Introduction to Ecology
advertisement

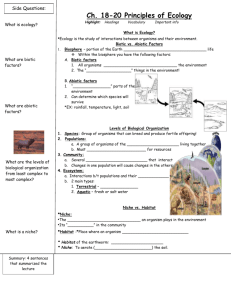
Introduction to Ecology Reading What is Ecology? Directions: Read the paragraph below. Use textual evidence to answer questions 1 – 17. Ecology is the study of the interactions between an organism and its surrounding environment. Ecology may seem to have a simple definition, but really the scientific study of ecology can be very broad. Some ecologists study ecosystems. An ECOSYSTEM consists of all biotic and abiotic factors in the environment. The environment can include ABIOTIC or non-living factors and BIOTIC or living factors. Abiotic factors can include things such as temperature, (5) different chemicals, physical environment (things such as rocks, fallen logs, water and sand), light and available nutrients. Biotic factors refer to plants or animals living in the ecosystem. Some ecologists study only individuals, while others study populations. A POPULATION consists of many individuals of the SAME SPECIES in the same area. Some ecologists study communities. A COMMUNITY consists of DIFFERENT SPECIES in the same area. These ecologists might study whole lakes, forests or streams. A community consists of a wide variety of organisms. PRODUCERS, or autotrophs, produce their own food. (10) There are different types of CONSUMERS, or heterotrophs. HERBIVORES consume, or eat, producers. CARNIVORES feed on other animals. PREDATORS are carnivores that hunt for its food, or prey. SCAVENGERS are carnivores that feed on dead animals they find. OMNIVORES are consumers that eat both producers and animals. DECOMPOSERS are organisms such as bacteria and fungi that break down dead organisms and return some of the (15) nutrients back into the soil to be used by plants. The place where an organism lives in an ecosystem is called its HABITAT. One habitat can contain hundreds or even thousands of species. Although they share the same habitat, each species has different requirements for its survival. As a result, each species has its own NICHE, or role in its environment. A niche can include how the species obtains its food, how it finds a mate, how it cares for its young and how it avoids danger. 1. Define the following terms: a. Ecology (1) ______________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________ b. Ecosystem (3) ____________________________________________________________________________________ c. Abiotic factors (4) _________________________________________________________________________________ d. Biotic factors (4) __________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What is an example of an abiotic factor? (4 – 6) __________________________________________________________ 3. What is an example of a biotic factor? (6) _______________________________________________________________ 4. Which term describes many organisms from one species living in the same area? (7 – 8) __________________________ 5. Which term describes different species living in the same area? (8 – 9) ___________________________________ 6. Which organisms can produce their own food? (10) _____________________________________ 7. Which organisms must eat because they cannot make their own food? (11) ____________________________________ 8. Which consumers only eat producers? (11) _____________________________________ 9. Which consumers only eat other animals? (11 – 12) _____________________________________ 10. Which carnivores hunt for their prey? (12) _____________________________________ 11. Which carnivores eat dead organisms they find?(12 – 13) _____________________________________ 12. Which consumers eat both producers and animals? (13) _____________________________________ 13. Which consumers break down dead organisms and return some of those nutrients back to the soil? (13 – 15)______________ 14. What is an example of a decomposer? (14) _______________________________________________________________ 15. What is an organism’s habitat? (16) ____________________________________________________________________ 16. What is an organism’s niche? (18) _____________________________________________________________________ 17. What is an example of a niche? (18 – 19) ________________________________________________________________ Introduction to Ecology Reading What is Ecology? Directions: Read the paragraph below. Use textual evidence to answer questions 1 – 17. Ecology is the study of the interactions between an organism and its surrounding environment. Ecology may seem to have a simple definition, but really the scientific study of ecology can be very broad. Some ecologists study ecosystems. An ecosystem consists of all biotic and abiotic factors in the environment. The environment can include abiotic or non-living factors and biotic or living factors. Abiotic factors can include things such as temperature, different chemicals, physical environment (things such as rocks, fallen logs, water and sand), light and available nutrients. Biotic factors refer to plants or animals living in the ecosystem. Some ecologists study only individuals, while others study populations. A population consists of many individuals of the same species in the same area. Some ecologists study communities. A community consists of different species in the same area. These ecologists might study whole lakes, forests or streams. A community consists of a wide variety of organisms. producers, or autotrophs, produce their own food. There are different types of consumers, or heterotrophs. Herbivores consume, or eat, producers. Carnivores feed on other animals. Predators are carnivores that hunt for its food, or prey. Scavengers are carnivores that feed on dead animals they find. Omnivores are consumers that eat both producers and animals. Decomposers are organisms such as bacteria and fungi that break down dead organisms and return some of the nutrients back into the soil to be used by plants. The place where an organism lives in an ecosystem is called its habitat. One habitat can contain hundreds or even thousands of species. Although they share the same habitat, each species has different requirements for its survival. As a result, each species has its own niche, or role in its environment. A niche can include how the species obtains its food, how it finds a mate, how it cares for its young and how it avoids danger. 1. Define the following terms: e. Ecology ______________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________ f. Ecosystem ____________________________________________________________________________________ g. Abiotic factors _________________________________________________________________________________ Biotic factors __________________________________________________________________________________ h. 2. Identify two examples of abiotic factors. _________________________________________________________________ 3. Identify two examples of a biotic factors ________________________________________________________________ 4. Identify the term that describes many organisms from one species living in the same area. _________________________ 5. Identify the term that describes different species living in the same area. ___________________________________ 6. Identify the organisms that can produce their own food. _____________________________________ a. Identify a process these organisms use to produce their own food. ____________________________________ 7. Identify the organisms that must eat because they cannot make their own food. _________________________________ 8. Identify consumers that only eat producers. _____________________________________ 9. Identify consumers that only eat other animals. _____________________________________ 10. Identify carnivores that hunt for their prey._____________________________________ 11. Identify carnivores that eat dead organisms they find. _____________________________________ 12. Identify consumers that eat both producers and animals. _____________________________________ 13. Identify consumers that break down dead organisms and return some of those nutrients back to the soil. ______________ 14. Identify two examples of decomposers. _______________________________________________________________ 15. Describe a habitat. ____________________________________________________________________ 16. Describe a niche._____________________________________________________________________ 17. Identify two examples of niches.________________________________________________________________ Introduction to Ecology What is Ecology? Directions: Use your textbook or the internet to define the following below on loose-leaf. Be sure to include the topics located at the top of this sheet. 1. Ecology 9. Herbivores 2. Ecosystem 10. Carnivores 3. Abiotic (include two examples) 11. Predators 4. Biotic (include two examples) 12. Scavengers 5. Population 13. Omnivores 6. Community 14. Decomposers (include two examples) 7. Producers (include the process used by these organisms) 15. Habitat 8. Consumers 16. Niche (include two examples) Introduction to Ecology What is Ecology? Directions: Use your textbook or the internet to define the following below on loose-leaf. Be sure to include the topics located at the top of this sheet. 1. Ecology 9. Herbivores 2. Ecosystem 10. Carnivores 3. Abiotic (include two examples) 11. Predators 4. Biotic (include two examples) 12. Scavengers 5. Population 13. Omnivores 6. Community 14. Decomposers (include two examples) 7. Producers (include the process used by these organisms) 15. Habitat 8. Consumers 16. Niche (include two examples) Introduction to Ecology What is Ecology? Directions: Use your textbook or the internet to define the following below on loose-leaf. Be sure to include the topics located at the top of this sheet. 1. Ecology 9. Herbivores 2. Ecosystem 10. Carnivores 3. Abiotic (include two examples) 11. Predators 4. Biotic (include two examples) 12. Scavengers 5. Population 13. Omnivores 6. Community 14. Decomposers (include two examples) 7. Producers (include the process used by these organisms) 15. Habitat 8. Consumers 16. Niche (include two examples) Introduction to Ecology What is Ecology? Directions: Use your textbook or the internet to define the following below on loose-leaf. Be sure to include the topics located at the top of this sheet. 1. Ecology 9. Herbivores 2. Ecosystem 10. Carnivores 3. Abiotic (include two examples) 11. Predators 4. Biotic (include two examples) 12. Scavengers 5. Population 13. Omnivores 6. Community 14. Decomposers (include two examples) 7. Producers (include the process used by these organisms) 15. Habitat 8. Consumers 16. Niche (include two examples)