Mental Health and Supporting Students

Mental Health and Supporting
Students
Dr Niamh Farrelly
Consultant Psychiatrist TCD
An Integrated Approach
How Disability Services can communicate with college-based and external health services and ensure best use of resources?
Overview
• 75% of mental health problems emerge before the age of 25
• 25% of 18-25 year olds experience MH problems each year : ¼ of whom access help
Estimate 20,000 students
25% = 5,000 students have MH problems
= 1,250 (25%) Actively access help (6% all stds)
Changing student profile
• more college students meet criteria for some form of learning disability .
• Lifestyle habits— eating patterns, sexual activity, sleeping and drinking—we also see evidence of markedly increasing maladaptive patterns.
More students, more complex needs…
Models of Support
Authoritarian
Autonomous: Age / maturity /Separation / individuation
Collaborative Care: blend of
‘authority’ (training, knowledge, experience) and
‘autonomy’ (knowledge , preference, experience)
Autonomy
• Do we hide behind autonomy (right to refuse recommendation) rather than attempt to recognise the clinical problem that lies at the root of the refusal
• Autonomy can be made an acceptable way of passing burdensome problem or decisions over to the student
• Abdication of responsibility for decisions from the college to the student
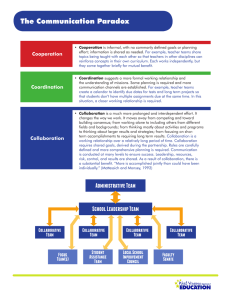
Collaborative Care
• blending of professional cultures: achieved though sharing skills and knowledge to improve the quality of patient care
• There are important characteristics that determine team effectiveness, including
members seeing their roles as important to the team, open communication, the existence of autonomy, collaborative education
Collaborative Care
• Individual becomes active partner
• Takes appropriate responsibility
• Agree joint decision
– At times balance between authority and collaboration may need to shift
– Emergencies trump collaboration but true collaboration plans for these exigencies
Friends
Student
Service supports
Academic supports
Student
Family supports
Extern al
Self help resource s
Collaborative Care Planning
• Student at the helm, support etc. crew
• Concordance on destination
• Concordance on route
• Concordance on contingency planning
– Advance directives/ planning if temporary absence of captain
• e.g. discussion re ‘what do you want me to do if you DNA?’
Outcome of collaborative care?
– Greater treatment concordance
– Better mental health outcomes
– Reduced hospitalisation
– Reduced time to relapse
– Reduced frequency of relapse
– Greater student retention
Consider perspective of all agencies
• Student *
• Disability officer *
• Tutor
• Academic supports
• Counselling supports
• Friends
• Doctor*
• OT
• Family*
What is competing with what?
• Student : academic / finances / relationship/
• Academic: funding / placement integrity
• Family: domestic issues / concerns/ isolation
• Friends : social life / formation of friendships
• Student Services: how is service shared/ how efficiently is this done
• Doctor
Medical role
• On site medical service
– Advantages: experienced in age group
– Disadvantages: lack 24/7 care access model
• Off site medical service
• May be most appropriate care setting especially if enduring difficulties likely to persist beyond college
• Provide continuity of care
• Broader scope to access service
• Emergency treatment provisions 24/7
Off site care
• Ability to be fully aware of demands and environmental challenges student faces?
• Day care facility
– notional structure and routine
– Inappropriate expectations of pastoral care
– Lack of awareness of financial implications of failure
– Assumptions made wrt. intellect and comparisons made with different core cohort of patients
– Educational experience of external provider
– Confidentiality
– Access to speak to somebody
External Care Provider
• How do you identify yourself?
• Most people do not know what a disability officer is?
• Concerns wrt confidentiality
• Speaking to somebody who knows individual
• Difficulties with continuity of care
• 450 points
• Articulate
• Likely higher SEG
CMHT
– Behavioural activation strategy
– Development of goal
– ? Full consideration of range of skills required to function as student who is unwell
Family
• Expectation to continue
• Assumptions to return
• ? Understanding of options
• Often
– left out in the cold
– Misinformed
– Lacking in knowledge of what is really going on
• Collaborative Care
– Sharing the same vision
– Aiming for the same destination
– Recognition of crew and their roles
– Contingency planning in event of a storm
COMMUNICATION
Communication
• Not just with student but with each other
• Attempting to understand different perspectives
• Development of relationships with core personnel / working out best person to speak with
• Meeting regularly / forming relationships
• Relationship with family
• Remember who you are dealing with!
• Pick up the phone!
• Networking
• Go and visit service