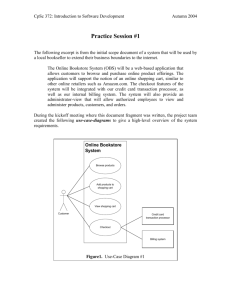
Object-Oriented Use Case Diagrams
advertisement

Use Cases Week 8 CMIS570 Refresher – Class Diagrams Appointment scheduling example Car Rental example E-Commerce example UML diagrams 9 diagrams Used throughout SDLC Use consistent syntax and notation. Key building block is the use-case. Use-Case Requires you to break system into use cases, small logical pieces of the system and deal with each separately. In contrast, DFDs and ERDs encompass the entire system in one diagram. Use-Case Diagrams Graphical specification of the system’s behavior from the perspective of the user(s). Describes what the system does without describing how the system does it. They are used to identify and communicate the high-level business requirements for the system. Use-Case contains: Actor Event/Use Case Association System boundary Example! Patient Admission system Example Car Rental System Another example E-commerce system Steps in creating a Use-Case 1. Identify use-cases (find major functions) 2. Draw the system boundary 3. Place use-cases on the diagram (6-8 use-cases per diagram) 4. Identify the actors 5. Add associations In addition… Text documents to document use-cases since use-case diagram does not describe how those use cases are carried out by the actors. When describing the use-case, you should focus on its external behavior – how it interacts with the actors, rather than how the use case is performed inside the system. Steps in Documentation 1. Create a use case template that has areas labeled Basic Course and Alternative Courses. 2. Ask “What happens?” 3. Ask “And then what happens?” 4. Ask, “What else can happen? Documentation examples Patient Admission Rent a car Search by Author TIPS Think usage scenario rather than functional requirements. Describe usage rather than attributes and methods. Don’t write use-case too tersely. Don’t ignore system responses. Don’t forget alternative courses of action Includes statement When one use-case needs to use another use-case Two types Internal – only other use-cases reference Both external actors and internal use-cases reference Examples Order Entry Class registration