Homeostasis - Resp.system
advertisement

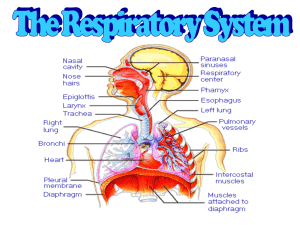
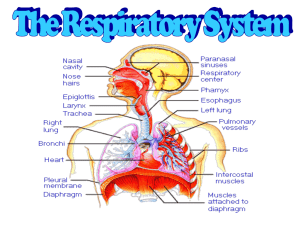
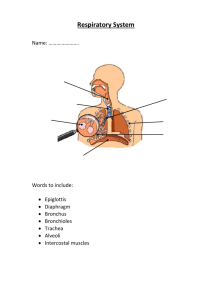
HOMEWORK: CASTLE LEARNING RESPIRATORY SYSTEM (due fri.) TEXTBOOK PGS. 594 Q’S 1-5 p.606 1-2 Do Now: Write a brief description that explain how this cartoon relates to respiration. Function of the respiratory system Gas Exchange Gas exchange Exchange of respiratory gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between an organism and the environment Molecules of oxygen and carbon dioxide are passively exchanged, by diffusion External respiration The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the environment and respiratory organs such as gills or lungs. Internal respiration The metabolic process by which living cells absorb oxygen and release carbon dioxide Which substance is needed for aerobic cellular respiration to occur? 1. 2. 3. 4. oxygen carbon dioxide nitrogen methane SUMMARY • DEFINE Gas exchange • EXPLAIN the difference between internal and external respiration Aim: How do the structures of the respiratory system assist in the breathing process? DO NOW: HOMEWORK: CASTLE LEARNING Which statement best describes the human respiratory system? “ Respiration” 1. It is composed of a network of moist passageways that 2. 3. 4. permit air to flow from the external environment to the lungs. Each cell of the human body is in direct contact with the external environment, and gas exchange occurs by diffusion The external body surface is kept moist to allow for gas exchange. Gases diffuse across membranes on both the external and internal surfaces of the body. Path of air through the respiratory system 1. Nose 2. Pharynx 3. Larynx 4. Trachea 5. Bronchi 6. Bronchioles 7. Alveoli List does not represent all repsiratory system organs Respiratory surfaces • Surface through which gases diffuse • 4 characteristics: – Thin – Moist – In contact with source of oxygen – In contact with a transport system Gills of dogfish shark Nose Contains nostrils: opening to the nasal passages nasal passages: lined with a mucus membrane with cilia Pharynx •Throat •Cavity in back of mouth •Contains the epiglottis Epiglottis Epiglottis •Flap of elastic cartilage tissue •Covers trachea when swallowing food or liquids to prevent from choking Larynx •Voice box •Upper part of the windpipe containing sound producing vocal cords Larynx Trachea •Windpipe •Supported by rings of cartilage •Lined with ciliated mucous membrane •Branches into 2 Bronchi Bronchi BRONCHI •Two main branches of trachea which enter lungs BRONCHI •Lined with cartilage and ciliated •Branch into smaller BRONCHIOLES SUMMARY The human trachea is a passageway that remains open due to the presence of 1. 2. 3. 4. bones ligaments skeletal muscles cartilaginous rings Choking on food is most likely caused by an interference with the proper functioning of the 1. 2. 3. 4. diaphragm nasal cavity bronchial tubes epiglottis Aim: How do the structures of the respiratory system assist in the breathing process? “Day 2” Do Now: The human trachea is a passageway that remains open due to the presence of 1. bones 2. ligaments 3. skeletal muscles 4. cartilaginous rings Deposits from cigarette smoke are most likely to interfere with the ciliated mucous membranes located in both the 1. trachea and esophagus 2. alveoli and liver 3. nasal cavity and trachea 4. epiglottis and esophagus Bronchioles Bronchioles • Smallest air tubes which end at the alveoli • first airway branches that no longer contain cartilage • They are smaller than one millimeter in diameter • Control of airflow resistance and air distribution in the lungs is controlled by the bronchioles Alveoli (Air sacs) • Site of respiratory gas exchange • Surrounded by capillaries Microscopic blood vessels • Made of very thin membranes • Moist surface Alveoli 1. Alveoli fill up with O2 2. O2 diffuses into the capillaries out of alveoli (into blood) 3. CO2 and H2O vapor diffuses out of capillaries (into alveoli) Diaphragm •Sheet of muscle underneath the lungs •Aids in breathing •Inhalation air traveling into the lungs Breathing •Exhalation air being pushed out of the lungs •Involves both the diaphragm and rib cage muscles Inhalation Demo •Diaphragm contracts and moves down •Rib cage expands •pressure decreases air rushes in Exhalation •Diaphragm relaxes and moves up •Rib cage contracts and comes in •pressure increases air is forced out of the lungs Summary nose mouth larynx pharynx Trachea Label the diagram lung Bronchi Bronchi Bronchioles Diaphragm Alveoli The human trachea is prevented from collapsing by the presence of 1. 2. 3. 4. mucous membranes cartilaginous rings muscle fibers bony networks Choking on food is most likely caused by an interference with the proper functioning of the 1. 2. 3. 4. diaphragm nasal cavity bronchial tubes epiglottis Diagrams A and B represent structures found in the human body. Diagram B represents the functional unit of which structure represented in diagram A? 1. 2. 3. 4. structure 1 structure 2 structure 3 structure 4 How do the structures of the respiratory system assist in the breathing process?