Aging in Place
advertisement

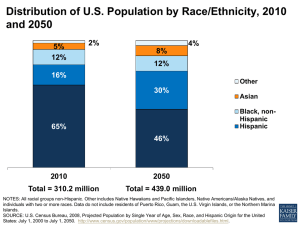
Aging in Place Judith L. Warren, Ph.D. Professor and Gerontology Specialist Texas Cooperative Extension Texas A&M University System September 2003 Demographics of Aging in America • • • • • • • • • Increasing numbers of older adults Migration to sunbelt Out-migration of youth in rural areas Aging in place Gender and income Increasing Hispanic population Household configuration Education Health and healthcare access Core Issues in an Aging Rural Society • Economic Development/Human Capital – Work and Volunteer Issues – Careers in an Aging Society • Independent Living – Housing and Services – Chronic Health Conditions • Elder Care – Formal and Informal – Family Caregiving Percent of Population by Age Group: 2003 – 2050 80 70 60 0-54 55-64 65-74 75-84 85+ 50 40 30 20 10 0 2003 2020 2050 Source: U.S. Census Population Projections Greatest Growth in Old-Old 85+ Age group increased 38% between 1990/2000 95+ Age group increased 34.7% Centenarians (100+) • 1990 - 37,306 • 2000 – 50,454 • Greatest # live in New York and California • Greatest % live in South Dakota and Iowa States With Highest Proportion of 65+ (2000) Florida 17.6% South Dakota 14.7% North Dakota 14.3% Pennsylvania 15.6% Rhode Island 14.5% Arkansas 14% West Virginia 15.3% Maine 14.4% Iowa 14% Baby Boomers are all in the same state “the state of denial” Age 65+ Males per 100 Females • Ratio declines with each age group • Increase in male to female ratio since 1990 65+ 65-74 • Are men getting healthier? 75-84 85+ • Are women at increased health risk? 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 1990 2000 Poverty Levels: 1959 & 1998 35 30 25 20 65+ Under 18 15 10 5 0 1959 1998 Sources of Income & Net Worth • Main source continues to be Social Security and Pensions • Between 1984 and 1999, the median net worth for 65+ head of households increased by 69%; for 45-64 – it declined by 23% • 1999 Median for White - $181,000; for African Americans - $13,000 Labor Force Participation 90 80 70 60 55-61 62-64 70+ 50 40 30 20 10 0 1963 1999 • Decline in participation rates • Most decline occurred prior to 1980 • Today, 8-10 boomers expect to work part or full time • Under $30,000 income -1/5th of boomers are at risk Percent of U.S. Population by Race & Hispanic Origin 80 70 60 50 Caucasian African Amer. Hispanic Other 40 30 20 10 0 2003 2020 2050 Percent of Population Over 65 by Race & Hispanic Origin 90 80 70 60 Caucasian African Amer. Hispanic Asian/Pacif. Is. Am. Indian/Alask. 50 40 30 20 10 0 2000 2050 Marital Status of 65+ (1998) 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 65-74 75-84 85+ Male, never Female, married never married Male, Divorced Female, Divorced Living Arrangements For 65+ 80 70 60 Live with spouse 50 Live with other relative Live with non-relative 40 30 20 Live alone 10 0 Men Women White Other Women Women Household Type & Expenditure • In 2000, 25.8% householders lived alone; 9.2% of these householders were over 65. • 21% of all household units were over 65 years of age: 10.9% 65-74; 7.8% 75-84; and 85+ 2.3%. • Housing burden varies by income with the bottom 1/5th of the median household income spending 36% and the top 1/5th spending 26% of their income on housing. Educational Attainment of 65+ (1998) 80 70 60 50 Non-Hispanic White Non-Hispanic Black Hispanic Asian/Pacific Isl. 40 30 20 10 0 High School Bachelor's Degree Chronic Health Issues of Older Adults • • • • • • • Arthritis Diabetes Hypertension Chronic Sinusitis Vision Osteoporosis Hearing • • • • • • Varicose Veins Heart Disease Deformity/Other Emphysema Dementia 34% are affected by more than 1 condition Chronic Diseases, Complications and Disability Will Increase • Today, obesity affects 20-30% of 4th graders; 50% of 9th & 10th graders • 2010: 50% of 20-30 year olds will have diabetes • 2020: 50% of 30-40 year olds will have complications and disability • 2020: 50% loss in workforce; 50% depend on Medicare/Medicaid/disability income Functional Limitations in 85+ • • • • • • Walking Getting outside Bathing Transferring Dressing Using toilet 35% 45% 30% 22% 17% 14% • • • • • Eating Preparing Meals Managing $$ Using the phone Light housework 4% 28% 26% 21% 31% Percentage of Total Out-of-pocket Expenditures Allocated to Health Care in Households Headed by Persons 65+ 16 14 Income Level 12 Lowest Fifth Second Fifth Third Fifth Fourth Fifth Highest Fifth 10 8 6 4 2 0 1987 1994 1998 Source: Consumer Expenditure Survey, Non-Institutionalized Elderly, Chartbook 2000, U. S. Census Percent of Elderly in Nursing Homes 25 20 All 65+ 65-74 75-84 85+ 15 10 5 0 1990 2000 Caregiver Profile • Est. 45-52 million individual caregivers • 10-25% of population provides care • Women represent 74% of primary caregivers • Spouses provide 36% of care; daughters 29% and sons, 8% • Average caregiver 63 years old • 69% live with care recipient Grandparent Caregiving • 11% of grandparents care for grandchildren for at least 6 months • At least 55% of children in relative care live with a grandparent • 77% are female grandparents • 62% are non-Hispanic white • Factors increasing chance for raising grandchildren: poverty level; being African-American; and divorce, drug abuse or incarceration of child’s mother The Two America’s of Retirement Security • • • • • • • More Secure Steady employment Married, dual income Employer pension 401(k) plan Health insurance Home equity Long-term investments • • • • • • • Less Secure Intermittent employment Divorced or single No pension No 401K No health insurance Rent No long-term investments or savings for emergencies Core Issues in an Aging Rural Society • Economic Development/Human Capital – Work and Volunteer Issues – Careers in an Aging Society • Independent Living – Housing and Services – Chronic Health Conditions • Elder Care – Formal and Informal – Family Caregiving Economic Development & Human Capital • Rural mainstays: schools, nursing homes, hospitals, small businesses • Long-term care jobs at poverty or near-poverty level; 92% turnover in Nurse Aides; Frontline caregivers increasingly non-English speaking • Aging workforce: – 22% eligible to retire in 2005 – Greater proportion of health care professionals are 55+ than other occupations – Increased need for geriatric training Work & Financial Security • Leading economic indicator of family hardship not unemployment but no health insurance • 2/3 of working poor have no health insurance • Personal savings remain low compared to other developed countries Independent Living • Housing • Services 1997 Title III Service Use • Lower usage rates in rural vs. urban areas • Rural, non-Hispanic Black elders participate at disproportionately higher rates than other 60+ users • Non-white Hispanic elders participate at disproportionately lower rates than other 60+ users Independent Living • Prevent Chronic Disease • Managing Chronic Disease Elder Care • Formal and Informal Care • Family Care Summary • We are an Aging Society-undeniably • Economic disparity between population segments continues to grow affecting health and quality of life outcomes • Disparity between rural and urban areas continues with high percentages of elders in rural areas and a declining economic base • Rural areas have opportunities to focus on health and care solutions • Public policies are needed which reward disease prevention and foster smaller scale eldercare solutions