Circuits
advertisement

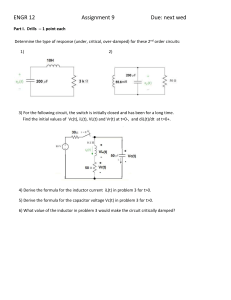
PHYS-1500 PHYSICAL MODELING Class 22a: Capacitors FALL 2006 NAME _________________________________ A capacitor is a device that stores charge. It can be viewed as two parallel plates placed close together. One plate carries positive charge and the other an equal amount of negative charge. The capacitor can be charged by connecting it to a voltage source, one plate to the high potential side and the other to the low. Then, the amount of charge that is deposited on the capacitor is proportional to the voltage applied. The constant of proportionality is called the capacitance, C. If the voltage difference between the two plates is V, and the magnitude of the charge on each plate is q, then q = CV. Conversely, if we wish to know the voltage across a charged capacitor, it is V = q/C. In this exercise, you will examine how capacitors react when connected in series with a voltage source and a resistor. The sketch shows the situation. The source provides a voltage E, and it must equal the sum of the voltage across the resistor, iR, and that across the capacitor. Then, E = iR + q/C. This equation is modeled in the spreadsheet that has been provided. The spreadsheet calculates changes in q as q = it, and, from the equation above, i = (E/R) – q/(RC). E can be either D.C., A.C., or a mixture of both, since it is given by E = E 1 + E 2 sin 0t. The quantity RC, which appears in the equation for i, is called the time constant of the circuit. 1. Consider q0 = 0, E1 = 10 V, E2 = 0, C = 1.0 ×10-6 F, and R = 1.0 ×106 . a) What is the time constant of the circuit? RC =__________________ units b) Use t = 0.05 s. Sketch the graph of q vs. t. What is the value of q at t = RC? q =__________________ units 1 2. Set R = 2.0 ×106 , but leave everything else the same. a) What is the time constant of the circuit? RC =__________________ units b) Use t = 0.05 s. Sketch the graph of q vs. t. What is the value of q at t = RC? q =__________________ units 3. Set R = 0.50 ×106 , but leave everything else the same. a) What is the time constant of the circuit? RC =__________________ units b) Use t = 0.05 s. Sketch the graph of q vs. t. What is the value of q at t = RC? q =__________________ units 4. Set R = 1.0 ×106 , set E1 = 0, and q0 = 1.0 ×10-5 C, but leave everything else the same. a) What is the time constant of the circuit? RC =__________________ units b) Use t = 0.05 s. Sketch the graph of q vs. t. What is the value of q at t = RC? What is the relationship between the value of q found in this section and that found in part 1? q =__________________ units 2 5. Set q0 = 0, E1 = 0, E2 = 10 V, C = 1.0 ×10-6 F, and R = 1.0 ×106 . Find i(max), the maximum value of i, for 0 = 0.05, 0.2, 1.0, 10, and 100 rad/s. Then do the same for C = 2.0 ×10-6 F. Enter the results in the table shown, and graph i(max) vs. 0 for both values of C on the same graph. t 1.5 0.5 0.1 0.01 0.001 o i (max) C 1.0 ×10-6 2.0 ×10-6 0.05 0.2 1.0 10 100 Sketch the graph below. 6. Is an RC circuit a better conductor of current at high frequency or low frequency? (Circle the correct answer.) HIGH FREQUENCY LOW FREQUENCY Which capacitor is the better conductor of current, the larger or the smaller? (Circle the correct answer.) LARGER SMALLER 3 Class 22b: Inductors An inductor is a device that stores energy in a magnetic field. It can be viewed as a closely wound coil of wire. When the inductor carries a current, it produces a magnetic field within the coil. The inductor can be charged by connecting it to a voltage source, with a resistor in series, one end to the high potential side and the other to the low. Then, the voltage difference between the two ends of the inductor is proportional to the rate of change of the current through the inductor. The constant of proportionality is called the inductance, L. Then, the voltage difference between the two ends is V = L di/dt. In this exercise, you will examine how inductors react when connected in series with a voltage source and a resistor. The sketch shows the situation. The source provides a voltage E, and it must equal the sum of the voltage across the resistor, iR, and that across the inductor. Then, E = iR + L(di/dt). This equation is modeled in the spreadsheet that has been provided. The spreadsheet calculates changes in i as i = (di/dt)t, and, from the equation above, di/dt = (E/L) – q/(L/R). E can be either D.C., A.C., or a mixture of both, since it is given by E = E 1 + E 2 sin 0t. The quantity L/R, which appears in the equation for di/dt, is called the time constant of the circuit. 1. Consider i0 = 0, E1 = 10 V, E2 = 0, L = 1.0 ×10-1 H, and R = 1.0 ×101 . a) What is the time constant of the circuit? L/R =__________________ units b) Use t = 0.0005 s. Sketch the graph of i vs. t. What is the value of i at t = L/R? i =__________________ units 4 2. Set L = 2.0 ×10-1 H, but leave everything else the same. a) What is the time constant of the circuit? L/R =__________________ units b) Use t = 0.0005 s. Sketch the graph of i vs. t. What is the value of i at t = L/R? i =__________________ units 3. Set L = 0.5 ×10-1 H, but leave everything else the same. a) What is the time constant of the circuit? L/R =__________________ units b) Use t = 0.0005 s. Sketch the graph of i vs. t. What is the value of i at t = L/R? i =__________________ units 4. Set L = 1.0 ×10-1 H, set E1 = 0, and i0 = 1.0 A, but leave everything else the same. a) What is the time constant of the circuit? L/R =__________________ units b) Use t = 0.0005 s. Sketch the graph of i vs. t. What is the value of i at t = L/R? What is the relationship between the value of i found in this section and that found in part 1? i =__________________ units 5 5. Set i0 = 0, E1 = 0, E2 = 10 V, L = 1.0 ×10-1 H, and R = 1.0 ×101 . Find i(max), the maximum value of i, for 0 = 10, 100, 500, and 1000 rad/s. Then do the same for L = 2.0 ×10-1 H. Enter the results in the table shown, and graph i(max) vs. 0 for both values of L on the same graph. t 0.01 0.005 0.0005 0.0002 o i (max) L 1.0 ×10-1 2.0 ×10-1 10 100 500 1000 Sketch the graph below. 6. Is an LR circuit a better conductor of current at high frequency or low frequency? (Circle the correct answer.) HIGH FREQUENCY LOW FREQUENCY Which inductor is the better conductor of current, the larger or the smaller? (Circle the correct answer.) LARGER SMALLER 6