diploma qualifications or other qualifications deemed to be equivalent. Intending students who have successfully completed Certificate IV Course details (2001) page 199 Workplace Training (Category 2) from a recognised trainer may use this award toward credit in the second year (subject to first-year equivalence). Graduates of the degree may apply to enter the Bachelor of Adult and Vocational Education (Honours) program or a range of vocationally relevant Graduate Certificate programs. All units in the Graduate Certificate programs may, on application, be credited one-for-one against units in the Master of Education program. Students with outstanding Bachelor of Adult and Vocational Education (Honours) results of First class honours of at least GPA 4.00 and a distinction for the dissertation or Second class upper division of GPA 3.75 and a distinction for the dissertation may articulate directly into the Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) program. Turn to page xx for the postgraduate Education courses. Profile of mature-aged entry applicants Those who apply for entry to this course may be 'mature-age' and the University has separate provisions for entry for mature-aged students. Such applicants are usually employed, often have families and responsible community positions. Their study is therefore unlike the student entering from Year 12 directly into full-time university study. Some examples are listed for students to consider: 1 2 3 4 University study: the student may have completed some studying at a university. If they have completed the equivalent of one year of study (and have 3 years appropriate work experience) they may be admitted directly to year 2 of the BAdVocEd. Trade background: should have completed an apprenticeship or an equivalent vocational course. General Studies background: should have an appropriate professional qualification. Technical background: should have passed an appropriate degree, diploma or Technicians Certificate. Schedule Unit Title Year 1 Taken in another faculty or equiv Year 2 Compulsory units Teaching and Learning 1 Communication Managing Learning Communication Strategies Foundations of Adult Learning campus-sem weight code Lf~Hf L1/2~H1/2 L1~H1 L1~H1 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% ESV204 ESV201 ESV202 ESV205 L2~H2 12.5% ESV203 Course details (2001) Curriculum Development L2~H2 Assessment and Evaluation L2~H2 Issues and Contexts in AVE L2~H2 Conversion (A&WPT) L1/2~H1/2 Year 3 Compulsory units Teaching and Learning 2 Lf~Hf Research and Methods in AVE L1~H1 On-line Learning and Teaching in AVE Lw2~Hw2 Managing AVE Lf~Hf Research Practice in AVE L2~H2 Elective units Choose two of ESV305, 307, 309, 311 Workplace Learning and Training 1 L1~H1 Community and Public Education 1 L1~H1 Instructional Design in AVE 1 L1~H1 Language, Literacy and Numeracy in AVE 1 L1~H1 Choose one of ESV306, 308, 310, 312 Workplace Learning and Training 2 L2~H2 Community and Public Education 2 L2~H2 Instructional Design in AVE 2 L2~H2 Language, Literacy and Numeracy in AVE 2 L2~H2 page 200 12.5% 12.5% ESV206 ESV207 12.5% 12.5% ESV208 ESV209 12.5% ESV301 12.5% ESV302 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% ESV313 ESV314 ESV315 12.5% ESV305 12.5% ESV307 12.5% ESV309 12.5% ESV311 12.5% ESV306 12.5% ESV308 12.5% ESV310 12.5% ESV312 Bachelor of Adult and Vocational Education with Honours (Abbreviation: BAdVocEd(Hons)) Course code: E4G The honours program is an additional year of the Bachelor of Adult and Vocational Education course for selected students offered by the Faculty of Education at Launceston. Course details (2001) page 201 Admission & prerequisites Candidates for the degree of Bachelor of Adult and Vocational Education with Honours shall be qualified for entry if they have been admitted to the degree of Adult and Vocational Education, or equivalent award, with a Grade Point Average (GPA) of at least 3.25 in the final two years of the course. The GPA may be altered at the academic dean's discretion. Candidates for the degree shall complete the requirements in no less than one year of full-time study (or its equivalent) and not more than two years, from the time of first enrolment. Course objectives The course provides students with the opportunity to engage in adult and vocational education research at an appropriate level as preparation for future higher degree study. Course structure The candidate shall successfully complete all units prescribed for the Bachelor of Adult and Vocational Education (or its equivalent), as outlined in the schedule accompanying the specifications for the Bachelor of Adult and Vocational Education. In addition, the candidate shall complete all of the units shown in Schedule A. Candidates are required to present a dissertation in the prescribed form. Articulation Students from other universities with prerequisites acceptable to the Faculty may be accepted as candidates for the Bachelor of Adult and Vocational Education (Honours) degree. This course is designed to articulate with existing research higher degrees. Schedule Full-time Study (completed in one year) Unit Title About Research in AVE Doing Research in AVE Dissertation campus-sem L1/2 L1/2 L2 weight 25% 25% 50% code ESV401 ESV402 ESV403 weight code Part-time Study (completed in two years) Unit Title campus-sem Course details (2001) page 202 Year 1 About Research in AVE Doing Research in AVE Year 2 Dissertation (Part A) Dissertation (Part B) L1/2 L1/2 25% 25% ESV401 ESV402 L1/2 L1/2 25% 25% ESV404 ESV405 Bachelor of Education (Abbreviation: BEd) Course code: E3A This on-campus 4-year (minimum) full-time, or equivalent part-time, course is offered by the Faculty of Education at the Launceston campus, with year 1 being available at the North-West Centre. Admission & prerequisites Normal University entry requirements apply. Course objectives The Bachelor of Education prepares students for teaching appointments in early childhood (kindergarten, prep, grade 1 and 2), and primary (grades 3-6) situations. Secondary teaching specialisations are offered in the Bachelor of Teaching. Career outcomes Successful completion of this course should make students eligible for employment as early childhood/primary teachers. Employment opportunities in other communication-based careers such as industry and commercial training and sales have been obtained by past graduates. Course structure Within the two specialisations in the Bachelor of Education students undertake a course of study that includes the following elements: • • • • Liberal Studies within which there is a program of study for two years. Education Studies School Experience Curriculum Studies Course details (2001) page 203 A student who completes the first three years of the course with sufficient merit may apply and be admitted to continue into the fourth year as an honours candidate. Such a student will complete many of the normal coursework requirements of the degree in year four together with an honours dissertation. Articulation Students who have undertaken an appropriate course at another Australian, overseas institution or TAFE college may receive credit for such study. Applications for credit can be made following admission to the Bachelor of Education course. Schedule Unit Title campus-sem Year 1 Liberal studies unit(s) 1 Curriculum Studies 1 Lf~Bf Education 1 Lf~Bf 25% Liberal studies unit(s) 2 School Experience 1 (ECE/Primary) Lf~Bf Year 2 Liberal studies unit 1 Curriculum Studies 2A (English, Mathematics, LOTE) Lf Curriculum Studies 2B – Science & Technology Lf Curriculum Studies 2C – SOSE, Physical & Health Education Lf Curriculum Studies 2D – Arts Education Lf Education 2 Lf 12.5% School Experience 2 (ECE/Primary) Lf Liberal studies unit 2 Year 3 Education 3 Lf 25% School Experience 3 (ECE/Primary) Lf Curriculum Studies 3A (English, Mathematics) L2 Contemporary Curriculum Developments A L1 weight 25% 12.5% EPF150 25% 12.5% code EPC150 EPT150 12.5% 12.5% EPC250 12.5% EPC251 12.5% EPC252 12.5% EPF250 EPC253 12.5% 12.5% EPT250 EPF350 25% EPT350 12.5% EPC350 12.5% EPC351 Course details (2001) page 204 Curriculum Investigations A Modes of Curriculum Inquiry A Year 4 Education 4 Lf Education 5 Lf Curriculum Studies 4A (English, Mathematics) Contemporary Curriculum Development B Curriculum Investigations B Modes of Curriculum Inquiry B School Experience 4 (Early Childhood/Primary) L2/3 12.5% EPC352 L2 12.5% EPC353 12.5% 12.5% EPF450 EPF451 L1 12.5% EPC450 L1 12.5% EPC451 L1&3 12.5% EPC452 L2 12.5% EPC453 Lf 25% EPT450 Bachelor of Education Liberal Studies units Unit Title Applied Food Science (Primary) Consumer Textiles (Primary) Design and Technology 3 (Primary) Design & Technology 1 (Primary) Design & Technology 1 (Primary) Design & Technology 2 (Primary) Design & Technology 4 (Primary) Technology 3 (Primary) Technology 6 (Primary) campus-sem weight code L2 12.5% EST130 L1 12.5% EST230 Lf 25% EST226 L1 12.5% EST117 [na] 12.5% EST118 [na] 12.5% EST128 [na] [na] [na] 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% EST121 EST210 EST410 Bachelor of Education with Honours (Abbreviation: BEd(Hons)) Course code: E4A Course details (2001) page 205 This is an alternative final year of the Bachelor of Education course; one which is offered to some students by the Faculty of Education at Launceston. Admission & prerequisites Students in year three of the Bachelor of Education course are able to express their interest in undertaking the final year as an honours student. Such students who have attained a Grade Point Average (GPA) of at least 3.25 on their complete year 3 results as well as having demonstrated high proficiency in teaching practice may then be invited to join the honours program. In addition, students should have gained a Credit or better in the research method module in either EPC351 Contemporary Curriculum Developments A or EPC353 Modes of Curriculum Inquiry A in semester 2 of year 3. It should be noted that the minimum GPA may be raised at the Head of School's discretion. Invitations are made by the heads of the Education schools for students in any specialisation of the Bachelor of Education. Course objectives The Bachelor of Education (Honours) prepares students for teaching in either the early childhood or primary specialisation. The course provides students with the opportunity to engage in educational research at an appropriate level as preparation for future higher degree study. Career outcomes Successful completion of this course should make students eligible for employment as early childhood/primary teachers. Employment opportunities in other communication-based careers such as industry and commercial training and sales have been obtained by past graduates. A first class or second class upper division award within this course provides a pathway into doctoral level study. Course structure The honours year includes most facets of the Bachelor of Education, but makes provision for students to undertake an honours seminar and dissertation. Articulation Students from other universities with prerequisites acceptable to the Faculty may be accepted as candidates for the Bachelor of Education (Honours) degree. Schedule Unit Title Honours Dissertation campus-sem Lf weight 25% code EPF400 Course details (2001) page 206 Education 4 Lf 12.5% EPF450 Curriculum Studies 4A (English, Mathematics) L1 12.5% EPC450 Education 5 Lf 12.5% EPF451 School Experience 4 (Early Childhood/Primary) Lf 25% EPT450 and one of the following [a] Contemporary Curriculum Development B L1 12.5% EPC451 Curriculum Investigations B L1&3 12.5% EPC452 Modes of Curriculum Inquiry B L2 12.5% EPC453 [a] Students will be advised on the most suitable unit to select when they enrol Note: Honours students will have already completed a special 12.5% Honours research methods module/unit in semester 2 of year 3. Bachelor of Education (In-Service) (Abbreviation: BEd(In-Service)) Course code: E3B This course is offered by the Faculty of Education in Launceston and Hobart by flexible delivery (which may include distance education, summer school, winter school, video conferencing, use of email, or part time on-campus days or weekends or evening lectures. Admission & prerequisites Normal University admission requirements apply. Applicants must submit details of their qualifications and work experience so that an assessment can be made of their standing in the program. Course objectives The Bachelor of Education (In-Service) program is designed to help mature-age students pursue studies leading to the award of the Bachelor of Education or to provide for further professional development for teachers. The course is designed for working persons who wish to upgrade their qualifications to a four-year Bachelor of Education while continuing in their employment. Career outcomes Course details (2001) page 207 The course is a general four-year teaching qualification enabling graduates to work as teachers. Course structure Completion of the degree requirements varies, depending on the number of units required by the individual student. This is determined on entry into the course, based on professional qualification and academic history. Candidates for the degree shall complete requirements in not more than eight years from the time of first enrolment. In accordance with the determined number of units in each student's personal program, (see 'Articulation') students will select units from the schedule of subjects for this award. The units offered through the In-Service program are listed in the following schedule. Whether or not units are offered in 2001 depends on sufficient enrolments and staff availability. Requirements for upgrading Those wishing to upgrade qualifications will be expected to undertake a balanced program with the requirements shown below. Requirements for upgrading to 4 year BEd status depending on allowance for previous study/experience 1 year status 2 years status 3 years status Introductory Educational Studies (4 units) 2 core educational units 2 core educational units 6 electives 6 electives 2 electives 2 core educational units <tbz> Those already in the program will be expected to complete the remainder of their units according to the above scheme, in a pro-rata fashion, with advice from the Assistant Head of the program. Bachelor of Education (In-Service) Schedule of Units For detailed study information, course advice or application and admission forms, phone (03) 6324 3045, or contact Dr Heather Smigiel, Assistant Head for the BEd(In-Service), on (03) 6324 3261 or (03) 6324 3045. To complete the Introductory Education Studies in Launceston, students enrol in course code E3B. The units to be offered in the 2001 are listed below: Course details (2001) page 208 Introductory Education Studies Purpose The four Introductory Educational Studies units are designed to provide an introduction to the fundamental principles of education. In addition, the studies act as an entry vehicle to In-Service BEd studies. This program is designed for: • those who wish to undertake the BEd (In Service) but do not have the educational study prerequisites other than teaching experience; • those with technical/academic qualifications (equating to one year of training) who wish to undertake the BEd (In Service). It should be noted that the Introductory Educational Studies are corequisites for students with one year status rather than prerequisites. Unit titles and summaries ESI471 Introductory Educational Studies 1 Deals with the planning and presentation of teaching ESI472 Introductory Educational Studies 2 Deals with the psychological and sociological aspects of teaching and learning ESI473 Introductory Educational Studies 3 Deals with the philosophy of education ESI474 Introductory Educational Studies 4 The Practicum Students participate in an extensive period of supervised teaching <tbz> Students participate in an extensive period of supervised teaching. Each of these units is of equal weighting and, together, they constitute the equivalent of a year of tertiary study. Articulation Passes in units in other courses (completed or otherwise) in this University or another approved tertiary examining body may be credited towards this degree, provided the Faculty may specify what more a candidate so credited shall be required to do to qualify for the degree. Students cannot normally transfer from one incomplete undergraduate teacher education program in Tasmania to another, until they have ceased enrolment in the original program for one year. Course details (2001) page 209 Credit is granted for qualifications more than 10 years old, only if the applicant can demonstrate current competency in that study. Schedule Unit Title campus-sem weight code 1. Core Units Studies in Teaching L3 25% ESI439 School and Classroom Based Curriculum Development H3f~L3f~D3f 25% ESI475 2. Electives 2001 may be chosen from the following list Bases of Educational Decision L3~D3 25% ESI407 Education Study Lf~Df 25% ESI408 Mathematics and Education Lf~Df 25% ESI414 Music and Education L3 25% ESI420 Introduction to Special Education H3 25% ESI428 Education Study (Part 1) L1/2~D1/2 25% ESI433 Education Study (Part 2) L1/2~D1/2 25% ESI434 Studies in Teaching L3 25% ESI439 Drama in Education Lf~Df 25% ESI453 Studies in Classroom Management L3 25% ESI455 Research Investigation (In-Service) Lf 25% ESI457 Literature for Children Lf 25% ESI467 School and Classroom Based Curriculum Development H3f~L3f~D3f 25% ESI475 Special Study: Summer School L3 25% ESI478 Comparative Curriculum Issues C3 25% ESI491 3. Foundation units Introductory Educational Studies 1 [a] Lf~Df 25% ESI471 Introductory Educational Studies 2 [a] Lf~Df 25% ESI472 Introductory Educational Studies 3 [a] Lf~Df 25% ESI473 Introductory Educational Studies 4 [a] Lf~Df 25% ESI474 [a] These full-year units may be studied as Part 1 and Part 2 as follows: Introductory Educational Studies 1 (Part 1) L1~D1 12.5% ESI421 Introductory Educational Studies 1 (Part 2) L2~D2 12.5% ESI447 Course details (2001) Introductory Educational Studies 2 (Part 1) L~D 12.5% Introductory Educational Studies 2 (Part 2) L~D 12.5% Introductory Educational Studies 3 (Part 1) Lf~Df 12.5% Introductory Educational Studies 3 (Part 2) Lf~Df 12.5% Introductory Educational Studies 4 (Part 1) L1/2~D1/2 12.5% Introductory Educational Studies 4 (Part 2) L1/2~D1/2 12.5% 4. Honours units (Course code: E4C) See Bachelor of Education (In-Service) with Honours course details page 210 ESI422 ESI448 ESI423 ESI449 ESI424 ESI450 Bachelor of Education with Honours (In-Service program) (Abbreviation: BEd(Hons)) Course code: E4C BEd(Hons) program will normally be completed in one full year or two years part time. Admission & prerequisites This course is for teachers who have at least three years teaching experience and who have completed at least a three-year education qualification. The Students will need to attain a credit or better in the unit Educational Research Methods before being allowed to continue in the Honours program. Course objectives For those students who wish to pursue a higher degree by research this honours program provides a sound basis for future study. Those students gaining a first class honours degree or an upper second award are able to proceed into a doctoral program. Students with a lower second class award or third class honours have access into master degree research programs. Career outcomes Course details (2001) page 211 For those students wishing to pursue a higher degree by research, the Honours program will provide a sound basis for future study. Those students gaining a first class honours degree or an upper second award are able to proceed to a doctoral program. Students with a lower second class award or third class honours will have access to the master degree by research program. Course structure The course structure is summarised in the following schedule of units. Schedule Unit Title campus-sem weight code Educational Research Methods [a] [na] 25% ESI464 Contemporary Issues in Education [na] 25% ESI465 Honours Dissertation [na] 50% ESI466 [a] All students are expected to complete this unit during Summer School or over the summer period as a prerequisite to the rest of their honours program. Students may be able to claim recognition of prior learning for past professional development in Contemporary Issues in Education. Bachelor of Human Movement (Abbreviation: BHM) Course code: E3J This on-campus 4-year (minimum) full-time course is offered through the Faculty of Education's Centre for Human Movement at the Launceston campus. Admission & prerequisites Minimum University entry requirements apply. Applicants are advised to study TCE subjects relevant to the Human Movement program: English, Sport Science, Physical Science, Biology would be of advantage. Course objectives The Bachelor of Human Movement is designed to produce well educated and adaptable graduates with appropriate professional skills and knowledge Course details (2001) page 212 necessary to equip them for employment in a variety of human movement fields. Course structure Students must complete a core program in the first two years of full-time study, prior to choosing their area of specialisation in years 3 and 4. The course includes three strands of specialisation: Exercise and Sport Science, Sports Management, and Health and Physical Education Teaching. The program of units for the course is set out in the schedule which follows. Schedule A Unit Title campus-sem weight Year 1 Interdisciplinary strand Introduction to Human Biology L1 12.5% Anatomy and Physiology 1 L2 12.5% Chemistry for Life Sciences L1 12.5% Kinesiology L2 12.5% Foundation strand Computing for Human Movement L1 12.5% Research Concepts L2 12.5% Human Movement strand Movement Concepts L1 12.5% Human Movement Laboratory 1 L2 12.5% Year 2 Interdisciplinary strand Anatomy and Physiology 2 L1 12.5% Applied Physiology and Nutrition L2 12.5% Psycho-Social Aspects of Physical Activity L1 12.5% Motor Learning and Skill Development 1 L2 12.5% Foundation strand Health Fitness & Physical Activity L1 12.5% Introduction to Management H1/2~L1/2~B1 12.5% or (for intending Exercise & Sport Science students only): Introduction to Biochemistry L2 12.5% code CRA161 CRA172 KJC161 ESP132 KXA111 ESP141 ESP140 ESP136 CRA273 ESP237 ESP220 ESP233 ESP230 BMA101 KJC162 Course details (2001) page 213 Human Movement strand Coaching Theory & Practice L1 12.5% ESP210 Professional Experience 1 L2 12.5% ESP214 or (for intending Exercise & Sport Science students only): Sport Injuries L2 12.5% ESP304 Year 3 Health & Physical Education Major Human Movement Pedagogy 1 L1 12.5% ESP310 Adapted Physical Activity L1 12.5% ESP307 Event and Operations Management L1 12.5% ESP315 Human Movement Laboratory 2 L1 12.5% ESP335 Human Movement Pedagogy 2 L2 12.5% ESP311 Sport Injuries L2 12.5% ESP304 Human Movement Laboratory 3 L2 12.5% ESP336 Professional Experience 2 L2 12.5% ESP314 Sport Management Major Event and Operations Management L1 12.5% ESP315 and 1 of the following: Adapted Physical Activity L1 12.5% ESP307 Biomechanics L1 12.5% ESP301 Health and Fitness Issues L1 12.5% ESP411 or another unit as arranged and approved Exercise & Sport Governance [na] 12.5% ESP325 and 1 of the following: Sport Injuries L2 12.5% ESP304 Sport Psychology L2 12.5% ESP320 Exercise Assessment and Prescription L2 12.5% ESP308 or another unit as arranged and approved either Human Resource Management units or Marketing units or a combination as approved HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT UNITS Organisational Behaviour H1~L1 12.5% BMA201 [a] Principles of Marketing H3/2~L3/2 12.5% BMA151/251 Management of Human Resources [a] H3/2~L3/2 12.5% BMA121/221 and 1 of the following: Strategic Management H2~L2 12.5% BMA302 Employee Relations H2~L2 12.5% BMA321 Unit to be advised Financial Management [a] H2~L2 12.5% BFA181/281 Course details (2001) MARKETING UNITS Principles of Marketing [a] H3/2~L3/2 Marketing Research H2 and 1 of the following: Marketing Communications H1 International Marketing H2 Financial Management [a] H2~L2 or other units as negotiated. Exercise and Sport Science Major Biomechanics L1 Exercise Physiology L1 Immunology L1 Chemistry 1 Lf~Bf Exercise Assessment and Prescription L2 Sport Psychology L2 Microbiology and Health L2 Year 4 Health & Physical Education Major Human Movement Pedagogy 3 L1 Special Topics in Human Movement 1 L1 Professional Experience 3 L1 AND 1 of the following: Biomechanics L1 Exercise Physiology L1 Event & Sport Marketing [na] Health and Fitness Issues L1 or another unit as arranged and approved Human Movement Pedagogy 4 L2 Special Topics in Human Movement 2 L2 Professional Experience 4 L2 AND 1 of the following: Exercise & Sport Governance [na] Sport Psychology L2 Exercise Assessment and Prescription L2 Issues in Sport & Recreation Management L2 or another unit as arranged and approved Sport Management Major Event & Sport Marketing [na] page 214 12.5% 12.5% BMA151/251 BMA253 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BMA255 BMA282 BFA181/281 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 25% ESP301 ESP337 CRA321 KJC103 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% ESP308 ESP320 CRA276 12.5% ESP410 12.5% 12.5% ESP402 ESP414 12.5% 12.5% ESP301 ESP337 12.5% 12.5% ESP435 ESP411 12.5% ESP420 12.5% 12.5% ESP403 ESP415 12.5% 12.5% ESP325 ESP320 12.5% ESP308 12.5% ESP445 12.5% ESP435 Course details (2001) page 215 Special Topics in Human Movement 1 L1 12.5% ESP402 Issues in Sport & Recreation Management L2 12.5% ESP445 Special Topics in Human Movement 2 L2 12.5% ESP403 Professional Experience 4 L2 12.5% ESP415 and 1 of the following: Motor Learning & Skill Development 2 [na] 12.5% ESP433 Sport Psychology L2 12.5% ESP320 Exercise Assessment and Prescription L2 12.5% ESP308 or another unit as arranged and approved either Human Resource Management units or Marketing units or a combination as approved HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT UNITS 2 of the following: Human Resource Development [b] H2~L2 12.5% BMA224 International Human Resource Management H1~L1 12.5% BMA381 Contract of Employment H1~L1 12.5% BMA241 a 12.5% (School of Management) Human Resources unit: students should contact their course coordinator for details. MARKETING UNITS Services Marketing H1 12.5% BMA353 and 1 of the following: Marketing Management H1 12.5% BMA351 or other units as negotiated Exercise and Sport Science Major Advanced Physiology and Nutrition [na] 12.5% ESP437 Special Topics in Human Movement 1 L1 12.5% ESP402 Biomedical Science 1 (Nutrition & Neurobiology) L1 12.5% CRA385 Biochemistry 1 Lf 25% KJC263 Motor Learning & Skill Development 2 [na] 12.5% ESP433 Special Topics in Human Movement 2 L2 12.5% ESP403 AND 1 of the following: Biomedical Science 2 (Pharmacology & Pathophysiology) L2 12.5% CRA386 Course details (2001) Human Molecular Biology L2 12.5% [a] students should use the level 200 enrolment code (eg BMA251) [b] students should use the level 300 enrolment code (eg BMA324) page 216 CRA200 Note: elective units in years 3 and 4 will be offered subject to student enrolment numbers. Bachelor of Human Movement with Honours (Abbreviation: BHM(Hons)) Course code: E4J The honours program is an alternative final year of the Bachelor of Human Movement course for selected students offered by the Faculty of Education at Launceston. Admission & prerequisites Students in year three of the Bachelor of Human Movement course are able to express their interest in undertaking the final year as an honours student. Such students would have successfully completed all units in years 1 and 2 and have attained a Grade Point Average (GPA) of at least 3.25 in their year 3 results. It should be noted that the GPA may be altered at the Dean's discretion on advice from the Head of School. Invitations are made by the Head of School of Secondary and Post Compulsory Education to students in any specialisation of the Bachelor of Human Movement. Course objectives The Bachelor of Human Movement (Honours) provides students with the opportunity to develop the knowledge, skills and attitudes necessary to conduct research in the diverse fields of human movement knowledge. This course will also prepare students for future higher degree study. Course structure The honours year includes most facets of the Bachelor of Human Movement course but makes provision for students to undertake the Research Seminar and the Honours Seminar and Dissertation. Schedule A outlines the BHM year 4 program for each of the approved specialisations while Schedule B outlines the BHM (Hons) program for these specialisations. Course details (2001) page 217 Students from other universities with prerequisites acceptable to the Faculty may be accepted as candidates for the Bachelor of Human Movement (Honours) degree. Schedule B Unit Title campus-sem weight code Human Movement Pedagogy 3 L1 12.5% ESP410 Professional Experience 3 L1 12.5% ESP414 Research Seminar L1 12.5% ESP460 AND 1 of the following: Biomechanics L1 12.5% ESP301 Exercise Physiology L1 12.5% ESP337 Event & Sport Marketing [na] 12.5% ESP435 Health and Fitness Issues L1 12.5% ESP411 or another unit as arranged and approved Human Movement Pedagogy 4 L2 12.5% ESP420 Professional Experience 4 L2 12.5% ESP415 Honours Seminar and Dissertation L2 25% ESP465 Specialisation: Sport Management Event & Sport Marketing [na] 12.5% ESP435 Research Seminar L1 12.5% ESP460 Issues in Sport & Recreation Management L2 12.5% ESP445 Professional Experience 4 L2 12.5% ESP415 Honours Seminar and Dissertation L2 25% ESP465 either Human Resource Management units or Marketing units, or a combination as approved Human Resource Management units 2 of the following: Human Resource Development H2~L2 12.5% BMA224 International Human Resource Management H1~L1 12.5% BMA381 Contract of Employment H1~L1 12.5% BMA241 a 12.5% (School of Management) Human Resources unit: students should contact their course coordinator for details. Marketing units Services Marketing H1 12.5% BMA353 and 1 of the following: Marketing Management H1 12.5% BMA351 Specialisation: Exercise and Sport Science Course details (2001) page 218 Advanced Physiology and Nutrition Research Seminar Biomedical Science 1 (Nutrition & Neurobiology) Biochemistry 1 Motor Learning & Skill Development 2 Honours Seminar and Dissertation [na] L1 12.5% 12.5% ESP437 ESP460 L1 Lf 12.5% 25% CRA385 KJC263 [na] 12.5% ESP433 L2 25% ESP465 Bachelor of Teaching – Preliminary Studies Note: this is a non-award course. In special cases, the Faculty may accept a candidate for the Bachelor of Teaching course who does not satisfy normal admission requirements but has qualifications and relevant experience which it deems to be a suitable preparation for admission to the course. In so doing, the Faculty will require the candidate to undergo appropriate preliminary studies. Preliminary studies is a one year full-time (part-time equivalent), non-award bridging program consisting of 8 degree-level units each weighted at 12.5% or equivalent. The units are tailored to the needs of individual candidates and will require approval of the BTeach Admissions Committee. Preliminary Studies is normally required only for those candidates wishing to undertake the technology strand of the degree. The units suitable for such studies may come from existing degree-level units within the Faculty of Education or from other faculties and will allow for development of content knowledge in some depth (provided any prerequisites can be satisfied) as well as breadth. Furthermore the qualifying course may be structured in such a way as to enable students to gain considerable credit toward another degree at a later date and/or to build expertise in a second or third teaching area. Thus a student with an existing broad content background who wishes to undertake the technology specialisation may be advised or required to undertake appropriate units, for example: Course objectives Schedule (Preliminary Studies ) Course details (2001) page 219 Unit Title Applied Food Science Design and Technology 3 Design & Technology 2 Human Nutrition 1 Technology 3 Technology 4 Technology 5 Technology 6 Technology 7 Technology 8 Textiles Computing for Human Movement Introduction to Electronics campus-sem L2 Lf weight 12.5% 25% code EST113 EST216 L2 L1 L1 L2 Lf L2 [na] [na] L1 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 25% 12.5% 15% 15% 12.5% EST127 EST214 EST213 EST221 EST220 EST312 EST411 EST412 EST203 L1 12.5% KXA111 L1~B1 12.5% KJP131 Bachelor of Teaching (Abbreviation: BTeach) Course code: E3H The Bachelor of Teaching is a 2-year postgraduate pre-service course taken after the completion of a first degree. The course is intended to provide teaching practice and skills to enable the beginning teacher to cope with the early years of teaching and to lay a foundation for further professional development in both theory and practice of education. The Early Childhood and Primary stream is offered at the Launceston campus. The Primary and Middle School stream is offered at the Hobart campus. The Professional Studies units will be run in a flexible delivery mode. It is anticipated that the Secondary specialisations will be taught as follows: Hobart: Art, English, Information Science, LOTE, Mathematics, Science and Studies of Society and Environment (SOSE) Launceston Technology (MDT), Performing Arts (Drama and Music), and English. Course details (2001) page 220 Admission & prerequisites A first degree. Applicants who do not meet the normal admission requirements may be required to undertake the Preliminary Studies which are described on page xx. Course objectives The BTeach program prepares beginning teachers in all the appropriate major areas of professional competence which have been identified by relevant professional organisations. These include an understanding of, and ability to practice teaching as an active, interactive process involving the mutual construction of ideas, understandings, sensibilities and skills rather than the mere transmission of information; an understanding of the content, conceptual ordering and methods of inquiry of relevant subject areas; of how students learn and develop with individual differences; of the relationship between content knowledge and the process of teaching and the ability to plan and manage the teaching and learning process in an effective, inclusive and engaging manner; of alternative teaching practices in particular contexts with particular kinds of content; and of students, their development, the contexts that they live and learn in, including how teaching and learning outcomes are embedded in, and structured by, a variety of broad cultural and social processes. The program enables beginning teachers to communicate, interact and work with students of diverse abilities, interests and backgrounds and to engage them actively in the learning process in an inclusive and non-discriminatory manner. Beginning teachers acquire an understanding of, and ability to use, alternative assessment (monitoring, evaluating, reporting) procedures in different pedagogical contexts; a commitment to interrogate reflectively and evaluate their own particular conceptions of students, teaching, knowledge, the school curriculum, learning and education and to alter their professional practices if necessary after such reflection; a positive attitude to, and competency in the use of information technology in education. They are enabled to undertake research relevant to the improvement of professional practice and school effectiveness; and to gain a developed notion of the character and justification of a liberal democratic education and the normative expectations it imposes on teachers, schools, administrators, governments and the public generally. Career outcomes The course is designed for those who wish to become teachers. However, there is a range of other professional activities available to teacher graduates. Course structure Course details (2001) page 221 The course is structured as outlined in the following schedules A. Note: for details of the units and the campuses on which they will be offered, please contact the Faculty of Education office. Schedule A (Early Childhood and Primary) Unit Title campus-sem weight Year 1 Professional Studies 1 Hf~Lf 25% Curriculum and Method Studies Curriculum and Method Studies: Each Childhood and Primary Education (K–6) Lf 50% School Experience The Practice of Teaching & School Experience 1 – Observation Hf~Lf 12.5% School Experience 2 (ECE/Primary) L2 12.5% Year 2 Professional Studies 2 Hf~Lf25% (E4H 12.5%) Curriculum and Method Studies Curriculum and Method Studies: Early Childhood and Primary Education (K-6) Lf 50% School Experience School Experience 3: Primary Education H1~L1 12.5% School Experience 4: (Internship) (Primary) H2 12.5% Schedule A (Primary) Year 1 Professional Studies 1 Hf~Lf 25% ESA102 Curriculum and Method Studies Curriculum and Method Studies: Primary Education Hf 50% ESA146 School Experience The Practice of Teaching & School Experience 1 – Observation Hf~Lf 12.5% ESA103 School Experience 2 (Primary) H2 12.5% ESA148 Year 2 Professional Studies 2 Hf~Lf 25% (E4H 12.5%) Curriculum and Method Studies ESA202 code ESA102 ESA109 ESA103 ESA142 ESA202 ESA209 ESA253 ESA254 Course details (2001) page 222 Curriculum and Method Studies: Primary Education Hf 50% ESA252 School Experience School Experience 3: Primary Education H1~L1 12.5% ESA253 School Experience 4: (Internship) (Primary) H2 12.5% ESA254 Schedule A (Middle School) Year 1 Professional Studies 1 Hf~Lf 25% ESA102 Curriculum and Method Studies Curriculum and Method Studies: Middle School Hf 50% ESA145 School Experience The Practice of Teaching & School Experience 1 – Observation Hf~Lf 12.5% ESA103 School Experience 2 (Middle School) H2 12.5% ESA147 Year 2 Professional Studies 2 Hf~Lf 25% (E4H 12.5%) Curriculum and Method Studies Curriculum and Method Studies: Middle School Education Hf 50% ESA246 School Experience School Experience 3: Middle School Education H1 12.5% ESA247 School Experience 4: (Internship) (Middle) H2 12.5% ESA248 ESA202 Schedule A (Secondary) Unit Title campus-sem Year 1 Professional Studies 1 Hf~Lf Curriculum and Method Studies Single Method – (choose TWO of the following) Curriculum and Method Studies: English Literacy A Hf~Lf Curriculum and Method Studies: Information Technology A Hf Curriculum and Method Studies: Languages Other Than English (LOTE) A Hf weight code 25% ESA102 25% ESA110 25% ESA111 25% ESA112 Course details (2001) Curriculum and Method Studies: Mathematics A Hf 25% Curriculum and Method Studies: Science A Hf 25% Curriculum and Method Studies: Society and Environment (SOSE) A Hf 25% Curriculum and Method Studies: Performing Arts: Drama Lf 50% Curriculum and Method Studies: Performing Arts – Music A Lf 25% Curriculum and Method Studies: Performing Arts – Music – Performance Practice A Lf 25% Curriculum and Method Studies: Special Secondary A Hf~Lf 25% Curriculum and Method Studies: Technology Education A Lf 25% Double Method – (choose ONE of the following) Curriculum and Method Studies: Art A Hf 50% Curriculum and Method Studies: Technology Education A Lf 50% School Experience The Practice of Teaching & School Experience 1 – Observation Hf~Lf 12.5% School Experience 2 (Secondary) H2~L2 12.5% Year 2 Professional Studies 2 Hf~Lf25% (E4H 12.5%) Curriculum and Method Studies Single Method – (continue with same disciplines as for Year 1) Curriculum and Method Studies: English Literacy B Hf~Lf 25% Curriculum and Method Studies: Information Technology B Hf 25% Curriculum and Method Studies: Languages Other Than English (LOTE) B Hf 25% Curriculum and Method Studies: Mathematics B Hf 25% Curriculum and Method Studies: Science B Hf 25% page 223 ESA113 ESA114 ESA115 ESA116 ESA117 ESA118 ESA120 ESA123 ESA121 ESA122 ESA103 ESA132 ESA202 ESA210 ESA211 ESA212 ESA213 ESA214 Course details (2001) Curriculum and Method Studies: Society and Environment (SOSE) B Hf Curriculum and Method Studies: Performing Arts: Drama B Lf Curriculum and Method Studies: Performing Arts – Music B Lf Curriculum and Method Studies: Performing Arts – Music – Performance Practice B Lf Curriculum and Method Studies: Special Secondary B Hf~Lf Curriculum and Method Studies: Technology Education B Lf Double Method – (choose ONE of the following) Curriculum and Method Studies: Art B Hf Curriculum and Method Studies: Technology Education B Lf School Experience School Experience 3: Secondary H1~L1 School Experience 4: (Internship) (Sec) H2~L2 page 224 25% ESA215 50% ESA216 25% ESA217 25% ESA218 25% ESA220 25% ESA223 50% ESA221 50% ESA222 12.5% ESA231 12.5% ESA232 Bachelor of Teaching with Honours (Abbreviation: BTeach(Hons)) Course code: E4H The honours program is an alternative final year of the Bachelor of Teaching course for selected students. Candidates for the degree of Bachelor of Teaching with honours shall be qualified for entry by attaining a Grade Point Average (GPA) of at least 4.0 on their course work year-one results (excluding School Experience) in the Bachelor of Teaching course as well as having demonstrated high proficiency in teaching practice. Candidates for the degree shall complete the requirements in no fewer than two years of full-time study (or its equivalent) and not more than six years, from the time of first enrolment. Course details (2001) page 225 Course objectives Career outcomes The course is designed for those who wish to become teachers. However, there is a range of other professional activities available to teacher graduates. An honours degree also leads to opportunities in research. Course structure The candidate shall successfully complete all units prescribed for the Bachelor of Teaching, as outlined in the schedule accompanying the specifications for the Bachelor of Teaching. In addition, the candidate shall complete all of the units shown in Schedule B. Candidates are required to present a dissertation in the prescribed form. Bachelor of Teaching with Honours (Early Childhood & Primary) Year 1 as for Bachelor of Teaching (Early Childhood & Primary). Students undertake the units listed in Schedule B which includes the Honours component in Year 2. Bachelor of Teaching with Honours (Middle) Year 1 as for Bachelor of Teaching (Middle). Students undertake the units listed in Schedule B which includes the Honours component in Year 2. Bachelor of Teaching with Honours (Secondary) Year 1 as for Bachelor of Teaching (Secondary). Students undertake the units listed in Schedule B which includes the honours component in Year 2. Schedule B Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Early Childhood & Primary as for Year 1 of BTeach (Early Childhood & Primary) Schedule A Secondary as for Year 1 of BTeach (Secondary) Schedule A Year 2 Early Childhood & Primary as for Year 2 of BTeach (Early Childhood & Primary) Schedule A, plus the Honours units as listed below Primary as for Year 2 of BTeach (Primary) Schedule A, plus the Honours units as listed below Course details (2001) page 226 Middle School as for Year 2 of BTeach (Middle School) Schedule A, plus the Honours units as listed below Secondary as for Year 2 of BTeach (Secondary) Schedule A, plus the Honours units as listed below Professional Studies 2 Hf~Lf25% (E4H 12.5%) Curriculum and Method 2 Hf~Lf 37.5% Either ESA235 or ESA245 or ESA251 or ESA258 School Experience 3 & 4: (Internship) (Sec) Hf~Lf 12.5% School Experience 3 & 4: (Internship) (ECE/Prim) Hf~Lf 12.5% School Experience 3 & 4: (Internship) (Middle) Hf 12.5% School Experience 3 & 4: (Internship) (Primary) Hf 12.5% Honours Seminar H1~L1 0% Honours Dissertation Hf~Lf 37.5% ESA202 ESA240 ESA235 ESA245 ESA251 ESA258 ESA280 ESA281 Graduate Certificate of Education (Abbreviation: GradCertEd) Course code: E5E Graduate Certificate of Education Master of Education Master of Education (Honours) The three courses are designed to allow students to build on their studies ultimately to reach the level of award they desire. All Graduate Certificate units are approved at a post graduate level and may be used toward gaining a Master of Education award. It is possible to earn a Graduate Certificate by successfully completing four of the units in the approved schedule of units offered from the general schedule or to select four required units in one of the specialisations listed after the schedule. Specialisations are available in Counselling and Development, Community Education, On-Line Learning, Inclusive Education, TESOL, LOTE, Classroom Management, Studies in Asia for Teachers and Mathematics Education. Course details (2001) page 227 There are various pathways available to complete the Master of Education award. Please refer to the chart below for details. Students complete the Master of Education award entirely by coursework. Course structure <gif>pgEd.GIF<fig> General structure and relationship of Postgraduate Coursework Awards in Education: Minimum Maximum (Consecutive years) Graduate Certificate of Education 4 x 12.5% units 6 months 18 months Master of Education 8x12.5% units 1 year 3 years Master of Education (Honours) 2x25% units 18 months 6 years <tbz> Articulation Full credit may be gained toward the Master of Education for work completed while enrolled in the Graduate Certificate. Full credit may be gained towards the Master of Education (Honours) for work completed in the Master of Education. Note: Entry is dependent on the average of a credit at the Master of Education level. Self Paced Flexible Delivery Candidates are advised that a number of postgraduate coursework units are being developed into self-paced flexible delivery formats (print based and website) and details are available from the Assistant Head of School: postgraduate coursework, ph (03) 6324 3312. There may be restrictions on the availability of some units. These are noted on the schedule of units. It should also be noted that special application must be made for entry into the Counselling and Development specialisation at all levels. Note: There will be no new intake into Counselling and Development in 2001 as the specialisation is under review in 2000. GradCertEd, GradDipEd, MEd schedule of units NOTE: For schedules of specialisations, see next Course details (2001) page 228 Unit Title campus-sem weight specialisation code Contemporary Educational Issues A Lp123~Hp123~Dp123 12.5% ESG700 Contemporary Educational Issues (B) L/1&/2&f~OsL3&~H/1&/2&//3&~D/1&/2&//3 12.5% ESG701 Research Methods A 12.5% ESG702 Research Methods B 12.5% ESG703 Dissertation Part A 12.5% ESG704 Dissertation Part B 12.5% ESG705 Dissertation L~H~D 25% ESG706 Teaching Studies A 12.5% ESG707 Teaching Studies B 12.5% ESG708 Understanding and Promoting Young Children's Social and Emotional Learning in K–2 A L3/1/2 12.5% ESG709 Understanding and Promoting Young Children's Social and Emotional Learning in K-2 B L3/1/2 12.5% ESG710 Statistics Education – Data Handling 12.5% ESG711 Statistics Education – Data Reduction and Chance D 12.5% ESG712 Statistics Education –Inference and Advanced Topics D 12.5% ESG713 Current Issues in Second Language Learning [k] L3/1/2~H3/1/2~D3/1/2 12.5% ESG714 Aspects of Linguistics L3/1/2~H3/1/2~D3/1/2 12.5% ESG715 Language, Culture and Society [k] L3/1/2~H3/1/2~D3/1/2 12.5% ESG716 Teaching English as a Second/Foreign Language [k] L3/1/2~H3/1/2~D3/1/2 12.5% ESG717 Curriculum and syllabus in TESOL L3/1/2~H3/1/2~D3/1/2 12.5% ESG718 Curriculum issues in TESOL L3/1/2~H3/1/2~D3/1/2 12.5% ESG719 Special Project in TESOL L3/1/2~H3/1/2~D3/1/2 12.5% ESG720 Language and Communication [k] L3/1/2~H3/1/2~D3/1/2 12.5% ESG721 Course details (2001) Language Learning for Specific Purposes L3/1/2~H3/1/2~D3/1/2 Numeracy and the Mathematics Curriculum A [na] Numeracy and the Mathematics Curriculum B [na] Diagnosis and Intervention in Mathematics A [f] Diagnosis and Intervention in Mathematics B [f] Issues in Mathematics Education A [f] Issues in Mathematics Education B [f] Thinking and Working Mathematically A [na] Thinking and Working Mathematically B [na] Comparative Curriculum A ESG731 Comparative Curriculum B ESG732 Professional In-Country Development: LOTE – Part A ESG733 Professional In-Country Development: LOTE – Part B ESG734 Language Other Than English A C3 12.5% Language Other Than English B C3 12.5% New Directions in Art Education 1 A [o] New Directions in Art Education 1 B [o] New Directions in Art Education 2 A [o] New Directions in Art Education 2 B [o] Reason, Truth and Knowledge A [g] [na] Reason, Truth and Knowledge B [g] [na] What Is a Person? A [g] What Is a Person? B [g] page 229 12.5% ESG722 12.5% ESG723 12.5% ESG724 L3/2 12.5% ESG725 L3/2 12.5% ESG726 L3/1/2 12.5% ESG727 L3/1/2 12.5% ESG728 12.5% ESG729 12.5% [l] ESG730 C3 12.5% [l] C3 12.5% [l] C3 12.5% [l] C3 12.5% L3 12.5% ESG737 L1 12.5% ESG738 [na] 12.5% ESG739 [na] 12.5% ESG740 12.5% ESG741 12.5% [na] [na] ESG742 12.5% 12.5% ESG735 ESG736 ESG743 ESG744 Course details (2001) Teaching Asia D3/1/2 Asia in the Curriculum [e] Education Project [e] ESG747 Education Project 1 Community Education & Learning A [n] Community Education & Learning B [n] Community Development A ESG751 Community Development B ESG752 The Pedagogy of On-Line Learning A [m] The Pedagogy of On-Line Learning B [m] Creating an On-Line Teaching Course A [m] L3/2 Creating an On-Line Teaching Course B [m] L3/2 Difference, disability and diversity A [h] Difference, disability and diversity B [h] Inclusive curriculum leadership A [h] Inclusive curriculum leadership B [h] Classroom management: theory and practice A [j] Classroom management: theory and practice B [j] Challenging behaviours and curriculum practices A [j] Challenging behaviours and curriculum practices B [j] Curriculum Issues in Arts Education 1 A [d] Curriculum Issues in Arts Education 1 B [d] Curriculum Issues in Arts Education 2 A [d] Curriculum Issues in Arts Education 2 B [d] Drama in Education 1 A [d] page 230 12.5% ESG745 D3/1/2 12.5% ESG746 H0/3/1/2~L0/3/1/2~D3/1/2 12.5% 25% ESG748 [na] 12.5% ESG749 L3/1 [n] 12.5% [na] ESG750 12.5% [n] [na] 12.5% L3/1 12.5% ESG753 L3/1 12.5% ESG754 12.5% ESG755 12.5% ESG756 H1~D1 12.5% ESG757 H1~D1 12.5% ESG758 H3~D3 12.5% ESG759 H3~D3 12.5% ESG760 H2~D2 12.5% ESG761 H2~D2 12.5% ESG762 H2~D2 12.5% ESG763 H~D 12.5% ESG764 L3/1/2 12.5% ESG765 L3/1/2 12.5% ESG766 L3/1/2 12.5% ESG767 L3/1/2 L3/1/2 12.5% 12.5% ESG768 ESG769 Course details (2001) Drama in Education 1 B [d] L3/1/2 12.5% Drama in Education 2 A [d] L3/1/2 12.5% Drama in Education 2 B [d] L3/1/2 12.5% Reflections in Music Education A [d] L3/1/2 12.5% ESG773 Reflections in Music Education B [d] L3/1/2 12.5% ESG774 Language and Literacy in Education A H2~D2 12.5% ESG775 Language and Literacy in Education B [na] 12.5% ESG776 Literature for Children [na] 12.5% ESG777 Language, Gender and Communication in Education [i] [na] ESG778 Literature, Gender and Education [i] [na] 12.5% ESG779 Education of Women and Girls [i] [na] 12.5% ESG780 Education and Womenís Careers [i] H2~D2 12.5% ESG781 Special Study 1 L3/1/2~H3/1/2~D3/1/2 25% Effective Implementation A [b] L3 12.5% ESG783 Effective Implementation B [b] L3 12.5% ESG784 Leadership and Supervision [b] L3 12.5% Educational Administration [b] L3 12.5% Tertiary Teaching A [c] L3/1/4 12.5% Tertiary Teaching B [c] L3/1/4 12.5% Adult Learning [c] L1/2 12.5% Special Topic: Translating Value into Practice [c] Professional In-Country Experience: SOSE C3 12.5% ESG791 Introduction to Counselling Skills [cd] /3/1/4 16.67% ESN721 Special Project in Counselling and Development [cd] 1 16.67% Family Counselling [cd] f 16.67% Adolescent Counselling [cd] 2 16.67% Approaches in Counselling Research and Assessment [me] H1~L1 16.67% page 231 ESG770 ESG771 ESG772 12.5% ESG782 ESG785 ESG786 ESG787 ESG788 ESG789 ESG790 ESN782 ESN783 ESN784 ESN770 Course details (2001) Supervised Practicum in Counselling [me] Professional Seminar in Counselling [me] page 232 /1/2 16.67% ESN793 2 16.67% ESN794 Graduate Certificate of Education Specialisations Code numbers (A) General Schedule No specific specialisation Choose any three non-restricted units in schedule. Unit Title (B) Educational Administration Effective Implementation A Effective Implementation B Leadership and Supervision Educational Administration campus-sem weight code L3 12.5% ESG783 L3 12.5% ESG784 L3 12.5% ESG785 L3 12.5% ESG786 Unit Title (C) Tertiary Teaching Tertiary Teaching A Tertiary Teaching B Adult Learning Special Topic: Translating Value into Practice campus-sem weight code L3/1/4 L3/1/4 L1/2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% ESG787 ESG788 ESG789 L1/2 12.5% ESG790 Unit Title (D) Arts Education Curriculum Issues in Arts Education 1 A Curriculum Issues in Arts Education 1 B and two of the following: Curriculum Issues in Arts Education 2 A Curriculum Issues in Arts Education 2 B Drama in Education 1 A campus-sem weight code L3/1/2 12.5% ESG765 L3/1/2 12.5% ESG766 L3/1/2 12.5% ESG767 L3/1/2 L3/1/2 12.5% 12.5% ESG768 ESG769 Course details (2001) Drama in Education 1 B Drama in Education 2 A page 233 L3/1/2 L3/1/2 12.5% 12.5% ESG770 ESG771 Unit Title campus-sem weight code (E) Studies in Asia for Teachers Asia in the Curriculum D3/1/2 12.5% ESG746 Teaching Asia D3/1/2 12.5% ESG745 For details of the other two units, please contact Dr Mary Fearnley-Sandcer (ph) 03 6226 2557. Unit Title (F) Mathematics Education Diagnosis and Intervention in Mathematics A Diagnosis and Intervention in Mathematics B Issues in Mathematics Education A Issues in Mathematics Education B campus-sem weight code L3/2 12.5% ESG725 L3/2 12.5% ESG726 L3/1/2 12.5% ESG727 L3/1/2 12.5% ESG728 Unit Title (G) Philosophy in Education Not offered in 2001 Reason, Truth and Knowledge A Reason, Truth and Knowledge B What Is a Person? A What Is a Person? B campus-sem weight code [na] 12.5% ESG741 [na] [na] [na] 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% ESG742 ESG743 ESG744 Unit Title (H) Inclusive Education Difference, disability and diversity A Difference, disability and diversity B Inclusive curriculum leadership A Inclusive curriculum leadership B campus-sem weight code H1~D1 12.5% ESG757 H1~D1 12.5% ESG758 H3~D3 12.5% ESG759 H3~D3 12.5% ESG760 Course details (2001) page 234 Unit Title campus-sem (I) Gender Issues Language, Gender and Communication in Education [na] Literature, Gender and Education [na] Education of Women and Girls [na] Education and Women's Careers H2~D2 weight code 12.5% ESG778 12.5% ESG779 12.5% ESG780 12.5% ESG781 Unit Title (J) Classroom Management Classroom management: theory and practice A Classroom management: theory and practice B Challenging behaviours and curriculum practices A Challenging behaviours and curriculum practices B campus-sem weight code H2~D2 12.5% ESG761 H2~D2 12.5% ESG762 H2~D2 12.5% ESG763 H~D 12.5% ESG764 Unit Title campus-sem weight (K) TESL/TEFL (Teaching English as a Second or Foreign Language) Current Issues in Second Language LearningL3/1/2~H3/1/2~D3/1/2 12.5% Language, Culture and Society L3/1/2~H3/1/2~D3/1/2 12.5% Teaching English as a Second/Foreign LanguageL3/1/2~H3/1/2~D3/1/212.5% Language and Communication L3/1/2~H3/1/2~D3/1/2 12.5% code ESG714 ESG716 ESG717 ESG721 Unit Title campus-sem (L) Cross-Cultural Educational Issues Comparative Curriculum A C3 Comparative Curriculum B C3 Professional In-Country Development: LOTE – Part A C3 Professional In-Country Development: LOTE – Part B C3 weight code 12.5% 12.5% ESG731 ESG732 12.5% ESG733 12.5% ESG734 Unit Title weight code campus-sem Course details (2001) page 235 (M) On-Line Learning The Pedagogy of On-Line Learning A The Pedagogy of On-Line Learning B Creating an On-Line Teaching Course A Creating an On-Line Teaching Course B L3/1 12.5% ESG753 L3/1 12.5% ESG754 L3/2 12.5% ESG755 L3/2 12.5% ESG756 Unit Title (N) Community Education Community Education & Learning A Community Education & Learning B Community Development A Community Development B campus-sem weight code [na] 12.5% ESG749 L3/1 [na] [na] 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% ESG750 ESG751 ESG752 Unit Title (O) Art Education New Directions in Art Education 1 A New Directions in Art Education 1 B New Directions in Art Education 2 A New Directions in Art Education 2 B campus-sem weight code L3 12.5% ESG737 L1 12.5% ESG738 [na] 12.5% ESG739 [na] 12.5% ESG740 Graduate Certificate and Master of Education The following tables should be used with reference to the Grad Cert Schedules Note: There will be no new intake in 2001 as the structure and content of this program is under review. Continuing students in this program will need to enrol in the appropriate ESN units listed below. Unit Title campus-sem <cd>Counselling and Development Introduction to Counselling Skills /3/1/4 Special Project in Counselling and Development 1 weight code 16.67% ESN721 16.67% ESN782 Course details (2001) page 236 Family Counselling Adolescent Counselling f 2 16.67% 16.67% ESN783 ESN784 Unit Title campus-sem <me>For the Master of Education Approaches in Counselling Research and Assessment H1~L1 Supervised Practicum in Counselling /1/2 Professional Seminar in Counselling 2 weight code 16.67% ESN770 16.67% ESN793 16.67% ESN794 Master of Education (Abbreviation: MEd) Course code: E7E The degree of Master of Education by coursework or by research is available from Launceston and Hobart campuses. The following information is for the Master of Education by coursework. Admission & prerequisites This degree course is available to graduates in Education or graduates in other disciplines with a Diploma of Education or Bachelor of Teaching, or to those holding equivalent qualifications. The University requires applicants for admission to the Master of Education degree to have four-year teacher training (ie either Bachelor of Education or an undergraduate degree plus Bachelor of Teaching) or qualifications deemed to be equivalent and at least two years experience in teaching or training. Course objectives The degree is intended to enable competent, experienced professionals to broaden, deepen, update and integrate knowledge of their specialised area of interest and expertise. Both the coursework and written assignments or projects undertaken by the student should thus reflect this specialisation. For this reason there is a wide variety of course work units available, with general areas of specialisation ranging from Administration to Curriculum Design, from Inclusive Education to Arts in Education, from Teaching English as a Second Language to Adult Learning and University Teaching, from On-line learning to LOTE. Course details (2001) page 237 Career outcomes The Master of Education has international standing and is seen as a prestigious qualification for educators who wish to become leaders in their chosen fields. Course structure The coursework units and/or research projects which will make up the course of study of an individual are determined by the candidate in consultation with the Assistant Head of School. The requirements to complete the Master of Education is met through all coursework. Master of Education requires completion of Research Methods. A number of units are available in a self-paced, flexible delivered mode. Completion of these 2 programs can lead to entry in PhD and EdD. Master of Education study amounts to two semesters of full time work. However, not all of this time needs to be spent in Tasmania. Arrangements can be flexible. The course is offered in the two normal semesters (late February to early June, and mid July to end October) and also in our Summer School (January). Many units do not require attendance and applicants are advised to contact the Assistant Head of School for specific details. The attendance requirements can also be completed by intensive study in Tasmania either from January to early June in one year, or from mid July one year to the end of January in the next. For interstate or overseas students the dissertation/project can be completed in the candidate's own state/country and consultation about it and assessment of it conducted at a distance. Education Summer Schools The Summer School has proven a most successful way for students to attend our master degree programs. It has attracted candidates from all over Australia, and overseas. The Summer School runs for two weeks normally in January and classes are held six days a week from early morning into the evening. The School is staffed by experts from the Faculty's staff and by visiting professors who are international leaders in their fields of expertise. Articulation Candidates who possess components of post graduate studies of comparable quality can present these for consideration by the Faculty for advanced standing. Course details (2001) page 238 International Students The Faculty encourages international student enrolment in both undergraduate and post graduate degree courses. Staff within the Faculty have gained considerable experience in teaching and supervising students from many international countries including Malaysia, China, Thailand and Indonesia. Master of Education (Honours) (Abbreviation: MEd(Hons)) Course code: E7D The Master of Education (Honours) (1.5 years minimum to 6 years maximum) is for students who have completed the Master of Education. The course requires a mimimum half a year of study in addition to the minimum of one year spent on the Master of Education. Admission & prerequisites Students will need to have attained a credit or better in the Master of Education before being allowed to apply for entry into the Honours Program. Course objectives For those students who wish to pursue a higher degree by research, this honours program provides a sound basis for future study. Those students gaining a first class honours degree or an upper second award are eligible to apply for entry into a doctoral program. Career outcomes For those students wishing to pursue a higher degree by research, the Honours program will provide a sound basis for future study. Those students gaining a first class honours degree or an upper level second award are eligible to apply for entry to a doctoral program. Course structure The course structure is summarised in the MEd(Hons) schedule of units. MEd(Hons) Schedule of Units Unit Title campus-sem weight code Course details (2001) Research Methods A Research Methods B Dissertation OR Dissertation Part A Dissertation Part B page 239 L~H~D 12.5% 12.5% 25% ESG702 ESG703 ESG706 L~H~D L~H~D 12.5% 12.5% ESG704 ESG705 Graduate Certificate of Human Movement Graduate Diploma of Human Movement Master of Human Movement The graduate program in Human Movement is planned to meet the needs of practising Health and Physical Education teachers, sport scientists, health and fitness professionals, coaches and community recreation specialists for advanced academic qualification. The program comprises four specialty areas: Health and Physical Education Teaching (Pedagogy), Outdoor Education, Exercise and Sport Science and Exercise and Wellness. The Graduate Certificate, Graduate Diploma of Human Movement and Master of Human Movement are structured into a progressive sequence allowing for a completion of each course before, if desired, enrolment into a subsequent level. All Graduate Certificate and Graduate Diploma units are approved at the postgraduate level and may be used towards the Master of Human Movement. It is possible to complete the first level of postgraduate qualification, a Graduate Certificate, by completing one unit from the core sequence and two units from one of the specialty areas as listed after the schedule. Students who wish to obtain a Graduate Diploma in Human Movement must successfully complete three units from the core sequence and three units from their specialty area. Course objectives The Master of Human Movement was constructed to allow students the choice of a variety of pathways. First option permits students to combine two Graduate Certificates with additional three units from any specialization area listed below. The second alternative provides opportunity for adding three units from any specialization to the Graduate Diploma. Thirdly, it is possible to successfully complete the Master of Human Movement by obtaining credit for nine units from prescribed coursework with four of these being core units. Course details (2001) page 240 There may be restrictions on the availability of some units. These are noted on the schedule of units. Course structure General structure and relationship of Postgraduate Coursework Awards in Human Movement Minimum Maximum (Consecutive years) Graduate Certificate of Human Movement 3x16.67% units (including one unit from the core) 0.5yrs 3 yrs Graduate Diploma of Human Movement 6x16.67% units (including 3 units from the core) 1 yr 4 yrs Master of Human Movement 2 Graduate Certificates plus 3 units or 1 Graduate Diploma plus 3 units or 9x16.67% coursework units 1.5yrs 6yrs <tbz> Graduate Certificate of Human Movement (Abbreviation: GradCertHM) Course code: E5J The Graduate Certificate of Human Movement is a one-semester full-time course offered primarily to Human Movement Graduates who hold a minimum 3-year qualification or equivalent status or other individuals working in related fields who hold equivalent status. Course objectives Course structure See Master of Human Movement for specialisations and schedule Graduate Diploma of Human Movement Course details (2001) page 241 (Abbreviation: GradDipHM) Course code: E6J The Graduate Diploma of Human Movement is 1-year full-time course offered primarily to Human Movement Graduates who hold a minimum 3-year qualification or equivalent status or other individuals working in related fields who hold equivalent status. Course objectives Course structure See Master of Human Movement for specialisations and schedule Master of Human Movement (Abbreviation: MHM) Course code: E7J The Master of Human Movement is a 1.5-year full-time course offered primarily to Human Movement Graduates who hold a minimum 3-year qualification or equivalent status or other individuals working in related fields who hold equivalent status. Course objectives Specialisations: Health and Physical Education Teaching Prepares individuals to provide leadership in instructional design and curriculum development in traditional Health and Physical Education settings and also in the Health Enhancement paradigm. Outdoor Education This specialisation focuses on knowledge and skills necessary for a harmonious interaction between the mankind and environment. It takes a full advantage of unique Tasmanian ecology and immense opportunities for lifetime sports and outdoor adventure. Course details (2001) page 242 Exercise and Sport Science This specialisation is structured to investigate, analyse and apply scientific knowledge, particularly in Exercise Physiology, Biomechanics, Nutrition and Sport Psychology, to apparently healthy population in order to increase athletic performance Exercise and Wellness The program is designed around the components of health-related fitness and their impact on human health. Emphasis is given to analysis and applications of behavioural modification strategies to confront the problem of sedentary lifestyles, smoking and obesity from the epidemiological and behavioural perspectives. GradCertHM, GradDipHM, MHM schedule of units Listed below is the schedule of postgraduate units. It is expected that units will be offered subject to sufficient enrolment numbers and available staff. Unit Title Research and Investigation in Human Movement Behavioural Health and Fitness Exercise Metabolism Human Movement Graduate Seminar Instructional Design in Health and Physical Education Health Enhancement Curriculum Learning Motor Skills Advanced Studies in Sport Performance Nutrition and Performance Exercise Adherence Health, Fitness and Lifestyle Risk Analysis and Management Environmental Interpretation Outdoor Pursuits – Land Based and Water Based Special Topics in Human Movement 1 campus-sem weight code L3 16.67% ESP700 [na] [na] 16.67% 16.67% ESP701 ESP702 L1/2 16.67% ESP703 L1/2 16.67% ESP704 L1/2 L1/2 16.67% 16.67% ESP705 ESP706 [na] [na] [na] 16.67% 16.67% 16.67% ESP707 ESP708 ESP709 [na] 16.67% ESP710 L3 16.67% ESP711 [na] 16.67% ESP712 L3 16.67% ESP713 L3/1/2 16.67% ESP714 Course details (2001) Special Topics in Human Movement 2 page 243 [na] 16.67% ESP715 Professional Doctorate in Education – Launceston (Abbreviation: EdD) Course code: E9Z The Professional Doctorate in Education will normally be three years full time or five years part time. The maximum periods of candidature will normally be four years full time or eight years part time. In appropriate circumstances, and following recommendations by the candidate's supervisor, the EdD Program Committee may consider an application for extension of the time by which the dissertation must be submitted. This extension will normally be no longer than one year. It will be possible for candidates to complete the coursework components as full-time candidates in four semesters, and then complete the EdD dissertation as part-time candidates. This will be particularly attractive to interstate and overseas students. Delivery modes will include an appropriate mix of weekend schools, block release periods, summer schools and winter schools to meet the 45 contact hour requirements per unit per semester. Admission & prerequisites Normally, applicants may be considered eligible for admission to the award if they have been admitted to an appropriate master degree by research or course work offered by the University of Tasmania, or a degree deemed to be equivalent. A coursework master or master with honours degree in education will be accepted as eligible for admission providing applicants have completed successfully at least one research methodology unit at master degree level and can demonstrate, through documented evidence and by interview, a commitment and potential capacity to meet the research requirements of the program. Course details (2001) page 244 Applicants who possess such other qualifications and professional experience deemed by the EdD Program Committee to provide a preparation for study equivalent to that indicated above may be accepted into the award. In addition, applicants normally will be required to possess at least two years of appropriate professional experience. Course objectives The EdD will serve the needs of professionals in the field of education who wish to undertake doctoral level study so as to improve the quality of their services as educators and leaders, and to expand their theoretical understanding of educational practice. The course will provide predominantly course based study at the doctoral level. The focus will be on the systematic review of educational research in relevant areas of professional practice and the improvement of professional practice in education. The course includes an original research component accounting for one-third of the program. This professional doctorate will be distinguished from other similar courses by: (a) (b) (c) (d) targeted assignments within generic areas to help candidates pursue their own interests; the extensive use of practical and problem based learning; a direct relationship with the leading research programs of the Education Faculty; and flexible delivery modes attractive to part-time, full-time and overseas students. Career outcomes The course is designed for mid-career educators who wish to prepare for a major leadership role in the field of education. Successful completion of the doctorate provides graduates with a substantial theoretical and practical background that should enhance promotional opportunities within the educational arena. Course structure The program will have two stages. Stage 1 will require satisfactory completion of eight approved units in Education of semester (or equivalent) length and a comprehensive examination. The units are: 1 2 3 The Political Economy of Education in International Perspective Learning and Development: Practices and Theories Intellectual Foundations of Education Course details (2001) 4 5 6 7 8 page 245 Research Methods Curriculum and Assessment Governance and Leadership Teaching and Assessment Educational Policy and Professional Practice The eight coursework units encompass the principal foundational and applied areas of professional practice in education. They are simultaneously the basis for understanding and appraising critically the present educational processes and practices and developing informed and effective reforms. Stage 2 will require a research project in an applied area of education, the defence of a research proposal, and the preparation of a dissertation consisting of approximately 40,000 words. The program structure is contained in Schedule A. Part-time study as well as full-time study are options. The detailed content of the units is provided in the appropriate section of this handbook. Candidates wishing to pursue specialised study in particular areas of the National Curriculum will have an opportunity to do so within the various units. The distribution of assignment totals yields a 67:33 ratio for coursework to research dissertation. Students may be permitted to take an elective unit which will substitute for one of the following units: Curriculum and Assessment, Teaching and Assessment, School Governance and Leadership, or Educational Policy and Professional Practice. Substitute units may be selected from master degree programs across the University, subject to the approval of the EdD Program Committee. Articulation On the grounds of demonstrated equivalence to a prescribed unit(s), and on the recommendation of a unit coordinator(s), an applicant may be granted exemption from a coursework unit(s), providing that: (a) (b) (c) the unit(s) has been completed successfully in an EdD Program at a recognised university elsewhere; the unit(s) has not been counted towards the award of any degree elsewhere; and that exemptions do not total more than one third of the requirements of the EdD. Administration and location of the course Course details (2001) page 246 The course will be administered and taught as a cross-campus program. The course will be administered by a subcommittee of the Faculty of Education – the EdD Program Committee, which will take responsibility for ensuring that appropriate resources and facilities such as library, class materials, research laboratories, computing etc. are available to candidates on a cross-campus basis. An academic supervisor will be appointed to each EdD candidate. Teaching and supervision Extensive but not sole use will be made of problem-based learning to teach the eight units. Problem-based learning has been a developing feature of teaching in the Faculty of Education for some time. Problem-based learning is an instructional strategy with two variants; problem-stimulated learning and student-centred learning. Whatever the combination of teaching methods, major and contemporary problems of practice and policy will be in the foreground, so that students (a) (b) (c) obtain research-based knowledge from foundational disciplines, select and employ a range of disciplinary perspectives, and then develop, present and defend appropriate plans and proposals. A feature of the program is a structured, careful supervision program for each candidate which will implement the University's Code of Conduct in Supervision and Code of Conduct in Research. (See Research Higher Degrees Handbook.) An academic supervisor will be appointed to each candidate at the beginning of the course. Assessment methods for the dissertation The dissertation will be examined by a minimum of two appropriately qualified examiners external to the University of Tasmania. At least one of the examiners will be an educationist of international repute. Examiners will be appointed by and report to the EdD Program Committee. Application procedures Applications should be forwarded on the appropriate application form attainable from: The EdD Coordinator, Faculty of Education, University of Tasmania, PO Box 1214, Launceston, Tas 7250, Australia. Schedule Unit Title campus-sem weight code Course details (2001) Year 1 Curriculum and Assessment Teaching and Assessment Educational Policy and Professional Practice The Intellectual Foundations of Education Year 2 Research Methodology The Political Economy of Education in International Perspective Learning and Development: Practices and Theories Governance and Leadership Year 3 Dissertation page 247 L1 L1 25% 25% ESF910 ESF901 L2 25% ESF902 L2 25% ESF911 L1 25% ESF905 L1 25% ESF912 L2 L2 25% 25% ESF904 ESF900 f 50% ESF903 Bachelor of Biomedical Science (Abbreviation: BBiomedSc) Course code: M3E This three and a half-year full-time course is offered in Launceston by the School of Biomedical Science. Admission & prerequisites Minimum University requirements, including *CH856 Chemistry and any one of the approved Mathematics subjects (*MT730 Mathematics Applied, *MT841 Mathematics Stage 2 or *MT843 Mathematics Stage 3) in the Tasmanian Certificate of Education or its equivalent. Course objectives The course is designed to give students a solid grounding in Science subjects followed by specialised units which provide the knowledge and skills suitable to the needs of the modern pathology laboratory. Students will be proficient in all major disciplines such as Clinical Chemistry, Haematology, Blood Transfusion, Medical Microbiology and Histopathology. Career outcomes Course details (2001) page 248 There are various career options open to medical scientists, especially in hospital clinical and pathology laboratories, private pathology services, blood transfusion services and public health laboratories. Other areas of employment are found in universities, veterinary laboratories and as representatives for diagnostic companies. Professional recognition Graduates from this course meet the academic requirements for direct entry into the Australian Institute of Medical Scientists. Course structure A fixed three and a half-year (7 semester) course described in the following Schedule. Articulation Credit for appropriate studies completed in TAFE and other university courses may be granted. Anyone interested in pursuing an honours course should contact the Head of School. Schedule Unit Title Year 1 Mathematics in Life Sciences 1 Chemistry 1 Cell Biology Medical Laboratory Practice Anatomy and Physiology 1 Histology Computer Applications Year 2 Histopathology General and Medical Microbiology Biochemistry 1 Anatomy and Physiology 2 Haematology 1 Clinical Chemistry 1 Human Molecular Biology Year 3 campus-sem weight code L2 Lf~Bf L1 12.5% 25% 12.5% KMA165 KJC103 CRA171 L1 L2 L2 H1~L1~B1 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% CRA101 CRA172 CRA121 KXA153 L1 12.5% CRA222 L1 Lf L1 L2 L2 L2 12.5% 25% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% CRA241 KJC263 CRA273 CRA231 CRA251 CRA200 Course details (2001) Immunology (MLS) Haematology 2 Clinical Chemistry 2 Medical Microbiology A Transfusion Science Clinical Chemistry 3 (Endocrinology) Medical Microbiology B Biomedical Science 2 (Pharmacology & Pathophysiology) Year 4 Professional Practice Medical Laboratory Practice 2 page 249 L1 L1 L1 L1 L2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% CRA311 CRA332 CRA352 CRA342 CRA333 L2 L2 12.5% 12.5% CRA353 CRA343 L2 12.5% CRA386 1 37.5% CRA410 L1 12.5% CRA401 Bachelor of Biomedical Science with Honours (Abbreviation: BBiomedSc(Hons)) Course code: M4E This on-campus course is offered at Launceston and requires a minimum of 1 year full-time study. Admission & prerequisites Applicants need to have qualified for admission to the degree of Bachelor of Biomedical Science or equivalent. Anyone interested in pursuing the honours course should contact the Head of School. Course objectives The honours degree in Biomedical Science is designed to provide students with the foundations necessary for research in Biomedical Science, to assume a leadership role in their profession and to gain a greater expertise in the discipline. Career outcomes See 'Career outcomes' in the Bachelor of Biomedical Science. Course details (2001) page 250 Professional recognition See 'Professional recognition' in the Bachelor of Biomedical Science. Course structure One year full-time work. Candidates will be required to submit a research thesis on work undertaken as part of the honours course. All candidates will be required to study analysis and presentation of scientific data. Completion of a unit in electron microscopy will be required for students studying in an area requiring such knowledge. Other requirements for the course include a literature review, directly related to the thesis, and a dissertation. Students will be required to present their research work at a seminar. Articulation Graduates from other higher education institutions may be accepted into this course. Assessment Research thesis and seminar (65%), essay and coursework units (35%). Bachelor of Health Science (Abbreviation: BHlthSc) Course code: M3H This 3-year, undergraduate course is offered at the Launceston Campus. It consists of units taught by the Faculty of Health Science in conjunction with the four other Faculties (Arts, Commerce and Law, Education, Science and Engineering). Candidates must complete the requirements of the degree in a minimum of 3, and a maximum of 8, separate years of full time study from the time of first enrolment. The course may also be undertaken on a part-time basis. Admission & prerequisites Applicants for the Bachelor of Health Science must meet normal University admission requirements. Course details (2001) page 251 While Year 12 Chemistry *CH856 and Mathematics *MT730 or *MT841 or *MT843 (or their equivalents) are not essential, they will be an advantage to those who elect to study units in the Bioscience stream. Applications for credit based on previous relevant university or TAFE study will be considered. Course objectives The Bachelor of Health Science is a foundation degree which prepares students for a range of career paths in the health sector, including administration, management, finance and research, as well as for entry to graduate programs in medicine and other health specialties. Career outcomes There are employment opportunities in government and non-government medical and general health services and in health research organisations. More specifically, they occur in areas such as administration, management, finance, health promotion, sales representation across a broad range of medical and health products (including diagnostic equipment and pharmaceuticals), project management, clinical research, community health groups, self-help groups, rehabilitation centres, welfare agencies, sports science and health and physical education. The course is also relevant to practising and potential health care professionals seeking a degree qualification. Professional recognition The Bachelor of Health Science is not limited to a single, professional discipline. It is a generic health science degree which qualifies its graduates to undertake further, more specialised, study in a number of disciplines (including alternative medicine and health care) and to pursue various career opportunities in the health sector. Course structure Year 1 units provide a foundation in the life sciences and an introduction to community health care and business management. In Year 2 students undertake three core units in conjunction with one or more elective units from one or more of four specialist streams – Bioscience, Education, Business/Commerce or Social Science/Psychology. In Year 3 students undertake two core units in conjunction with two or more elective units from one or more of the streams. Course details (2001) page 252 The Bioscience stream provides an understanding of the structure and function of the human body, in both health and disease, and of the effects of nutrition, micro-organisms and drugs. The Business/Commerce stream provides a background in fundamental business procedures and an opportunity to study foundation commerce units. The Education stream provides students with effective and interactive communication skills, an understanding of community education and development and an overview of the changing patterns of health and fitness in Australia. The Social Science/Psychology stream provides an understanding of health, and health-related, issues for children, adolescents and the aged and an opportunity to study a range of Psychology units. Articulation There is no articulation from other courses. However, some outstanding Year 1 Bachelor of Health Science students may be able to transfer into Year 2 of the Bachelor of Biomedical Science if places are available. These students must have completed Year 12 Chemistry *CH856 and Mathematics *MT730 or *MT841 or *MT843 and obtained results of a high standard in Year 1 of the Bachelor of Health Science. Schedule It should be noted that, at the time the Handbook was printed, Year 2 and Year 3 units were subject to change. Unit descriptions for CRA102 and CRH300 were not available. Students are advised to contact the University for further information. Unit Title Year 1 Semester 1 Either KJC161 or KJC103 Chemistry for Life Sciences Chemistry 1 [a] Computer Applications Cell Biology Health Care Where People Live and Work 1 Semester 2 Either KJC162 or KJC103 contd Introduction to Biochemistry Chemistry 1 [a] Microbiology and Health Anatomy and Physiology 1 campus-sem weight code L1 Lf~Bf H1~L1~B1 L1 12.5% 25% 12.5% 12.5% KJC161 KJC103 KXA153 CRA171 L1 12.5% CNA126 L2 Lf~Bf L2 L2 12.5% 25% 12.5% 12.5% KJC162 KJC103 CRA276 CRA172 Course details (2001) page 253 Introduction to Management H1/2~L1/2~B1 12.5% BMA101 Year 2 Semester 1 Core units Legal and Ethical Issues in Health Care L1 12.5% CNA308 Anatomy and Physiology 2 L1 12.5% CRA273 Electives: choose two units from one or more of the following streams: Bioscience stream Either CRA102/CRA241 or KJC103/KJC263 Diagnostic Testing L1 12.5% CRA102 General and Medical Microbiology L1 12.5% CRA241 Chemistry 1 Lf~Bf 25% KJC103 [b] Biochemistry 1 Lf 25% KJC263 Business/Commerce stream Economics for Business [c] H1~L1~B1 12.5% BEA110 Accounting and Financial Decision Making [c] H1~L1~B1 12.5% BFA103 Organisational Behaviour H1~L1 12.5% BMA201 Education stream Health Fitness & Physical Activity L1 12.5% ESP230 Communication Strategies L1~H1 12.5% ESV205 Social Science/Psychology stream Society, Culture and Health 1 L1 12.5% HGA138 Psychology 1A H1~L1~B1 12.5% KHA101 Semester 2 Core unit Foundations of Adult Learning L2~H2 12.5% ESV203 Electives: choose three units from one or more of the following streams: Bioscience stream Histology L2 12.5% CRA121 Chemistry 1 contd Lf~Bf 25% KJC103 contd Biochemistry 1 Lf 25% KJC263 Business/Commerce stream Accounting Context and Method [d] H2~L2~B2 12.5% BFA104 Commercial Transactions H2~L2~B2 12.5% BFA141 Management of Human Resources [e] H3/2~L3/2 12.5% BMA121/221 Principles of Marketing H3/2~L3/2 12.5% BMA151/251 Education stream Course details (2001) page 254 Human Movement Laboratory 1 L2 12.5% ESP136 Social Science/Psychology stream Perspectives on Ageing L2 12.5% CNA246 Child and Adolescent Health L1 12.5% CNA245 Psychology 1B H2~L2~B2 12.5% KHA102 Year 3 Semester 1 Core unit Immunology L1 12.5% CRA321 Electives: choose three units from one or more of the following streams: Bioscience stream Histopathology L1 12.5% CRA222 Biomedical Science 1 (Nutrition & Neurobiology) L1 12.5% CRA385 Applied and Environmental Microbiology L2 12.5% KQA218 Business/Commerce stream Contract of Employment [f] H1~L1 12.5% BMA241 Education stream Adapted Physical Activity L1 12.5% ESP307 Community and Public Education 1 L1~H1 12.5% ESV307 Social Science/Psychology stream Child and Adolescent Health L1 12.5% CNA245 Research Methods in Psychology H1~L1 12.5% KHA201 Organisational Psychology L1 12.5% KHA215/315 Semester 2 Core unit Health Infomatics L2 12.5% CRA102 Electives: choose three units from one or more of the following streams: Bioscience stream Human Molecular Biology L2 12.5% CRA300 Biomedical Science 2 (Pharmacology & Pathophysiology) L2 12.5% CRA386 Business/Commerce stream Quantitative Methods 1 H2~L2~B2 12.5% BEA140 Accounting Context and Method [f] H2~L2~B2 12.5% BFA104 [g] Principles of Marketing H3/2~L3/2 12.5% BMA151/251 Introduction to International Business [h] H2~L2 12.5% BMA181/281 Education stream Course details (2001) page 255 Sport Injuries L2 12.5% ESP304 Community and Public Education 2 L2~H2 12.5% ESV308 Social Science/Psychology stream Management of Human Resources [g] H3/2~L3/2 12.5% BMA121/221 Developmental Psychology H2~L2 12.5% KHA202 Psychology of Health & Stress L2 12.5% KHA213/313 [a] students must have completed Year 12 Chemistry to enrol in this unit [b] available only to students who have completed Chemistry 1 [c] BEA110 and BFA103 can also be studied in Year 3, Semester 1 [d] students must have completed BFA103. This unit can also be studied in Year 3, semester 2. [e] this unit can also be studied in Year 3, semester 2 [f] students must have completed BFA103 [g] students should use level 200 enrolment code (eg BMA251) [h] students should use level 100 enrolment code (eg BMA181) Bachelor of Medical Science with Honours (Abbreviation: BMedSc(Hons)) Course code: M4A This on-campus course is offered at Hobart as part of the Advanced Study/Research program in semester 2 of year 4 of the Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery. Admission & prerequisites Applicants need to have completed the requirements for the degree of Bachelor of Medical Science which is awarded after successful completion of the first four years of the Bachelor of Medicine-Bachelor of Surgery. Course objectives The BMedSc(Hons) degree allows students to spend one semester of study to develop a more complete understanding of an area of medical science. This is achieved through research and academic involvement in a Discipline of the School of Medicine. Career outcomes Course details (2001) page 256 The BMedSc(Hons) program provides an ideal basis for a career in medical research, either immediately on completion of the degree or after completing the MBBS program. Students may proceed from the BMedSc(Hons) to a PhD, or if they complete the MBBS, to an MD. Graduates with BMEdSc(Hons) could expect to find employment in a variety of medically related areas. Course structure One-semester's full-time work in one of the following disciplines: Anatomy and Physiology Biochemistry Epidemiology General Practice Medicine Obstetrics and Gynaecology Paediatrics and Child Health Pathology Psychiatry Surgery Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery (Abbreviation: MBBS) Course code: M3B This on-campus, full-time course is offered mainly at Hobart and takes a minimum of 6 years. After successful completion of the first 4 years of the course, students are awarded the degree of Bachelor of Medical Science (BMedSc). The MBBS is awarded with honours (abbreviation MBBS(Hons); course code: M4B) based on the degree of merit shown by students throughout the course. Course details (2001) page 257 Admission & prerequisites Domestic applicants must have obtained at least Satisfactory Achievement awards in the following subjects of the Tasmanian Certificate of Education (TCE) or its equivalent: Biology (*BY826), Chemistry (*CH856), Mathematics (*MT841), Physics (*PH866). For school leaver applicants, only results obtained in the first two years of post-Year 10 study will be taken into account. Additionally, school leavers should have obtained a minimum score of 90 in the Tasmanian Certificate of Education (TCE) or its equivalent. All domestic applicants will be required to sit the Undergraduate Medicine and Health Sciences Admission Test (UMAT). Non school leaver applicants will be selected on the basis of their academic record and UMAT score, with relevant employment experience and skills also being considered. Selection within each of the entry categories will be competitive, with applicants being ranked by their UMAT scores. International applicants must have obtained the equivalent of TCE Satisfactory Achievement awards in Chemistry, Mathematics, Physics and English. Further information on admission to the MBBS program may be obtained by contacting the University Course Information Officer. Course objectives The course is designed to provide an appropriate foundation, to give the graduate sound clinical skills, a solid basic knowledge of Medicine and Medical Sciences, good communication skills and the capacity to build on all of these in the intern year and subsequently in specialist training. The graduate will have the knowledge and skills to pursue the many career paths available in Medicine. Career outcomes On completion of the MBBS, graduates work for at least one more year in an approved hospital undertaking general medical training as an intern to obtain registration for the independent practice of medicine. Further training is then required for the graduate to become a general practitioner or a specialist in one of a number of fields including anaesthetics, dermatology, obstetrics and gynaecology, ophthalmology, paediatrics, pathology, medicine, psychiatry, radiology and surgery. Specialist qualifications are obtained by passing examinations during and on completion of this additional training. The examinations are conducted by appropriate specialist colleges such as the Royal Australian College of Physicians and the Royal Australian College of Surgeons. Medical practitioners may work in private practice on their own, in group practices, in community health centres and in public and private hospitals. They may be located in cities, suburbs and towns or in rural and remote areas. Course details (2001) page 258 Course structure Students begin medically relevant studies from the beginning of first year, with dissection of the human body as part of Integrated Structure and Function, an introduction to social aspects of medicine (Community Health and Medicine) and an introduction to problem solving in clinical medicine (Foundation Medical Studies), which looks at case studies based on real patients. Students take an elective subject from outside the Health Science area in this year. The second year builds on the first with Structure and Function – Clinical Correlations, which includes medical physiology, pharmacology and medical anatomy approached on a systems basis. Community Health and Medicine continues and students are given a comprehensive coverage of biochemistry relevant to Medicine. To be eligible to progress to third year, students must complete a senior first aid certificate and by the end of third year must have completed a specified period of training with an approved ambulance service. In the third year, students learn clinical skills and begin to study the clinical specialties (surgery, obstetrics and gynaecology, paediatrics and internal medicine) while continuing their studies of the paraclinical subjects of pharmacology, neuroscience, pathology and microbiology. The first half of fourth year follows on closely from year 3, but the second semester is entirely set aside for optional advanced studies or research projects. A popular advanced studies option is tropical and travel medicine; advanced study and research projects may be carried out anywhere in the world, if suitable arrangements can be made. Years 5 and 6 are the pre-intern years and students rotate through the clinical specialties. Year 5 may be taken in Launceston or Burnie. The Burnie program (maximum of 12 students) emphasises aspects of medicine in a rural clinical setting. In year 6 students complete their clinical rotations in the Royal Hobart Hospital. Articulation The course does not articulate with any other courses. Schedule Unit Title Year 1 Community Health and Medicine I Foundation Medical Studies campus-sem weight code H1 12.5% CAM105 H2 12.5% CAM100 Course details (2001) page 259 Integrated Structure and Function Hf 50% CHG110 Electives (1 or 2 units from other disciplines – 12.5%+ 12.5% or 25%) in sem 1 &/or 2 Year 2 Structure and Function – Clinical Correlations Hf 37.5% CHG210 Pathological Basis of Disease 2 H2 12.5% CJA212 Biochemistry 2 (Medicine) Hf 25% CBA200 Community Health and Medicine Hf 25% CAM205 [a] Year 3 Introduction to Clinical Studies H1 22.5% CAM300 Neuroscience H1 15% CHP310 Pathological Basis of Disease 3 H1 12.5% CJA312 Special Pathology 3 H2 12.5% CJA315 Clinical Microbiology 3 H2 6.25% CJA325 Medicine H2 18.5% CMM300 Clinical Specialties H1 3.25% CAM310 Surgery H2 9.5% CKA320 [a] Year 4 Clinical Microbiology 4 H1 12.5% CJA400 Special Pathology 4 H1 5% CJA410 Medicine H1 12.5% CMM400 Clinical Specialties H1 3.1% CAM410 Surgery H1 9.4% CKA400 Students enrol in one of CAM400, CAM420 or CAM440 Advanced Study H2 50% CAM400 Research H2 50% CAM420 Additional Study H2 50% CAM440 Year 5 (Ltn) Medicine 5 [r] L 25% CMM500 Either CGC500 or CMP500 Paediatrics and Child Health 5 [r] L 25% CGC500 Psychiatry 5 [r] L 25% CMP500 Obstetrics and Gynaecology H~L 25% CGW500 Either CKA500 or CKA550 Surgery [r] L 25% CKA500 Surgical Specialties [r] L~B 25% CKA550 Year 5 (NWC) Rural Clinical Program Bf 100% CAM500 Year 6 (Hbt) Course details (2001) page 260 Community Health (General Practice) [r] H 25% CLA600 Medicine 6 [r] H 25% CMM600 Either CGC600 or CMP600 Paediatrics and Child Health 6 [r] H 25% CGC600 Psychiatry 6 [r] H 25% CMP600 Either CKA600 or CKA650 Surgery [r] H 25% CKA600 Surgical Specialties [r] H 25% CKA650 Integrated Examination [b] H3 0% CAM600 Note: [r] = on rotation [a] At the time of going to press, the weights of units in year 3, semester 2 and year 4 semester 1 were under review and may be subject to change [b] the full title is Integrated Examination, CPR and Well Woman Assessments Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery with Honours (Abbreviation: MBBS(Hons)) Course code: M4B See Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery. Bachelor of Nursing (Abbreviation: BN) Course code: H3D This on-campus full-time course is offered at Launceston, but the third year of the course is available in both Launceston and Hobart. In special circumstances, continuing students may be permitted to undertake part-time studies. The course length is a minimum of 3 years full-time study with a maximum time period of 6 years. Advanced standing pathways are offered for psychiatric nurses and enrolled nurses to upgrade their qualifications to a degree and at the same time become eligible for registration as a nurse (comprehensive). Registered general nurses, diplomates and nurses who have re-entered practice also have the opportunity to undertake studies through advanced standing pathways in Launceston and taught according to demand and the availability of resources in Hobart . Admission & prerequisites Course details (2001) page 261 Pre-Registration: University admission. In addition, TCE subjects should include English, Science and Humanities. Post Registration: To be eligible in 2001, applicants are required to: • • hold a current practising certificate; and have at least 12 months of recent experience in practice following graduation. Selection for Post-Registration applicants will take into account the educational background, and professional experience of the applicant. Applicants may also be required to submit written work. Course objectives The educational objectives of the Bachelor of Nursing are: • • • to prepare students for a broad spectrum of first level practice roles in community health nursing, acute care and mental health nursing; or to enable registered nurses to gain additional knowledge and skills to increase and/or enhance their scope of practice; to foster a commitment to life-long learning, critical reflective thinking and professional growth; to establish a discipline framework of knowledge in preparation for both professional life and graduate studies in nursing. Career outcomes Graduates may find employment in health centres, hospitals, occupational health and industry, health promotion and education, and many diverse health care contexts including rural settings. Professional recognition Graduates with a Bachelor of Nursing are recognised in many countries besides Australia. Course structure The course structure is outlined in the Bachelor of Nursing Schedules A, B, C, D, and E. • • Pre-Registration students undertake a full-time 3-year course. Sequence – see Bachelor of Nursing (Pre-Registration): Schedule A. Lectures and Clinical Learning (Pre-Registration) Lectures, tutorials, group and laboratory work are held at the Launceston Course details (2001) • • • • page 262 campus in years one and two. In second year students undertake three weeks of study each semester in the clinical divisions at either Launceston, Hobart or rural clinical settings. The majority of third year is also in the clinical divisions at Launceston and Hobart. Costs associated with travel, accommodation and uniforms are met by students. Students are expected to maintain a recommended immunisation schedule through their general practitioners throughout the course. Post-Registration students are required to undertake an 8 unit (semester equivalent) pathway. Sequence – see Bachelor of Nursing (Post-Registration): Schedule B. Diplomates undertake three units of study part-time. Sequence – see Bachelor of Nursing (Diplomates): Schedule C. Psychiatric nurses seeking comprehensive registration undertake two–four years of study part time. Sequence – see Bachelor of Nursing (Psychiatric Nurses): Schedule D Part time Enrolled nurses undertake ten units of study, two years full time. Sequence – see Bachelor of Nursing (Enrolled Nurses): Schedule E. The normal part-time course load is two units per semester. The specifications of the Bachelor of Nursing are listed in the Calendar. Academic progress For pre-registration, enrolment in first semester units is a prerequisite for enrolment in second semester units. Progression from year to year is dependent upon satisfactory completion of the previous year's work. Schedule A (Pre-Registration) Unit Title Year 1 Discipline Studies in Nursing Human Bioscience 1 &2 Health Care where People Live and Work Society, Culture and Health Year 2 Scientific Perspectives in Nursing Supportive Care in Hospital and Community Settings Child and Adolescent Health Perspectives on Ageing campus-sem weight code Lf 12.5% CNA105 Lf 25% CRA181 Lf 37.5% CNA125 Lf 25% HGA135 Lf 12.5% CNA205 Lf 37.5% CNA225 L1 L2 12.5% 12.5% CNA245 CNA246 Course details (2001) Human Bioscience 3 &4 Lf Year 3 Acute Care Nursing H1/2~L1/2~B1/2 Community Practice H1/2~L1/2 Professional Issues in Nursing Practice Hf~Lf Schedule B page 263 25% CRA282 37.5% 37.5% CNA315 CNA316 25% CNA307 Year 1 Discipline Studies in Nursing Lf 12.5% CNA105 Health Care where People Live and Work Lf 37.5% CNA125 Year 2 Professional Issues in Nursing Practice Hf~Lf 25% CNA307 Either (HGA138 and HGA139) or (HGA101 and HGA239) Society, Culture and Health 1 L1 12.5% HGA138 Society, Culture and Health 2 L2 12.5% HGA139 Sociology A H1~L1~B1~D1 12.5% HGA101 Health Sociology [na] 12.5% HGA239/339 Schedule C (Diplomates) Year 1 Discipline Studies in Nursing Lf 12.5% CNA105 Nursing Research Df 12.5% CNA365 Professional Issues in Nursing Practice Hf~Lf 25% CNA307 Schedule D (Psychiatric Nurses) (Part Time) Year 1 Either (HGA138 and HGA139) or (HGA101 and HGA239) Society, Culture and Health 1 L1 12.5% HGA138 Society, Culture and Health 2 L2 12.5% HGA139 Sociology A H1~L1~B1~D1 12.5% HGA101 Health Sociology [na] 12.5% HGA239/339 Human Bioscience 3 & 4 Lf 25% CRA282 Year 2 Either CNA245 or CNA246 Course details (2001) page 264 Child and Adolescent Health L1 12.5% CNA245 Perspectives on Ageing L2 12.5% CNA246 Community Practice H1/2~L1/2 37.5% CNA316 Year 3 Acute Care Nursing H1/2~L1/2~B1/2 37.5% CNA315 Professional Issues in Nursing Practice Hf~Lf 25% CNA307 Schedule E (Enrolled Nurses) Year 1 Discipline Studies in Nursing Lf 12.5% CNA105 Health Care where People Live and Work Lf 37.5% CNA125 Society, Culture and Health Lf 25% HGA135 Human Bioscience 3 & 4 Lf 25% CRA282 Year 2 Community Practice H1/2~L1/2 37.5% CNA316 Acute Care Nursing H1/2~L1/2~B1/2 37.5% CNA315 Professional Issues in Nursing Practice Hf~Lf 25% CNA307 Bachelor of Nursing with Honours (Abbreviation: BN(Hons)) Course code: H4A This on-campus full-time course is offered at Launceston and Hobart. The course length is a minimum of one year of full-time study and a maximum of two years. Admission & prerequisites To be admitted to the honours program a student must hold a Bachelor of Nursing, normally with a minimum of a credit average across both the second and third years of the degree. Course objectives The objectives of the Bachelor of Nursing with Honours are: Course details (2001) • • • page 265 to provide research training within nursing; to provide preparation for undertaking higher degrees by research in nursing; to provide advanced professional study within a field of nursing. Career outcomes Graduates of the Bachelor of Nursing with Honours may enter the graduate/professional development program in Australian healthcare systems. Graduates are prepared for further research roles and activities; and gain preferential access to postgraduate studies. Course structure The course structure is outlined in the Bachelor of Nursing with Honours: Schedule G. The specifications of the Bachelor of Nursing with Honours are given in the Calendar and are available from the Office at the Tasmanian School of Nursing at Launceston. Articulation Students who hold a Bachelor of Nursing from another university may be considered for admission to the Bachelor of Nursing with Honours. Schedule G (Honours) Unit Title Nursing Inquiry in Practice Research Seminars and Project campus-sem weight code Lf 30% CNA405 Lf 70% CNA435 Bachelor of Pharmacy (Abbreviation: BPharm) Course code: M3F This 4-year course is conducted in Hobart, with some practical training being undertaken in Years 3 and 4 at community and hospital pharmacy teaching sites elsewhere in Tasmania. Part-time study is available in the first and second years of the course. Course details (2001) page 266 Admission & prerequisites All applicants must have obtained Satisfactory Achievement awards in the following subjects of the Tasmanian Certificate of Education [TCE] or its equivalent: • • • Chemistry [*CH856] Mathematics [*MT841] Physics [*PH866] OR Biology [*BY826]. In Year 1 of the Pharmacy course, the Biophysics unit will assume relevant Physics background, mostly in electronics and optics, from Physics completed post year 10. It should be noted that in Tasmania enrolment in the TCE subject *CH856C Chemistry assumes completion of the Year 11 TCE subject *SC786 Applied Science–Physical Sciences. The *SC786 syllabus contains a substantial [approx. 50%] Physics component. Students who have completed Year 12 Biology (but not Year 12 Physics) or Year 12 Physics (but not Year 12 Biology) should seek advice from the School of Pharmacy before the beginning of semester one. Course objectives The main aim of the course is to provide students with a specialist education in the pharmaceutical sciences and to enable them to gain the skills and attitudes required for the responsible practice of pharmacy. Approximately five years of study and practical experience are required to become a registered pharmacist in Tasmania. At present this comprises four years for the Bachelor of Pharmacy degree and a period of one year's practical experience as a trainee. After this time graduates are eligible to sit the Pharmacy Board of Tasmania examinations for registration as a pharmacist. A pharmacist registered in Tasmania has reciprocity through Australia and in New Zealand and Great Britain. Career outcomes The combination of biomedical and pharmaceutical science and clinical expertise in drug use in a pharmacy degree prepares pharmacy graduates for work in a variety of fields. Graduates work as pharmacists in the community or in hospitals. Many pharmacists are involved in clinical trials used to evaluate new drug products and in preparing the documentation on the effectiveness and safety of new drugs (required for marketing approval). Pharmacists are involved extensively in the manufacturing, research, quality control and marketing of pharmaceuticals. Pharmacists are also employed in government health departments where they may be involved in regulation and approval of new pharmaceutical products. Some pharmacy graduates specialise in providing drug information to other health professionals, hospitals and Course details (2001) page 267 government departments, while others undertake postgraduate training for careers as academics or researchers or in more specialised fields such as toxicology. Professional recognition After a further period of practical experience (currently 12 months) graduates of the Bachelor of Pharmacy are eligible to sit for the Pharmacy Board of Tasmania examination for registration as a pharmacist. Registration is recognised throughout Australia, New Zealand and Great Britain. Course structure Year 1 is an introductory and basic sciences year, Year 2 involves the study of drugs and pharmaceutical sciences, Years 3 and 4 combine applied and clinical studies with advanced scientific study and research. An honours course option is included within the four-year time-frame and involves a 12.5% overload in Year 3 and a 17.5% overload in Year 4. A separate one-year honours course is also available. Articulation There is no articulation with other courses. Schedule Unit Title Year 1 Pharmacy in Health Care Pharmaceutical Science and Practice 1 Human Biology (Pharmacy) Chemistry (Pharmacy) Either KYA172 or KMA153 Biological Physics Data Handling and Statistics 1 Year 2 Biochemistry (Pharmacy) Microbiology (Pharmacy) Pharmacology Pharmaceutical Science and Practice 2 Medicinal Chemistry Organic Chemistry (Pharmacy) campus-sem weight code Hf 12.5% CSA105 Hf Hf Hf 25% 25% 25% CSA115 CHG101 KRA160 [na] 12.5% KYA172 H1/2~L1/2~B2 12.5% KMA153 Hf Hf Hf 12.5% 12.5% 25% CBA220 CJA211 CSA201 Hf H2 25% 12.5% CSA215 CSA225 H1 12.5% KRA262 Course details (2001) page 268 Year 3 Clinical Pharmacokinetics 3 H2 12.5% CSA311 Pharmaceutical Science and Practice 3 Hf 25% CSA315 Therapeutics 3 Hf 25% CSA323 Chemotherapy and Infection Hf 12.5% CSA325 Toxicology H1 12.5% CSA331 Clinical Pharmacy Residency 3 Hf 12.5% CSA350 [a] Research in Pharmacy Hf 12.5% CSA420 Year 4 Clinical Pharmacokinetics 4 Hf 12.5% CSA411 Pharmaceutical Science and Practice 4 Hf 12.5% CSA415 Research in Pharmacy Hf 12.5% CSA420 Therapeutics 4 H1 12.5% CSA423 [a] Honours Hf 30% CSA440 Clinical Pharmacy Residency 4 Hf 50% CSA450 [a] Only students undertaking honours as part of the four-year degree study CSA420 Research in Pharmacy (12.5%) in Year 3 and CSA440 Honours (30%) in Year 4. Bachelor of Pharmacy with Honours (Abbreviation: BPharm(Hons)) Course code: M4C This on-campus course is offered at Hobart on a full-time basis as part of the four-year degree. It is also available as a separate year (full-time) or two-year (part-time) course. Admission & prerequisites The honours course option included within the four-year BPharm degree course time-frame involves a 12.5% overload in Year 3 (CSA420 Research in Pharmacy) and a 17.5% overload in Year 4 (CSA440 Honours). Honours students will be selected at the beginning of third year from amongst students normally achieving at least a credit average, which they will be required to maintain in the honours program. Course details (2001) page 269 The separate one-year honours course is available to those students who do not enter the undergraduate honours program (CSA400 full time, CSA401 part time) and for graduates from other universities. Course objectives The honours degree in Pharmacy is designed to provide an introduction to research and consists of a major research strand, a minor research strand and an essay. Depending on the students' major interest and longer term education or career goals, they may study additional units. Their specific syllabus will be designed in consultation with the principal supervisor and the head of school. Career outcomes See 'Career outcomes' in the Bachelor of Pharmacy. Professional recognition After a further period of practical experience (currently 12 months) graduates of the 4-year Bachelor of Pharmacy with Honours course are eligible to sit for the Pharmacy Board of Tasmania examination for registration as a pharmacist. Registration is recognised throughout Australia, New Zealand and Great Britain. Course structure One year's full-time work in one of the following: • • • Clinical Pharmacy Pharmaceutical Science Pharmacology See CSA400/401on page xx. Articulation Students with BSc or similar qualification should contact the School for further details. Graduate Certificate of Advanced Nursing Course details (2001) page 270 (Abbreviation: GradCertAdvN) Course code: H5A This course is offered part-time only, over one year, or two semesters. The maximum time for completion is two years. The course is offered from Launceston, with arrangements made for students throughout the State. Please note that the offering of graduate programs is subject to student demand and the availability of School of Nursing resources. Admission & prerequisites Applicants will need to [i] [ii] be a registered nurse in Australia and possess a current practising certificate; have completed a tertiary qualification in nursing and have had at least one year full-time experience in nursing practice within the last two years or equivalent; or have a hospital certificate and experience deemed to be equivalent of both of the above. Course objectives The School of Nursing aims to create an educational environment which values critical, reflective thinking, life-long learning and professional development. The course prepares students for practice roles as registered nurses in specialised practice settings and serves the needs of many students, allowing them to obtain advanced knowledge, skills and qualifications in their chosen specialty. Specialisations include: Acute Care Nursing, Anaesthetic Nursing, Cancer Nursing, Community Nursing, Critical Care Nursing, Emergency Care Nursing, Gerontic Nursing, Mental Health/Psychiatric Nursing, Neonatal Intensive Care Nursing, Paediatric Nursing, Perioperative Nursing, and Rural/Remote Nursing. Career outcomes Graduates gain the opportunity to practise in a specialist area. Course structure Minimum Maximum (Consecutive years) Course details (2001) page 271 Graduate Certificate of Advanced Nursing 4x12.5% units 1 year 2 years Graduate Diploma of Advanced Nursing 8x12.5% units 2 years 4 years<tbz> <tbz> The schedule of units, with the exceptions which are noted there, is the same as Schedule B of the Graduate Diploma of Advanced Nursing. Sample course structure All specialties in the Graduate Certificate of Advanced Nursing follow the same essential pattern as the example given below: GradCertAdvN Structure Year 1 (Semester 2) Critical Care Nursing Practice A 12.5% CNA770 Critical Care Nursing Science A 12.5% CNA772 Year 2 (Semester 1) Critical Care Nursing Practice B 12.5% CNA771 Critical Care Nursing Science B 12.5% CNA773 <tbz> Graduate Diploma of Advanced Nursing (Abbreviation: GradDipAdvN) Course code: H6A This course is offered part-time only, over two years, or four semesters. The maximum time for completion is four years. The course is offered from Launceston, with arrangements made for students throughout the State. Please note that the offering of graduate programs is subject to student demand and the availability of School of Nursing resources. Admission & prerequisites To be eligible for selection, applicants must: Course details (2001) (a) (b) page 272 be a registered nurse in Australia and hold a current practising certificate; have completed a tertiary qualification in nursing and have had at least one year of full time experience in nursing practice within the last 2 years (or equivalent); or hold a hospital certificate qualification in a field of nursing and have substantial experience in practice. Or (c) have qualifications and experience deemed to be the equivalent of both of the above. Applicants may be interviewed as part of the selection process. Course objectives The School of Nursing aims to create an educational environment that values critical reflective thinking, life-long learning and professional development. The graduate diploma prepares graduates for practice roles as registered nurses in various specialised practice settings. It is structured around three curriculum strands: • • • Discipline Studies (Core); Health Studies; and Specialisation Studies. The basic course structure comprises eight, one semester length study units. Each study unit is the equivalent of 3–4 hours of contact time per week. The course structure is set out in Schedule A. Specialisations The following specialisations are currently approved: • • • • • • • • • • • • Acute Care Nursing Anaesthetic Nursing Cancer Nursing (not offered in 2001) Child and Family Health Nursing Community Nursing Critical Care Nursing Emergency Care Nursing Gerontic Nursing (not offered in 2001) Mental Health/Psychiatric Nursing Neonatal Intensive Care Nursing Paediatric Nursing Perioperative Nursing Course details (2001) • page 273 Rural/Remote Nursing Career outcomes Depending on the specialist strand chosen for their Graduate Diploma of Advanced Nursing, graduates may apply for formal endorsement of their qualification by Nursing Boards. Course structure The following pattern is prescribed for part-time enrolment: Schedule A Year 1, Semester 1 Discipline (Core) Studies units Year 1, Semester 2 Specialisation Acute Care Nursing A units Anaesthetic Nursing A units Child and Family Health Nursing B units Community Nursing A units Critical Care Nursing A units Emergency Care Nursing A units Mental Health/Psychiatric Nursing B units Neonatal Intensive Care Nursing A units Paediatric Nursing A units Perioperative Nursing A units Rural/Remote Nursing A units Year 2, Semester 1 Specialisation Course details (2001) page 274 Acute Care Nursing B units Anaesthetic Nursing B units Child and Family Health Nursing A units Community Nursing B units Critical Care Nursing B units Emergency Care Nursing B units Mental Health/Psychiatric Nursing A units Neonatal Intensive Care Nursing B units Paediatric Nursing B units Perioperative Nursing B units Rural/Remote Nursing B units Year 2, Semester 2 Health Studies units Articulation Applicants who have undertaken studies equivalent to units in the graduate diploma may be given credit for up to two units. Normally credit will not be given for the practice units in the areas of specialisation. Credit may be given for units, including practice units, in the area of specialisation where these units are identical to those required by the Graduate Diploma course. Schedule B Unit Title campus-sem weight code The following schedule (with exceptions noted) applies to both the Graduate Certificate of Advanced Nursing and the Graduate Diploma of Advanced Nursing Graduate units – Discipline Studies (Core) Advanced Practice in Nursing [na] 12.5% CNA705 Research in Nursing [na] 12.5% CNA706 Graduate units – Health Studies units Course details (2001) page 275 Neurobiology and Neuropharmacology L2 12.5% CNA710 Advanced Therapeutic Communication L2 12.5% CNA711 Health Promotion L2 12.5% CNA713 Graduate units – Specialisation Studies ACUTE CARE NURSING Acute Care Nursing Practice A H2~L2 12.5% CNA780 Acute Care Nursing Science A H2~L2 12.5% CNA782 Acute Care Nursing Practice B [na] 12.5% CNA781 Acute Care Nursing Science B [na] 12.5% CNA783 ANAESTHETIC NURSING Anaesthetic Nursing Practice A [na] 12.5% CNA790 Anaesthetic Nursing Science A [na] 12.5% CNA792 Anaesthetic Nursing Practice B H1 12.5% CNA791 Anaesthetic Nursing Science B H1 12.5% CNA793 CANCER NURSING Cancer Nursing Studies A [na] 12.5% CNA720 Cancer Nursing Practice A [na] 12.5% CNA722 Cancer Nursing Studies B [na] 12.5% CNA721 Cancer Nursing Practice B [na] 12.5% CNA723 CHILD AND FAMILY HEALTH NURSING (RESTRICTED TO GRADUATE DIPLOMA STUDENTS) Child and Family Health Nursing A L1 12.5% CNA730 Child and Family Health Nursing Practice A L1 12.5% CNA732 Child and Family Health Nursing B [na] 12.5% CNA731 Child and Family Health Nursing Practice B [na] 12.5% CNA733 COMMUNITY NURSING Community Nursing Practice A [na] 12.5% CNA794 Community Nursing Studies A [na] 12.5% CNA796 Community Nursing Practice B [na] 12.5% CNA795 Course details (2001) Community Nursing Studies B CRITICAL CARE NURSING Critical Care Nursing Practice A Critical Care Nursing Science A Critical Care Nursing Practice B Critical Care Nursing Science B EMERGENCY CARE NURSING Emergency Nursing Practice A Emergency Nursing Science A Emergency Nursing Practice B Emergency Nursing Science B GERONTIC NURSING Gerontic Nursing Studies A Gerontic Nursing Practice A Gerontic Nursing Studies B Gerontic Nursing Practice B MENTAL HEALTH/PSYCHIATRIC NURSING Mental Health/Psychiatric Nursing Studies A Mental Health/Psychiatric Nursing Practice A Mental Health/Psychiatric Nursing Studies B Mental Health/Psychiatric Nursing Practice B NEONATAL INTENSIVE CARE NURSING Neonatal Intensive Care Nursing Practice A Neonatal Intensive Care Nursing Science A Neonatal Intensive Care Nursing Practice B Neonatal Intensive Care Nursing Science B page 276 [na] 12.5% CNA797 [na] 12.5% CNA770 [na] 12.5% CNA772 H1 12.5% CNA771 H1 12.5% CNA773 [na] 12.5% CNA784 [na] 12.5% CNA786 H1 12.5% CNA785 H1 12.5% CNA787 [na] 12.5% CNA760 [na] 12.5% CNA762 [na] 12.5% CNA761 [na] 12.5% CNA763 L1 12.5% CNA740 L1 12.5% CNA742 [na] 12.5% CNA741 [na] 12.5% CNA743 [na] 12.5% CNA774 [na] 12.5% CNA776 H1 12.5% CNA775 H1 12.5% CNA777 Course details (2001) PAEDIATRIC NURSING Paediatric Nursing Practice A Paediatric Nursing Studies A Paediatric Nursing Practice B Paediatric Nursing Studies B PERIOPERATIVE NURSING Perioperative Nursing Practice A Perioperative Nursing Science A Perioperative Nursing Practice B Perioperative Nursing Science B RURAL/REMOTE NURSING Rural/Remote Nursing Practice A Rural/Remote Nursing Studies A Rural/Remote Nursing Practice B Rural/Remote Nursing Studies B page 277 [na] 12.5% CNA764 [na] 12.5% CNA766 H1 12.5% CNA765 H1 12.5% CNA767 L2 12.5% CNA754 L2 12.5% CNA756 [na] 12.5% CNA755 [na] 12.5% CNA757 [na] 12.5% CNA744 [na] 12.5% CNA746 [na] 12.5% CNA745 [na] 12.5% CNA747 Graduate Diploma of Midwifery (Abbreviation: GradDipMid) Course code: H6B This course is offered part-time, over a minimum of 2 years and a maximum completion time of 5 years. Admission & prerequisites Applicants must [i] be a registered nurse in Australia and hold a current practising certificate, or if an overseas applicant, have had his/her nursing qualifications assessed by the Australian Nursing Council and either be eligible for Course details (2001) page 278 registration or require no more than a 3-month course approved by the Nursing Board of Tasmania to become eligible for registration; [ii] have completed a tertiary qualification in nursing and have had at least one year of full-time experience in nursing practice within the last two years (or equivalent); or hold a hospital certificate qualification in a field of nursing and have substantial experience in practice; or [iii] have qualifications and experience deemed to be the equivalent of both of the above. Applicants may be interviewed as part of the selection process and those who have undertaken studies equivalent to units in a Graduate Certificate of Graduate Diploma may be eligible for credit. Course objectives Contacts For further details, students are advised to contact the Tasmanian School of Nursing on (03) 6226 4750. Graduate Diploma in Immunology and Microbiology (Abbreviation: GradDipImmunolMicrobiol) Course code: M6A This 1-year full-time or up to 3-years part-time graduate diploma course is offered at Hobart, internally and externally. The staff are: Prof HK Muller, Prof JM Goldsmid, Dr GM Woods and Assoc Prof SM Kirov. Assessment is by examination, the completion of a minor research report, seminars and an oral examination. Admission & prerequisites Degree or equivalent in Medicine, Veterinary Science, Science, Pharmacy, Agricultural Science or Applied Science. Course objectives Course details (2001) page 279 The course is designed for those who wish to advance their knowledge in Immunology and Microbiology. Specific objectives are to give candidates the theoretical knowledge of Immunology and Microbiology to undertake further graduate studies in these disciplines. The practical experience from this course would allow candidates to take up positions in Immunology and Microbiology laboratories. Career outcomes Students who complete the Graduate Diploma have their career opportunities enhanced because they are able to combine expertise gained from their first degree with knowledge of Immunology and Microbiology. This opens career paths in research and/or diagnostic and investigative laboratories. Professional recognition There is no professional body specially in this area but the course would allow Medical and Biomedical scientists to prepare for Fellowship examinations. Course structure Candidates attend lectures in Immunology and Medical Microbiology as outlined for CJA308 Medical Microbiology and Immunology, or CJA212 Pathological Basis of Disease (see page C-xx for details), advanced tutorials, and complete a minor research project. The lecture streams and research project have their own unit codes when taken as part of this Graduate Diploma, as shown below. External students are expected to submit essays or assignments instead of the lectures and tutorials. The research project is supervised by a staff member of the appropriate School or Discipline. For further details on the requirements of the research project, contact the School of Agricultural Science. Coursework and research is completed either: • • by a full-time candidate in one year of study, with an additional three months being allowed for submission of the minor research report; or by a part-time candidate in a maximum of three consecutive years of study. Enrolment master code CJA510 GradDipImmunolMicrobiol Master of Medical Science Course details (2001) page 280 (Abbreviation: MMedSc) Course code: M7A Applicants for the Master of Medical Science by research should contact the Office for Research, but applicants for a Master of Medical Science by coursework should contact the relevant Head of Discipline in the School of Medicine. For a list of the ten Disciplines, see the BMedSc(Hons) entry. Admission & prerequisites Applicants must have completed the requirements for the degree of MBBS, the degree of BSc(Hons), or the degree of BMedSc(Hons) which is awarded following successful completion of an Advanced Study or Research project in semester 2 of year 4 of the MBBS course. Course objectives Master of Nursing (Abbreviation: MN) Course code: H7A The course is offered full time over a minimum of 3 semesters or part time, with a maximum completion time of five years. The course is offered from Launceston, with arrangements made for students throughout the State. Admission & prerequisites To qualify for admission, a candidate for the Master of Nursing must: [i] be a registered nurse in Australia and hold a current practising certificate, or if an overseas applicant, have had his/her nursing qualifications assessed by the Australian Nursing Council and either be eligible for registration or require no more than a three month course approved by the Nursing Board of Tasmania to become eligible for registration; [ii] normally have had at least two years of full-time experience in nursing practice within the last two years (or equivalent); [iii] hold a four-year undergraduate degree in nursing with a grade point average of at least a credit, or equivalent; or hold an Honours degree in nursing; Course details (2001) page 281 or hold a three-year degree and a graduate diploma with a credit average; or [iv] have qualifications and experience deemed to be the equivalent of all of the above. Passes in subjects or units in other courses (completed or otherwise) in this University or another approved tertiary institution (or other approved professional examining body) may be credited towards the Master of Nursing for a maximum of one unit of credit. Applicants who hold a Graduate Diploma of Advanced Nursing may be eligible for advanced standing for up to two coursework units, excluding the thesis component (effectively up to one third of the course) but must continue with the same nursing specialty strand studied in the GradDipAdvN. Course objectives The Master of Nursing is designed to prepare graduates who can contribute to knowledge development within the discipline of nursing. It is expected that students enrolled in the course will have a strong practice base with expertise in an area of specialisation. The course focuses on a high level of conceptualisation within the discipline of nursing. Career outcomes Graduates of the Master of Nursing can expect to be competitive for positions in practice, management and research. Course structure All students undertake a coursework component, and a thesis which represents 33% of the course as a whole, and takes the form of a supervised project of approximately 20,000 words. The core curriculum is arranged around three themes: • • • Discipline Studies in Nursing, Research Methods in Nursing, and Contemporary Health Issues. Students usually take the following units in year 1 or part-time studies: Semester 1 Discipline Studies in Nursing Semester 2 Course details (2001) page 282 Contemporary Health Issues The course structure is set out in Schedule B. At the master degree level it is expected that students will have accumulated a considerable reservoir of experience which will serve as a rich learning resource, both for themselves and for others. Accordingly, the approach of teaching and learning adopted within the course is congruent with adult learning principles. Units are both theory and practice driven. Schedule B Unit Title Discipline Studies in Nursing Contemporary Health Issues Research Methods in Nursing Nursing Practice Thesis campus-sem weight code L1/2 25% CNA805 L1/2 25% CNA806 L1/2 25% L1/2 25% L1/2 25%/50% CNA807 CNA808 CNA809/810 Diploma in Aquaculture (Abbreviation: DipAq) Course code: S2B This 2-year full-time course is offered by the Faculty of Science and Engineering and is available at Launceston. Subject to attendance and timetable requirements, part-time enrolment may be possible. Admission & prerequisites University admission. There are no specific TCE subject prerequisites. Course objectives The Diploma course aims to produce aquacultural technicians who have a sound understanding of the scientific bases of aquaculture as well as advanced technical skills. In addition to fostering reliability, the course emphasises the development of skills which lead to independence in the work place and the ability to work in a team situation. Theoretical, technical and practical training is complemented by a minimum of two weeks of work experience in industry. Course details (2001) page 283 Career outcomes The practical nature of this course, together with the current expansion of the aquaculture industry, ensures ready employment as farm workers throughout Australia. Graduates are able to work in all facets of aquaculture, including fish, shellfish and algal culture as well as in hatcheries. This course is fully articulated with the degree courses for students who wish to continue with their aquaculture education. Course structure The Diploma in Aquaculture is a 2-year course (4 semesters) in which students are required to undertake core and elective studies in a range of disciplines, in physical sciences, applied science and aquaculture. Schedule A outlines the sequence of units for each semester. Articulation Credit for appropriate studies completed in TAFE and other university courses may be granted by the Faculty. Bachelor of Aquaculture Schedule A Unit Title Year 1 Mathematics for Aquaculture Chemistry for Life Sciences Zoology for Aquaculture Computer Applications Introduction to Biochemistry Aquatic Ecology I Introductory Aquaculture Technology Unspecified elective Year 2 General Microbiology Technology for Aquaculture Data Handling and Statistics 1 Applied Algology campus-sem weight code L1 12.5% KMA162 L1 L1 H1~L1~B1 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KJC161 KQA110 KXA153 L2 L2 12.5% 12.5% KJC162 KQA121 L2 12.5% KQA124 L1 12.5% KQA207 L1 12.5% KQA214 H1/2~L1/2~B2 L1 12.5% 12.5% KMA153 KQA220 Course details (2001) Finfish Culture [a] L2 12.5% [a] Molluscan Culture L2 12.5% Crustacean & Zooplankton Culture [a] L2 12.5% Aquatic Ecology II L2 12.5% [a] two weeks work experience related to one of these units page 284 KQA241 KQA242 KQA243 KQA212 Bachelor of Agricultural Science (Abbreviation: BAgrSc) Course code: S3A This on-campus, 4-year (minimum) full-time course is offered by the Faculty of Science and Engineering and is available at Hobart. Subject to attendance and timetable requirements, part-time study may be possible. Admission & prerequisites In addition to the University's general admission requirements, students entering first year Agricultural Science must have achieved a TCE Satisfactory Achievement (SA) result or higher in Chemistry *CH856, Mathematics Stage 2 *MT841 (or Mathematics Applied *MT730). *PH866 is desirable but not compulsory. Course objectives The objectives of the Bachelor of Agricultural Science degree are to: • • • Provide a sound basis in the physical and biological sciences in the first two years of study and an introduction to the main subject areas to be covered in years 3 and 4; Provide, in the final two years of study, opportunity for specialisation and advanced study of the major discipline areas of agricultural science; Produce graduates with scientific knowledge and skills in the principles of agricultural production and sustainable resource management which meet the needs of industry, business and government. Career outcomes Employment prospects for graduates are diverse, including positions in agribusiness, research, production agriculture, resource management, business management, government agencies, education, forestry, aquaculture, food processing, food technology, waste management, marine and Antarctic research. Course details (2001) page 285 Professional recognition Graduates from the course are eligible for membership of the Australian Institute of Agricultural Science and Technology (AIAST). Course structure Students undertaking a Bachelor of Agricultural Science degree study a common first two years which is mainly comprised of subjects in the physical and biological sciences area. In years three and four they choose a range of subjects from within the agricultural sciences (refer to Schedule A). If students gain sufficient merit in year three they may be able to undertake an honours program during the final year of the course. The Agricultural Science degree is an interesting and challenging course requiring motivation and commitment from the student. In its final stages, students work closely with staff and fellow students and become familiar with the latest developments in the various subject areas. Practical experience is gained through formal practical classes, excursions and vacational work experience of 15 weeks, which can be spread over the duration of the course. Schedule A below specifies the core and optional units of the course. Articulation Candidates with other tertiary studies may be granted status for work completed and deemed appropriate to this degree. Candidates with other tertiary studies may be granted status for work completed and deemed appropriate to this degree. Schedule A Unit Title Year 1 Plant Science for Agricultural Science Zoology for Agricultural Science Applied Physics Chemistry 1 (Agricultural Science) Sustainable Resource Management campus-sem weight code H1 12.5% KPA160 H1 H1 12.5% 12.5% KZA160 KYA171 Hf 25% KRA120 H2~B2 12.5% KLA115 Course details (2001) Data Handling and Statistics 1 [a] H1/2~L1/2~B2 Genetics and Cell Biology for Agricultural Science H2 Year 2 Biochemistry (Agriculture) H1 Organic Chemistry (Agricultural Science) H1 Agricultural Geology & Soil Science H1 Pasture and Animal Science H1 Field Agriculture H2 Microbiology 1 H2 Crop and Plant Physiology H2 Agricultural Technology H2 Year 3 Economics for Business H1~L1~B1 Research, Development and Extension Methods H2 plus six (75% weighting) of the following: Agronomy H1 Crop and Pasture Production [b] H2 Insect Diversity and Function [b] H1 Insect Ecology and Behaviour [b] H2 Horticultural Production Systems [b] H1 Horticultural Science [b] H2 Environmental and Resource Economics H1 [d] Principles of Marketing H3/2~L3/2 Food Microbiology [b] H1 [b] General Microbial Ecology H2 [b][c] Animal Production Systems [na] [b][c] Animal Science [na] Introduction to Plant Diseases [b][c] [na] Agricultural and Forest Pathology [b][c] [na] Soil and Land Resources [b][c] [na] Fundamentals of Soil Science [b][c] [na] Year 4 page 286 12.5% KMA153 12.5% KPZ162 12.5% CBA235 12.5% KRA222 12.5% KLA213 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KLA211 KLA215 KLA210 KLA214 KLA217 12.5% BEA110 12.5% KLA305 12.5% KLA331/431 12.5% KLA250/350 12.5% KLA254/354 12.5% KLA314/414 12.5% 12.5% KLA242/342 KLA365/465 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% BEA301 BMA151/251 KLA396/496 KLA398/498 KLA220/320 KLA326/426 12.5% KLA287/387 12.5% 12.5% KLA346/446 KLA381/481 12.5% KLA297/397 Course details (2001) page 287 Crop Health Management [e] H1 12.5% KLA329/429 Plant Nutrition & Soil Fertility [e] H2 12.5% KLA318/418 Plus six (75% weighting) of the following: Agronomy [e] H1 12.5% KLA331/431 Crop and Pasture Production H2 12.5% KLA450 Insect Diversity and Function H1 12.5% KLA454 Insect Ecology and Behaviour [e] H2 12.5% KLA314/414 Horticultural Production Systems H2 12.5% KLA442 [e] Horticultural Science H2 12.5% KLA365/465 Environmental and Resource Economics H1 12.5% BEA301 [d] Principles of Marketing H3/2~L3/2 12.5% BMA151/251 Food Microbiology [e] H1 12.5% KLA396/496 General Microbial Ecology [e] H2 12.5% KLA398/498 [c] Animal Production Systems [na] 12.5% KLA420 [e][c] Animal Science [na] 12.5% KLA326/426 Introduction to Plant Diseases [c] [na] 12.5% KLA487 Agricultural and Forest Pathology [e][c] [na] 12.5% KLA346/446 Soil and Land Resources [e][c] [na] 12.5% KLA381/481 Fundamentals of Soil Science [na] 12.5% KLA497 Honours H.6, 25% [a] Subject to timetable constraints and approval of the course coordinator, students who have completed TCE Mathematics *MT730, *MT841 or *MT843 may be permitted to replace KMA153 with another 12.5% unit. KPZ161 Ecology for Agricultural Science is the recommended unit. [b] use level 300 enrolment code (eg KLA350) [c] will be offered in 2002 [d] use level 200 enrolment code (eg BMA251) [e] use level 400 enrolment code (eg KLA418) Bachelor of Agricultural Science with Honours (Abbreviation: BAgrSc(Hons)) Course code: S4A Course details (2001) page 288 A candidate who has completed the Third Examination of the Bachelor of Agricultural Science with sufficient merit will be invited by the Faculty of Science and Engineering on the recommendation of the Degree Coordinator as a candidate for the degree of Bachelor of Agricultural Science with Honours. Admission & prerequisites Prospective honours students must average a 2.5 weighted grade average (WGA) or higher in the 3rd year of their degree. Course objectives The BAgrSc(Hons) program aims to provide: • • Advanced knowledge and scientific training in a specialised area of agricultural science; Training in research as preparation for employment in a research organisation or for postgraduate research in master degree or PhD programs. Career outcomes Students are well prepared for employment in research and other positions with industry, government and business organisations, generally and in their area of specialisation. An honours degree also provides students with the opportunity to undertake further research study leading to a master degree or PhD qualification. Course structure Honours students usually carry a 100% load in their 4th year, which will be made up of 75% unit electives and 25% for the honours project (KLA490). Those with less than a 100% load may still be allowed to enrol. The formal coursework grade will be assessed on a weighted grade average (WGA). WGA = (G x W) / 75 where G values are: HD = 4; DN = 3; CR = 2; PP = I. The same formula applies to students not carrying the full formal coursework load. A student in this latter situation may elect to enrol in additional subjects to make up the full 4th-year load. Assessment of honours is based on the combination of formal coursework (60%) and project thesis (40%) of the 4th-year program. Note: Course details (2001) page 289 Students wishing to enrol in honours must arrange an interview with the honours coordinator before enrolment. Three copies of the thesis must be submitted to the secretary by the first week in December. The honours thesis should be completed according to the notes and instructions available from the honours coordinator. There shall be the following grades of honours: 1st Class; 2nd Class, Upper Division; 2nd Class, Lower Division; 3rd Class. Students may withdraw from honours up to the end of semester 1, without penalty. However, to complete their degree, they must, in semester 2, enrol in a suitable unit weighted 12.5% and complete an extensive literature review (KLA483) which will be subject to an examination, possibly including a viva voce. (The topic of the literature review is to be decided after consultation with the degree coordinator). Bachelor of Applied Science (Abbreviation: BAppSc) Course code: S3E No new intake into this course in 2001 The last intake of students into the Bachelor of Applied Science was in 2000. The course will be taught out over the period 2001 to 2003. Current students may also transfer to a number of other courses within the Faculty and University. should contact Mrs Michelle Horder on (03) 63243863 if advice is needed. Admission & prerequisites University admission. In addition there are TCE prerequisites to some first year units. If applicants do not have these specific prerequisites, they may be able to undertake bridging units. Course objectives The course aims to provide students with a broad scientific background and specific orientation towards career paths and industrial applications, especially as a result of professional accreditation. The course will develop students' ability to communicate, both within and outside the scientific community, and to learn independently. Graduates will be equipped for the workforce, able to adapt and to contribute to technological advances, and able to use their scientific knowledge with wisdom and responsibility. Course details (2001) page 290 Career outcomes The Bachelor of Applied Science provides students with the skills and knowledge that are highly sought after by a variety of employers including: industrial and government chemical laboratories, industrial, agricultural and mining companies, computing and scientific instrumentation companies, environmental organisations, plant biotechnology companies and national parks and government agencies. Students completing a BAppSc have highly developed problem-solving skills, an inquiring mind, well developed communication skills and the ability to work accurately. The areas of in-depth study are varied and students who choose to study a Professional Chemistry major are eligible for membership of the Royal Australian Chemical Institute. At the completion of their studies students also have the option of specialising in a specific area of interest by studying for a BAppSc with Honours. There is also the opportunity to undertake higher degrees by research. Course structure The Bachelor of Applied Science is a 3-year course (6 semesters) in which students are required to complete major, minor and elective studies in a range of disciplines. An outline is given in Schedule 1 which follows. Specimen course A specimen course in Aquaculture, together with majors in Applied Biology, Applied Physics/Electronics, Biomedical Science, Chemistry, Computing, Geography, and Mathematics are given in the following Schedules 2–9. However, unless approved by Faculty, students may choose only one of Biomedical Science, Mathematics and Computing as majors in the BAppSc; and may choose only one of the Biology majors. The framework of the general applied science course follows. It is based on the semester-unit, which normally involves three hours of lectures and three hours of laboratory work for 13 weeks. The course requires the completion of 24 such units. The normal degree structure for a full-time student contains two major fields of study, one minor, and four electives as shown below. Schedule 1 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 1 Major 1 Major 1 Major 1 Major 1 Major 1 Major 2 Major 2 Major 2 Major 2 Major 1 Minor 1 Minor 1 Minor 1 Minor 1 Major 2 Elective 1 Elective 2 Elective 3 Elective 4 Major 2 Course details (2001) Semester 2 page 291 Major 1 Major 1 Major 2 Major 2 However, the structure of the Professional Chemistry and Professional Aquaculture specialisations are atypical and include an expanded major and normally two minors. Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 1 Semester 2 Major 1 Major 1 Major 1 Major 1 Major 1 Major 1 Elective 1 Elective 2 Major 1 Major 1 Major 1 Major 1 Minor 1 Minor 1 Minor 1 Minor 1 Major 1 Major 1 Minor 2 Minor 2 Minor 2 Minor 2 Elective 3 Elective 4 An alternative structure incorporating one major, two submajors and four electives is available to accommodate some careeer paths. Articulation Credit of up to one year may be given for work completed in appropriate TAFE and other university courses approved by the Faculty. The BAppSc leads on to Honours and postgraduate studies. Schedule 2 – Aquaculture Prerequisites: Normal BAppSc requirements. Unit Title campus-sem Year 1 Data Handling and Statistics 1 H1/2~L1/2~B2 Either KJC103 or KJC161 and KJC162 Chemistry 1 Lf~Bf Chemistry for Life Sciences L1 Introduction to Biochemistry L2 Zoology for Aquaculture L1 Computer Applications H1~L1~B1 Aquatic Ecology I L2 Genetics L2~B2 Introductory Aquaculture Technology L2 Year 2 Either KJC263 or KJC103 Chemistry 1 Lf~Bf Biochemistry 1 Lf weight code 12.5% KMA153 25% KJC103 12.5% KJC161 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KJC162 KQA110 KXA153 KQA121 KJB122 12.5% KQA124 25% 25% KJC103 KJC263 Course details (2001) page 292 General Microbiology L1 12.5% Technology for Aquaculture L1 12.5% Intensive Algal Culture L1 12.5% Applied and Environmental Microbiology L2 12.5% Intensive Crustacean & Zooplankton Culture L2 12.5% Aquatic Ecology II L2 12.5% Year 3 Practicum [a] Lf 0% Physiology of Aquatic Organisms L1 12.5% Nutrition of Aquatic Organisms L1 12.5% Scientific Analysis and Presentation for Aquaculture L1 12.5% Advanced Aquaculture Technology L1 12.5% Intensive Molluscan Culture L2 12.5% Intensive Finfish Culture L2 12.5% Aquatic Animal Health L2 12.5% Unspecified elective L2 12.5% [a] eight weeks work experience plus seminar attendance KQA207 KQA214 KQA201 KQA218 KQA228 KQA212 KQA311 KQA330 KQA319 KQA302 KQA325 KQA303 KQA320 KQA321 Schedule 3 – Applied Biology Major Prerequisites: Normal BAppSc requirements. Unit Title Year 1 Fauna of Tasmania Genetics Year 2 Plant Physiology Forest Ecosystems Year 3 Agroforestry Plant Biotechnology campus-sem weight code L1~B1 L2~B2 12.5% 12.5% KJB113 KJB122 L1 L2 12.5% 12.5% KJB205 KJB227 Lf Lf 25% 25% KJB307 KJB308 Schedule 4 – Biomedical Science Course details (2001) page 293 Prerequisites: Normal BAppSc requirements, including *CH856 or KJC161 Chemistry for Life Sciences and KJC162 Introduction to Biochemistry. Note that students taking this major will also need to enrol in the Biochemistry minor. Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Either CRA171 or CRA101 Cell Biology L1 12.5% CRA171 Medical Laboratory Practice [a] L1 12.5% CRA101 Anatomy and Physiology 1 L2 12.5% CRA172 Year 2 Anatomy and Physiology 2 L1 12.5% CRA273 Either CRA276 or KJB122 Microbiology and Health L2 12.5% CRA276 [a] Genetics L2~B2 12.5% KJB122 Year 3 Immunology L1 12.5% CRA321 Biomedical Science 1 (Nutrition & Neurobiology) L1 12.5% CRA385 Human Molecular Biology L2 12.5% CRA300 Biomedical Science 2 (Pharmacology & Pathophysiology) L2 12.5% CRA386 [a] Only available to those students also pursuing a microbiology sequence. This sequence may be in the form of a minor for students combining a chemistry major, or in the form of electives for others, as the biochemistry minor is a corequisite of the Biomedical Science major Schedule 5 – Chemistry Major Specialisation in Chemistry is available through a professionally accredited 12 unit Chemistry major. Students not wishing to pursue this expanded major may choose an 8 unit general Chemistry major. (i) Chemistry Major (Professional) This major provides a sound theoretical basis in chemistry which is enhanced by relevant industrial and biological applications, and meets the academic requirements for membership of the Royal Australian Chemical Institute. Membership regulations require, in addition to the Chemistry units, either first year Physics or first year Mathematics. Prerequisites: Normal BAppSc requirements, but including *CH856 and *MT841 and/or *PH866. Bridging units are available for students who lack specific prerequisites. Course details (2001) Unit Title Year 1 Chemistry 1 Year 2 Organic Chemistry 2 Inorganic Chemistry 2 Analytical Chemistry 2 Physical Chemistry 2 Year 3 Physical Chemistry 3 Instrumental Chemistry 3 Science Project (Chemistry) Inorganic Chemistry 3 Organic Chemistry 3 Biochemistry 1 [a] [a] Recommended elective page 294 campus-sem weight code Lf~Bf 25% KJC103 L1 L1 L2 L2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KJC231 KJC221 KJC212 KJC242 L1 L1 12.5% 12.5% KJC341 KJC311 Lf~Df L2 L2 Lf 25% 12.5% 12.5% 25% KJC353 KJC322 KJC332 KJC263 (ii) Chemistry Major (General) Curriculum Several variations of the general Chemistry major are possible by selection of units from the Professional Chemistry Major, and these can be chosen to complement the particular co-major. Prerequisites: Normal BAppSc requirements, but including *CH856. Bridging units are available for students who lack specific prerequisites. Unit Title Year 1 Chemistry 1 Year 2 Either KJC231 or KJC221 Organic Chemistry 2 Inorganic Chemistry 2 Either KJC212 or KJC242 Analytical Chemistry 2 Physical Chemistry 2 Year 3 Choose 2 of KJC231, 221, 341, 311 Organic Chemistry 2 Inorganic Chemistry 2 Physical Chemistry 3 Instrumental Chemistry 3 Choose 2 of KJC212, 242, 322, 332 Analytical Chemistry 2 campus-sem weight code Lf~Bf 25% KJC103 L1 L1 12.5% 12.5% KJC231 KJC221 L2 L2 12.5% 12.5% KJC212 KJC242 L1 L1 L1 L1 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KJC231 KJC221 KJC341 KJC311 L2 12.5% KJC212 Course details (2001) page 295 Physical Chemistry 2 Inorganic Chemistry 3 Organic Chemistry 3 L2 L2 L2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KJC242 KJC322 KJC332 Schedule 6 (i) – Computing Major Prerequisites: Normal BAppSc requirements. Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Choose two of KXA153, KXA151 or KXA154 Computer Applications H1~L1~B1 12.5% KXA153 Programming and Problem Solving H1~L1/2~B1 12.5% KXA151 Software Process H2~L2~B2 12.5% KXA154 Year 2 Choose two of the following: Algorithms and Metrics H1~L1 12.5% KXA251 Artificial Intelligence H1~L1 12.5% KXA252 Software Design H2~L2 12.5% KXA253 Operating Systems H2~L2 12.5% KXA254 [a] Year 3 Choose four of the following: Advanced Web Development [b] H1~L1 12.5% KXA281/381 [b] Computer Security H2~L2 12.5% KXA262/362 Knowledge-Based Systems L1 12.5% KXA335 Programming Systems L2 12.5% KXA337 Computer Assisted Learning L1 12.5% KXA339 Principles of Operating Systems L2 12.5% KXA334 Digital Networks L1 12.5% KXA336 Computer Graphics & Animation L2 12.5% KXA338 [a] Year 3 units are offered subject to student demand and availability of resources [b] use level 300 enrolment code (eg KXA361) Schedule 6 (ii) – Geography Major Prerequisites: Normal BAppSc requirements. Unit Title Year 1 campus-sem weight code Course details (2001) page 296 Population and Urbanisation The Physical Environment Year 2 Australian Natural Environments Natural Resources Management Year 3 Environmental Geomorphology Globalisation L1~B1~D1 L2~B2~D2 12.5% 12.5% KJG101 KJG102 L1~D1 12.5% KJG201 L2~D2 12.5% KJG202 L1~D1 L2~D2 25% 25% KJG301 KJG302 Schedule 6 (iii) – Mathematics Major Prerequisites: Normal BAppSc requirements, but including *MT841. Unit Title campus-sem Year 1 Mathematics I L1~D1 Mathematics II L2~D2 Year 2 Mathematics III L1~D1 Mathematics IV – Introductory Applied Statistics L2 Year 3 Mathematics Va L2 Mathematics Vb L1 Mathematics VIa L1 Mathematics VIb – Intermediate Applied Statistics L2 weight code 12.5% 12.5% KMA171 KMA172 12.5% KMA271 12.5% KMA272 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KMA371 KMA372 KMA373 12.5% KMA374 Schedule 7 – Applied Physics/Electronics Major Prerequisites: Normal BAppSc requirements, but including *PH866 or *EL750 and *MT841. Unit Title Year 1 Physics 1A Year 2 Physics 3A Physics 4E campus-sem weight code Lf 25% KJP103 L1 L2 12.5% 12.5% KJP201 KJP222 Course details (2001) page 297 Year 3 Physics 5E Physics 6E L1 L2 25% 25% KJP321 KJP322 Schedule 9 – Minor Sequences (i) Biochemistry Minor Unit Title Year 1 Chemistry 1 Year 2 Biochemistry 1 campus-sem weight code Lf~Bf 25% KJC103 Lf 25% KJC263 campus-sem weight code H1~L1~B1 H2~L2~B2 12.5% 12.5% KHA101 KHA102 L1 12.5% KHB215/315 L2 12.5% KHB209/309 campus-sem weight code L1 L2 12.5% 12.5% CRA171 CRA276 L1 L1 12.5% 12.5% CRA241 KQA207 L2 12.5% KQA218 campus-sem weight code (ii) Behavioural Science Minor Unit Title Year 1 Psychology 1A Psychology 1B Year 2 Behaviour in the Workplace Health, Stress and Coping (iii) Microbiology Minor Unit Title Year 1 Cell Biology Microbiology and Health Year 2 Either CRA241 or KQA207 General and Medical Microbiology General Microbiology Applied and Environmental Microbiology (iv) Computing Electronics Minor Unit Title Course details (2001) Year 1 Introduction to Electronics Digital and Microprocessor Systems Year 2 Computer Control and Communications Laboratory Instrumentation page 298 L1~B1 12.5% KJP131 L2~B2 12.5% KJP132 L1 12.5% KJP231 L2 12.5% KJP232 Unit Title campus-sem Year 1 Mathematics I L1~D1 Mathematics IV – Introductory Applied Statistics L2 Year 2 Mathematics Vb L1 Mathematics VIb – Intermediate Applied Statistics L2 weight code 12.5% KMA171 12.5% KMA272 12.5% KMA372 12.5% KMA374 (v) Statistics Minor (vii) Other Minors Four sequential units from any of the identified majors other than Aquaculture. Refer to the earlier schedules. Bachelor of Applied Science with Honours (Abbreviation: BAppSc(Hons)) Course code: S4C This 1-year full-time or 2-year part-time course is offered by the Faculty of Science and Engineering at Launceston. Admission & prerequisites A candidate for the degree of BAppSc(Hons) requires approval of Faculty. Except with the permission of Faculty, candidates shall have qualified for admission to the degree of BAppSc at this University or an equivalent qualification in which the specialisation prerequisites have been completed and Course details (2001) page 299 approved by Faculty for this purpose. Specialisation prerequisites are credit level or better in the final three semesters of study. Course objectives To provide advanced knowledge and training in a single area of applied science and training in research to prepare candidates for advanced research programs and/or employment in research organisations. Career outcomes A Bachelor of Applied Science with Honours provides the opportunity to consolidate skills and knowledge acquired in the BAppSc course. The Honours program provides practical research training through a specialised project which facilitates the design and conduct of future investigations in the student's chosen field of study. Graduates could expect to obtain employment in the same areas as those graduating with BAppSc but could expect to move into research based positions. The honours course also enables graduates to move into higher degrees by research. Course structure Each candidate will undertake coursework as prescribed, conduct research, and write a thesis. Fields of Study • • • • • Subject to staff supervision being available, candidates may be accepted in: Applied Biology Chemistry Earth Science (Geography) Physical Sciences Articulation Graduates from other institutions with degrees acceptable to the Faculty may be accepted into one of these fields of study. The BAppSc(Hons) leads on to research higher degrees. Bachelor of Applied Science (Agriculture) (Abbreviation: BAppSc(Agr)) Course details (2001) page 300 Course code: S3B This on-campus, 3-year (minimum) full-time course is offered by the Faculty of Science and Engineering and is available at Hobart. Subject to attendance and timetable requirements, part-time study may be possible. Admission & prerequisites Minimum University entry requirements including a satisfactory achievement (SA) or higher in any two of the following: TCE mathematics *MT730 (or *MT841 or *MT843), computer science *IF862, chemistry *CH856, geology *GL876, geography *GG833, or environmental science *EV846, physics *PH866, biology *BY826, applied science–physical sciences *SC786 (if neither physics nor chemistry counted), agricultural science *AG806. Course objectives The course gives students an opportunity to acquire knowledge and skills suited to the needs of a professional agriculturalist. Emphasis is given to scientific technology, its application and the management of agricultural enterprises. Career outcomes The course is designed to meet an identified demand by employers for graduates qualified and skilled in the application of scientific technology in agricultural industries. Graduates are qualified for positions within agribusiness, private sector, service consultancy, agricultural development and enterprise management, forestry and related industries. Professional recognition Graduates from the course are eligible for membership of the Australian Institute of Agricultural Science and Technology (AIAST) Course structure The course is arranged with a core of units in applied physical science, biological science and agricultural business, and these form a foundation for studies in applied agriculture. Field and practical work is required during semesters and in vacations. The course is detailed in the schedule below. Course details (2001) page 301 Articulation If students have a TAFE Diploma of Agriculture, or come from other recognised providers of agricultural or relevant science education, they should receive credit for work done. As a general rule, maximum credit transfer would be 100%. Application must be made to the Student Administration Graduates of the BAppSc(Agr) may progress to the Graduate Diploma of Agricultural Science or the Graduate Diploma of Agricultural Science with Honours. Schedule A Unit Title Year 1 Plant Science for Agricultural Science Zoology for Agricultural Science Applied Physics Introduction to Agriculture and Horticulture Chemistry 1 (Applied Agriculture) Sustainable Resource Management Business of Agriculture and Horticulture Science of Agriculture Year 2 Microbiology 1 Agricultural Geology & Soil Science Crop and Plant Physiology Field Agriculture Pasture and Animal Science Plus three of the following: Economics for Business Insect Diversity and Function [a] Crop and Pasture Production [a] Fundamentals of Soil Science [a][c] Introduction to Plant Diseases [a][c] campus-sem weight code H1 12.5% KPA160 H1 H1 12.5% 12.5% KZA160 KYA171 H1 12.5% KLA100 H2 12.5% KRA121 H2~B2 12.5% KLA115 H2 H2 12.5% 12.5% KLA105 KLA110 H2 12.5% KLA210 H1 H2 H2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KLA213 KLA214 KLA215 H1 12.5% KLA211 H1~L1~B1 12.5% BEA110 H1 12.5% KLA254/354 H2 12.5% KLA250/350 [na] 12.5% KLA297/397 [na] 12.5% KLA287/387 Course details (2001) Animal Production Systems [a][c] [na] Year 3 Crop Health Management H1 Principles of Marketing [a] H3/2~L3/2 Industry Project Hf Plant Nutrition & Soil Fertility [b] H2 Plus three of the following: Economics for Business H1~L1~B1 Insect Diversity and Function [b] H1 Crop and Pasture Production [b] H2 Fundamentals of Soil Science [b][c] [na] Introduction to Plant Diseases [b][c] [na] Animal Production Systems [b][c] [na] [a] Use level 200 enrolment code (eg KLA254) [b] Use level 300 enrolment code (eg KLA318) [c] will be offered in 2002 page 302 12.5% KLA220/320 12.5% 12.5% 25% KLA329/429 BMA151/251 KLA377 12.5% KLA318/418 12.5% BEA110 12.5% KLA254/354 12.5% KLA250/350 12.5% KLA297/397 12.5% 12.5% KLA287/387 KLA220/320 Bachelor of Applied Science (Horticulture) (Abbreviation: BAppSc(Hort)) Course code: S3C This on-campus, 3-year (minimum) course is offered by the Faculty of Science and Engineering, and is available at Hobart. Subject to attendance and timetable limits, part-time study may be possible. Admission & prerequisites Minimum entry requirements including a satisfactory achievement (SA) in any two of the following: TCE mathematics *MT843 (or *MT841 or *MT730), computer science *IF862, chemistry *CH856, geology *GL876, geography *GG833 (or environmental science *EV846), physics *PH866, biology *BY826, applied science–physical sciences *SC786 (if neither physics nor chemistry counted), agricultural science *AG806. Course objectives Course details (2001) page 303 The course is designed to give students an opportunity to acquire the knowledge, attitudes and skills suited to the needs of a professional horticulturalist. Emphasis is given to scientific technology, its application and the management of horticultural enterprises. Career outcomes The course meets an identified demand by employers for graduates qualified and skilled in the application of scientific technology in horticultural industries. It seeks to provide graduates qualified for positions within agribusiness, private sector, service consultancy, horticultural development and enterprise management, forestry and related industries. Professional recognition Graduates from the course are eligible for membership of the Australian Institute of Agricultural Science and Technology (AIAST) Course structure The course is arranged with a core of units in applied physical science, biological science and horticultural business, and these form a foundation for studies in applied horticulture. Field and practical work is required during semesters and in vacations. The course is detailed in the schedule which follows. Articulation If students have a TAFE Diploma of Horticulture, or come from other recognised providers of horticultural or relevant science education, they may receive credit for work done. As a general rule, maximum credit transfer would be 100%. Application must be made to the Student Administration Graduates of the BAppSc(Hort) may progress to the Graduate Diploma of Agricultural Science or the Graduate Diploma of Agricultural Science with Honours. Schedule A Unit Title Year 1 Plant Science for Agricultural Science Zoology for Agricultural Science campus-sem weight code H1 12.5% KPA160 H1 12.5% KZA160 Course details (2001) Applied Physics Introduction to Agriculture and Horticulture Chemistry 1 (Applied Agriculture) Sustainable Resource Management Business of Agriculture and Horticulture Science of Agriculture Year 2 Microbiology 1 Agricultural Geology & Soil Science Crop and Plant Physiology Field Agriculture Economics for Business Plus three of the following: Horticultural Production Systems [a] Insect Diversity and Function [a] Crop and Pasture Production [a] Fundamentals of Soil Science [a][c] Introduction to Plant Diseases [a][c] Horticultural Physiology and Technology [a][c] Year 3 Crop Health Management Principles of Marketing [a] Industry Project Plant Nutrition & Soil Fertility [b] Plus three of the following: Horticultural Production Systems [b] Insect Diversity and Function [b] Crop and Pasture Production [b] Fundamentals of Soil Science [b][c] Introduction to Plant Diseases [b][c] page 304 H1 12.5% KYA171 H1 12.5% KLA100 H2 12.5% KRA121 H2~B2 12.5% KLA115 H2 H2 12.5% 12.5% KLA105 KLA110 H2 12.5% KLA210 H1 H2 H2 H1~L1~B1 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KLA213 KLA214 KLA215 BEA110 H1 12.5% KLA242/342 H1 12.5% KLA254/354 H2 12.5% KLA250/350 [na] 12.5% KLA297/397 [na] 12.5% KLA287/387 [na] 12.5% KLA233/333 H1 H3/2~L3/2 Hf 12.5% 12.5% 25% KLA329/429 BMA151/251 KLA377 H2 12.5% KLA318/418 H1 12.5% KLA242/342 H1 12.5% KLA254/354 H2 12.5% KLA250/350 [na] 12.5% KLA297/397 [na] 12.5% KLA287/387 Course details (2001) page 305 Horticultural Physiology and Technology [b][c] [na] [a] Use level 200 enrolment code (eg KLA254) [b] Use level 300 enrolment code (eg KLA318) [c] will be offered in 2002 12.5% KLA233/333 Bachelor of Aquaculture (Abbreviation: BAqua) Course code: S3K This 3-year full-time course is offered by the Faculty of Science and Engineering and is available at Launceston. Subject to attendance and timetable requirements, the course may be available part time over 6 years. Admission & prerequisites University admission. In addition there are TCE prerequisites to some first-year units. If applicants do not have these specific prerequisites, they may be able to undertake bridging units. Course objectives The course aims to provide students with a broad scientific background in aquatic biology and specific orientation towards a career path in aquaculture. It will develop students' ability to communicate, both within and outside the scientific community, and to learn independently. As graduates, students will be able to adapt and contribute to technological advances and be able to use their scientific knowledge with wisdom and responsibility. Career outcomes The combined approach of broad-based aquatic biology with a comprehensive strand of specialist aquaculture subjects ensures graduates are highly employable throughout the aquaculture industry or in applied aquatic biology. Recent graduate surveys demonstrate 90% are either employed in this or related industries or are undertaking higher studies in aquaculture. Possible career paths include work in farming as an owner, manager or technician; or as a research assistant in aquaculture or applied aquatic biology, in university or government departments, or proceeding to higher qualifications to become a research scientist or consultant . Course structure Course details (2001) page 306 The Bachelor of Aquaculture is a three-year course (6 semesters) in which students are required to complete a set course of aquaculture and other science subjects in a range of disciplines. Articulation Credit of up to one year may be given for work completed in appropriate TAFE and other university courses approved by the Faculty. Graduates are eligible to progress to the Bachelor of Aquaculture with Honours program. Schedule Unit Title campus-sem Year 1 Data Handling and Statistics 1 H1/2~L1/2~B2 Either KJC103 or KJC161 and KJC162 Chemistry 1 Lf~Bf Chemistry for Life Sciences L1 Introduction to Biochemistry L2 Zoology for Aquaculture L1 Computer Applications H1~L1~B1 Aquatic Ecology I L2 Introductory Aquaculture Technology L2 Unspecified elective L1/2 Year 2 Either Unspecified elective and KJC252 or KJC103 Chemistry 1 Lf~Bf Analytical and Environmental Chemistry 2 L2 General Microbiology L1 Technology for Aquaculture L1 Intensive Algal Culture L1 Intensive Crustacean & Zooplankton Culture L2 Applied and Environmental Microbiology L2 Aquatic Ecology II L2 Year 3 Practicum [a] Lf weight code 12.5% KMA153 25% KJC103 12.5% KJC161 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KJC162 KQA110 KXA153 KQA121 12.5% KQA124 25% KJC103 12.5% 12.5% KJC252 KQA207 12.5% 12.5% KQA214 KQA201 12.5% KQA228 12.5% 12.5% KQA218 KQA212 0% KQA311 Course details (2001) Physiology of Aquatic Organisms L1 12.5% Nutrition of Aquatic Organisms L1 12.5% Scientific Analysis and Presentation for Aquaculture L1 12.5% Advanced Aquaculture Technology L1 12.5% Intensive Molluscan Culture L2 12.5% Intensive Finfish Culture L2 12.5% Aquatic Animal Health L2 12.5% Aquaculture Policy and Operations L2 12.5% [a] Eight weeks work experience plus seminar attendance page 307 KQA330 KQA319 KQA302 KQA325 KQA303 KQA320 KQA321 KQA326 Bachelor of Aquaculture with Honours (Abbreviation: BAqua(Hons)) Course code: S4M (This course replaces the Bachelor of Applied Science (Honours) specialising in Aquaculture (S4C)) This 1-year full-time or 2-year part-time course is offered by the Faculty of Science and Engineering at Launceston. Admission & prerequisites A candidate for the degree of BAqua(Hons) requires the permission of Faculty. Except with the permission of Faculty, candidates shall have qualified for admission to the degree of BAqua at this University or an equivalent qualification in which the specialisation prerequisites have been completed and approved by Faculty for this purpose. Specialisation prerequisites are credit level or better in the final three semesters of study. Course objectives The course provides advanced knowledge and training in aquaculture, and training in research to prepare candidates for advanced research programs and/or employment in research organisations. Career outcomes Course details (2001) page 308 A Bachelor of Aquaculture with Honours provides the opportunity to consolidate skills acquired in the BAqua course. The Honours program provides practical research training through a specialised project that facilitates the design and conduct of future investigations. Graduates could expect to obtain employment in the same areas as those graduating with a BAqua, but could expect to move into research-based positions. The Honours course allows graduates to move into higher degrees by research. Course structure The BAqua(Hons) is a 1-year full-time course of 2 semesters in which, under supervision, candidates undertake a research project. A candidate for the degree must submit a thesis on this work undertaken as part of the Honours course. The requirements for the degree may include examinations or other assessments as prescribed by Faculty. Articulation Graduates from other institutions with degrees acceptable to Faculty may be accepted into the Honours course. Graduates of the BAqua(Hons) course may enrol for a higher degree by research. Bachelor of Architecture (Abbreviation: BArch) Course code: D3B This 2-year graduate entry degree course is offered, full time only, by the Faculty of Science and Engineering and is available only at Launceston through the School of Architecture. Admission & prerequisites To enter the Bachelor of Architecture, applicants will have the Bachelor of Environmental Design or equivalent 3-year undergraduate degree. Applicants' first degree program will have been in environmental design, architectural studies, or equivalent, and the main emphasis or major will have been in architecture. In addition, students will be asked to attend an interview and submit a portfolio of work which preferably should include items both from their previous studies and from relevant activities, such as office practice. Course details (2001) page 309 Candidates should note that, because there are limited places available, the minimum requirements for admission will not automatically guarantee entry to the course. Course objectives The course is aimed specifically at the needs of the architectural profession and aims to equip students with the knowledge, skills, competencies and awareness which are necessary for a graduate to practise architecture. To complete the BArch successfully, students are required to demonstrate competence in the analysis, synthesis, judgement and communication of architectural ideas and solutions, as well as the ability to apply successfully acquired theoretical knowledge, and technical and professional skills. Career outcomes Architects deal with a broad range of issues. Consequently, the study of architecture covers a broad range of disciplines and skills. This means that architects may find a career in private architectural practice, government architectural offices, local government, performing arts, universities (as academics or in property management), and large companies. Architects may be engaged in a wide range of tasks: commercial, residential, retail and civic building design (conceptual and technical); client brief writing; urban design, planning appeal submissions, representation and also assessment; stage set and exhibition design; and property and construction management. Many Australian graduates in architecture have established careers in various countries around the world. Professional recognition The Bachelor of Architecture is recognised by the Royal Australian Institute of Architects (RAIA) as fulfilling the academic requirements for corporate membership. BArch graduates are eligible for registration by Australian Boards of Architects following an approved practical experience program and a pass in the Architectural Practice examination. The Bachelor of Architecture is also recognised by the Commonwealth Association of Architects and this offers opportunity for international recognition. Course structure The course structure is outlined in the following Schedule. Schedule A Unit Title Year 1 campus-sem weight code Course details (2001) page 310 Design Studio 7 (BArch) Professional Studies 1 Building Technology in Design 7 (BArch) Design Studio 8 (BArch) Theory in Design 1 (BArch) Building Technology in Design 8 (BArch) Year 2 Design Studio 9 (BArch) Theory in Design 2 (BArch) Professional Studies 2 (BArch) Professional Project (BArch) L1 L1 25% 12.5% KDA411 KDA412 L1 L2 12.5% 25% KDA413 KDA421 L2 12.5% KDA422 L2 12.5% KDA423 L1 25% KDA511 L1 12.5% KDA512 L1 12.5% KDA513 L2 50% KDA521 Bachelor of Architecture with Honours (Abbreviation: BArch(Hons)) Course code: D4B The Bachelor of Architecture with Honours is not a separate course and students undertake only the units which comprise the Bachelor of Architecture as detailed on page xx. The award of Bachelor of Architecture with Honours is conferred on those students who have completed the Bachelor of Architecture with sufficient merit, that is: • • having completed the requirements of the degree of Bachelor of Architecture without failing a unit and having complied with all specifications of the Bachelor of Architecture; and having achieved an Average Weighted Mark of 70% or above in both years of the Bachelor of Architecture degree. Course objectives Bachelor of Computing (Abbreviation: BComp) Course details (2001) page 311 Course code: S3F This on-campus 3-year full-time (4 years honours) course is offered by the Faculty of Science & Engineering and is available at Launceston and Hobart. The first year only is also offered at the North-West Centre. This course may be studied part-time. Admission & prerequisites Possession of the University's basic admission requirements. TCE Computing or Mathematics subjects are not required. Course objectives The Bachelor of Computing is a comprehensive 3-year degree course in the broad area of computer science with an applied orientation. The specific course objectives are as follows: • • • to provide a thorough introduction to the theory and practice of computing; to produce modern computing professionals with the ability to apply new and emerging computing technologies to create solutions in the workplace; to provide a broad base of computing knowledge to support lifelong learning in the field of computing. Career outcomes Students are prepared for careers and research in the area of Information Technology (IT). Current forecasts indicate a world wide shortage of IT professionals for at least the next ten years. Computing professionals get well paid, interesting positions in almost any area – government, commerce, industry. The range of activities is wide, including: website management, system administration, client support and training, program design, development and testing, and so on. Professional recognition Undergraduate students of the BComp are eligible for student membership of the Australian Computer Society (ACS) and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). On completion of the degree and entry into the computing profession, graduates can apply to become full members of these bodies. Course structure Course details (2001) page 312 The course is a 3-year (6-semester) course consisting of core and elective units. Year 1[a] 1st Year computing core units 75% non-computing electives 25% Year 2 2nd Year computing core units 50% computing or non-computing electives 25% non-computing electives 25% Year 3[a] 3rd Year computing units 50% Project 25% computing or non-computing electives 25% <tbz> [a] With the permission of the Dean, a candidate may replace up to two first-year core units (25%) and/or two third-year computing electives (25%) with non-computing units. Articulation If students have completed the TAFE Diploma of Information Technology they may be granted up to one year's advanced standing. The BComp articulates into the Bachelor of Computing with Honours. Schedule Unit Title Year 1 Computer Applications Programming and Problem Solving Professional Computing Multimedia and Web Applications Computer Organisation and Architecture Software Process Year 2 Algorithms and Metrics Artificial Intelligence Software Design Operating Systems Elective units Advanced Web Development [a] campus-sem weight code H1~L1~B1 12.5% KXA153 H1~L1/2~B1 H2~L2~B2 12.5% 12.5% KXA151 KXA155 H2~L2~B2 12.5% KXA156 H1~L1~B1 H2~L2~B2 12.5% 12.5% KXA152 KXA154 H1~L1 H1~L1 H2~L2 H2~L2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KXA251 KXA252 KXA253 KXA254 H1~L1 12.5% KXA281/381 Course details (2001) page 313 Computer Security [a] H2~L2 12.5% KXA262/362 Year 3 Computing Project A L1/2 12.5% KXA331 Computing Project B L1/2 12.5% KXA332 Elective units Availability of the following units depends on student demand and availability of resources Advanced Web Development [b] H1~L1 12.5% KXA281/381 [b] Computer Security H2~L2 12.5% KXA262/362 Principles of Operating Systems L2 12.5% KXA334 Knowledge-Based Systems L1 12.5% KXA335 Digital Networks L1 12.5% KXA336 Programming Systems L2 12.5% KXA337 Computer Graphics & Animation L2 12.5% KXA338 Computer Assisted Learning L1 12.5% KXA339 [a] Use level 200 enrolment code (eg KXA262) [b] Use level 300 enrolment code (eg KXA362) Major in computing for non-computing students This major provides a thorough introduction to the theory and practice of computing. It is an opportunity for students who wish to combine computing with their specialisation to obtain a qualification in computing within a non-computing degree structure. A major consists of a sequence of 8 units (9 units for BSc students) taken over a three-year full-time degree program or equivalent part time. Students must select a sequence of units from the computing units as listed in the schedule of units for a major in computing which follows the BComp Schedule. (At least four of the units must be at third-year level.) Students in the BSc program should consult the schedules for that course. Computing major for non-computing students – Schedule Unit Title CORE UNITS Year 1 Programming and Problem Solving campus-sem weight code H1~L1/2~B1 12.5% KXA151 Course details (2001) page 314 Software Process H2~L2~B2 12.5% KXA154 Other units are available subject to approval Year 2 Choose two of the following: Algorithms and Metrics H1~L1 12.5% KXA251 Artificial Intelligence H1~L1 12.5% KXA252 Software Design H2~L2 12.5% KXA253 Operating Systems H2~L2 12.5% KXA254 Year 3 Availability of the following units depends on student demand and availability of resources. Choose four of the following: Computer Security [b] H2~L2 12.5% KXA262/362 Principles of Operating Systems L2 12.5% KXA334 Knowledge-Based Systems L1 12.5% KXA335 Digital Networks L1 12.5% KXA336 Programming Systems L2 12.5% KXA337 Computer Graphics & Animation L2 12.5% KXA338 Computer Assisted Learning L1 12.5% KXA339 [b] Use level 300 enrolment code (eg KXA362) Bachelor of Computing with Honours (Abbreviation: BComp(Hons)) Course code: S4D This 1-year full-time or 2-year part-time course is offered by the Faculty of Science & Engineering at Launceston. Admission & prerequisites Bachelor of Computing or equivalent qualification approved by the School of Computing. Applicants will normally be expected to have achieved an average grade of credit or better in year three of their degree. Course objectives To provide in-depth knowledge and advanced training in a major area of computing; and to provide the opportunity to practice research methodologies in preparation for research in higher degrees (eg PhD) or employment in research organisations. Course details (2001) page 315 Career outcomes Students are prepared for careers and research in the area of Information Technology (IT). Current forecasts indicate a world wide shortage of IT professionals for at least the next ten years. Computing professionals get well paid, interesting positions in almost any area – government, commerce, industry. The range of activities is wide, including: website management, system administration, client support and training, program design, development and testing, and so on. Professional recognition Undergraduate students of the BComp are eligible for student membership of the Australian Computer Society (ACS) and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). On completion of the degree and entry into the computing profession, graduates can apply to become full members of these bodies. Course structure A candidate must meet all the coursework requirements and submit a thesis on a topic approved by the school and supervised by a member of staff. (See unit details for KXA450, KXA451) Articulation Candidates with qualifications from other tertiary institutions may be accepted in the course subject to approval by the Faculty of Science & Engineering. The BComp(Hons) leads on the MSc and PhD. Schedule Unit Title Computing Honours Full time Computing Honours Part time campus-sem weight code Lf 100% KXA450 Lf 50% KXA451 Bachelor of Engineering (Abbreviation: BE) Course code: N3A Course details (2001) page 316 This 4-year (minimum) full-time course is offered by the Faculty of Science and Engineering. The first two years of the course may be studied in either Hobart or Launceston. The remainder of the course must be completed in Hobart. Note: Students intending to study at Launceston should contact the School for advice prior to enrolling. Admission & prerequisites If students are entering first year Engineering in either Hobart or Launceston, they must have met the University admission requirements including a TCE Satisfactory Achievement (SA) result or higher in Mathematics Stage 2 *MT841 and Applied Science: Physical Science *SC786. Although not essential for entry, students are encouraged to study additional TCE science subjects such as Chemistry, Computer Science, Mathematics Stage 3, Physics, etc as they provide a useful background for first-year BE units. A TAFE diploma in Civil, Mechanical or Electrical Engineering may be accepted as an alternative prerequisite for admission to the Bachelor of Engineering course with advanced standing. Interstate or overseas qualifications, which are deemed equivalent by the University, may also be accepted. Course objectives The objectives of the Bachelor of Engineering degree are: • • • • to provide a sound basis in the physical sciences, mathematics and basic engineering science in the first two years of study, along with some degree of specialisation; to provide, in the final two years of study, specific theory and practice in one of the specialised engineering fields; to train students to a graduate level whereby they meet the academic requirements for admission to the Institution of Engineers, Australia and like institutions; and to produce well-rounded graduates who can develop their professional and managerial skills in their places of employment. The engineering degree is interesting and challenging, requiring motivation and commitment from the student. In its final stages, students work and become familiar with the very latest developments in the various disciplines. Professional recognition Course details (2001) page 317 The Bachelor of Engineering is accredited by The Institution of Engineers Australia (IEAust) as providing qualification for Graduate membership of the Institution. It is also recognised in a number of other countries such as UK and USA through agreements between the IEAust and like professional bodies overseas. The computer systems engineering specialisation is also accredited by the Australian Computer Society for graduate entry. Course structure Students both in Hobart and Launceston take a common first two years. This gives a breadth of subjects which enables students to select the area of engineering to which they are best suited and in which they wish to specialise. The six broad areas of specialisation are: • • • • • • civil engineering mechanical engineering electrical power engineering electronics and communication engineering computer systems engineering mechatronics The standard routes of progression through each of the four years to these specialisations are shown in the following Chart. A major feature of the engineering course is the emphasis placed on laboratory work; students will be required to write regular reports on their work. The design classes provide them with opportunities to learn the techniques of developing safe and reliable designs. In the fourth year, each student may undertake an individual project which involves an analysis of requirements, feasibility study, and design and development usually resulting in a prototype. For both the laboratory and the design classes, extensive use is made of computers. Engineering students are also required to undertake a recognised first-aid course (ie Workplace Level 2, First Aid Certificate, offered by either St John Ambulance or Red Cross) and to complete a prescribed amount of industrial experience work in the vacations. Where possible, the work experience placements are arranged through the School of Engineering, and students are paid by their employers at the appropriate award rate. Articulation Course details (2001) page 318 In certain circumstances the Faculty may grant status in units of the BE degree course to students who have completed equivalent work in other institutions. All such cases are treated on their merits. Special admission conditions apply to the acceptance of some overseas students. Approved diplomates of certain overseas polytechnics may be granted advanced standing of up to four semesters toward the four-year Bachelor of Engineering degree. Special courses for overseas students with advanced standing are outlined in the Specimen Courses under the heading Overseas Students with Diplomas in Civil, Mechanical or Electrical Engineering. If students wish to specialise in other branches of Engineering (eg Aeronautical, Agricultural, Chemical, Manufacturing, Maritime, Materials, Mining, Naval Architecture, Petroleum), it is generally possible for them to start their studies at the University of Tasmania and later transfer to an institution offering the course. If this is the student's intention, it is important that the students see the Degree Coordinator before starting their University studies as it may be necessary to follow a specially prescribed course. Specimen courses Specimen courses are outlined below. Students should note that their choice of units should conform with the specimen courses, unless otherwise determined by the Degree Coordinator. If students have previously attempted all or part of an examination they will not be permitted to count units with overlapping content. Policy on use of calculators in examinations Engineers use calculators a great deal, and it is essential that each engineering student has a calculator. Because of the advantage that advanced (and generally expensive) calculators might give in examinations, a uniform policy on calculators for use in engineering examinations in the earlier years of the course has been adopted. Only the following types of calculator will be permitted in first year engineering examinations: Hewlett-Packard HP32S, Sharp EL-5120 and EL-531GH, Casio FX-82 Super and FX-100S. Students should note that this list includes some programmable, specialist scientific calculators as well as some more basic types. They should consider their options carefully. Students taking units taught by the Australian Maritime College in Launceston should note the particular calculator requirements of those units. Course details (2001) page 319 The list of permitted calculators will be kept as stable as possible, subject to the availability of the various models. Figure 1 PLACE CHART (ENG_1.eps) HERE Specimen courses The revised first year, which was introduced in 1999, and the revised second year introduced in 2000, are common to all Bachelor of Engineering streams and may be studied at Hobart or Launceston. The Launceston course units (except where otherwise noted) are taught by the Australian Maritime College. Students intending to study at Launceston should contact the School for information prior to enrolling. Unit Title campus-sem Year 1 (Common to all streams) Hobart Programming and Problem Solving H1~L1/2~B1 Computer Aided Design and Communication H1 Engineering Mechanics H1 Chemistry of Materials H2 Engineering Profession and Industry H2 Electrical Engineering H2 Calculus and Applications 1 Hf (Common to all streams) Launceston Introduction to Computing L2 Principles of Programming L2 Engineering Graphics and Design A L1 Engineering Graphics and Design B L2 Engineering Mechanics A L1 Engineering Mechanics B L2 Electrical Fundamentals Lf Materials Technology 1 Lf Thermofluid Dynamics 1 L2 Physics L1 weight code 12.5% KXA151 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KNE111 KNE112 KRA170 12.5% 12.5% KNE121 KNE122 25% KMA150 3.15% 3.15% KNT111 KNT112 6.25% KNT121 6.25% 6.25% 6.25% 12.5% 12.5% 6.25% 6.25% KNT122 KNT123 KNT124 KNT115 KNT116 KNT118 KNT119 Course details (2001) Engineering Profession and Industry L1 Mathematical Methods L1~D1 Calculus and Linear Algebra L2~D2 Year 2 (Common to all streams) Hobart Engineering Design and Project Management H2 Thermal and Fluid Engineering H1 Electronic Engineering H1 Engineering Mathematics H1 Mechanics and Structures H1 Software Process H2~L2~B2 Plus one Science option from: Surveying for Engineers H2 Engineering Physics H2 Operating Systems H2~L2 Plus one Engineering option from: Materials and Manufacturing H2 Microprocessors and Data Acquisition H2 (Common to all streams) Launceston Microprocessor and Data Acquisition L2 Computer Aided Design A L1 Computer Aided Design B L2 Engineering Design Lf Technical Review L1 Electronic Engineering L1 Thermodynamics L2 Fluid Mechanics L1 Strength of Materials Lf Engineering Dynamics L2 Calculus of Several Variables L1~D1 Linear Algebra for Engineering L2~D2 CIVIL/MECHANICAL OPTION Materials L1 Ocean Science [a] L2 ELECTRICAL SOFTWARE OPTION Electrical Systems L1 Software Process (AMC) L2 page 320 6.25% 12.5% KNT120 KNT125 12.5% KNT126 12.5% KNE211 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KNE213 KNE222 KME271 KNE212 KXA154 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KGG215 KYA275 KXA254 12.5% KNE210 12.5% KNE232 7.5% 5% 5% 10% 2.5% 10% 5% 5% 10% 10% KNT224 KNT225 KNT226 KNT214 KNT215 KNT216 KNT217 KNT218 KNT219 KNT220 8.33% KNT227 4.17% KNT228 5% 10% KNT221 KNT222 7.5% 7.5% KNT223 KNT229 Course details (2001) [a] page 321 This requirement may be filled by undertaking AMC unit E03268 Ocean Science or any science unit offered by the University of Tasmania. Civil Engineering Unit Title campus-sem weight Year 3 Engineering Numerical Methods H1 12.5% Geotechnical Engineering 1 H1 12.5% Steel and Timber Structures H1 12.5% Fluid Mechanics 1 H1 12.5% Engineering Project Management and Economics H2 12.5% Structural Mechanics H2 12.5% Transportation Engineering H1 12.5% Concrete Structures H2 12.5% Year 4 Revisions to Year 4 will be introduced in 2002 Engineering Management and Law H16% N3H6.25% Business Strategies and Marketing for Engineers H26% N3H6.25% Engineering Design 3 (Civil) Hf 20% Structural Mechanics 3 H1 8.5% Stress Analysis H1 8.5% Hydraulics H1 8.5% Geomechanics 2 H2 8.5% Traffic and Highway Engineering H2 8.5% Environmental Engineering H2 8.5% Civil Engineering Project H2 8.5% Geotechnical Engineering 1 H1 12.5% code KME300 KNE313 KNE315 KNE351 KNE301 KNE312 KNE314 KNE316 ACM462 AEA461 ACC454 ACC413 ACC414 ACC431 ACC434 ACC445 ACC446 ACC447 KNE313 Mechanical Engineering Unit Title Year 3 Engineering Numerical Methods campus-sem weight code H1 12.5% KME300 Course details (2001) page 322 Fluid Mechanics 1 H1 12.5% Dynamic Systems H? 12.5% Design for Manufacture Hf 12.5% Engineering Project Management and Economics H2 12.5% Structural Mechanics H2 12.5% Manufacturing, Maintenance and Quality H2 12.5% Thermal Energy Systems H1 12.5% Year 4 Revisions to Year 4 will be introduced in 2002 Engineering Management and Law H16% N3H6.25% Business Strategies and Marketing for Engineers H26% N3H6.25% Engineering Design 3 (Mechanical) Hf 20% Robotics, Dynamics and Control H2 8.5% Aerodynamic Design H1 8.5% Gas Dynamics and Turbomachines H2 8.5% Refrigeration and Air Conditioning H1 8.5% Heat and Mass Transfer H2 8.5% Advanced Manufacturing H1 8.5% Stress Analysis H1 8.5% Environmental Engineering H2 8.5% KNE351 KNE352 KNE355 KNE301 KNE312 KNE353 KNE354 ACM462 AEA461 ACM456 ACM401 ACM420 ACM423 ACM460 ACM470 ACM475 ACC414 ACC446 Electrical Power Engineering Unit Title Year 3 Engineering Numerical Methods Advanced Circuit Analysis Digital Electronic Systems Signals and Linear Systems Electrical Design Management and Law Instrumentation and Control Electrical Materials and Machines campus-sem weight code H1 H1 12.5% 12.5% KME300 KNE331 H2 12.5% KNE332 H1 12.5% KNE333 H2 12.5% KNE335 H2 12.5% KNE336 H2 12.5% KNE341 Course details (2001) page 323 Power Systems 1 H2 12.5% Year 4 Revisions to Year 4 will be introduced in 2002 Engineering Management and Law H16% N3H6.25% Business Strategies and Marketing for Engineers H26% N3H6.25% Engineering Design 3 (Electrical Power) Hf 20% Control Engineering H1 8.5% Signal Processing H1 8.5% Power Systems 2 H1 8.5% Power Electronic Drive Systems H1 8.5% Industrial Power Engineering Applications H2 8.5% Plus three of the following: Electronic Systems [na] 8.5% Engineering Systems H2 8.5% Computer and Data Networks H2 8.5% Knowledge Engineering H1 8.5% Computer Systems 2 H1 8.5% Digital Communications H1 8.5% One other unit approved by HoS. KNE342 ACM462 AEA461 AEA452 AEA408 AEA431 AEA441 AEA445 AEA446 AEA407 AEA409 AEA412 AEA413 AEA416 AEA432 Electronics and Communications Engineering Unit Title campus-sem Year 3 Engineering Numerical Methods H1 Advanced Circuit Analysis H1 Digital Electronic Systems H2 Signals and Linear Systems H1 Communication Systems 1 H2 Electrical Design Management and Law H2 Instrumentation and Control H2 Power Systems 1 H2 Year 4 Revisions to Year 4 will be introduced in 2002 weight code 12.5% 12.5% KME300 KNE331 12.5% KNE332 12.5% 12.5% KNE333 KNE334 12.5% KNE335 12.5% 12.5% KNE336 KNE342 Course details (2001) page 324 Engineering Management and Law Business Strategies and Marketing for Engineers Engineering Design 3 (Electronics and Computer Engineering) Control Engineering Computer and Data Networks Computer Systems 2 Signal Processing Digital Communications Plus three of the following: Electronic Systems Engineering Systems Knowledge Engineering Image Processing and Computer Vision One other unit approved by HoS. H16% N3H6.25% ACM462 H26% N3H6.25% AEA461 Hf H1 20% 8.5% AEA453 AEA408 H2 H1 H1 H1 8.5% 8.5% 8.5% 8.5% AEA412 AEA416 AEA431 AEA432 [na] H2 H1 8.5% 8.5% 8.5% AEA407 AEA409 AEA413 H2 8.5% AEA414 Computer Systems Engineering Unit Title campus-sem weight Year 3 Engineering Numerical Methods H1 12.5% Signals and Linear Systems H1 12.5% Networks and Protocols H1 12.5% Algorithms and Metrics H1~L1 12.5% Communication Systems 1 H2 12.5% Instrumentation and Control H2 12.5% Software Design H2~L2 12.5% one 12.5% computing unit to be advised. Year 4 Revisions to Year 4 will be introduced in 2002 Software Engineering Project Hf 25% Computer Architecture H1 12.5% Engineering Management and Law H16% N3H6.25% Business Strategies and Marketing for Engineers H26% N3H6.25% code KME300 KNE333 KCA321 KXA251 KNE334 KNE336 KXA253 KCA444 KCA443 ACM462 AEA461 Course details (2001) page 325 Plus electives (preferably two KCA and three AEA units) drawn from the following: Electronic Systems [na] 8.5% AEA407 Control Engineering H1 8.5% AEA408 Computer and Data Networks H2 8.5% AEA412 Computer Systems 2 H1 8.5% AEA416 ASIC Design H1 8.5% AEA419 Signal Processing H1 8.5% AEA431 Digital Communications H1 8.5% AEA432 Advanced Lambda Calculus H 12.5% KCA421 Concurrency H 12.5% KCA422 UNIX H 12.5% KCA423 Software Engineering Management H 12.5% KCA427 Intelligent Systems H1 12.5% KCA441 Image Processing and Computer Vision H2 12.5% KCA442 [i] Units with an overlap in content will not both be counted towards the degree; [ii] Contact the School of engineering for details on availability of elective units; [iii] Candidates for Honours shall also enrol in the unit AEA494 Computer Systems Engineering Honours Thesis; [iv] One other unit may be substituted with the approval of HoS. Mechatronic Engineering Unit Title campus-sem Year 3 Engineering Numerical Methods H1 Dynamic Systems H? Design for Manufacture Hf Signals and Linear Systems H1 Engineering Project Management and Economics H2 Instrumentation and Control H2 Manufacturing, Maintenance and Quality H2 Mechatronic Systems 1 H2 Mechatronic Systems 1 H2 Year 4 Year 4 units will be introduced in 2002 weight code 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KME300 KNE352 KNE355 12.5% KNE333 12.5% KNE301 12.5% KNE336 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KNE353 KNE364 KNE364 Course details (2001) page 326 Overseas Students with a Diploma in Civil, Mechanical or Electrical Engineering; and 3-semester Advanced Standing Unit Title Electrical Diplomates Commencing February campus-sem weight code Course prescribed by Head of School, requiring 6 semester to complete. Commencing July Computing and Mathematics Engineering Physics Software Process Either KCA254 or KCA202 Microprocessors and Data Acquisition Operating Systems Civil and Mechanical Diplomates Commencing February H2 H2 H2~L2~B2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KNE225 KYA275 KXA154 H2 H2~L2 12.5% 12.5% KNE232 KXA254 Course prescribed by Head of School, requiring 6 semester to complete. Commencing July Mechanics and Structures Computing and Mathematics Software Process Either KYA275 or KNM210 Engineering Physics Materials and Manufacturing H1 H2 H2~L2~B2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KNE212 KNE225 KXA154 H2 12.5% KYA275 H2 12.5% KNE210 Bachelor of Engineering with Honours (Abbreviation: BE(Hons)) Course code: N4A A candidate who has completed the Third Examination of the Bachelor of Engineering with sufficient merit will be invited by the Faculty of Science and Engineering on the recommendation of the Degree Coordinator as a candidate for the degree of Bachelor of Engineering with Honours. Admission & prerequisites Course details (2001) page 327 Acceptance for honours is based on the value of WAM3, a weighted average mark computed from the candidate's results in the Third Examination of the Bachelor of Engineering course (see Note below). Course objectives The BE honours program exists to serve two purposes. Firstly, it enables outstanding academic performance by students in the final two years of the degree course to be acknowledged. Secondly, and as part of this process, it requires the student to perform and present a substantial piece of work by way of an investigative project, leading to an oral presentation and a written thesis describing the work. Course structure Students enrolled in honours must undertake an individual research and development project of a standard and scope appropriate to the degree of Bachelor of Engineering with Honours. The award of Honours is assessed on the basis of the student's academic record. Assessment of the examinations of the Bachelor of Engineering degree are described in Note. The class of honours awarded, which may be either first class or second class (upper or lower division), is based on a candidate's overall weighted average mark (WAM). Note A Weighted Average Mark (WAM) shall be computed from the candidate's results in the Third and Fourth Examination for the Bachelor of Engineering degree according to the formula: WAM=0.8 x (2xWAM3 + 3 x WAM4)/5 + 0.2 x THESIS. WAM n is the Weighted Average Mark in the n th examination of the Bachelor of Engineering degree, computed from the formula: WAM n = ∑(G x W s )/∑W s where G is the subject examination grade on the scale HD = 10, DN = 7, CR = 3, PP = 0, SP,TP,FP = -2, NN = -4, and Ws is the fractional subject weighting given in the Handbook of the year of enrolment in each subject. THESIS is calculated from the examination of the candidate's final year project thesis. The thesis will be marked on a 0 to 10 scale in which a mark of 5/10 represents the minimum standard for the award of honours. THESIS is calculated from the thesis mark according to the formula: Course details (2001) page 328 THESIS = 1.4 x (Thesis mark) -4.0. A copy of the Bachelor of Engineering with Honours specifications and/or further details are available from the relevant Head of School. Honours (Thesis) Unit codes Unit Title campus-sem Civil Engineering Honours Thesis Hf Mechanical Engineering Honours Thesis Hf Electrical Power Engineering Honours Thesis Hf Electronics and Computer Engineering Honours Thesis Hf Computer Systems Engineering Honours Thesis Hf weight code 0% ACC490 0% ACM495 0% AEA492 0% AEA493 0% AEA494 Bachelor of Environmental Design (Abbreviation: BEnvDes) Course code: D3A This 3-year degree course is available, full time, on-campus by the Faculty of Science and Engineering and is available through the School of Architecture. Admission & prerequisites The Faculty considers for admission students who have a broad academic background and a demonstrated interest in, commitment to and aptitude for design. Apart from the University's general admission requirements, there are no additional prerequisites for the BEnvDes degree. HSC/TCE subjects preferably should not be restricted to a narrow discipline, but rather span two or more areas (e.g. art and science). A limited number of quota places is available to applicants who do not meet the normal University entry requirements. Such applicants will be required to attend an interview and present a folio of creative work and/or demonstrate skills and knowledge that suggest they could successfully undertake the course. Course details (2001) page 329 Course objectives The Bachelor of Environmental Design is seen primarily as a pre-professional course and thus aims to produce graduates whose creative abilities are developed to a level of competence necessary to gain admission to the Bachelor of Environmental Design with Honours, Bachelor of Architecture, and equivalent courses in the fields of architecture, town planning and related design areas. Examples of other areas in which students have continued their studies include: Landscape Architecture, Design Education, Building, Environmental Studies, Urban Design and Conservation. Career outcomes In order to gain work experience and skills in preparation for further studies, graduates of this course may find employment as professional assistants in professional offices, in local, in state or in national government offices. Professional recognition The course is a prerequisite for entry to the Bachelor of Architecture, which fulfils the academic requirements for membership of the Royal Australian Institute of Architects. Course structure The course structure is outlined in the following Schedule. Articulation Applicants who have completed the Associate Diploma of Applied Science (Building and Architecture), which is offered by TAFE Tasmania, will be granted one year of credit towards the degree. Applicants who have passed subjects or units in other approved courses (completed or otherwise) at another approved tertiary institution may have such studies credited towards the degree, provided that the Faculty may specify what more must be done to qualify for the degree. Schedule A Unit Title Year 1 Environmental Design 1A Environmental Design 1B History & Theory in Design 1 campus-sem weight code L1 L1 12.5% 12.5% KDA111 KDA112 L1 12.5% KDA114 Course details (2001) Building Technology in Design 1 Environmental Design 2A Environmental Design 2B History & Theory in Design 2 Building Technology in Design 2 Year 2 Design Studio 3 History & Theory in Design 3 Building Technology in Design 3 Specialised Studio 1 Design Studio 4 History and Theory in Design 4 Building Technology in Design 4 Specialised Studio 2 Year 3 Design Studio 5 History & Theory in Design 5 Building Technology in Design 5 Specialised Studio 3 Design Studio 6 History and Theory in Design 6 Building Technology in Design 6 Specialised Studio 4 page 330 L1 L2 L2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KDA115 KDA121 KDA122 L2 12.5% KDA124 L2 12.5% KDA125 L1 12.5% KDA211 L1 12.5% KDA212 L1 L1 L2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KDA213 KDA214 KDA221 L2 12.5% KDA222 L2 L2 12.5% 12.5% KDA223 KDA224 L1 12.5% KDA311 L1 12.5% KDA312 L1 L1 L2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KDA313 KDA314 KDA321 L2 12.5% KDA322 L2 L2 12.5% 12.5% KDA323 KDA324 Bachelor of Environmental Design with Honours (Abbreviation: BEnvDes(Hons)) Course code: D4A Course details (2001) page 331 This 1-year full-time or 2-year part-time course is offered on-campus by the Faculty of Science and Engineering and is available through the School of Architecture. Admission & prerequisites Before beginning their course of study for the degree of BEnvDes(Hons) students shall have – (a) (b) qualified for admission to the degree of Bachelor of Environmental Design (BEnvDes) in this University or qualified for admission to a degree in another design course in a tertiary institution approved by the Faculty of Science and Engineering; and achieved an Average Weighted Mark of at least 62.5% in the units of the final year of the BEnvDes course or an equivalent design course in another tertiary institution approved by the Faculty. Course objectives The course is designed to provide research training and to develop more specialised knowledge in selected areas of design which are especially relevant to today's environmental concerns and which are already incorporated in the programs of the School. Career outcomes The honours course is aimed specifically at students who wish to continue further studies in a related research field. Graduates of the course are eligible to enter a higher degree in most related fields. The School provides a Master of Design by research degree course. Course structure The course structure is outlined in the following Schedule. Schedule A Unit Title Dissertation 1 (BEnvDes Hons) Environmental Design (BEnvDes Hons) Design Theory (BEnvDes Hons) Dissertation 2 (BEnvDes Hons) campus-sem weight code L1 25% KDA471 Lf 37.5% KDA472 Lf 12.5% KDA473 L2 25% KDA481 Course details (2001) page 332 Bachelor of Geomatics (Abbreviation: BGeom) Course code: N3H This 4-year (minimum) full-time or part-time course is offered by the Faculty of Science and Engineering. The degree is available at Hobart and, subject to demand, the first year may also be offered at Launceston. Honours requires one year of additional study. Admission & prerequisites In addition to satisfying the normal University admission requirements, students entering first year Geomatics must have obtained a TCE Satisfactory Achievement (SA) result or higher in both Mathematics Stage 2 (*MT841) and Physical Sciences (*SC786). If applicants do not have these prerequisites they should discuss their qualifications with the degree coordinator. Interstate or overseas qualifications which are deemed equivalent by the University may also be accepted, subject to approval by the degree coordinator. Prerequisites are currently under review. Course objectives Geomatics is a term that describes a number of closely related disciplines. These include surveying, spatial and geographic information systems, photogrammetry, remote sensing, geodesy and cartography. The name Geomatics, derived from the French term 'science geomatique', has been adopted internationally to describe the scope of the spatial information sciences. In recent years, there has been an explosion of ideas and technology in Geomatics. Tools such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS), Global Positioning Systems (GPS), remote sensing, image processing, and digital photogrammetry have impacted dramatically, with GIS and GPS becoming ubiquitous. For graduates choosing a career in land surveying, these technologies will be as important as the traditional instruments such as the theodolite. For other students an understanding of these new technologies presents a wide range of career opportunities within the geomatics disciplines. The aim of the Bachelor of Geomatics is to prepare students for employment in vocations requiring a knowledge of the geomatic sciences. These include: Course details (2001) • • • • • page 333 land surveying – measuring and defining land ownership boundaries; spatial control for projects such as roads and bridges; spatial and geographic information systems – computer management, mapping and analysis of spatial information; photogrammetry and remote sensing – measurement, mapping and data analysis from aircraft and satellite sensors; geodesy and geodetic surveying – science of the measurement and mapping of the earth's surface using terrestrial and/or satellite data; hydrographic surveying – measuring and mapping in a marine environment. To achieve this aim, the course imparts to students: • • • • • • an understanding of the scientific principles underlying the geomatic sciences; a knowledge of the way in which these principles are implemented in current surveying and mapping technology; appropriate scientific analysis, problem solving and design skills; appropriate communication skills; a general knowledge of associated disciplines that will facilitate communication and professional interaction; and an appreciation of the professional standards and practices of relevant professional institutions. Career outcomes Graduates of the Spatial Information Systems stream who wish to proceed towards registration must complete the coursework units from the fourth year of the Land Surveying stream. Further information is available from the degree coordinator. Graduates may find employment in a wide range of areas including spatial data management, land administration, surveying and mapping, cadastral and engineering surveying, GIS industries, and geodetic agencies. Professional recognition The Bachelor of Geomatics is recognised by the Institution of Surveyors, Australia as providing qualification for graduate membership of the Institution. Corporate membership is granted after an approved period of professional experience. For registration as authorised surveyors by the Tasmanian Surveyors' Board, graduates of the Land Surveying stream must complete two years of supervised practical experience and pass the Board's oral and practical examinations. The Course details (2001) page 334 fourth year of the course counts towards the professional experience required by the Board. Course structure The Bachelor of Geomatics may be undertaken in either of two specialisations: Land Surveying or Spatial Information Systems. Each of these consists of four years of academic study, including a minimum of 20 weeks of professional experience in the final year. Students do not need to choose their specialisation until the final year. The course structure is outlined in the schedule which follows. Articulation Students may be granted credit if they have completed equivalent work in other institutions. For example, students who have successfully completed the TAFE Associate Diploma of Applied Science (Surveying) will be granted credit for 25% of the course requirements, including the units Geomatics 1 and Applied Physics. If students have 12 months or more of appropriate work experience they may also be granted credit for the Professional Experience component of the course. Note Candidates for the degree shall pass all of the units prescribed for either the Land Surveying stream or the Spatial Information Systems stream. However, the Degree Board Chair may, with the approval of the relevant Head of School, in a special case, allow a candidate to substitute another unit for a unit which has been prescribed. Schedule A Unit Title Hobart Year 1 (First Examination) Geomatics 1a – Introduction to Geomatics Geomatics lb – Studio Geomatics 1c – Surveying Programming and Problem Solving Software Process Calculus and Applications 1A campus-sem weight code H1~Lv1 H2~L2 12.5% 12.5% KGG145 KGG150 H2~Lv2 12.5% KGG155 H1~L1/2~B1 H2~L2~B2 12.5% 12.5% KXA151 KXA154 H1 12.5% KMA152 Course details (2001) Data Handling and Statistics 1 H1/2~L1/2~B2 12.5% Applied Physics H1 12.5% Launceston Year 1 (First Examination) Geomatics 1a – Introduction to Geomatics H1~Lv1 12.5% Geomatics lb – Studio H2~L2 12.5% Geomatics 1c – Surveying H2~Lv2 12.5% Programming and Problem Solving H1~L1/2~B1 12.5% Software Process H2~L2~B2 12.5% Mathematics I L1~D1 12.5% Data Handling and Statistics 1 H1/2~L1/2~B2 12.5% a 12.5% physics unit to be advised Year 2 (Second Examination) Geomatics 2a: Surveying H1 12.5% Geomatics 2b: Remote Sensing & Photogrammetry H1 12.5% Geomatics 2d: Transformations and Projections H2 12.5% Geomatics 2e: Analysis of Observations H2 12.5% Information Modelling H2~L2~B2 12.5% Geomatics 2f: Studio H2 12.5% Computational Mathematics & Linear Algebra (Geomatics) H1 12.5% Geomatics 2c: Introduction to GIS H1 12.5% Year 3 (Third Examination) Engineering Management and Law H16% N3H6.25% Business Strategies and Marketing for Engineers H26% N3H6.25% Environmental Remote Sensing H1 12.5% Geomatics 3e: Studio H2 12.5% Geomatics 3a: Surveying H1 12.5% Geomatics 3b: Remote Sensing & Photogrammetry H1 12.5% Geomatics 3c: Advanced Geographic Information Systems (GIS) H2 12.5% Geomatics 3d: Geodesy H1 12.5% page 335 KMA153 KYA171 KGG145 KGG150 KGG155 KXA151 KXA154 KMA171 KMA153 KGG220 KGG230 KGG260 KGG270 BSA102 KGG280 KMA265 KGG240 ACM462 AEA461 KGA365 KGG355 KGG320 KGG330 KGG340 KGG350 Course details (2001) Earth Sciences H2 Year 4 (Fourth Examination) The following unit is common to both streams Professional Experience H1/2 Land Surveying Stream Municipal Engineering for Surveyors H1 Land Development Planning H1 Land Law and Cadastral Studies H1 Surveying Practice H1 Spatial Information Systems Stream Either BSA203 or KCA342 Information Management H2~L2~B2 Image Processing and Computer Vision H2 Advanced Spatial Data Analysis H2 GIS Application Development H2 Geographic Information Systems Project H1/2 page 336 12.5% KGG360 50% KGG401 12.5% 12.5% ACM405 KGG405 12.5% 12.5% KGG407 KGG425 12.5% BSA203 12.5% KCA342 12.5% KGG435 12.5% KGG440 12.5% KGG445 Bachelor of Geomatics with Honours (Abbreviation: BGeom(Hons)) Course code: N4H This 1-year full-time or 2-year part-time course is offered by the Faculty of Science and Engineering at Hobart. Admission & prerequisites To be eligible to enrol for the degree applicants must either have qualified for admission to the degree of Bachelor of Geomatics in this University or have qualified in another university or tertiary institution for a degree deemed by the Faculty of Science and Engineering to be equivalent to that degree. In either case, the standard of pass must be of sufficient merit to satisfy the Faculty of Science and Engineering. Course objectives The course objectives are: Course details (2001) • • • • page 337 to provide advanced in-depth knowledge in a single area of spatial information science; to provide opportunity for training in research; to prepare students for postgraduate research in the Master of Spatial Information Science and PhD programs as well as for employment in research organisations; and to provide advanced courses in selected areas of spatial information science Career outcomes The Honours course provides students with advanced skills and research experience in a specialised area of Geomatics or surveying. Graduates are likely to find employment in Commonwealth or State government agencies, or large private organisations. Professional recognition The Bachelor of Geomatics with Honours is recognised by the Institution of Surveyors, Australia providing qualification for graduate membership of the Institution. Corporate membership is granted after an approved period of professional experience. Course structure The Honours course consists of lectures, project work and thesis as prescribed by the degree coordinator for the Centre of Spatial Information Science. Lectures and project work will be appropriate for the particular research topic chosen and will constitute 50% of the assessment. With the agreement of the degree coordinator, candidates may select from Group 2, 3 and 4 units offered by the Faculty of Science and Engineering. Project work may consist of a specific set of reading programs or coursework as specified by the degree coordinator. The coursework and thesis topics can be selected from the following areas of specialisation: • • • • • Advanced Photogrammetry Advanced GIS Advanced Geodesy Advanced Adjustment Theory Advanced Instrumentation and Techniques. The overall enrolment code for full-time students is KGG510 and for part-time students KGG515. See KGG510/511on page xx. Course details (2001) page 338 Bachelor of Natural Environment and Wilderness Studies (Abbreviation: BNatEnvWildStud) Course code: S3T Course coordinator: Professor J Kirkpatrick This three years full-time or six years part-time course is offered internally at Hobart and Launceston. The first year of the course is also available at the North-West Centre. Admission & prerequisites Satisfaction of the University's minimum entry requirements for degree courses. Subject prerequisites apply within the course. Course objectives The Bachelor of Natural Environment and Wilderness Studies is for students who are interested in gaining a wide interdisciplinary understanding of natural environments and wilderness and developing knowledge, skills and techniques that are useful in employment or other activities related to natural environments and wilderness. The structure of the degree ensures that students gain a broad understanding of the field, while being able to specialise in areas of interest to them. The program develops a wide range of general abilities including: • • • • • communication skills; data collection skills; analytical skills; information retrieval, manipulation and presentation skills; the ability to work across traditional discipline areas. Career outcomes This interdisciplinary course is designed to provide students with the opportunity to develop knowledge and skills that will help them gain employment related to natural environments and wilderness. Opportunities for such employment exist in a wide variety of areas such as nature-based tourism, natural area management and natural area interpretation. The broad nature of Course details (2001) page 339 the course also provides more general employability in the same way as the Bachelor of Science or Bachelor of Arts. Course structure Students must satisfactorily complete appropriate units with a total weighting of 300%. The first 100% (i.e. the first year) must be made up of level 100 units with at least 25% taken from those listed in Schedule A and 25% from those listed in Schedule B. The remaining 50% of first year units should be chosen from either schedule A or B or any first year units not so listed, with a maximum of 25% from unlisted units. The remaining 200% must be made up of level 200 and level 300 units chosen within the following constraints: at least 25% must be taken from each of schedules C, D, E and F; no more than 25% of units in total should be taken outside schedules C, D, E and F; at least 75% of units should be at level 300. Articulation Credit for relevant units will be given to transferring students. Another related course offered by this University is the Bachelor of Science (Natural Environment and Wilderness Management) with Honours. Schedule A Unit Title campus-sem Sustainable Resource Management H2~B2 Geology 1 Hf Geography and Environmental Studies 1 Hf Fauna of Tasmania L1~B1 Genetics L2~B2 Chemistry 1 Lf~Bf Chemistry for Life Sciences L1 Introduction to Biochemistry L2 The Physical Environment L2~B2~D2 Data Handling and Statistics 1 H1/2~L1/2~B2 Botany 1G Hf Botany 1E Hf Aquatic Ecology I L2 weight code 12.5% 25% KLA115 KEA100 25% 12.5% 12.5% 25% KGA100 KJB113 KJB122 KJC103 12.5% KJC161 12.5% 12.5% KJC162 KJG102 12.5% 25% 25% 12.5% KMA153 KPA150 KPA151 KQA121 Course details (2001) Zoology 1G Zoology 1E Chemistry 1A Chemistry 1B Natural Vegetation of Tasmania Applied Physics page 340 Hf Hf Hf Hf 25% 25% 25% 25% KZA150 KZA151 KRA110 KRA130 H2 H1 12.5% 12.5% KPA152 KYA171 campus-sem weight code H1/2~L1/2~B1 12.5% BMA101 H1 12.5% FST101 H2 12.5% FST102 L1~B1~D1 H1 H2~L2~B2~D2 H1~L1~B1~D1 H2~L2~B2~D2 H13 H2/3 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HEA101 HEA103 HEA104 HGA101 HGA102 HPA101 HPA102 L1~D1 12.5% HPA181 L2~D2 12.5% HPA182 H1~L1~B1 12.5% HSG101 H2~L2~B2 Hf Lf~Bf 12.5% 25% 25% HSG102 HTA100 HTA101 Hf 25% KGA100 Hf 25% KGA101 L1~B1~D1 12.5% KJG101 weight code Schedule B Unit Title Introduction to Management Introduction to Art and Design Theory 1A Introduction to Art and Design Theory 1B Introduction to English: Australian Literature English 1A English 1B Sociology A Sociology B Philosophy 1A Philosophy 1B Introduction to Philosophy 1A Introduction to Philosophy 1B Introduction to Government A Introduction to Government B History 1 History 1 Geography and Environmental Studies 1 Geography and Environmental Studies 1A Population and Urbanisation Schedule C Unit Title campus-sem Course details (2001) Agricultural Geology & Soil Science Introduction to Plant Diseases Insect Diversity and Function Geology 2 Fossils and Environments Through Time Sedimentary Environments Geology for Environmental Scientists Biogeography and Climatology Microclimatology Forest Ecosystems Australian Natural Environments Environmental Geomorphology Botany 2 Alternative Terrestrial Lifestyles – The Fungi Aquatic Botany Evolution and Biodiversity Field Botany Plant Ecology General Microbiology Aquatic Ecology II Applied and Environmental Microbiology Chemistry for Life Sciences Zoology 2 Antarctic Ecology Environmental Adaptation Evolutionary Biology & Biogeography Freshwater Ecology Marine Ecology page 341 H1 12.5% KLA213 [na] 12.5% KLA287/387 H1 Hf 12.5% 33.33% KLA254/354 KEA200 H1 H1 16.67% 12.5% KEA266 KEA338 Hf 25% KEA365 H1 H2 L2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KGA209 KGA321 KJB227 L1~D1 12.5% KJG201 L1~D1 Hf 25% 33.33% KJG301 KPA200 [na] H1 12.5% 12.5% KPA371 KPA372 H2 H3 H1 L1 L2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KPA374 KPA375 KPA379 KQA207 KQA212 L2 12.5% KQA218 H1 Hf H2 H2 16.67% 33.33% 12.5% 12.5% KRA205 KZA210 KZA351 KZA352 H2 H2 H1 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KZA353 KZA355 KZA356 weight 12.5% code FST205/305 Schedule D Unit Title Picturing the Wilderness campus-sem H3 Course details (2001) Art, Natural Environment and History Art, Natural Environment and Wilderness Wilderness and Natural Environment Dynamics of Indigenous Cultures Tourism, Sport and Leisure Sociology of Nature Social Ecology Environmental Ethics Ecophilosophy Australian Environmental Policy Global Environmental Policy Asian Environmental Justice Sex, Drugs and Toxic Waste: The Politics of Regulation Sustainable Communities and Local Environments Literature and Environment Historical Geography page 342 H3 12.5% FSZ250/350 H1 12.5% FSZ251/351 L1 12.5% FFA235/335 H1~Lv1 12.5% HAB253/353 H1 [na] H2~L2 H1 [na] 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HGA251/351 HGA261/361 HGE203/303 HPA277/377 HPA278/378 [na] 12.5% HSD230/330 H2~L2 12.5% HSD229/329 [na] 12.5% HSD239/339 [na] 12.5% HSD207/307 H2 12.5% KGA254/354 H1 H2 12.5% 12.5% KGA272/372 KGA240/340 weight 12.5% 12.5% code KEA348 KGA331 12.5% KGA332 12.5% KGA227 12.5% KGA327 12.5% KGA381 12.5% 12.5% KGA278/378 KGA223/323 Schedule E Unit Title campus-sem Environmental Geology H2 Vegetation Management H1 Fauna Conservation Management H1 Conservation Geomorphology [a] H2 Conservation Geomorphology [a] H2 Environmental Impact Assessment and Decision Making H2 Wilderness and Natural Area Management: Natural and Cultural Values H2 Environmental Management H1 Course details (2001) page 343 Agroforestry Lf 25% Natural Resources Management L2~D2 12.5% Fisheries & Wildlife Management H1 12.5% [a] Students enrol in either KGA227 or KGA327, not KGA285 KJB307 KJG202 KZA354 Schedule F Unit Title campus-sem Social & Environmental Accounting H2 Strategic Management H2~L2 Management and the Natural Environment [na] Social and Political Research L1~H1 Survey Research H3 Environmental Design 1B L1 Qualitative Research Methods H1~L2 Environmental Remote Sensing H1 Natural Environment Field Techniques H3~L3~B3 Introduction to GIS H1 Field Mapping and Measurement H2 Advanced Geographic Information Systems (GIS) H2 Social Psychology [na] Data Handling and Statistics 2 H2 Scientific Analysis and Presentation for Aquaculture L1 Analytical & Environmental Chemistry H2 Quantitative Methods in Biology H1 weight code 12.5% 12.5% BFA207/307 BMA302 12.5% BMA272/372 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% HGA203/303 HGA204/304 KDA112 12.5% HGA230/330 12.5% KGA365 12.5% 12.5% KGA213 KGG245 12.5% KGG275 12.5% 12.5% KGG345 KHA207/307 16.67% KMA253 12.5% KQA302 16.67% KRA203 12.5% KZA357 Bachelor of Science (Abbreviation: BSc) Course details (2001) page 344 Course code: S3G This 3-year (minimum) full-time course is offered by the Faculty of Science and Engineering and is available at Hobart. Subject to attendance and timetable requirements, part-time studies may be available. Admission & prerequisites Minimum University entrance requirements and a satisfactory achievement (SA) in any two of the following: *MT843 Mathematics Stage 3 (or *MT841 Mathematics Stage 2 or *MT730 Mathematics Applied); *IF862 Computer Science; *CH856 Chemistry; *GL876 Geology; *GG833 Geography (or *EV846 Environmental Science); *PH866 Physics; *BY826 Biology; *SC786 Applied Science-Physical Sciences (if neither Physics nor Chemistry counted) OR a TCE score of 80 or more for applicants not having two of the preceding TCE units. Subject (unit) prerequisites also apply. Course objectives The course aims to: • • • • provide students with opportunities to acquire knowledge, attitudes and skills in a range of basic physical, computational, mathematical, earth and life sciences; introduce students to scientific method through a range of disciplines; provide graduates with advanced knowledge in one or more of the science disciplines; and meet the needs of industry, business and government agencies. Career outcomes Graduates of the Bachelor of Science can expect to find employment in a wide variety of positions. Please refer to the following discipline entries for more specific information: Biochemistry on page C-xx Chemistry on page C-xx Computing on page C-xx Geography and Environmental Studies on page C-xx Geology on page C-xx Mathematics on page C-xx Course details (2001) page 345 Microbiology/Immunology on page C-xx Plant Science on page C-xx Physics on page C-xx Psychology on page C-xx Zoology on page C-xx Professional recognition Graduates of the BSc are eligible for membership of a number of professional organisations. Specific details are provided under individual discipline entries. Course structure In order to gain the award of Bachelor of Science students must gain 300% from Schedule A provided that: • • • • • • • • • • at least 75% is from Group 1 units listed in Schedule C which consists of 25% combinations offered by three different Schools (students can study 50% from mathemtics to satisfy two 25% requirements from two Schools); at least 100% and not more than 125% is from units in Groups 1 and 1A; not more than 25% is from Group 1A units; at least 66.67% is from Group 2 units listed in Schedule C which consists of combinations of 33.33% (37.5% for Computer Science) offered by two different Schools (students can study 66.67% from mathemtics to satisfy this requirement); not more than 66.67% is from Group 2 and Group 2A units offered by any one School; not more than 37.5% is from Group 2A units; at least 75% is from units listed as Groups 3 and 3A; at least 50% of full passes is from Group 3 units listed in Schedule C as offered by one School; not more than 50% is from units listed as Group 3A; and not more than 37.5% is counted from units in which terminating passes have been awarded. In summary, students must gain 300%, studying at least 4 year-1 units to the value of between 100% and 125%; year-2 units to the value of between 66.67% and 125%; and year-3 units to the value of between 75% and 133.33%. Year-3 majors are based on first and second-year prerequisites. Certain prerequisites and core enrolments must be met. All programs must include a minimum of three Group 1 core units and two Group 2 core units as listed in Schedule C. Articulation Course details (2001) page 346 A successful first year may lead to the five-year combined degrees with Law or Engineering. Credit is possible for studies completed in some TAFE diplomas and in other tertiary studies. Majors Candidates for the BSc can major (3 years of studies) in one or two of the following fields of specialisation: • • • • • • • • • • • Biochemistry Chemistry Computer Science Geography & Environmental Studies Geology Mathematics Microbiology/Immunology Physics Plant Science Psychology Zoology Specimen courses Candidates for the BSc can complete four-year specimen courses which are detailed in Schedule D in the following fields of specialisation: • • • • Economic Geology Forest Ecology Marine, Freshwater and Antarctic Biology Natural Environment and Wilderness Management Schedule D should be read in conjunction with Schedules A and C. The Specimen Courses, which follow the Bachelor of Science Schedule D, detail a number of three-year combinations. Many other combinations are possible. Students should note that all specimen courses must meet the degree requirements of the BSc which are summarised under 'Course structure'. Schedule A Unit Title Year 1 (Group 1) Chemistry Chemistry 1A Chemistry 1B Computer Science campus-sem weight code Hf Hf 25% 25% KRA110 KRA130 Course details (2001) page 347 Programming and Problem Solving H1~L1/2~B1 12.5% KXA151 Software Process H2~L2~B2 12.5% KXA154 Computer Science 1 Hf 25% KXA150 Geography & Environmental Studies Geography and Environmental Studies 1 Hf 25% KGA100 Geology Geology 1 Hf 25% KEA100 Mathematics Calculus and Applications 1 Hf 25% KMA150 Calculus and Applications 1A H1 12.5% KMA152 Data Handling and Statistics 1 H1/2~L1/2~B2 12.5% KMA153 Calculus and Applications 1B H2 12.5% KMA154 Mathematics for Computer Science 1 H1 12.5% KMA155 Calculus and Applications 1S H1 12.5% KMA156 Essential Mathematics H1 12.5% KMA157 Physics Physics 1A H1 12.5% KYA101 Physics 1B H2 12.5% KYA102 Applied Physics H1 12.5% KYA171 Biological Physics [na] 12.5% KYA172 Plant Science Botany 1G [a] Hf 25% KPA150 Botany 1E Hf 25% KPA151 Psychology Psychology 1A H1~L1~B1 12.5% KHA101 Psychology 1B H2~L2~B2 12.5% KHA102 Zoology Zoology 1G Hf 25% KZA150 [a] Zoology 1E Hf 25% KZA151 Year 1 (Group 1A) Students are permitted to enrol in not more than 25% of first-year units offered under other degree courses, except that there are some limitations for units offered by scientific-related disciplines, including Engineering, Medicine (including Pharmacy), and Agricultural Science. A list of permitted units is available from the Faculty office. Sustainable Resource Management H2~B2 12.5% KLA115 Natural Vegetation of Tasmania H2 12.5% KPA152 Course details (2001) page 348 Computer Organisation and Architecture H1~L1~B1 12.5% KXA152 Computer Applications H1~L1~B1 12.5% KXA153 Professional Computing H2~L2~B2 12.5% KXA155 Multimedia and Web Applications H2~L2~B2 12.5% KXA156 Astronomy H1 12.5% KYA181 [a] Students who wish to study Botany and Zoology together in the one year must study KPA150 and KZA151. Unit Title campus-sem Year 2 (Group 2) Biochemistry Biochemistry and Microbiology 2 Hf Chemistry Chemistry 2 Hf Analytical & Environmental Chemistry H2 Chemistry for Life Sciences H1 Computer Science Microprocessors and Data Acquisition H2 Algorithms and Metrics H1~L1 Artificial Intelligence H1~L1 Software Design H2~L2 Operating Systems H2~L2 Geography & Environmental Studies Geography and Environmental Studies 2 [a] Hf Natural Environment Field Techniques H3~L3~B3 Introduction to GIS [b] 0% Conservation Geomorphology H2 Biogeography and Climatology H1 Geography of Asia H1 The Global Space Economy H2 Environmental Management H1 Historical Geography H2 Urban Planning: Space, Place and Society H1 weight code 33.33% CBA250 33.33% KRA200 16.67% KRA203 16.67% KRA205 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KNE232 KXA251 KXA252 KXA253 KXA254 33.33% KGA200 0% KGA287 KGA286 0% KGA285 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% KGA290 KGA291 KGA292 KGA293 KGA294 0% KGA295 Course details (2001) page 349 Wilderness and Natural Area Management: Natural and Cultural Values H2 0% KGA296 Sustainable Communities and Local Environments H2 0% KGA298 Geology Geology 2 Hf 33.33% KEA200 Introduction to Geophysics & Computer Applications H2 16.67% KEA222 Fossils and Environments Through Time H1 16.67% KEA266 Mathematics Algebra and Applications 2 H2 16.67% KMA251 Calculus and Applications 2 H1 16.67% KMA252 Data Handling and Statistics 2 H2 16.67% KMA253 Mathematical Analysis & Applications 2 H2 16.67% KMA254 Operations Research 2 H1 16.67% KMA255 Physics Physics 2A H1 16.67% KYA201 Physics 2B H2 16.67% KYA202 Plant Science Botany 2 Hf 33.33% KPA200 Psychology Psychology 2 (Science) Hf 33.33% KHA200 Zoology Zoology 2 Hf 33.33% KZA210 Year 2 (Group 2A) Students are permitted to enrol in not more than 37.5% of second-year units offered under other degree courses, except that there are some limitations for units offered by scientific-related disciplines, including Engineering, Medicine (including Pharmacy) and Agricultural Science. A list of permitted units is available from the Faculty office. Agricultural Science Field Agriculture H2 12.5% KLA215 Animal Production Systems [na] 12.5% KLA220/320 Horticultural Production Systems H1 12.5% KLA242/342 Crop and Pasture Production H2 12.5% KLA250/350 Insect Diversity and Function H1 12.5% KLA254/354 Course details (2001) page 350 Introduction to Plant Diseases [na] 12.5% KLA287/387 Fundamentals of Soil Science [na] 12.5% KLA297/397 Geography & Environmental Studies Geography of Asia H1 12.5% KGA202/302 The Global Space Economy H2 12.5% KGA208/308 Biogeography and Climatology H1 12.5% KGA209 Natural Environment Field Techniques H3~L3~B3 12.5% KGA213 Environmental Management H1 12.5% KGA223/323 Conservation Geomorphology H2 12.5% KGA227 Historical Geography H2 12.5% KGA240/340 Urban Planning: Space, Place and Society H1 12.5% KGA253/353 Sustainable Communities and Local Environments H2 12.5% KGA254/354 Literature and Environment H1 12.5% KGA272/372 Wilderness and Natural Area Management: Natural and Cultural Values H2 12.5% KGA278/378 Introduction to GIS H1 12.5% KGG245 Field Mapping and Measurement H2 12.5% KGG275 Note: Units coded KGA2xx/3xx or KLA2xx/3xx may be studied as Group 2A units or as Group 3A units. When enrolling in one of these units as a Group 2A unit, use KGA2xx (e.g. KGA202 Geography of Asia) or KLA2xx. If enrolling in the unit as a Group 3A unit, use KGA3xx or KLA3xx. [a] Students studying KGA200 must enrol in three 0% units. A minimum of two must be studied from KGA285, KGA286, KGA287 and KGA290. [b] For details of this unit, contact the School of Geography and Environmental Studies Unit Title Year 3 (group 3) Biochemistry Molecular Biochemistry: Techniques and Theory Chemistry Chemistry 3A campus-sem weight code Hf 50% CBA327 Hf 25% KRA301 Course details (2001) Chemistry 3B Instrumental Analytical Chemistry Biosynthesis & Function of Natural Products Computer Science Software Engineering Project Software Systems Programming Paradigms Networks and Protocols Intelligent Systems Image Processing and Computer Vision Computer Architecture Communications and Data Networks Geography & Environmental Studies Microclimatology Conservation Geomorphology Vegetation Management Fauna Conservation Management Environmental Remote Sensing Environmental Impact Assessment and Decision Making Advanced Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Geology Geology 3 Computers in Geoscience Ore Deposit Geology Sedimentary Environments Exploration Geophysics Ore Deposit Geochemistry Environmental Geology Geology for Geophysicists Geology for Environmental Scientists Mathematics Computational Techniques 3 Algebra and Applications 3 Analysis 3 page 351 Hf 25% KRA302 H2 12.5% KRA303 H1 12.5% KRA305 Hf H1 H2 H1 H1 25% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KCA300 KCA311 KCA312 KCA321 KCA341 H2 H1 12.5% 12.5% KCA342 KCA343 H2 12.5% KCA354 H2 12.5% KGA321 H2 H1 12.5% 12.5% KGA327 KGA331 H1 12.5% KGA332 H1 12.5% KGA365 H2 12.5% KGA381 H2 12.5% KGG345 Hf H2 H1 H1 H1 H2 H2 Hf 50% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 25% KEA300 KEA332 KEA336 KEA338 KEA342 KEA346 KEA348 KEA355 Hf 25% KEA365 H1 12.5% KMA350 H1 H2 12.5% 12.5% KMA351 KMA352 Course details (2001) Data Handling and Statistics 3 Mathematical Analysis & Applications 3 Operations Research 3 Principles of Statistics 3 Topics in Advanced Mathematics 3 Topics in Applied Statistics 3 Topics in Applied Algebra Microbiology (Agricultural Science) Microbial Ecology Pathology Medical Microbiology and Immunology Physics Physics 3A Physics 3B Physics 3C Dynamical Systems and Chaos Fluid Mechanics Plant Science Alternative Terrestrial Lifestyles – The Fungi Aquatic Botany Cell Biology Evolution and Biodiversity Field Botany Genetics Molecular Evolution Plant Science Research Plant Ecology Psychology Assessment and Research Methods Human Neuroscience Psychophysiology & Emotion Clinical Psychology Cognition and Memory Social Psychology [c] Advanced Research Methods page 352 H1 12.5% KMA353 H1 H2 12.5% 12.5% KMA354 KMA355 H2 12.5% KMA356 H2 12.5% KMA357 H1 H2 12.5% 12.5% KMA358 KMA359 Hf 25% KLA309 Hf 25% CJA308 H1 H2 H2 25% 12.5% 12.5% KYA301 KYA302 KYA303 H2 [na] 12.5% 12.5% KYA314 KYA315 [na] H1 H1 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KPA371 KPA372 KPA373 H2 H3 H1 H2 H1/2 H1 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KPA374 KPA375 KPA376 KPA377 KPA378 KPA379 H1 H1 12.5% 12.5% KHA301 KHA303 H1 H1 H2 [na] H2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KHA304 KHA305 KHA306 KHA207/307 KHA308 Course details (2001) page 353 Health & Rehabilitation Psychology [c] H1 12.5% KHA209/309 Peace, Conflict & Law [c] H2 12.5% KHA212/312 Learning & Skilled Performance H2 12.5% KHA314 Individual Differences H1 12.5% KHA318 Educational Psychology H1 12.5% KHA319 Zoology Antarctic Ecology H2 12.5% KZA351 Environmental Adaptation H2 12.5% KZA352 Evolutionary Biology & Biogeography H2 12.5% KZA353 Fisheries & Wildlife Management H1 12.5% KZA354 Freshwater Ecology H2 12.5% KZA355 Marine Ecology H1 12.5% KZA356 Quantitative Methods in Biology H1 12.5% KZA357 Reproductive Biology: Strategies and Mechanisms H1 12.5% KZA358 Year 3 (Group 3A) Students are permitted to enrol in not more than 50% of third-year units offered under other degree courses, except that there are some limitations for units offered by scientific-related disciplines, including Engineering, Medicine (including Pharmacy) and Agricultural Science. A list of permitted units is available from the Faculty office. Agricultural Science See Group 2A Agricultural Science units. all units which have both 200/300 level codes may be used. Students should use the KLA3xx code for enrolling as a Group 3A unit. Insect Ecology and Behaviour H2 12.5% KLA314/414 Plant Nutrition & Soil Fertility H2 12.5% KLA318/418 Crop Health Management H1 12.5% KLA329/429 Agronomy H1 12.5% KLA331/431 Horticultural Science H2 12.5% KLA365/465 Soil and Land Resources [na] 12.5% KLA381/481 Geography & Environmental Studies See Group 2A Geography & Environmental Studies units. All units which have both 200/300 level codes may be used. Students should use the KGA3xx code for enrolling as a Group 3A unit. [c] Students enrol at level 300 (eg KHA307 not KHA207) Bachelor of Science – Schedule B Course details (2001) page 354 Note: Students are advised that information concerning mutual exclusions (contained in Schedule B) of the Bachelor of Science course specifications is held in the Faculty Office. Bachelor of Science – Schedule C – Core units School Group 1 core Group 2 core Group 3 Major Biochemistry CBA250 CBA327 Chemistry Stream 1 KRA110 KRA200 50% from: KRA301, KRA302, KRA303, KRA305 Chemistry Stream 2 KRA110 or KRA130 KRA203 and KRA205 KRA302, KRA303, and KRA305 Computer Science KXA150 or (KXA151 and KXA154) Any three of KNE232, KXA251, KXA252, KXA253, KXA254 50% from KCA300, KCA311, KCA312, KCA321, KCA341, KCA342, KCA343, KCA354 Geography & Environmental Studies KGA100 KGA200 Any four level 300 KGA units. Three must be selected from KGA321, KGA327, KGA331, KGA332, KGA365, KGA381, KGG345 Geology KEA100 KEA200 50% from: KEA300, KEA332, KEA336, KEA338, KEA342, KEA346, KEA348, KEA355, KEA365 Mathematics KMA150 or any two units from KMA152, KMA153, KMA154, KMA155, KMA156, KMA157 Any two units from KMA251, KMA252, KMA253, KMA254, KMA255 Any four units from KMA350, KMA351, KMA352, KMA353, KMA354, KMA355, KMA356, KMA357, KMA358, KMA359 Microbiology/Immunology See Biochemistry KLA309 and CJA308 Physics (KYA101 and KYA102) or (KYA171 and KYA172) KYA201 and KYA202 KYA301 and KYA302 plus one unit from KYA303 , KYA314, KYA315 Plant Science KPA150 or KPA151 KPA200 Any four units from KPA371, KPA372, KPA373, KPA374, KPA375, KPA376, KPA377, KPA378, KPA379 Psychology KHA101 and KHA102 KHA200 KHA301 plus three of KHA303, KHA304, KHA305, KHA306, KHA307, KHA308, KHA309, KHA312, KHA314, KHA318, KHA319 Course details (2001) page 355 Zoology KZA150 or KZA151 KZA210 Any four units from KZA351, KZA352, KZA353, KZA354, KZA355, KZA356, KZA357, KZA358 Bachelor of Science Four-year Honours programs Schedule D 1. Forest Ecology Course Structure Major code: KFE In the first 3 years students need to pass course units to a total of 300 percent. This is achieved by a mix of compulsory and optional units to a value of 100 percent in each year. The course coordinator will assist with the planning of the student's course. A special unit (Plant Science Research KPA378) will be offered to Forest Ecology students in third year. This will involve a series of lectures presented by specialist foresters and a research project in one of the disciplines outlined. Tutorials will be held for all Forest Ecology students near the middle of semesters 1 and 2 (students will be notified of timing). These will provide an opportunity for students to discuss the course and new developments in Forestry in Australia. Unit Title campus-sem Year 1 Zoology 1E Hf Botany 1G Hf Data Handling and Statistics 1 H1/2~L1/2~B2 and the balance from: Either KRA110 or KRA130 Chemistry 1A Hf Chemistry 1B Hf Programming and Problem Solving H1~L1/2~B1 Software Process H2~L2~B2 Geography and Environmental Studies 1 Hf Calculus and Applications 1B H2 [a] Geology 1 Hf Year 2 Botany 2 Hf and the balance from: weight code 25% 25% KZA151 KPA150 12.5% KMA153 25% 25% KRA110 KRA130 12.5% 12.5% KXA151 KXA154 25% KGA100 12.5% 25% KMA154 KEA100 33.33% KPA200 Course details (2001) page 356 Agricultural Geology & Soil Science [a] H1 12.5% KLA213 Insect Diversity and Function [b] H1 12.5% KLA254/354 Introduction to Plant Diseases [b] [na] 12.5% KLA287/387 Fundamentals of Soil Science [b] [na] 12.5% KLA297/397 Zoology 2 Hf 33.33% KZA210 Biochemistry and Microbiology 2 Hf 33.33% CBA250 Biogeography and Climatology H1 12.5% KGA209 Conservation Geomorphology [b] H2 12.5% KGA227 Data Handling and Statistics 2 H2 16.67% KMA253 Mathematical Analysis & Applications 2 H2 16.67% KMA254 or approved Computer Science units Year 3 Field Botany H3 12.5% KPA375 Plant Ecology H1 12.5% KPA379 Genetics H1 12.5% KPA376 Plant Science Research H1/2 12.5% KPA378 Either KPA377 or KZA357 Molecular Evolution H2 12.5% KPA377 Quantitative Methods in Biology H1 12.5% KZA357 and the balance from: Insect Diversity and Function [c] H1 12.5% KLA254/354 Introduction to Plant Diseases [c] [na] 12.5% KLA287/387 Fundamentals of Soil Science [c] [na] 12.5% KLA297/397 Agricultural and Forest Pathology [c] [na] 12.5% KLA346/446 [c] Soil and Land Resources [na] 12.5% KLA381/481 Evolution and Biodiversity H2 12.5% KPA374 Vegetation Management H1 12.5% KGA331 Environmental Impact Assessment and Decision Making H2 12.5% KGA381 or approved Computer Science and Mathematics (especially statistics) units Year 4 Course code for fourth year: S4J Course details (2001) page 357 Unit enrolment codes: KPA460 Forest Ecology (Honours) Full time; KPA461 Forest Ecology (Honours) Part time. Students who have completed a BSc and have satisfied the course prerequisites will be permitted to enrol in Honours in Forest Ecology provided they have achieved an adequate standard, normally at least 50% in third year units, and a suitable project and supervisor are available. The fourth year of the course, the 'Honours year', includes the following main components: 1. A research project of 9 months duration. This would normally be carried out in the School of Plant Science but after consultation with the course coordinator may be carried out in other Schools such as Zoology, Agricultural Science, Geography and Environmental Studies or Mathematics and Physics. Where appropriate, scientists from outside the University may act as co-supervisors, especially if the project necessitates work being undertaken in laboratories of other institutions. 2. A reading thesis based on a literature-based review or other coursework as appropriate. 3. Attendance at seminars given by research scientists working in the field (Plant Science and CRC seminars). [a] Geology 1 and Agricultural Geology & Soil Science are mutually exclusive because of overlap in subject matter [b] Students use level 200 enrolment code (eg KLA287) [c] Students use level 300 enrolment code (eg KLA354) Schedule D 2. Marine, Freshwater and Antarctic Biology Course Structure Major code: KAB In the first three years of the course students need to pass course units to a total of 300%. This is achieved by taking a mix of compulsory and optional units to a value of 100% in each year. Unit Title Year 1 Botany 1G Zoology 1E Either KRA110 or KRA130 Chemistry 1A Chemistry 1B and the balance from: Physics 1A Physics 1B campus-sem weight code Hf Hf 25% 25% KPA150 KZA151 Hf Hf 25% 25% KRA110 KRA130 H1 H2 12.5% 12.5% KYA101 KYA102 Course details (2001) page 358 Geography and Environmental Studies 1 Hf 25% KGA100 Geology 1 Hf 25% KEA100 Calculus and Applications 1 Hf 25% KMA150 Calculus and Applications 1A H1 12.5% KMA152 Calculus and Applications 1B H2 12.5% KMA154 Data Handling and Statistics 1 H1/2~L1/2~B2 12.5% KMA153 Computer Science 1 Hf 25% KXA150 Programming and Problem Solving H1~L1/2~B1 12.5% KXA151 Software Process H2~L2~B2 12.5% KXA154 Year 2 Botany 2 Hf 33.33% KPA200 Zoology 2 Hf 33.33% KZA210 and either CBA250 or (KRA205 and KRA203) or KRA200 or 33.3% mathematics Biochemistry and Microbiology 2 Hf 33.33% CBA250 Chemistry for Life Sciences H1 16.67% KRA205 Analytical & Environmental Chemistry H2 16.67% KRA203 Chemistry 2 Hf 33.33% KRA200 Calculus and Applications 2 H1 16.67% KMA252 and another mathematics unit Year 3 Aquatic Botany H1 12.5% KPA372 Antarctic Ecology H2 12.5% KZA351 Marine Ecology H1 12.5% KZA356 Freshwater Ecology H2 12.5% KZA355 plus 12.5% of Zoology units (it is strongly recommended that students choose one of Fisheries and Wildlife Management or Quantitative Methods in Biology) or 37.5% botany units to complete a major and a further 50% selected from units in botany, zoology, microbiology, biochemistry, chemistry and mathematics after consultation with the course coordinator. Year 4 Course code for fourth year: S4K Unit enrolment codes: KZA450 Marine, Freshwater and Antarctic Biology (Honours) Full time KZA451 Marine, Freshwater and Antarctic Biology (Honours) Part time The fourth (Honours) year of the course, includes the following main components: Course details (2001) • • • • page 359 Cruise on a Fisheries Training ship to learn a range of fish capture techniques; Directed studies; Reading project, in which students will carry out a literature-based review and prepare a critical appraisal in the form of a dissertation; and A research project of about six months duration which is supervised by a member of the University staff. Where appropriate, scientists from outside the University may act as co-supervisors, especially if the project necessitates work being undertaken in laboratories of other institutions. Schedule D 3. Natural Environment and Wilderness Management Course Structure Major code: KNE The course is necessarily multidisciplinary; involving the following components: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Ecosystem pattern and process; Ecosystem and wilderness management; Cultural heritage management in natural areas; People management in natural areas; Natural area ecological engineering – track and road construction, waste management, water management; Information systems in natural area management – remote sensing, spatial data manipulation, work and finance management systems; Interpretation – literature and environment, art and environment, music and environment, environmental design, interpretation skills; Philosophy, politics, law and administration of natural environment and wilderness. The following schedule provides students with an opportunity to develop expertise in all these areas and also ensures that they gain expertise in the core areas related to natural environment and wilderness management. Unit Title Year 1 Geography and Environmental Studies 1 Botany 1G Zoology 1E and 25% from the following: Geology 1 Fine Arts 1 [a] campus-sem weight code Hf Hf Hf 25% 25% 25% KGA100 KPA150 KZA151 Hf 25% KEA100 Course details (2001) page 360 Students choosing Sociology must study both HGA101 and HGA102 Sociology A H1~L1~B1~D1 12.5% HGA101 Sociology B H2~L2~B2~D2 12.5% HGA102 Chemistry 1A Hf 25% KRA110 Chemistry 1B Hf 25% KRA130 or another first-year unit approved by the BSc degree coordinator Year 2 (Note: where units are shown with 200/300 codes, use the 200 level, eg KGA223 not KGA323) Geography and Environmental Studies 2 Hf 33.33% KGA200 and one or two of the following: Zoology 2 Hf 33.33% KZA210 Botany 2 Hf 33.33% KPA200 and one or, at least, 33.33% of the following or other approved level 200 units (if KZA210 and KPA200 both not studied): Fine Arts 2 [a] Analytical & Environmental Chemistry H2 16.67% KRA203 Tourism, Sport and Leisure H1 12.5% HGA251/351 Sociology of Nature [na] 12.5% HGA261/361 Historical Geography H2 12.5% KGA240/340 Environmental Management H1 12.5% KGA223/323 Australian Environmental Policy [na] 12.5% HSD230/330 Environmental Ethics H1 12.5% HPA277/377 Year 3 (Note: where units are shown with 200/300 codes, use the 300 level, eg KGA378 not KGA278) Vegetation Management H1 12.5% KGA331 Fauna Conservation Management H1 12.5% KGA332 Wilderness and Natural Area Management: Natural and Cultural Values H2 12.5% KGA278/378 Conservation Geomorphology H2 12.5% KGA327 Introduction to Management H1/2~L1/2~B1 12.5% BMA101 Social & Environmental Accounting H2 12.5% BFA207/307 and 25% from the following: Evolutionary Biology & Biogeography H2 12.5% KZA353 Fisheries & Wildlife Management H1 12.5% KZA354 Course details (2001) page 361 Freshwater Ecology H2 12.5% KZA355 Marine Ecology H1 12.5% KZA356 Alternative Terrestrial Lifestyles – The Fungi [na] 12.5% KPA371 Aquatic Botany H1 12.5% KPA372 Evolution and Biodiversity H2 12.5% KPA374 Field Botany H3 12.5% KPA375 Plant Ecology H1 12.5% KPA379 Historical Geography H2 12.5% KGA240/340 Environmental Impact Assessment and Decision Making H2 12.5% KGA381 Microclimatology H2 12.5% KGA321 Environmental Remote Sensing H1 12.5% KGA365 Tourism, Sport and Leisure H1 12.5% HGA251/351 Sociology of Nature [na] 12.5% HGA261/361 Environmental Management H1 12.5% KGA223/323 Australian Environmental Policy [na] 12.5% HSD230/330 Strategic Management H2~L2 12.5% BMA302 Management and the Natural Environment [na] 12.5% BMA272/372 Environmental Ethics H1 12.5% HPA277/377 Year 4 Course code for fourth year: S4L Unit enrolment codes: KGA450 Natural Environment and Wilderness Management (Honours) Full time KGA451 Natural Environment and Wilderness Management (Honours) Part time Thesis 50% and some of the following units, plus work as agreed to with the Head of School: Evolutionary Biology & Biogeography H2 12.5% KZA353 Fisheries & Wildlife Management H1 12.5% KZA354 Freshwater Ecology H2 12.5% KZA355 Marine Ecology H1 12.5% KZA356 Alternative Terrestrial Lifestyles – The Fungi [na] 12.5% KPA371 Aquatic Botany H1 12.5% KPA372 Evolution and Biodiversity H2 12.5% KPA374 Field Botany H3 12.5% KPA375 Plant Ecology H1 12.5% KPA379 Historical Geography [b] H2 12.5% KGA240/340 Course details (2001) page 362 Environmental Impact Assessment and Decision Making H2 12.5% KGA381 Microclimatology H2 12.5% KGA321 Environmental Remote Sensing H1 12.5% KGA365 Tourism, Sport and Leisure H1 12.5% HGA251/351 Sociology of Nature [na] 12.5% HGA261/361 Environmental Management H1 12.5% KGA223/323 Australian Environmental Policy [na] 12.5% HSD230/330 Strategic Management H2~L2 12.5% BMA302 Management and the Natural Environment [na] 12.5% BMA272/372 Environmental Ethics H1 12.5% HPA277/377 [a] Contact the School for code number, availability and details [b] use enrolment code KGA340 Schedule D 4. Economic Geology Major code: KEE The Economic Geology specimen course aims to:• provide students with training in ore deposit geology, genesis and exploration techniques; • provide graduates with advanced knowledge of hydrothermal ore deposits; • meet the needs of the minerals industry and government agencies; • provide students to continue into MSc & PhD courses in the Centre for Ore Deposit Research (CODES SRC). The Economic Geology specimen course is accredited by the Australian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy (AusIMM) as required training for geoscientists working in the Australian Minerals Industry. Course structure In the first three years of the course students need to pass units to a total value of 300%. This is achieved by taking a mix of compulsory and optional units to a value of 100% in each year, as detailed below. Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Compulsory Geology 1 Hf 25% KEA100 AND completion of three Group 1 cores (25% each) from three different schools as listed in Schedule C. The three cores must be studied from Course details (2001) page 363 Mathematics, Chemistry, Physics, Computer Science, and Geography & Environmental Studies; OR completion of two Group 1 cores (25%) from the above list plus completion of BEA110 and BEA130: Economics for Business H1~L1~B1 12.5% BEA110 Foundations of Economic Policy H2~L2~B2 12.5% BEA130 Year 2 Compulsory Geology 2 Hf 33.33% KEA200 Introduction to Geophysics & Computer Applications H2 16.67% KEA222 AND Completion of one Group 2 core (33.3%) as listed in Schedule C. The core must be chosen from either Chemistry, Physics, Computer Science or Geography and Environmental Studies. Plus 16.67% from the following or any other second year units offered by the University: Fossils and Environments Through Time H1 16.67% KEA266 Analytical & Environmental Chemistry H2 16.67% KRA203 Year 3 Compulsory Geology 3 Hf 50% KEA300 Ore Deposit Geology H1 12.5% KEA336 Ore Deposit Geochemistry H2 12.5% KEA346 Exploration Geophysics H1 12.5% KEA342 Plus 12.5% from KEA332, KEA338, KEA348, BEA301 Computers in Geoscience H2 12.5% KEA332 Sedimentary Environments H1 12.5% KEA338 Environmental Geology H2 12.5% KEA348 Environmental and Resource Economics H1 12.5% BEA301 Year 4 BSc(Hons) Course code for fourth year: S4L The fourth-year component of the course comprises the compulsory unit KEA450 or KEA451, and includes a field-based research thesis on an economic geology-based project, plus selected coursework. Unit enrolment codes: KEA450 Economic Geology 4 (Honours) Full time KEA451 Economic Geology 4 (Honours) Part time Bachelor of Science Specimen Courses Course details (2001) page 364 In addition to the courses shown in Schedule D above, the following are offered: (i) Life Sciences Unit Title campus-sem weight Year 1 Either KRA110 or KRA130 Chemistry 1A Hf 25% Chemistry 1B Hf 25% Botany 1G Hf 25% Zoology 1E Hf 25% and 25% other Group 1 science units from Schedule C Year 2 Chemistry for Life Sciences H1 16.67% Analytical & Environmental Chemistry H2 16.67% Zoology 2 Hf 33.33% Botany 2 Hf 33.33% Year 3 Units from Zoology 50% Units from Botany 50% code KRA110 KRA130 KPA150 KZA151 KRA205 KRA203 KZA210 KPA200 (ii) Chemical Sciences Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Chemistry 1A Hf 25% KRA110 and other Science units chosen to enable double majors with Chemistry, in particular Biochemistry, Geology, Plant Science, Mathematics, Physics, Zoology Year 2 Chemistry 2 Hf 33.33% KRA200 Analytical & Environmental Chemistry H2 16.67% KRA203 and other Science units leading to possible double majors Year 3 at least 50% chosen from: Chemistry 3A Hf 25% KRA301 Chemistry 3B Hf 25% KRA302 Instrumental Analytical Chemistry H2 12.5% KRA303 Biosynthesis & Function of Natural Products H1 12.5% KRA305 Course details (2001) page 365 (iii) Computer Science Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Computer Science 1 Hf 25% KXA150 Computer Organisation and Architecture H1~L1~B1 12.5% KXA152 Multimedia and Web Applications H2~L2~B2 12.5% KXA156 Mathematics units (2x12.5% units) Third BSc Group 1 core 25% (from one School) Year 2 Algorithms and Metrics H1~L1 12.5% KXA251 Artificial Intelligence H1~L1 12.5% KXA252 Software Design H2~L2 12.5% KXA253 Operating Systems H2~L2 12.5% KXA254 Microprocessors and Data Acquisition H2 12.5% KNE232 Elective (12.5%) Second BSc Group 2 core 33.33% (from one School) Year 3 Software Engineering Project Hf 25% KCA300 Software Systems H1 12.5% KCA311 Programming Paradigms H2 12.5% KCA312 Networks and Protocols H1 12.5% KCA321 Communications and Data Networks H2 12.5% KCA354 Plus two electives that should include one or two of the following units, depending on the field of specialisation Intelligent Systems H1 12.5% KCA341 Image Processing and Computer Vision H2 12.5% KCA342 Computer Architecture H1 12.5% KCA343 (iv) Physical Sciences, Psychology or Humanities Unit Title campus-sem Year 1 Chemistry 1A Hf Physics 1A H1 Physics 1B H2 Mathematics 25% Either (KHA101 and KHA102) or HTA100 Psychology 1A H1~L1~B1 weight code 25% 12.5% 12.5% KRA110 KYA101 KYA102 12.5% KHA101 Course details (2001) page 366 Psychology 1B H2~L2~B2 12.5% KHA102 History 1 Hf 25% HTA100 Year 2 Chemistry units (with total weight of 33.33%) Physics units (with total weight of 33.33%) and either KHA200 or History 2 units (with a total weight of 33.33%) Psychology 2 (Science) Hf 33.33% KHA200 Year 3 Any two of the following to give 100% Chemistry units History units Mathematics units Psychology units A minimum of 50% must be studied from chemistry or mathematics or physics units. (v) Biochemistry, Microbiology Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Either KRA110 or KRA130 Chemistry 1A Hf 25% KRA110 Chemistry 1B Hf 25% KRA130 At least one of the following: Botany 1G [a] Hf 25% KPA150 [a] Zoology 1G Hf 25% KZA150 Human Biology (Science) Hf 25% CHG100 Plus other suitable units in accordance with the specifications of the BSc Year 2 Biochemistry and Microbiology 2 Hf 33.33% CBA250 Examples of suitable complementary units include: Human Physiology and Pharmacology Hf 33.33% CHP205 Chemistry 2 Hf 33.33% KRA200 Analytical & Environmental Chemistry H2 16.67% KRA203 Chemistry for Life Sciences H1 16.67% KRA205 Zoology 2 Hf 33.33% KZA210 Botany 2 Hf 33.33% KPA200 Year 3 Molecular Biochemistry: Techniques and Theory Hf 50% CBA327 Microbial Ecology Hf 25% KLA309 Course details (2001) page 367 Medical Microbiology and Immunology Hf 25% CJA308 [a] If both Botany and Zoology are studied, students must study KPA150 and KZA151 (vi) Geology See the Discipline entry for Geology in the Unit details section of the Handbook. Bachelor of Science with Honours (Abbreviation: BSc(Hons)) Course code: S4E This 1 year full-time, 2 year part-time (maximum) course is available at Hobart and, subject to available supervision, at Launceston. Note that part-time studies are available in some Schools. Admission & prerequisites Bachelor of Science degree or equivalent with prerequisites in the field of study. Admission is subject to appropriate supervision being available. Graduates from other universities with prerequisites acceptable to the Faculty may be accepted as candidates for the Bachelor of Science with Honours degree. Course objectives The course aims to provide: • • • advanced training in the major area of the student's pass degree, opportunity for training in research, to prepare candidates for further research study, eg MSc and PhD programs and employment in research organisations, and in-depth knowledge in a single area of science. Career outcomes Honours graduates are highly competitive for professional careers in their area of specialisation. Employment opportunities also exist in more general areas as detailed in the following discipline entries: Biochemistry on page C-xx Course details (2001) page 368 Chemistry on page C-xx Computing on page C-xx Geography and Environmental Studies on page C-xx Geology on page C-xx Mathematics on page C-xx Microbiology/Immunology on page C-xx Plant Science on page C-xx Physics on page C-xx Psychology on page C-xx Zoology on page C-xx Professional recognition Graduates of the BSc(Hons) are eligible for membership of a number of professional organisations. Specific details are provided under individual discipline entries in the Handbook. Course structure Each candidate will conduct research and write a thesis. In addition, candidates MAY BE required to study and pass one or more advanced level units and undertake other activities which may include the preparation of literature reviews, essays and grant applications and the presentation of seminars. Students should refer to the School entries in the 'Unit details' section for more information. Honours candidates are accepted in: • • • • • • • • • Biochemistry Botany Chemistry Computer Science Economic Geology [a] Forest Ecology [a] Genetics Geochemistry Geography and Environmental Studies Course details (2001) • • • • • • • • • • • • page 369 Geology Geophysics Marine, Freshwater and Antarctic Biology [a] Mathematics Microbiology Natural Environment and Wilderness Management [a] Pathological sciences Physics Physiology Psychology Software Engineering Zoology [a]**These honours have a prerequisite of three years in special BSc programs. Students enrol in a separate course, each with its own course code which differs from the BSc(Hons). Bachelor of Surveying with Honours (Abbreviation: BSurv(Hons)) Course code: N4B This 1-year full-time or 2-year part-time course is offered by the Faculty of Science and Engineering at Hobart. Admission & prerequisites To be eligible to enrol for the degree applicants must have either qualified for admission to the degree of Bachelor of Surveying in this University or have qualified in another university or tertiary institution for a degree deemed by the Faculty of Science and Engineering to be equivalent to that degree. In each case, the standard of pass must be of sufficient merit to satisfy the Faculty of Science and Engineering. Course objectives The course objectives are: • • • to provide advanced in-depth knowledge in a single area of surveying and spatial information science; to provide opportunity for training in research; to prepare students for postgraduate research in the Master of Spatial Information Science and PhD programs as well as for employment in research organisations; and Course details (2001) • page 370 to provide advanced courses in selected areas of surveying and spatial information science. Career outcomes The Honours course provides students with advanced skills and research experience in a specialisation of geomatics or surveying. Graduates are likely to find employment in Commonwealth or State government agencies, or large private organisations. Professional recognition The Bachelor of Surveying with Honours is recognised by the Institution of Surveyors, Australia providing qualification for graduate membership of the Institution. Corporate membership is granted after an approved period of professional experience. Course structure Honours candidates are required to pursue a course of study in Advanced Surveying Theory and Practice with lectures and project work being prescribed by the degree coordinator. The overall enrolment code for full-time students is KGS500 and for part-time students is KGS505. Coursework will be selected from the following topics: • • • • • Advanced Photogrammetry Advanced GIS Advanced Geodesy Advanced Adjustment Theory Advanced Instrumentation and Techniques With the agreement of the degree coordinator candidates may select units from Groups 2, 3 and 4 offered by the Faculty of Science and Engineering up to a maximum of 25%. See KGS500on page xx. Bachelor of Technology (Abbreviation: BTech) Course code: N3M Students interested in the Bachelor of Technology degree program should consult the Head of the School of Engineering for details on the various technology streams and schedules being offered. Course details (2001) page 371 This 3-year degree course may be studied full time or part time. At present, 4 streams are available: Electronics & Computers, Civil Technology, Electrical Power, and Mechanical Technology. All streams are available only as articulating programs, credit transfer for TAFE Diplomas being incorporated into the requirements for the three years of the BTech. The Environmental Technology and Manufacturing Technology streams have been discontinued. Admission & prerequisites Applicants would normally hold a TAFE diploma or associate diploma in Civil, Mechanical or Electrical Engineering. The course structure is based on the student's holding a Tasmanian TAFE Associate Diploma. Prospective students holding the new Tasmanian TAFE Diploma or other TAFE qualification should contact the School of Engineering for details. Course objectives The Bachelor of Technology leads to a para-professional qualification designed to satisfy the requirements of the Institution of Engineers Australia for affiliate membership. Course objectives are: • • • • to provide a sound basis in mathematics, the basic sciences and engineering sciences and management; to produce engineering technologists who will work in collaboration with more experienced engineering technologists, or assist professional engineers to undertake tasks which require accuracy and adherence to prescribed methods of analysis, design or computation; to develop skills in analysis, synthesis, design and communication; and to promote student interaction and activities which develop the key interpersonal skills required to balance academic achievements. Course structure Entry is normally at advanced standing through a diploma and requires the equivalent of a further 1.5 years approximately of University study. This may be done full-time or on a part-time basis, in conjunction with suitable employment. Students contemplating a course of part-time study should contact the School of Engineering to ensure their proposed course is acceptable within the framework of proposed course changes. To qualify for the degree, candidates must also undertake a prescribed period of industrial experience and obtain a first-aid certificate. Course details (2001) page 372 Articulation Articulation from a TAFE diploma is a specific design feature of the course, and holders of this award may be granted up to approximately three semesters advanced standing in the course. After successful completion of the Bachelor of Technology, students may also elect to continue their study and articulate to the Bachelor of Engineering in the appropriate specialisation, to become professional engineers. (Civil Technology) Schedule B Year 1 33-200 CE Drafting 33-233 Applied Mechanics 33-370 Concrete Technology 33-439 CE Computer Applications 33-462 Municipal Design 33-473 Structural Drafting 33-512 Structures 1 34-211 Surveying 1A 40-544 Applied Calculus Year 2 33-440 Structures 2 33-509 Civil Engineering Hydraulics Note: for a detailed schedule of units offered by the University of Tasmania, students are advised to consult the Head of School of Engineering. (Mechanical Technology) Schedule B Year 1 33-233 Applied Mechanics 33-512 Structures 1 35-134 EE Calculus 1 35-374 Introductory Electronics 40-131 Engineering Drawing 1 40-132 Engineering Drawing 2 40-555 Introductory Computing 40-587 Engineering Mechanics 40-624 Fluid Mechanics 40-910 Properties and Testing of Materials 42-617 Computer Aided Drafting (Eng) Year 2 40-657 Mechanical Design 1 40-717 Applied Energy Systems Course details (2001) page 373 42-628 CAD Projects Note: Students are advised to consult the Head of School of Engineering for a detailed schedule of units. Combined degreesBachelor of Arts and Bachelor of Applied Science (Abbreviation: BA–BAppSc) Course code: R3G The last intake of students into the combined BA–BAppSc degree was 2000. The BAppSc is being taught out over the period 2001 to 2003. Students should refer to the BA and BAppSc schedules as listed in this handbook; but for other details may refer to the Course and Unit Handbook 2000. Current students should contact Mrs Michelle Horder on (03) 6324 3863 if advice is needed. Bachelor of Arts and Bachelor of Computing (Abbreviation: BA–BComp) Course code: R3L This four year (minimum) combined degree of Bachelor of Arts–Bachelor of Computing is offered on the Launceston campus by the Faculty of Arts and Faculty of Science and Engineering. The course is studied on-campus, although some Bachelor of Arts units are offered by distance education. Subject to attendance and timetable requirements, part-time studies are also available. Students have a maximum of ten years to complete the course. Admission & prerequisites Applicants are expected to meet the normal requirements set by the University for entry to degree courses. No specific course or subject prerequisites apply. Course objectives Refer to course objectives for the Bachelor of Arts and Bachelor of Computing on pages B-xx and B-xx. Career outcomes Course details (2001) page 374 Refer to 'Career outcomes' for the respective degree courses. Course structure Students are required to complete 400% weighting of units, half of them taken from the Bachelor of Arts schedule and the other half from the Bachelor of Computing schedule. Where two or more units of the same name or content are offered within the University, only one may be counted towards the degree. The student's choice of units and the order in which they are taken are subject to approval by the deans of the respective faculties. Articulation Articulation arrangements are the same as for the Bachelor of Arts and the Bachelor of Computing. Bachelor of Arts and Bachelor of Science (Abbreviation: BA–BSc) Course code: R3H The 5-year full-time combined degree of Bachelor of Arts–Bachelor of Science is offered on the Hobart campus by the Faculty of Arts and the Faculty of Science and Engineering. Some Arts units are available by Distance Education. In addition, some units are offered to students commencing in July. Admission & prerequisites Minimum University entrance requirements and a satisfactory achievement (SA) in any two of the following: *MT843 Mathematics Stage 3 (or *MT841 Mathematics Stage 2 or *MT730 Mathematics Applied); *IF862 Computer Science; *CH856 Chemistry; *GL876 Geology; *GG833 Geography (or *EV846 Environmental Science); *PH866 Physics; *BY826 Biology; *SC786 Applied Science-Physical Sciences (if neither Physics nor Chemistry counted) OR a TCE score of 80 or more for applicants not having two of the preceding TCE units. Subject (unit) prerequisites also apply. Course objectives Course details (2001) page 375 Students who wish to combine scientific knowledge with a liberal education will be attracted to this degree. Unique discipline combinations are possible; for example, majors in Journalism and Asian Studies combined with a major in Computer Science and Mathematics; or majors in Chinese and Political Science with Geology and Geography. Students' programs can be tailored to meet the needs of an ever-changing world. They will acquire knowledge and skills through a wide range of disciplines chosen from: Aboriginal Studies, Ancient Civilisations, Ancient Greek, Asian Studies, Biochemistry, Chemistry, Chinese, Computer Science, English, French, Geography and Environmental Studies, Geology, German, History, Indonesian, Japanese, Journalism and Media Studies, Latin, Mathematics, Microbiology/Immunology, Natural Environment and Wilderness Studies, Philosophy, Physics, Plant Science, Political Science, Psychology, Public Policy, Social Ecology, Sociology, Women's Studies, Zoology. The program develops general abilities in the following areas: • • • • • • • • written expression linguistic skills creative self-expression capacity to analyse and interpret in a dispassionate and objective manner capacity for reasoned criticism data acquisition and analysis research techniques marshalling facts in support of arguments evaluating the possible outcomes of alternative courses of action, with the emphasis varying according to the particular program chosen. Career outcomes See career outcomes entry under the BA and BAppSc degrees. Professional recognition Refer to professional recognition entry under the BA and BSc degrees. Course structure To qualify for the combined degree students must complete 500% from units in Groups 1, 2 and 3 of the BSc and BA combined schedules. In the Bachelor of Arts component students must select units to meet the requirements of majors in two disciplines. A major sequence is defined as sequential studies in one discipline by completion of 25% at level 100 (except where not required for enrolment at level 200 in a language) and 75%-87.5% at levels 200/300. Course details (2001) page 376 For the Bachelor of Science component students must meet the following requirements: • • • • 2 x 25% from level 100 Group 1 units of the BSc schedule; 2 x 33.3% from level 200 Group 2 units of the BSc schedule; 1 x 50% of clear passes from level 300 Group 3 units of the BSc schedule forming one major; and 50% comprising 25% from level 200 Group 2 or level 300 Group 3 units of the BSc schedule and 25% from level 300 Group 3 units of the BSc schedule. Units studied outside the BA or BSc schedules will not count towards the combined degree. The course structure is summarised in the following table. Year 1 Level 100 Arts discipline 25% Level 100 Level 100 Level 100 Arts discipline Science core 25% Science core 25% 25% Year 2 Level 200 Level 200 Level 200 Arts discipline 25% Science core 33.33% Arts/Science electives [a] 50% Year 3 Level 200 Arts discipline 25% Level 200 Science core 33.33% Level 200/300 Arts/Science electives [a] Year 4 Level 300 Arts discipline 25% Level 300 Arts discipline 25% Level 300 Science major 25% Level 200/300 Science electives Year 5 Level 300 Arts discipline 25% 25% 50% Course details (2001) Level 300 Level 300 Level 300 Arts discipline Science major 25% Science electives page 377 25% 25% <tbz> [a]up to 25% of electives may be studied from level 100 Science units. Articulation Credit for units included in the schedules of the BA and BSc degrees will be awarded to students who transfer to the combined degree. Up to one year of credit for TAFE programs will be awarded for the BSc component of the combined degree. Bachelor of Science and Bachelor of Engineering (Abbreviation: BSc–BE) Course code: N3C This 5-year (minimum) full-time course is available at Hobart. Admission & prerequisites The intention of the combined degree is to cater for students with a demonstrated aptitude in science and engineering. Only students who have higher achievements or outstanding achievements in mathematics and applied science at advanced secondary level and who obtain distinctions or higher in KNM112 Engineering Mechanics, KNE122 Electrical Engineering, KMA150 Calculus and Applications 1 will be considered for the combined degree. Students must therefore have completed Year 1 of the BE before enrolling in the course. Enrolment requires a timetable overload and must have the approval of the Faculty. Course objectives The Bachelor of Science–Bachelor of Engineering combined degree provides an opportunity for students to study not only engineering units but to study in a selected field of science at an in-depth level with a view to a future career in research. Career outcomes Course details (2001) page 378 Graduates of the combined degree could expect to find employment in such fields as are detailed in the Bachelor of Engineering (page B-xx) and Bachelor of Science (page B-xx) course descriptions. Course structure Students are required to complete: • • the four examinations of the Bachelor of Engineering degree; and either 100% of Group 3 units from the BSc Schedule A or at least 150% from Group 1 (not more than 50%), 2 and 3 units in the BSc Schedule A, which units must include one new major subject. Students' choice of units must conform to the specifications (rules) of both the BE and BSc degrees. They may be permitted to proceed to the Bachelor of Science with Honours, or Bachelor of Engineering with Honours, or both, in the combined degree of Bachelor of Science–Bachelor of Engineering. Choices other than science majors in Mathematics, Geology, Physics and Computer Science may be difficult due to timetable constraints. Articulation There is no formal articulation other than by gaining credit for work completed in another degree. Other degrees combined with Science or Engineering courses Bachelor of Commerce–Bachelor of Applied Science (C3A). There will be no new enrolments in this course. Bachelor of Commerce–Bachelor of Computing (C3X) (see page B-xx). Bachelor of Science–Bachelor of Laws (L3G) (see page B-xx). Institute of Antarctic and Southern Ocean Studies (Abbreviation: IASOS) The Institute of Antarctic and Southern Ocean Studies is a National Key Centre for Teaching and Research established with the aid of federal government funding in 1988 to promote and focus Australian academic activity concerned with Antarctica and its surrounding ocean. IASOS is housed in the Course details (2001) page 379 well-equipped Centenary Building in a central position on the Hobart campus of the University of Tasmania. The Director of IASOS is Professor GW Paltridge and there are key staff in major discipline areas: physical sciences – Dr KJ Michael; life sciences – Dr A McMinn, Dr G Jackson; and legal and policy studies – Dr MG Haward. Other staff with primary roles in other Schools of the University and in major research establishments with interests in the region are affiliated with IASOS, and participate in its teaching and research program. IASOS has a close working arrangement with the Australian Antarctic Division, CSIRO Marine Research, the Bureau of Meteorology and the Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR) in Hobart. These agencies are involved in the coursework programs, in supervising postgraduate students, and providing laboratory and support facilities for thesis projects. The Australian Antarctic Division, CSIRO Marine Research, the Bureau of Meteorology, the Australian Geological Survey Organisation and the Institute of Antarctic and Southern Ocean Studies (IASOS) have formed an Antarctic Cooperative Research Centre based on the campus. With a staff of 65 and more than 15 honours year and 55 research higher degree students, the Centre is one of the largest in the world conducting research in the polar regions and is mainly concerned with the large-scale interactions of the south polar region with the global climate and environment. Major scientific disciplines include physical, chemical and biological oceanography; atmospheric physics and chemistry; climatology; glaciology; polar region biology and palaeo-climatic reconstruction. Legal and policy work concerns environmental management , the operation of the Antarctic Treaty System and climate change policy. Students work closely with world-class scientists involved in national and international research programs and have access to the extensive facilities not only of the Antarctic CRC itself but also of the partner agencies in Hobart. Great use is made of very expensive, publicly-funded, research facilities such as the ice-class research vessel Aurora Australis, the Tasmanian Earth Resources Satellite Station (TERSS), and the CRAY high-performance computing facility at the University. A major objective of the overall Antarctic CRC scheme is to knit postgraduate teaching closely to the developing research programs of the participating institutions. IASOS, in association with the Antarctic CRC, offers the following options for graduate students: • • Bachelor of Antarctic Studies with Honours Graduate Diploma of Science (Antarctic and Southern Ocean Studies) Course details (2001) • • • page 380 Graduate Diploma of Science (Antarctic and Southern Ocean Studies) with Honours Master of Meteorology and Oceanography Research Higher Degrees (MSc, MA and PhD) Theme area All units taught by the Institute of Antarctic and Southern Ocean Studies fall within the Antarctic and Southern Ocean Studies theme area. Specific courses taught by IASOS under this theme are the Bachelor of Antarctic Studies with Honours, Graduate Diploma of Science (Antarctic and Southern Ocean Studies), Graduate Diploma of Science (Antarctic and Southern Ocean Studies) with Honours, and Master of Meteorology and Oceanography. Bachelor of Antarctic Studies with Honours (Abbreviation: BAntSt(Hons)) Course code: S4G Course objectives Graduate Diploma of Science (Antarctic and Southern Ocean Studies) (Abbreviation: GradDipSc(ASOS)) Course code: S6D Course objectives Course details (2001) page 381 Graduate Diploma of Science (Antarctic and Southern Ocean Studies) with Honours (Abbreviation: GradDipSc(ASOS)(Hons)) Course code: S6X These courses provide both a general overview of Antarctic and Southern Ocean matters and specialist training in areas of the physical and biological sciences; policy and law; and polar and environmental technology. The program has the flexibility to respond to the particular backgrounds and experience of each year's students and can be taken in one year full-time or two years part-time study. Candidature is open to graduates in all disciplines. Selection into the honours stream is based on the applicant's undergraduate record and work experience, if appropriate. The honours degree is fully equivalent to an honours degree within a University School and satisfies the usual eligibility requirements for research higher degrees and postgraduate scholarships. The first half of the program consists of a multi-disciplinary course in the form of seminar style sessions in five sub-disciplines: social sciences, life sciences, physical sciences and Antarctic operations. The remainder of the honours program requires the completion of an approved research project, with the results presented in a thesis. For students not taking honours, a reading thesis style specialist unit, supervised by an appropriate staff member, is undertaken. The coursework is assessed through a series of assignments, while the thesis is formally examined by internal and external experts. Interested students are encouraged to contact the Institute of Antarctic and Southern Ocean Studies directly (ph) (03) 6226 2971. Course objectives Career outcomes Graduates of the Honours program are eligible for membership of a variety of professional organisations, for instance: International Glaciological Society, American Geophysical Union, Australian Meteorological and Oceanographic Society, American Meteorological Society, Australian Marine Science Course details (2001) page 382 Association, Australian Geological Society. The society or societies they may belong to depends somewhat on the nature of the research that they undertook. The course leads to career opportunities in oceanography, glaciology, climate modelling, meteorology, ice core chemistry, sedimentology, marine biology, terrestrial ecology, international relations. Course structure Bachelor of Antarctic Studies with Honours KSA410 Full time KSA411 Part time Graduate Diploma of Science (Antarctic and Southern Ocean Studies) KSA505 Full time KSA506 Part time Graduate Diploma of Science (Antarctic and Southern Ocean Studies) with Honours KSA510 Full time KSA511 Part time Graduate Diploma of Agricultural Science (Abbreviation: GradDipAgrSc) Course code: S6A Course objectives Graduate Diploma of Agricultural Science with Honours (Abbreviation: GradDipAgrSc(Hons)) Course code: S6Y A (minimum) 1-year course. Admission & prerequisites Course details (2001) page 383 Admission is open to graduates holding a recognised degree in a science-based discipline. Selection for the honours program is based on the applicant's undergraduate record and work experience, where appropriate. Course objectives These courses are intended to provide academic advancement to individuals who hold an undergraduate degree. At honours level, the course provides access to the Master of Agricultural Science or PhD degree courses. Career outcomes Graduates will have improved their career potential in their chosen profession, and, in the case of Honours graduates, gained access to a higher degree course. Course structure Either course is normally completed in one full-time year or two years part time, although an extra 3 months may be allowed for Graduate Diploma candidates to complete the research project. The course coordinator may grant an extension of time to a candidate who has been prevented by illness or other serious cause from completing the requirements of the course within the prescribed period. A GradDipAgrSc candidate must undertake at least 50% coursework chosen from Schedule A of the BAgrSc or S3B and S3CBAppSc awards. The balance (making 100%) to comprise a supervised research project. A GradDipAgrSc(Hons) candidate must undertake at least 50% supervised research project, the balance (100%) comprising units chosen from Schedule A of the BAgrSc or S3B and S3CBAppSc awards, and not counted towards a previous degree. Articulation Any recognised science-based bachelor degree may lead into the GradDipAgrSc courses. Graduates of the GradDipAgrSc(Hons) may progress to Master or PhD. Graduate Diploma in Aquaculture (Abbreviation: GradDipAqua) Course details (2001) page 384 Course code: S6K (This course replaces the Graduate Diploma of Applied Science in Aquaculture (S6C)) This course acts as a bridging course for graduates from non-aquaculture programs who wish either to work in the aquaculture industry or to pursue a higher degree qualification in aquaculture. Traditional degrees in Australia, or those containing one or two broad based aquaculture units, lack the necessary 'hands-on' component for aquaculture and seldom provide the necessary in-depth knowledge on aquatic husbandry. The course covers the important components of commercial aquaculture: biology, husbandry, technology and animal health. The course ensures that students obtain an education in aquaculture under Australian conditions. They may seek careers on all types of aquaculture farms and as research officers in fishery departments. Alternatively, graduands may undertake the degree of Master of Applied Science in Aquaculture or Honours. Admission & prerequisites Applicants should possess a relevant pass degree in biological sciences (preferably aquatic). However, prospective students may be admitted to the course if they can demonstrate to the satisfaction of the Head of School that they have been awarded a pass degree containing science units deemed relevant to aquaculture. Course objectives Career outcomes This postgraduate bridging program enables graduates of other courses to learn the specialist aquaculture skills necessary for work in the industry or in government policy and research departments. Alternatively, it is possible for graduates of this course to undertake a Master of Applied Science in Aquaculture, in order to obtain expertise as a researcher. Course structure The full-time program is one year in duration. The program for a part-time student would follow a similar pattern taken over two years. Articulation Course details (2001) page 385 An approved degree program Bachelor of Aquaculture with Honours, Master of Applied Science in Aquaculture Units approved for Graduate Diploma in Aquaculture Unit Title campus-sem Semester 1 Nutrition of Aquatic Organisms L1 Physiology of Aquatic Organisms L1 Technology for Aquaculture L1 Intensive Algal Culture L1 Semester 2 Intensive Crustacean & Zooplankton Culture L2 Intensive Finfish Culture L2 Aquatic Animal Health L2 Intensive Molluscan Culture L2 Two weeks work experience is required weight code 12.5% KQA319 12.5% KQA330 12.5% 12.5% KQA214 KQA201 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KQA228 KQA320 KQA321 12.5% KQA303 Note: Students wishing to progress to a BAqua(Hons) year should undertake KQA302 Scientific Analysis and Presentation or have completed an equivalent statistical unit. Graduate Diploma of Computing (Abbreviation: GradDipComp) Course code: S6J This is offered on-campus at Launceston. It is normally studied part-time over two years, but can be completed in one year of full time study. Admission & prerequisites Possession of a Bachelor degree (or equivalent) from a recognised university. Course objectives Course details (2001) page 386 The course is specifically designed for people with a tertiary qualification in a discipline other than computing who wish to make a career change and become computing professionals, or who wish to combine computing skills with their current specialisations. Specific objectives are: • • to provide an introduction to the theory and practice of computing to enable professionals to apply new and emerging computing technologies in their areas of expertise Career outcomes (See BComp, page B-xx). Students who complete the Graduate Diploma have their career opportunities enhanced because they are able to combine expertise gained from their first degree with knowledge of computing technologies. Course structure The program consists of four core units and four elective units. The units are chosen from the Bachelor of Computing units and are selected according to the individual student's background, taken over not less than one full-time year and in not more than three consecutive years. Units approved for the Graduate Diploma of Computing Unit Title campus-sem weight code Core units Computer Applications H1~L1~B1 12.5% KXA153 Programming and Problem Solving H1~L1/2~B1 12.5% KXA151 Professional Computing H2~L2~B2 12.5% KXA155 Multimedia and Web Applications H2~L2~B2 12.5% KXA156 Computer Organisation and Architecture H1~L1~B1 12.5% KXA152 Software Process H2~L2~B2 12.5% KXA154 Algorithms and Metrics H1~L1 12.5% KXA251 Artificial Intelligence H1~L1 12.5% KXA252 Software Design H2~L2 12.5% KXA253 Operating Systems H2~L2 12.5% KXA254 Elective units Availability of the following units depends on student demand and availability of resources Artificial Intelligence H1~L1 12.5% KXA252 Digital Networks L1 12.5% KXA336 Programming Systems L2 12.5% KXA337 Course details (2001) Computer Assisted Learning Principles of Operating Systems Knowledge-Based Systems Computer Graphics & Animation Advanced Web Development page 387 L1 12.5% KXA339 L2 L1 12.5% 12.5% KXA334 KXA335 L2 H1~L1 12.5% 12.5% KXA338 KXA281/381 Graduate Diploma of Computing with Honours (Abbreviation: GradDipComp(Hons)) Course code: S6S this 1-year full-time or 2-year part-time course is offered by the Faculty of Science and Engineering at Launceston. The Graduate Diploma of Computing with Honours is designed for those with a tertiary qualification in computing, or for computing professionals who wish to gain a further qualification in specialised areas of applied computing. It may provide up to one year of credit towards a Master of Computing degree. Admission & prerequisites Possession of a degree in computing or a non-computing degree with several years of professional experience in computing. Course objectives The Graduate Diploma with Honours is designed to produce graduates capable of specialising in a wide range of professional computing areas. Career outcomes (See BComp, page xx). Students who complete the Graduate Diploma have their career opportunities enhanced because they are able to combine expertise gained from their first degree with knowledge of computing technologies. Course structure Course details (2001) page 388 The program consists of eight advanced computing units taken over not less than one full-time year and in not more than three consecutive years. The eight units are chosen from the following list, subject to availability. Articulation The course provides students with an undergraduate degree in computing a pathway towards a Master of Computing Units approved for the Graduate Diploma of Computing with Honours Unit Title campus-sem weight code Computation and Functional Programming L? 12.5% KXA412 Spatial Information Systems L? 12.5% KXA415 Advanced Computer Security L? 12.5% KXA418 Multimedia & Internet Applications L? 12.5% KXA430 Machine Learning L2 12.5% KXA431 Java Applications L? 12.5% KXA433 Other units as approved by the Head of School The availability of these units will depend on student demand and availability of resources. Graduate Diploma of Engineering with Honours (Abbreviation: GradDipEng(Hons)) Course code: N6Z Not offered in 2001 Graduate Diploma of Environmental Studies (Abbreviation: GradDipEnvSt) Course code: S6B Course details (2001) page 389 Lecturers: Assoc Prof JJ Todd, Dr PR Hay, Dr PB McQuillan, Dr JA Russell, Dr LK Kriwoken, Dr E Stratford, Prof JB Kirkpatrick, and others. This course is offered by the School of Geography and Environmental Studies at the Hobart campus. The course is offered on a 1 year full-time or up to 3 years part-time basis. Extensions may be possible for a candidate whose work has been interrupted by illness or other unavoidable cause, or to complete any project prescribed as a component of the course. Admission & prerequisites Applicants should have a bachelor degree from any discipline, or equivalent. Course objectives The Graduate Diploma in Environmental Studies is specifically designed for those with a tertiary qualification, who wish to gain a first qualification in Environmental Studies. It is appropriate for those wishing to make a career change to an environmental management area, for those wishing to combine environmentally based skills with their current specialisation, or for those who wish to increase their knowledge out of interest. The course provides a broad, interdisciplinary approach to environmental management. Career outcomes The GradDipEnvSt can lead to positions in environmental management, environmental policy making or environmental education. Course structure The Graduate Diploma in Environmental Studies consists of four units: Environmental Values, Environmental Technology, Environmental Planning, and Ecosystems. Two of the units are offered each semester. The Coordinator can provide information on which units are available in each semester. Assessment: The four Environmental Studies units are assessed on the basis of essays, seminars and research projects. Unit Title campus-sem weight code Course details (2001) page 390 Environmental Technology H2 0% KGE512 Ecosystems H1 0% KGE513 Environmental Planning H2 0% KGE514 Environmental Values H1 0% KGE515 An approved combination of units from elsewhere in the University may, under certain circumstances, be substituted for one of the above units. Students must enrol in one of the following weighted umbrella codes and in the appropriate units Graduate Diploma of Environmental Studies (full time) [a] H 100% KGE500 Graduate Diploma of Environmental Studies (part time) [a] H 50% KGE501 [a] The appropriate 'umbrella' code must be entered on all GradDipEnvSt enrolments, in addition to the individual units' code. A weighting of 0% must be entered against the individual unit codes. Graduate Diploma of Environmental Studies with Honours (Abbreviation: GradDipEnvSt(Hons)) Course code: S6W Lecturers: Assoc Prof JJ Todd, Dr PR Hay, Dr PB McQuillan, Dr JA Russell, Dr LK Kriwoken, Dr E Stratford, Prof JB Kirkpatrick, and others. This course is offered internally on the Hobart campus, on a 1 year full-time or 2 years part-time basis. Extensions may be possible for a candidate whose work has been interrupted by illness. The Graduate Diploma in Environmental Studies with Honours is specifically designed for those with a tertiary qualification of suitable standard who wish to gain a first qualification in Environmental Studies which can then act as a bridge to higher degrees. It is also appropriate for those wishing to make a career change into an environmental management area, for those wishing to combine environmentally based skills with their current specialisations, and for those who wish to increase their knowledge out of interest. Admission & prerequisites Course details (2001) page 391 Applicants should possess a bachelor degree in any discipline, or equivalent. Undergraduate grades must average Credit or better, unless entry approval is given by the course coordinator. Course objectives The course is designed to demonstrate research ability in interdisciplinary environmental studies and environmental management Career outcomes The course provides entry into research-based higher degree study, and can lead to employment in environmental management, environmental policy formation, or environmental education. Course structure Students take two of the units required for the Graduate Diploma of Environmental Studies, as approved by the Coordinator of Environmental Studies, and must also complete an honours thesis. Assessment: The Environmental Studies units (50%) are assessed on the basis of essays, seminars and research projects. The thesis (50%) is assessed by one external and one internal examiner. Unit Title campus-sem weight code Environmental Technology H2 0% KGE512 Ecosystems H1 0% KGE513 Environmental Planning H2 0% KGE514 Environmental Values H1 0% KGE515 Honours Thesis H 0% KGE540/541 Students must also enrol in one of the following weighted umbrella codes and in the appropriate units Graduate Diploma of Environmental Studies with Honours (full time) [a] H 100% KGE505 Graduate Diploma of Environmental Studies with Honours (part time) [a] H 50% KGE506 [a] The appropriate 'umbrella' code must be entered on all GradDipEnvSt(Hons) enrolments, in addition to the individual units' code. A weighting of 0% must be entered against the individual unit codes. Graduate Diploma in Rehabilitation Counselling Course details (2001) page 392 (Abbreviation: GradDipRehabCouns) Course code: S6R This is a full fee-paying course which can be undertaken on a one year full-time or two years part-time study basis, and comprises eight 12.5% units. The course is available on the Hobart campus. Admission & prerequisites Requirements for entry to the course are completion of a Bachelor of Arts with 175% in psychology, or Bachelor of Science with 133.3% in psychology, and applicants should meet Faculty of Arts admission requirements and prerequisites for Honours (GPA of 6.0 or better at 200/300 level). Consideration for admission will also be given to people with a single major in psychology and relevant work experience. Course objectives The Graduate Diploma in Rehabilitation Counselling is a skill based course which aims to provide students with the fundamental knowledge and skills required for employment in a broad range of rehabilitation counselling roles. These include vocational rehabilitation, rehabilitation following head injury or as a consequence of physical illness or injury, counselling roles associated with death and dying, rehabilitation following criminal incarceration, and drug and alcohol rehabilitation. The course focuses on the theoretical basis of rehabilitation and the acquisition of counselling skills, both in general and specific to particular work areas. The practice of rehabilitation is covered in relation to specific work areas, examining particular issues that may arise and community resources available both for clients and their families. Professional recognition Intending students should note that the Graduate Diploma in Rehabilitation Counselling is not an accredited fourth year program in psychology and a graduate will not be eligible for registration as a psychologist. Schedule Unit Title Rehabilitation Counselling 1 Rehabilitation Counselling 2 Research Project 1 Research Project 2 campus-sem weight code H1 12.5% KHA501 H2 H1 H2 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% KHA502 KHA503 KHA504 Course details (2001) Rehabilitation Theory and Practice Vocational and Legal Rehabilitation Topics in Rehabilitation Rehabilitation in Medical Settings Enrolment master code Graduate Diploma in Rehabilitation Counselling page 393 H1 12.5% KHA505 H2 H1 12.5% 12.5% KHA506 KHA507 H2 12.5% KHA508 Hf 0% KHA500/510 Graduate Diploma of Science (Abbreviation: GradDipSc) Course code: S6D Available in the specialisations shown in the table which follows. Graduate Diplomas provide graduates with professional skills in a specialised area. Applications are open to graduates from all disciplines provided that the prerequisites for the field of specialisation are met, or other evidence of fitness to undertake the work is provided. Admission & prerequisites Completion of a Bachelor of Science, another approved bachelor degree or other tertiary qualification deemed by the Faculty to be equivalent for admission purposes. To be admitted candidates must satisfy the prescribed prerequisites for their specialisation or provide evidence that they are able to undertake the work for the award. Course objectives The course aims to provide students with opportunities to acquire knowledge, attitudes and skills in an area of specialisation that is different from the concentrations they completed in their undergraduate degree. Career outcomes The course diversifies the career options available to graduates from their initial qualifications. The career outcomes section of the Bachelor of Science degree course (page B-xx) provides references to the individual discipline entries where these expected outcomes are specified. Course details (2001) page 394 Professional recognition Depending on the area of specialisation, graduates may be eligible for membership of a number of professional organisations. Course structure A candidate for the Graduate Diploma works within one of the fields of specialisation listed below and is subject to any further conditions imposed by the School. Graduate diplomas generally involve a set menu of units, sometimes involving projects. Assessment is usually based on assignments, essays and examinations for each unit. A candidate may not count more than 12.5% of Terminating Passes towards the diploma. The Diploma must be completed in one year of full-time study or a maximum of three consecutive years of part-time study, but a candidate whose work has been interrupted by illness, or other unavoidable cause, may be allowed to complete the course over a longer period. An extension of time may also be granted to submit a project. The approved abbreviation for the Diploma shall be GradDipSc The following specialisations are offered: SchoolField of specialisation Chemistry Chemistry Computing Computer Science Computing Software Engineering Earth Sciences Geology Earth Sciences Geophysics Mathematics & Physics Computational Mathematics Mathematics & Physics Operations Research Mathematics & Physics Statistical Applications Mathematics & Physics Physics Mathematics & Physics Antarctic and Southern Ocean Studies (ASOS) <tbz> Chemistry Specialisation: Chemistry Course details (2001) page 395 Additional prerequisites An applicant will normally be exptected to have successfully completed first-year university-level chemistry. An applicant who does not satisfy the prerequisites but who has extensive practical experience in chemistry or a chemistry-related profession may be admitted subject to the requirement that additional coursework is undertaken as part of the Graduate Diploma. Course Structure The Graduate Diploma of Science, specialising in Chemistry, consists of a total of 100%, chosen from Group 2 and Group 3 units and Honours [a] units offered by the School of Chemistry. The laboratory components of units chosen may be replaced by assignment and project [b] work as appropriate for the particular needs of individual students. Any unit which has been counted towards a previous degree or diploma may not be counted as part of the Graduate Diploma. With permission from the Dean and on the recommendation of the Head of the School of Chemistry, units offered by other schools of the University may be counted towards the Graduate Diploma. [a] [b] KRA583 Honours unit valued at 8.33% KRA586 Honours unit(s) valued at 16.67% KRA589 Honours unit(s) valued at 25% KRA580 Project if substituted for laboratory work Computing Specialisation: Computer Science Specialisation: Software Engineering These specialisations are intended to meet the needs for professional development and training in computer science or software engineering. Additional prerequisites Knowledge or experience in computer programming. Course structure Coursework (75%) comprising units chosen from levels 200 and 300 of Computer Science(KCA) units or other approved units, and Project (25%). For details, students should contact the School of Computing (03) 6226 2922. Earth Sciences (Geology) Course details (2001) page 396 Specialisation: Geology Additional prerequisites The applicant's undergraduate degree should normally include at least 25% of geology. Candidates shall complete the following work with the School of Earth Sciences: (a) (b) An assignment, project or fieldwork equivalent to 16.67% and 83.33% of coursework from Schedule A (page B-xx) of the BSc specifications. Honours units A minimum of 50% shall be chosen from Group 3 and Honours units with a maximum of 33.33% from Group 2 units. Specimen courses See also the introduction to the School of Earth Sciences which will be found under 'Geology'in the Unit Details section of this handbook (page C-xx). Students should contact (03) 6226 2819 for details concerning possible courses. Specialisation: Geophysics Additional prerequisites The applicant's undergraduate degree should normally include at least 41.67% of physics. Candidates shall complete the following work with the School of Earth Sciences: (a) (b) An assignment, project or fieldwork equivalent to 16.67% and 83.33% of coursework from Schedule A (page B-xx) of the BSc specifications. Honours units A minimum of 50% shall be chosen from Group 3 and Honours units with a maximum of 33.33% from Group 2 units. Specimen courses Course details (2001) page 397 See also the introduction to the School of Earth Sciences which will be found under 'Geology'in the Unit Details section of this handbook (page C-xx). Students should contact (03) 6226 2819 for details concerning possible courses. Mathematics and Physics The School of Mathematics and Physics offers four programs of study leading to the Graduate Diploma of Science, specialising in Operations Research, Statistical Applications, Computational Mathematics and Physics. The specialisations are intended to meet needs for professional development. Specialisation: Computational Mathematics The specialisation in Computational Mathematics familiarises the student with some important parts of modern applied mathematics and provides practical experience in the use of some associated computing tools. Additional prerequisites 41.33% (or their equivalent) in mathematics units. Course structure Students should contact (03) 6226 2450 for details concerning course structure. Specialisation: Operations Research Additional prerequisites 41.33% (or their equivalent) in mathematics units. Course structure Students should contact (03) 6226 2450 for details concerning course structure. Specialisation: Statistical Applications This specialisation is intended for science graduates who wish to develop statistical expertise in their own discipline. The course is largely project oriented and requires the student to undertake literature searches and reviews; to develop computing skills and knowledge; and to acquire both oral and written skills in the presentation of statistical information. Additional prerequisites Course details (2001) page 398 The applicant should have a science-based major and experience in conducting scientific experiments or quantitative investigations. Course structure Students should contact (03) 6226 2450 for details concerning course structure. Specialisation: Physics Additional prerequisites An applicant will normally be expected to have successfully completed first-year university-level physics. An applicant who does not satisfy the prerequisites but who has extensive practical experience in physics or a physics-related profession may be admitted, subject to the requirement that additonal coursework is undertaken as part of the Graduate Diploma. Specimen courses The Graduate Diploma of Science, specialising in Physics, consists of a total of 100% chosen from Group 2 and 3 units and Honours units offered in Physics. The laboratory components of units chosen may be replaced by assignment and project work as appropriate for the particular needs of individual students. The units and lecture courses constituting the course of study will be determined at the time of initial enrolment. Any unit which has been counted towards a previous degree or diploma may not be counted as part of the Graduate Diploma. Subject to approval, units offered by other schools of the University may be counted towards the Graduate Diploma. For enrolment codes, contact (03) 6226 2396. Antarctic and Southern Ocean Studies Graduate Diploma of Science (ASOS) See IASOS (and following pages) on page B-xx. Graduate Diploma of Science with Honours (Abbreviation: GradDipSc(Hons)) Course code: S6X Course details (2001) page 399 The Graduate Diploma of Science with Honours allows non-science graduates to obtain the necessary prerequisites for higher degrees in Science. It is offered by all the schools of the Faculty at Hobart. Admission & prerequisites A graduate who does not hold a Science degree may be accepted as a candidate for a Graduate Diploma with Honours provided that the candidate's preparation for the course is adequate. Course objectives The course aims to provide: • • advanced training in the area of study chosen, and the opportunity for training in research, to prepare candidates for further research study and employmnet in research organisations. Career outcomes Graduates of the Graduate Diploma of Science with Honours will be competitive for professional careers in their area of specialisation. Employment opportunities also exist in more general areas as detailed in the career outcomes section of the Bachelor of Science (page B-xx) which provides references to the individual discipline entries where these expected outcomes are specified. Professional recognition Depending on the area of specialisation, graduates may be eligible for membership of a number of professional organisations. Course structure In all other aspects the requirements of the Bachelor of Science with Honours apply and candidates should refer to these for particulars. Further information is usually provided by the School. Work as a full-time student must be completed within 12 months of the commencement date. Specific school information Some additional information provided by schools on their specialisations within the Graduate Diploma of Science with Honours course follows. All Hobart Science Schools offer a course at this level; if no information is shown here then the School should be contacted for details. Course details (2001) page 400 Agricultural Science Specialisation: Microbiology For details, see Agricultural Science Honours course (KLA415/416) on page C-xx. Enrolment master codes KLA515 Full time 100% KLA516 Part time 50% Specialisation: Immunology and Microbiology Enrolment master codes KLA517 Full time 100% Antarctic and Southern Oceans Studies Specialisation: ASOS For details, see IASOS (and following pages) on page B-xx. Biochemistry The Discipline of Biochemistry within the School of Medicine offers a number of courses which are open to Science graduates. Specialisation: Biochemistry For details, see Biochemistry Honours course (CBA410)on page C-xx. Chemistry Specialisation: Chemistry For details, see Chemistry Honours course (KRA400/401) on page C-xx. Enrolment master codes KRA500 Full time 100% KRA501 Part time 50% Course details (2001) page 401 Computing Specialisation: Computer Science Specialisation: Software Engineering These specialisations are designed to help students develop the necessary skills and knowledge to undertake research within the computing field. For details, contact the School of Computing on (03) 6324 3347. Enrolment master codes KCA500 Full time 100% KCA501 Part time 50% Geography Specialisation: Geography For details, see Geography Honours course (KGA400/401) on page xx. Enrolment master codes KGA500 Full time 100% KGA501 Part time 50% Geology Specialisation: Geology/Geophysics/Geochemistry The School of Earth Sciences offers specialisations in Geology, Geophysics and Geochemistry to enable graduates whose major studies were in another area to switch to Geology for postgraduate studies. For details of the units to be studied see the entry under Geology 4 (Honours). Enrolment master codes Geology KEA510 Full time 100% KEA511 Part time 50% Geophysics KEA520 Full time 100% KEA521 Part time 50% Course details (2001) page 402 Geochemistry KEA540 Full time 100% KEA541 Part time 50% Mathematics and Physics Specialisation: Mathematics For details, see Mathematics Honours course (KMA400/401) on page xx. Enrolment master codes KMA500 Full time 100% KMA501 Part time 50% Specialisation: Physics For details, see Physics Honours course (KYA410/411) on page xx. Enrolment master codes KYA510 Full time 100% KYA511 Part time 50% Plant Science Specialisation: Botany For details, see Botany Honours course (KPA400/401) on page xx. Enrolment master codes KPA500 Full time 100% KPA501 Part time 50% Specialisation: Genetics For details, see Genetics Honours course (KPA410/411) on page xx. See also Honours course in Forest Ecology page xx. Enrolment master codes KPA510 Full time 100% Course details (2001) page 403 Zoology Specialisation: Zoology For details, see Zoology Honours course (KZA400/401) on page xx. Enrolment master codes KZA500 Full time 100% KZA501 Part time 50% Graduate Diploma in Spatial Information Science with Honours (Abbreviation: GradDipSIS(Hons)) Course code: N6Y This diploma meets the needs for professional development and training for people working primarily in land based sciences (e.g. foresters, geographers, town planners, surveyors) who need to apply spatial information science technology in their work or study. Admission & prerequisites Possession of a bachelor degree from the University of Tasmania, or an equivalent qualification from other recognised universities. Course objectives The course aims to: • • • provide students with opportunities to acquire knowledge and skills in areas of spatial information science; provide graduates with advanced knowledge in one of the disciplines of spatial information science; meet the needs of industry, business and government agencies for relevant spatial information skills. Career outcomes Graduates of the Graduate Diploma in Spatial Information Science with Honours will find employment opportunities in Commonwealth or State Government agencies, local Councils or large private organisations, largely in land-based sciences. Opportunities for such employment exist in a wide variety Course details (2001) page 404 of areas such as Forestry, Antarctica, Environmental management, Transport, Land Planning, Geodetic Agencies, cadastral and engineering surveying. Course structure Candidates must complete the course in one year of full-time study or not more than two years of part-time study. The overall enrolment code for full-time students is KGG500 and for part-time students KGG501. Candidates, in conjunction with their supervisor, select a course which has the following components: Coursework Coursework will be selected from units offered by the Centre for Information Science or other such units offered by other Schools as the Faculty may prescribe from time to time. A weighting of 0% must be entered against the individual unit codes. Project KGG580 Graduate Diploma Project Work Fees This is a fee-paying course. However, some HECS places will be available in 2001. Master of Applied Science (Abbreviation: MAppSc) Course code: S7P The Master of Applied Science is a four semester full-time or eight semester part time course offered on the Hobart and Launceston campuses by most Schools of the Faculty of Science & Engineering. While the course for full-time students is the equivalent of four semesters, students with an acceptable science background may be able to complete the course in three semesters over one calendar year. Admission & prerequisites Course details (2001) page 405 A bachelor degree in Science or Applied Science at the University of Tasmania or an equivalent award from another university or tertiary institution. Entry points To recognise the variety of science and non-science tertiary education backgrounds of applicants, the course has the following three entrance points: • • • Advanced Component – applicants who have completed a suitable three year degree with a major in the area of study of application in the MAppSc, for example a student with a BSc majoring in mathematics who wishes to study mathematics in the MAppSc; Consolidation Component – applicants who have completed a suitable three year degree with a major in a different area of study to that proposed in the MAppSc, for example a student with a BSc majoring in mathematics who wishes to study computer science in the MAppSc; and Bridging – all other applicants admitted to the course. Course objectives The course aims to: • • • provide students with opportunities to acquire knowledge, attitudes and skills in a range of basic physical, computational, mathematical, earth and life sciences; provide graduates with advanced knowledge in one science discipline; and meet the needs of industry, business and government agencies. Career outcomes Graduates of the Master of Applied Science will find employment opportunities in their areas of specialisation. These opportunities are similar to those listed under the career outcomes sections of the Bachelor of Science (including Honours). Professional recognition Depending on the area of specialisation, graduates may be eligible for membership of a number of professional organisations. Course structure The structure of the MAppSc is necessarily flexible to cater for the varied backgrounds of students entering the course. An individual program of study will be agreed between each student and the Dean or representative of the Dean upon entry to the course. Successful applicants to the course are asked to Course details (2001) page 406 contact the Faculty of Science & Engineering on (03) 6226 2008 to discuss enrolment codes. The MAppSc comprises four components: 1. 2. 3. 4. A three to six week bridging component (0% weight) in research training, computing, mathematics and any other required disciplines; A one semester consolidation component comprising 50% of undergraduate units with no level 1 units permitted and a maximum of 25% at level 2; A 100% (two semesters) advanced component comprising 75% honours and third level units, and a 25% project. The coursework units will include a minimum of 25% Honours level units. The project will normally be spread over the two semesters to allow the completion of 37.5% coursework in each semester. On approval of the relevant Head of School, the 25% project may be replaced with a further 25% coursework at Honours level; and A 50% thesis. Exit points Students who satisfactorily complete the coursework components of the course (up to and including the advanced component) shall be eligible for the award of the Graduate Diploma of Applied Science. Areas of specialisation Agricultural Science Agricultural Science Horticultural Science Microbiology Sustainable Resource Management Chemistry Chemistry Computing Computing Earth Sciences Earth Sciences Geography & Environmental Studies Course details (2001) page 407 Geography Environmental Studies Remote Sensing and GIS Mathematics & Physics Mathematics and Physics Plant Science Plant Science Psychology Behavioural Science Articulation There is no articulation with other courses. Master of Applied Science in Aquaculture (Abbreviation: MAppScAqua) Course code: S7C This Master of Applied Science program involves a combination of coursework and research. Students normally are required to undertake the coursework units of the Graduate Diploma program, a research dissertation, a literature review and work experience. The research is normally undertaken on campus. The research dissertation is assessed on the basis of a manuscript and a poster, while the literature review requires a manuscript and a seminar. Admission & prerequisites Either a Bachelor of Science or a Bachelor of Applied Science degree. Course objectives Articulation Graduate Diploma in Aquaculture Course details (2001) page 408 Doctor of Philosophy Curriculum Unit Title campus-sem weight code Year 1 Nutrition of Aquatic Organisms L1 12.5% KQA319 Physiology of Aquatic Organisms L1 12.5% KQA330 Technology for Aquaculture L1 12.5% KQA214 Intensive Algal Culture L1 12.5% KQA201 Intensive Crustacean & Zooplankton Culture L2 12.5% KQA228 Intensive Finfish Culture L2 12.5% KQA320 Aquatic Animal Health L2 12.5% KQA321 Intensive Molluscan Culture L2 12.5% KQA303 Students progressing to BAqua(Hons) should also undertake KQA302 or have completed an equivalent statistical unit. Two weeks work experience is required Year 2 Scientific Analysis and Presentation for Aquaculture L1 12.5% KQA302 Literature Review L1/2 25% KQA817 Research Dissertation L1/2 25%/50% KQA818/819 Specialist Practical Skills L1/2 0% KQA820/821 Master of Computing (Abbreviation: MComp) Course code: S7K This course is designed for people who already have a degree in computing and wish to study an advanced course in computing. It consists of 1.5 years full-time coursework and an individual project requiring supervised applied research. Admission & prerequisites Possession of a degree or graduate diploma in computing. Course details (2001) page 409 Applicants will normally be expected to have achieved an average grade of credit or better in the final year of their degree. Course objectives The master degree program provides a knowledge of advanced material in computing which will both encompass current computing technology and serve as a basis for future growth. Career outcomes Students are prepared for careers and research in the area of Information Technology (IT). Current forecasts indicate a world wide shortage of IT professionals for at least the next ten years. Computing professionals get well paid, interesting positions in almost any area – government, commerce, industry. The range of activities is wide, including: website management, system administration, client support and training, program design, development and testing, and so on. Professional recognition Undergraduate students of the BComp are eligible for student membership of the Australian Computer Society (ACS) and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). On completion of the degree and entry into the computing profession, graduates can apply to become full members of these bodies. Units approved for the Master of Computing Unit Title campus-sem weight code Computation and Functional Programming L? 12.5% KXA412 Spatial Information Systems L? 12.5% KXA415 Multimedia & Internet Applications L? 12.5% KXA430 Advanced Computer Security L? 12.5% KXA418 Machine Learning L2 12.5% KXA431 Java Applications L? 12.5% KXA433 Other units approved by the Head of School The availability of these units will depend on student demand and availability of resources. Master of Economic Geology Course details (2001) page 410 (Abbreviation: MEconGeol) Course code: S7F The Master of Economic Geology, course code S7F, is in teach-out, having been replaced by the Master of Economic Geology, course code S7R. Continuing students, already enrolled in S7F, should consult the Course and Unit Handbook 2000. Any enquiries should be addressed to the Admin Officer on (03) 6226 2819 or fax (03) 6226 7662. Master of Economic Geology (Abbreviation: MEconGeol) Course code: S7R This is a specialised master degree course in Economic Geology for industry and government geologists. It forms the nucleus of the postgraduate teaching program at the Centre for Ore Deposit Research (CODES). From 2001 the course will form part of the National Masters Program sponsored by the Minerals Council of Australia and the DETYA Science Lectureship Scheme. Admission & prerequisites Bachelor of Science with Honours is the normal entry qualification. However, for students without this qualification the entry requirements will depend on whether the applicants come from a professional industry background. Applicants from industry without a Bachelor of Science with Honours degree will require the following: • • • Bachelor of Science or Bachelor of Science (Applied); and A minimum of two years' experience working as professional geologist in industry or a government institution; and Completion of a significant geological company report or paper, based on some aspect of work carried out during employment as a professional geologist. Course objectives Course objectives are to update knowledge and skills required by geoscientists for the exploration and exploitation of mineral deposits. These are accomplished through completion of six short courses and a small in depth Course details (2001) page 411 research project OR eight short courses. The courses will cover a spectrum of topics relevant to the exploration mining industries. Career outcomes This course is for geoscientists who want to gain a thorough up-date on advances across the spectrum of economic geology applied to mineral exploration. Professional recognition The course will become part of the G3 National Masters course sponsored by the Mineral Council of Australia and the Commonwealth Government (DETYA). Units will be taught by the University of Tasmania, the University of Western Australia and James Cook University. Course structure The Master of Economic Geology is a coursework master degree. A thesis can be undertaken which amounts to 40% of the overall assessment and is examined by the School of Earth Science and CODES staff. The course work consists of the following units, each weight at 20% of a full year's load. A minimum of two units must be taken at either James Cook University or the University of Western Australia. A minimum of four units must be undertaken at the University of Tasmania. Schedule of units Unit Title campus-sem weight code Ore Deposit Studies and Exploration Models H1 20% KEA841 Volcanology and Mineralisation in Volcanic Terrains H1 20% KEA843 Exploration Geophysics, Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systems H1 20% KEA844 [a] Geochemistry, Hydrology and Timing of Hydrothermal Systems 20% [a] Ore Deposits of South America 20% Each unit is taught in an intensive program of lectures, seminars, practicals and field work over a 2 week period amounting to 65 lecture equivalents. [a] Contact the School of Earth Sciences for details and code numbers Research Thesis Course details (2001) page 412 The research thesis is on a well defined and concise topic in the field of economic geology that may be related to a specific aspect of the candidateís current exploration or mine geology work. The six units of coursework are taken over an eighteen months period; three units a year will be offered in March, June-July and October-November. The research thesis must be submitted within 30 months of the enrolment date. In special circumstances candidates may be allowed to suspend their enrolment or, where they have failed to meet one or more of the requirements, to repeat them. Master of Environmental Management (Abbreviation: MEnvMgt) Course code: S7D Lecturers: Assoc Prof JJ Todd, Dr PR Hay, Dr PB McQuillan, Dr JA Russell, Dr LK Kriwoken, Dr E Stratford, Prof JB Kirkpatrick, and others. The Master of Environmental Management (MEnvMgt) is offered internally by the School of Geography and Environmental Studies at the Hobart campus. The coursework-plus-thesis program aims to attract people who are interested in environmental management, or who anticipate responsibility for environmental policy formation, or a role in environmental education. The course extends the professional expertise of people working in such fields as agriculture, community welfare, economics, education, engineering, forestry, law, medicine, planning, public health, political economy, science, and resource management. The course is of two years duration for full-time study or up to four years part-time. Full-time students The course runs for two calendar years. In the first year, students take the four coursework units. The major research project constitutes the work of the second year. Part-time students Part-time students may undertake the degree on a unit basis, project work being done in the student's own time. Variations in lecture times are designed to enable part-time students to still meet the needs of their employment. Prospective part-time students are invited to discuss ways of undertaking the course with the Coordinator. Course details (2001) page 413 External Study is not normally available for the coursework degree. Admission & prerequisites Applications for direct entry to the course are considered from those who have a suitable tertiary qualification or its equivalent. Applicants with a university degree and substantial professional experience (a minimum of two years' appropriate employment) are directly admissible, as are honours graduates and graduates with a four-year professional qualification. Diplomas and other such awards can be counted towards the four-year qualification. Applicants with a three year bachelor degree are directly admissible provided their standard of achievement is acceptable to the Faculty. People holding other than university tertiary qualifications are admissible subject to agreement by the Faculty that such qualifications are equivalent to those directly acceptable. Students completing the GradDipEnvSt may count their coursework towards the MSc(EnvMgt) degree provided they do not take out the Graduate Diploma and their work has reached a standard considered satisfactory by the Coordinator. To ensure entry to this course, application for admission should be made as early as possible. Some students may be required to complete a preliminary reading unit. Such preparation is normally done before the commencement of the formal teaching in the first year of the course. Course objectives Several basic assumptions underlie the University's program for the degree. • • • Those who frame the alternatives from which environmental policy choices will be made must necessarily make highly significant value judgements. Public understanding of administrative decision-making will be enhanced when people are willing to make explicit the values underlying policy formation. Accordingly, emphasis is placed on developing a student's sense of values. While the economic, social, cultural, legal and physical aspects of any major environmental policy problem can be distinguished analytically, these aspects need to be viewed together if policy-makers are to come up with workable solutions. Therefore, the program stresses the need for integrative modes of thought. The character of the solutions required from environmental policy-makers is changing rapidly. Categorical solutions are no longer appropriate; more and more people are recognising the interdependence of public problems. Thus, the solutions which policy makers provide must be integrative in an Course details (2001) • page 414 additional sense. In order for governments to make authoritative decisions, the aspirations of competing institutions must be brought into direct relationship with one another so that, through a process during which these aspirations are modified, solutions which have a wide degree of acceptance are produced. This acceptance must be achieved in stages during which the point of view of all participants gradually changes. In recognition of the importance of the integrative approach, the course prepares students for policy making through a program which stresses the multifaceted nature of environmental problems. The methods adopted by universities for teaching environmental studies will vary depending on the character of the groups being served and on the special strength of the university concerned. The University of Tasmania is particularly well suited to carry out a variety of programs integrating natural and social phenomena, as Tasmania provides a wide range of environments within a relatively small area. Although the course is aimed at exploiting this advantage, it is recognised that there is no one best way of preparing people for effective environmental study. Career outcomes This course provides the knowledge and skills background appropriate to careers within environmental management, environmental policy formation, and environmental education. Course structure Students taking the course attend the lectures, practicals, seminars and excursions and complete the projects and reading organised in four major units: • • • • Environmental Planning Environmental Technology Ecosystems Environmental Values Students carry out a major research project on an environmental problem resulting in a thesis, sometimes as part of a multi-disciplinary team. The project provides for a practical involvement in the task of assessing and integrating results of studies conducted in diverse disciplines. Thus, this program stresses both 'what to do' and 'how to do it' in the context of value choices. There are five basic components: four coursework units and a research project thesis involving problem-oriented research, which can be undertaken as part of a multi-disciplinary team. The major research project component constitutes one half of the course. Students may take equivalent load postgraduate or undergraduate units offered by the School of Geography and Environmental Studies or other schools in Course details (2001) page 415 place of one of the four coursework units, subject to approval by the Coordinator. Unit Title campus-sem Environmental Technology H2 Ecosystems H1 Environmental Planning H2 Environmental Values H1 Research Project Thesis H The following are the 'umbrella' codes Master of Environmental Management (full time) weight 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% code KGE812 KGE813 KGE814 KGE815 KGE840 H 100% KGE808 Master of Environmental Management (full time) [a] H 100% KGE808 Master of Environmental Management (part time) [a] H 100% KGE809 [a] The appropriate 'umbrella' code must be entered on all MEnvMgt enrolments, in addition to the individual units' code. A weighting of 0% must be entered against the individual unit codes. [a] Master of Environmental Studies (Abbreviation: MEnvSt) Course code: S7B There is no new intake into this course which is in teach-out The Master of Environmental Studies (Coursework) is available only to continuing students as it is being superseded by the Master of Environmental Management. Continuing students should refer any queries about course arrangements to the Coordinator. Course structure Continuing students enrolling in MEnvSt (Coursework) units need to enrol in one of the following umbrella codes. Unit Title campus-sem weight code [a] Master of Environmental Studies (Coursework) (full time) H 100% KGE810 [a] Master of Environmental Studies (Coursework) (part time) H 100% KGE811 Other units are the same as those listed for MEnvMgt above, but the following code is required for the thesis component: Course details (2001) page 416 Research Project Thesis H 0% KGE840 [a] The appropriate 'umbrella' code must be entered on all MEnvSt enrolments, in addition to the individual unit and/or project code. A weighting of 0% must be entered against the individual unit codes. Master of Meteorology and Oceanography (Abbreviation: MMet&Oc) Course code: S7N The Master of Meteorology and Oceanography is a 3-semester full-time or 6-semester part-time course offered on the Hobart campus by the Institute of Antarctic and Southern Ocean Studies and the School of Mathematics and Physics. Admission & prerequisites An undergraduate degree in the physical sciences or in engineering with a mathematical background at least to the level of introductory calculus equivalent to first year university standard. Course objectives The course aims to equip students with the skills to enter national programs concerned with the atmospheric and oceanographic sciences, and/or to equip them with the basic skills appropriate to higher degree research in meteorology and oceanography. Career outcomes Graduates of the degree could expect to find employment as a meteorologist, oceanographer, atmospheric scientist, climate modeller, or applied mathematician. Course structure First semester: 140 lectures divided into three basic topics – namely: meteorology, oceanography, and techniques in applied mathematics. Second and Third Semesters: 'Specialised Reading' leading to a research project. The research project will be at a standard equivalent to that required Course details (2001) page 417 for entrance to research higher degrees as stated in the Rules of Higher Degrees by Research. Students enrol in the following unit codes: Full-time students KSA802 Master of Meteorology and Oceanography 100% Part-time students KSA803 Master of Meteorology and Oceanography 50% Articulation There is no articulation with other courses. Master of Psychology (Clinical Psychology) (Abbreviation: MPsych(Clin)) Course code: S7J The Master of Psychology course is offered on the Hobart campus. There are two streams to the degree course; one in clinical psychology and one in developmental and educational psychology. The degree is awarded in terms of the specialisation undertaken. Graduates who have undertaken the specialisation in clinical psychology use the abbreviation MPsych(Clin) while graduates who have undertaken the specialisation in developmental and educational psychology (course code: S6Q) use the abbreviation MPsych(Devel&Ed). Admission & prerequisites To be admitted to the course, applicants must hold the degree of Bachelor of Arts or Bachelor of Science of the University of Tasmania, with at least first or second class honours in Psychology. Applicants who hold the Diploma of Psychology of the University of Tasmania obtained at the level 'Pass with Credit', or a degree or diploma from an approved university or tertiary institution at a standard equivalent to those referred to above, and which contains an equivalent component of coursework and research in psychology, may be considered for admission to the degree course. Course details (2001) page 418 In special cases applicants who hold a Diploma of Psychology from the University of Tasmania obtained at the level of 'Pass', or a degree or diploma of equivalent standing, and appropriate professional experience may be considered for admission. All applicants must satisfy the School of Psychology that they are suitable candidates for professional training in psychology. Course objectives Both streams of the Master of Psychology degree course have particular vocational outcomes and are intended to prepare students for professional work as psychologists through the development of advanced professional skills, in tandem with theoretical and empirical knowledge, in line with the scientist-practitioner model. Professional recognition Master of Psychology graduates who have undertaken studies in either the clinical stream or the developmental and educational stream meet the academic requirements for registration as a psychologist, membership of the Australian Psychological Society and, following two years of supervised professional experience, membership of the appropriate APS College. Course structure To qualify for the degree, candidates are required to undertake one of the two programs. Core units are grouped in terms of those taken in the first and second years of full-time enrolment. Other units are offered in a two-year cycle. Year A and Year B, and may be taken in either the first or second year of enrolment (see the course schedule for each program for units offered.) Progress A candidate who fails to make satisfactory progress may be required by the Faculty to withdraw from the course. Thesis The thesis must embody the results of a research investigation on a topic approved by the course coordinator. The investigation must be carried out under the supervision of a staff member of the School. The thesis must be submitted by 30 November of the second year of study unless the Faculty has approved an extension of time. Course details (2001) page 419 Enrolment Master codes KHA750 KHA780 Clinical Psychology Educational Psychology Clinical Psychology – Schedule Course Coordinator: Dr CL Williams The program consists of coursework, supervised clinical work and a research thesis. Candidates are also required to complete 1000 hours of supervised practical work over the period of enrolment. In order to meet the requirements for continuing state registration and professional accreditation by the Australian Psychological Society, core units will be taught each year, while other components of the program are taught in alternate years. Candidates may enter the course at the beginning of each year and those contemplating part-time study are advised to consult the course coordinator to determine their program. A thesis proposal is required in the first year of full-time enrolment, whether Year A or Year B. Unit Title campus-sem weight First Year units (must be taken in first year of enrolment) Research Thesis 1 Hf 25% Ethical Issues & Professional Practice 1 Hf 27% Behaviour Change 1 H1 8% Current Issues in Assessment H1 8% Second Year units (must be taken in second year of enrolment) Research Thesis 2 Hf 25% Ethical Issues & Professional Practice 2 Hf 27% Behaviour Change 2 H1 8% Advanced Assessment H1 8% Units taught in alternate years (may be taken in either the first or second year of enrolment) Year A Psychophysiology & Psychopathology H1 8% Research Design H2 8% Adult Psychopathology H2 8% Clinical Psychophysiology H2 8% Year B Not offered in 2001 code KHA718 KHA717 KHA714 KHA711 KHA728 KHA727 KHA724 KHA721 KHA712 KHA716 KHA713 KHA715 Course details (2001) Neuroanatomy for Psychologists Clinical Child Psychology Community & Forensic Psychology Clinical Neuropsychology Enrolment master code Clinical Psychology page 420 [na] [na] 8% 8% KHA726 KHA722 [na] [na] 8% 8% KHA723 KHA725 Hf 0% KHA750 Master of Psychology (Developmental & Educational Psychology) (Abbreviation: MPsych(Devel&Ed)) Course code: S7Q The Master of Psychology course is offered on the Hobart campus. There are two streams to the degree course; one in clinical psychology and one in developmental and educational psychology. For further details See MPsych(Clin). Developmental & Educational Psychology – Schedule Course Coordinator: Dr T Thompson The program consists of coursework, supervised educational experience and a research thesis. Candidates are required to complete 1,000 hours of supervised practical work over the period of enrolment. In order to meet the requirements for continuing state registration and professional accreditation by the Australian Psychological Society, core units will be taught each year, while other components of the program are taught in alternate years. Candidates may enter the course at the beginning of each year and those contemplating part-time study are advised to consult the course coordinator to determine their program. A thesis proposal is required in the first year of full-time enrolment, whether Year A or Year B. Unit Title campus-sem First Year units (must be taken in first year of enrolment) Research Thesis 1 Hf weight code 25% KHA778 Course details (2001) Ethical Issues & Professional Practice 1 Hf 27% Behaviour Change 1 H1 8% Interviewing & Counselling H1 8% Second Year units (must be taken in second year of enrolment) Research Thesis 2 Hf 25% Ethical Issues & Professional Practice 2 Hf 27% Behaviour Change 2 H1 8% Advanced Interviewing & Counselling H1 8% Units taught in alternate years (may be taken in either the first or second year of enrolment) Year A Psychoeducational Assessment H2 8% Research Design H2 8% Methods in School Psychology H1 8% Applied Issues in Educational Psychology H2 8% Year B Not offered in 2001 Applied Developmental Psychology: Adolescence & Adulthood [na] 8% Applied Developmental Psychology: Childhood [na] 8% Clinical Child Psychology [na] 8% Exceptionality & Special Children [na] 8% Enrolment master code Developmental & Educational Psychology Hf 0% page 421 KHA777 KHA774 KHA771 KHA788 KHA787 KHA784 KHA781 KHA772 KHA776 KHA773 KHA775 KHA786 KHA785 KHA782 KHA783 KHA780 Master of Science Studies (Abbreviation: MScSt) Course code: S7E The program is designed to provide professional training for scientists/science educators from overseas countries. Currently it is offered by the Schools of Course details (2001) page 422 Agricultural Science (Microbiology); Chemistry; Computing (Computer Science); Earth Sciences (Geology); Geography and Environmental Studies; Mathematics and Physics; Medicine (Biochemistry); Plant Science (Botany); Psychology; and Zoology. Admission & prerequisites Candidates for the degree must have: • • • • an approved bachelor degree with first or second class Honours; or an approved eight-semester higher education qualification and potential to complete the degree as demonstrated in study and/or professional performance; or an approved six-semester higher education qualification, together with at least two years' relevant professional experience; or other qualifications equivalent to those in paragraphs shown above. In addition to the academic admission requirement stated above all candidates must be proficient in written and spoken English. Candidates whose basic language is not English should sit an English language test arranged by the nearest Australian diplomatic mission and are required to attend up to four months of intensive English tuition in Tasmania. A candidate for the degree may not enrol for another degree or diploma course of the University or another higher education institution. Course objectives Career outcomes Graduates of the Master of Science Studies find that opportunities for employment exist in the area of their specialisation. Professional recognition Depending on area of study, graduates of the MScSt may be eligible for membership of a number of professional organisations. Course structure The program consists of three parts: • • • Foundation Studies Professional Development Research training. Course details (2001) page 423 These parts can be flexibly arranged over three or four semesters, as shown in the examples which follow. In special cases, a candidate may be exempted from Foundation Studies. The degree requires at least 1 year full-time research or study. All requirements for the degree must be completed within two years of the date of commencement of candidature, except that a candidate may be allowed to enrol for the degree on a part-time basis. Foundation studies Students, especially those from developing countries, who lack the background necessary to proceed immediately to the Master degree course, may be (aside from their language tuition) required to undertake a period of preliminary studies, including selected background reading and attendance at certain lectures. Classwork Enrolment in this part of the course (professional development) is conditional on satisfactory performance in the preliminary foundation studies. The coursework program will be drawn up individually for each candidate by the School and will consist of at least 100% of formal classwork over two or three semesters. A maximum of 33.33% of second year units can be taken and the balance of the points is to be made up from third and fourth year units. Clear passes (or higher grades) must be obtained in all coursework except that up to 12.5% of Terminating Passes may be counted. Research training The project is an important part of the program, involving a substantial investigation in some area of scientific research or science education. It represents one third of the total course and should take a minimum of four months full time or eight months part time. Project work normally begins after the progress review, but the starting date for the project may be varied in consultation with the adviser and the head of the appropriate School. A thesis is required at the end of the program. The project should be on a topic directly relevant to the needs of the home country or employing institution of the student. Thesis discussions should begin as early as possible with the School, preferably before the student leaves home to begin the program, in order to satisfy the student's and sponsor's needs. Course details (2001) page 424 The standard of the thesis will be based on the normal honours requirements for a particular School. Supervisors On enrolment, each student will be assigned a suitable course adviser who will counsel the student for the duration of the coursework. In addition, a supervisor will be appointed for each candidate on the recommendation of the relevant head of School, at the end of the first semester, to oversee the candidate's research project. The progress of a candidate is reviewed annually and unsatisfactory performance may result in termination of candidature. Examination Assessment of coursework is by written examinations and assignments. The written thesis on the research project must be submitted for separate examination. Normally, there will be two examiners who may be internal. Enrolment master codes On the enrolment form each candidate must enter the code numbers of the units selected; plus the appropriate 'umbrella' code chosen from this list: Code Number Course Weight KLA861 MScSt Coursework (Microbiology) 0% KLA875 MScSt Thesis Project (Microbiology) 100% CBA861 MScSt Coursework (Biochemistry) 0% CBA875 MScSt Thesis Project (Biochemistry) 100% KPA861 MScSt Coursework (Botany) 0% KPA875 MScSt Thesis Project (Botany) 100% KRA861 MScSt Coursework (Chemistry) 0% KRA875 MScSt Thesis Project (Chemistry) 100% KCA861 MScSt Coursework (Computer Science) 0% KCA875 MScSt Thesis Project (Computer Science) 100% KGA861 MScSt Coursework (Geog & EnvSt) 0% KGA875 MScSt Thesis Project (Geog & EnvSt) 100% KEA861 MScSt Coursework (Geology) 0% KEA875 MScSt Thesis Project (Geology) 100% KMA861 MScSt Coursework (Mathematics) 0% KMA875 MScSt Thesis Project (Mathematics) 100% KYA861 MScSt Coursework (Physics) 0% KYA875 MScSt Thesis Project (Physics) 100% KHA881 MScSt Coursework (Psychology) 0% KHA875 MScSt Thesis Project (Psychology) 100% KZA861 MScSt Coursework (Zoology) 0% Course details (2001) KZA875 page 425 MScSt Thesis Project (Zoology) 100% Master of Technology (Abbreviation: MTech) Course code: N7A It is essential for practising engineers and scientists to keep up with the rate of technological advancement. Important developments have occurred in computer hardware and software systems, communications systems and networking, VLSI and ASIC technology, robotics, signal processing, artificial intelligence and knowledge based systems and networking, to mention but a few. A more advanced knowledge than that offered by the Bachelor of Engineering or the Bachelor of Science is required in order to understand and to explore the full potential of investment in technology. Admission & prerequisites To be accepted as a candidate for the degree of Master of Technology students must either: • • • have an approved bachelor degree (with honours) from an Australian higher education institution; have satisfactorily completed an approved eight-semester higher education program and have potential to complete the degree as demonstrated in study and/or professional performance; or have satisfactorily completed a degree or equivalent qualification, and have potential to complete the degree as demonstrated by study and/or professional performance, and have knowledge and skills equivalent to those of a candidate as shown above. Prospective students should contact the Head of School to obtain approval to enrol in the course. Course objectives The course provides professional updating and upgrading opportunities for engineers and computing professionals who have gained a first degree and have been in employment for some years. The Master of Technology is also suitable for those graduates who wish for a change of career. The course is also suitable for young graduates who feel that their undergraduate training is inadequate for the specialisation they are seeking. Career outcomes Course details (2001) page 426 The Master of Technology maximises the candidate's employment value by the involvement of experienced and academically qualified engineers and/or computing professionals from industry in the teaching of the program. Course structure Each candidate for the degree must: • • satisfactorily pass the equivalent of six graduate units representing two semesters of full-time study (see the Specimen courses below); and submit for examination and satisfactorily pass a thesis representing the equivalent of one semester of full-time research investigation. Candidates are advised to discuss and finalise their thesis topic with a supervisor and be adequately prepared for the thesis investigation as soon as possible after enrolment. Candidates are encouraged to suggest projects which are relevant to their jobs or careers, although the Faculty reserves the right to modify or reject such suggestions. In special circumstances, with the approval of the Head of School, part of the thesis work may be conducted off-campus. The course as described above will normally be completed in 16–18 months of full-time study. The maximum duration for part-time study is three years. The School of Engineering offers the following coursework streams: Enrolment master codes ACC824 ACM822 ACM823 AEA850 ACM820 Civil Engineering (not offered in 2001) Energy and Fluid Systems (not offered in 2001) Mechanical & Production Engineering (not offered in 2001) Power Engineering and Process Control Information Systems and Autoation Fees The fee is to be advised. Specimen courses Courses of study in the different areas of specialisation are given below. However, depending on the interests of the particular student and after discussion with the course coordinator, one or more of the units may be replaced by other units listed in Schedule A below. All courses and units are also subject to minimum enrolment. Course details (2001) page 427 Civil Engineering Not offered in 2001. Mechanical and Production Engineering Not offered in 2001. Power Engineering and Process Control Unit Title campus-sem weight code Digital Signal Processing H1 16.67% AEA831 Intelligent Systems Engineering H2 16.67% AEA835 Transient Behaviour in Power Systems H 16.67% AEA860 Optimisation in Power Systems H 16.67% AEA861 Industrial Measurement Systems H1 16.67% AEA863 Plus one other unit selected with the approval of the course supervisor. Information Systems and Automation Unit Title campus-sem weight code Digital Signal Processing H1 16.67% AEA831 Intelligent Systems Engineering H2 16.67% AEA835 Computer Organisation and Interfacing H2 16.67% AEA841 Corporate Information & Transmission Networks H2 16.67% AEA836 Plus two additional units from the following according to the student's interest and background: Robot Kinematics, Dynamics and Control [na] 16.67% ACM803 Advanced Manufacturing [na] 16.67% ACM875 Image Processing, Computer Vision and Graphics H 16.67% AEA833 Industrial Measurement Systems H1 16.67% AEA863 Schedule A Units approved for the Master of Technology [a] Course details (2001) Unit Title Civil Engineering Thesis Project Energy and Fluid Systems Thesis Project Mechanical and Production Engineering Thesis Project Information Systems and Automation Thesis Project Power Engineering and Process Control Thesis Project Stress Analysis Advanced Hydraulics Advanced Geomechanics Advanced Management Robot Kinematics, Dynamics and Control Mechanical Noise and Vibration Control Advanced Structural Mechanics Advanced Fluid Mechanics Energy Management and Systems Heat Transfer and Process Drying Advanced Manufacturing Modern Manufacturing and Quality Control CNC Machining – Theory and Practice Occupational Health and Safety Digital Signal Processing Robotics and Automatic Control Image Processing, Computer Vision and Graphics Intelligent Systems Engineering Corporate Information & Transmission Networks Integrated Services Digital Networks Management of Information Systems page 428 campus-sem weight code [na] 50% ACC825 [na] 50% ACM826 [na] 50% ACM827 50% AEA825 [na] [na] [na] [na] 50% 16.67% 16.67% 16.67% 16.67% AEA855 ACC814 ACC831 ACC834 ACM802 [na] 16.67% ACM803 [na] 16.67% ACM805 [na] [na] 16.67% 16.67% ACM813 ACM820 [na] 16.67% ACM860 [na] [na] 16.67% 16.67% ACM865 ACM875 [na] 16.67% ACM876 [na] 16.67% ACM877 [na] H1 16.67% 16.67% ACM878 AEA831 H 16.67% AEA832 H 16.67% AEA833 H2 16.67% AEA835 H2 16.67% AEA836 H 16.67% AEA837 H1 16.67% AEA838 Course details (2001) Computer Organisation and Interfacing Transient Behaviour in Power Systems Optimisation in Power Systems Modelling and Control of Processes Industrial Measurement Systems Special Studies in Power Engineering and Process Control Selected Course Unit [c] Special Studies in Information Systems Selected Study Unit A [b] Selected Study Unit B [b] Selected Study Unit C [b] Selected Course Unit A [c] Selected Course Unit B [c] Notes: [a] [b] [c] page 429 H2 16.67% AEA841 H 16.67% AEA860 H 16.67% AEA861 H 16.67% AEA862 H1 16.67% AEA863 H 16.67% 16.67% AEA865 AEA866 16.67% 16.67% 16.67% 33.33% 16.67% 16.67% AEA870 AEA880 AEA881 AEA882 AEA883 AEA884 Not all the units listed here are offered in a particular semester. A specific enquiry is necessary to determine which units will be offered within each student's course duration. Each of these units is used for a program of directed study in a topic specifically approved for each student. A long study unit is equivalent to two graduate units in workload. A supervisor is responsible for assessing the program of study. No more than two equivalent graduate units may be chosen from the set of Selected Study units. The Head of School may grant approval to a student undertaking up to two graduate units from other programs.