Introduction, History and Computer Basics - Worksheet computer design
advertisement

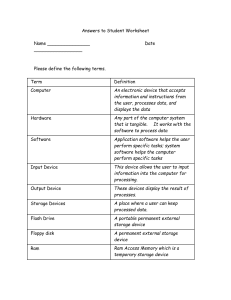
Introduction, History and Computer Basics - Worksheet Computer Science: The discipline that seeks to build a scientific foundation for such topics as: computer design computer programming information processing _____________________________ Algorithm: A _______________________ that defines how a task is performed Program: A representation of an _________________ Programming: The process of developing a program Software: Programs and algorithms Hardware: Equipment used to input information (data) and output the results of the programs, algorithms. The Euclidean algorithm 1 Origins of Computing Machines Early computing devices ____________: positions of beads represent numbers ______________________________ (1600s-1800s) Positions of gears represent numbers Blaise Pascal, Wilhelm Leibniz, Charles Babbage Early Data Storage • ________________________________ – First used in Jacquard Loom (1801) to store patterns for weaving cloth – Storage of programs in Babbage’s Analytical Engine – Popular through the 1970’s • The Jacquard loom was the ______________________ to use • _________________________ to control a sequence of operations. Did not do computation, but important in history of computer science. Augusta Ada Byron • Mainly known for having written a description of Charles Babbage's early mechanical general-purpose computer, the analytical engine. • She is also known as the ___________________________________ First Generation – _________________________________ 1930’s – Vacuum tubes were used as _________________________ or ______________________________________ 1946 - ENIAC First large-scale electronic digital computer was __________________ (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Calculator) ______ additions every second, (incredibly slow by today’s standards). 2 _________________________________, one of the first programmers on the ENIAC and the developer of the programming language _________________, says, “It was the first machine that assisted the power of man’s brain instead of the strength of his arm.” ENIAC was developed long before the days of silicon chips or microchips, even before the transistor was invented. Like ABC, ENIAC was made up of vacuum tubes, over _____________ of them! 1951- UNIVAC 1 • • 1951 the first commercially available computer was developed, the UNIVAC I (UNIVersal Automatic Computer) using vacuum tubes 3,000 additions every second. • In 5 years we were going a _____________________ times faster. Second Generation – _________________________________ • 1947 - Walter Brittain and Willaim Shockley invented the transistor at Bell Laboratories • Replaced the vacuum tube as an ________________________________ Transistors were: ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ Third Generation – ___________________________________ • • 1959, Jack Kirby and Robert Noyce at Fairfield Semiconductor (who was later to become the cofounder of Intel Corp.) developed the first integrated circuit (silicon chip or microchip). An integrated circuit (IC) _______________________________________________________________. _______________________________________________________________ 1960 – IBM 360 1 addition every billionth of a second (_________________), or a billion additions every second 3 Third Generation – _____________________________________ ICs, chips, were ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ Fourth Generation - ____________________________ • A microprocessor is a ____________________________________________________________ • 1971, ______________________ introduced the first microprocessor chip. Computer Basics What is a computer? • A ______________________ is a electromechanical device which can be programmed to change (process) information from one form to another. – Do exactly as they are told. – Digital devices: Understand only _____________ different states (_________________________) Hardware versus Software • Hardware = _____________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ • Software = _____________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ The Processor ________________________ = a board with integrated circuits (microchips) • system board or motherboard • interface boards or expansion boards 4 The Processor: The CPU CPU (_____________________________________) = A complex collection of electronic circuits on one or more integrated circuits (chips) which: 1. ________________________________________________________________ 2. communicates with other parts of the computer system, especially RAM and input devices INPUT SYSTEM UNIT OUTPUT PERMANENT STORAGE System Unit - Revisited System Unit: • CPU (Central Processing Unit) • Memory – RAM – ROM or ROM BIOS • expansion slots RAM (Random Access Memory) RAM (__________________________________) = integrated circuits (chips) used to __________________________________ store software (programs, instructions) and data RAM is _______________________________ memory RAM is _______________________________ 5 ROM (Read Only Memory) ROM (________________________________________) = integrated circuits (microchips) that are used to _____________________________ store start-up (boot) instructions and other critical information Read Only = information which: • Cannot be _________________ • Cannot be _________________ • Cannot be appended (added to) • Fixed by manufacturer ROM is sometimes known as ROM ______________ (Basic Input Output System software) ROM permanently contains: • • ____________________________________________ instructions to do “low level” processing of input and output devices, such as the communications with the keyboard and the monitor ________________________ = software program which is stored permanently on a microchip, such as the software on the ROM chip Computer Performance _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ Application Software Written for a specific _____________________________________________________ Operating System Software – Controls _______________________________________ – Permits you to ______________________________________ – Acts as intermediary between ___________________________________________ 6 7 1975 - Altair 8800 • ___________________________________ and the first microcomputer or personal computer (for the consumer) the Altair 8800 1972 - ______________________________ Xerox Alto – first microcomputer 1976 - ______________________________ • Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak developed the Apple I microcomputer in their basement. 1977 – ______________________________ 1981 – IBM PC • __________________________________ and IBM 1984 – ______________________________ 1985 – ______________________________ 1987 – ______________________________ 8 9