Digestive System Review
advertisement

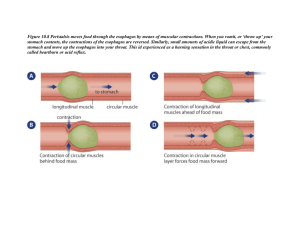
Nutrition and Digestive System Review 1. Identify the following information for the food to the left. a. Serving size 2 crackers b. Total carbohydrates 10g c. Calories 60 d. Protein 2g 2. How many calories would you consume if you ate 2 servings of these crackers? 120 calories Identify each structure labeled in the diagram. oral cavity gall bladder large intestine stomach pancreas small intestine rectum 1. Where does chemical digestion begin? In the oral cavity 2. What is the function of F? Absorb water 3. Where are nutrients absorbed into the blood? In the small intestine 4. What kind of digestion occurs in B? Mechanical and chemical 5. What does C produce? Where does it go? Pancreatic juice Goes to the small intestine 6. What is the function of G? store bile 7. Chemical digestion is completed in this structure. small intestine 8. What type of digestion occurs in A? mechanical and chemical 1.What is the name of this process? What is its function? •peristalsis •To push food through the digestive tract 1.Where in the digestive tract does this process occur? esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine 1. What is structure F? What is the function of this substance? •to produce bile •liver 2. Identify structure B. What kind of digestion occurs here? •stomach •Mechanical and chemical digestion 3. What is the function of structure A? The esophagus pushes food down into the stomach using peristalsis. 1. Through which of these structures does food pass? Esophagus (A) Small intestine (D) Stomach (B) 1. Which organs are not part of the gastrovascular tract? How do they aid in digestion? •Liver (F) – produces bile that goes to the SI •Gall bladder (E) – stores bile •Pancreas (C) – releases pancreatic juice into SI Describe the role of the small intestine in digestion. •Where most chemical digestion occurs •Where chemical digestion is completed •Lined with VILLI which absorb nutrients into the blood Identify the labeled organs. A - Oral cavity B - Esophagus C – Stomach D – Pancreas E - Large intestine F - Appendix G - Small intestine H – Gall bladder I - Liver 1. Through what organs does food pass? (in order) Oral cavity Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Rectum Anus 2. In which structures does peristalsis occur? Esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum 1. Where excess water reabsorbed? Large intestine 2. What occurs in structure G? Villi absorb nutrients into blood 3. What does I produce? Where does it go? Bile – into small intestine 4. This is where chemical digestion begins. Oral cavity 5. This is where chemical digestion ends. Small intestine Identify organs where there is no digestion occurring. Esophagus Liver Salivary glands Pancreas Glass bladder Let’s Review: Identify the digestive organ described. 1. Where chemical digestion begins. Oral cavity 2. Site of water absorption. Large intestine 3. All chemical digestion is completed here.Small intestine 4. Where bile is stored. Gall bladder 5. Where feces is formed. Large begins. intestine 6. Where mechanical digestion 7. Releases many enzymes into the SI.Oral cavity Pancreas 8. Pushes food into the stomach. Esophagus 9. Produces saliva. Salivary glands 10. Where the absorption of nutrients occurs.Small intestine 11. Lining is protected by a mucus layer. Stomach 12. Lined with villi. 13. Produces bile. Small intestine Liver The main function of the human digestive system is to 1) rid the body of cellular waste materials 2) break down large molecules so they can enter cells 3) break down glucose in order to release energy 4) change amino acids into proteins and carbohydrates Food is ingested through the 1) salivary glands 2) small intestine 3) mouth 4) rectum Mechanical digestion in the oral cavity is primarily the result of 1) peristalsis 2) chewing food 3) absorption 4) egestion Chemical digestion in the mouth is the result of 1) enzymes 2) hydrochloric acid 3) bile 4) pancreatic juice Food that is swallowed enters the 1) stomach 2) small intestine 3) esophagus 4) large intestine The esophagus pushed food down into the stomach by the involuntary process of 1. digestion 2. peristalsis 3. absorption 4. excretion Identify the type of digestion that takes place in the stomach. 1) mechanical digestion 2) chemical digestion 3) both mechanical and chemical digestion How does mechanical digestion in the stomach occur? 1) enzymes 2) hydrochloric acid 3) peristalsis 4) mucus How does chemical digestion in the stomach occur? 1) peristalsis 2) enzymes 3) mucus 4) ulcers Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? 1. intestinal glands 2. villi 3. pseudopodia 4. cilia Identify how the stomach lining is protected from hydrochloric acid. 1) peristalsis 2) mucus 3) enzymes 4) bacteria Identify the type of digestion that occurs in the small intestine. 1) mechanical digestion 2) chemical digestion 3) both mechanical and chemical digestion Which statement regarding the small intestine is incorrect? 1. Villi on the lining of the small intestine absorb nutrients into the blood. 2. Chemical digestion is completed in the small intestine. 3. Mechanical digestion is completed in the small intestine. 4. The small intestine is where most digestion occurs. Which structures in the small intestine absorb nutrients into the blood? 1. intestinal glands 2. villi 3. pseudopods 4. cilia Which substances are released into the small intestine of a human and aid in the digestion of food? 1) bile, pancreatic juice, and intestinal juice 2) hydrochloric acid, pancreatic juice, and intestinal juice 3) salivary amylase, intestinal juice, and pancreatic juice 4) bile, hydrochloric acid, and salivary amylase https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_QYwscALNng Which statement regarding the large intestine is correct? 1. The large intestine absorbs nutrients. 2. Chemical digestion is completed in the large intestine. 3. Mechanical digestion is completed in the small intestine. 4. The large intestine absorbs excess water.