Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
advertisement

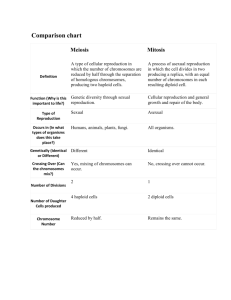
Topic: Reproduction Aim: Describe the processes of asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction. Do Now: Take out your asexual and Sexual Reproduction Reading Notes. HW: Castle Learning Skeletal, Muscular and Immune Systems due the day we wome back from break. Immunity Review 1.What is your body’s first line of defense against pathogens? Skin 2.Identify the structures found on the surface of pathogens. Antigens 3.Identify what is produced when a pathogen enters the body. Antibodies Immunity Review 4. Why is passive immunity short term? You are not making antibodies. You receive them. 5. Why is active immunity long term? You produce your own antibodies. 6. Identify the two ways you can get active immunity to a disease. Getting the disease. Getting a vaccine. 7. Contrast infectious and noninfectious diseases. Infectious diseases can be transmitted. Non-infectious diseases cannot be. Where is DNA found in a cell? • In the nucleus • Chromosomes: – Made of genes DNA gene ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION Number of parents Genetic information compared to the parents Complexity of organisms that use this method Example of an organism that uses this method Type of cell division used Number of daughter cells produced as a result of cell division Number of chromosomes in daughter cells of cell division 1 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION 2 Asexual Reproduction 50 chromosomes 50 50 Sexual Reproduction ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION Number of parents Genetic information compared to the parents Complexity of organisms that use this method Example of an organism that uses this method Type of cell division used Number of daughter cells produced as a result of cell division Number of chromosomes in daughter cells of cell division SEXUAL REPRODUCTION 1 2 Identical Not identical Asexual Reproduction 50 chromosomes 50 chromosomes in each daughter cell Sexual Reproduction ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION Number of parents SEXUAL REPRODUCTION 1 2 Genetic information compared to the parents Identical Not identical Complexity of organisms that use this method Not complex Example of an organism that uses this method Type of cell division used Number of daughter cells produced as a result of cell division Number of chromosomes in daughter cells of cell division Bacteria, fungi, some plants Complex Animals Asexual Reproduction 50 chromosomes 50 chromosomes in each daughter cell Sexual Reproduction ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION Number of parents SEXUAL REPRODUCTION 1 2 Genetic information compared to the parents Identical Not identical Complexity of organisms that use this method Not complex Example of an organism that uses this method Bacteria, fungi, some plants Complex Animals Type of cell division used Mitosis Number of daughter cells produced as a result of cell division Number of chromosomes in daughter cells of cell division 2 Meiosis 4 Mitosis Meiosis ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION Number of parents SEXUAL REPRODUCTION 1 2 Genetic information compared to the parents Identical Not identical Complexity of organisms that use this method Not complex Example of an organism that uses this method Bacteria, fungi, some plants Complex Animals Type of cell division used Mitosis Number of daughter cells produced as a result of cell division Number of chromosomes in daughter cells of cell division 2 Same # Meiosis 4 Half # Mitosis Meiosis 46 46 23 46 46 23 23 23 ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION Number of parents SEXUAL REPRODUCTION 1 2 Genetic information compared to the parents Identical Not identical Complexity of organisms that use this method Not complex Example of an organism that uses this method Bacteria, fungi, some plants Complex Animals Type of cell division used Mitosis Number of daughter cells produced as a result of cell division Number of chromosomes in daughter cells of cell division 2 Same # Meiosis 4 Half # A B MEIOSIS MITOSIS Identify processes A and B. Support your answer. A B 100 chromosomes 100 chromosomes 50 chromosomes in each cell How many chromosomes would be found in the daughter cells of each process is the parent cell contains 100 chromosomes? 1. Describe the meaning of the phrase “genetically identical.” • The SAME DNA/genes 2. Identify the cells in animals that use MITOSIS to reproduce? • Body cells • Somatic cells 3. Identify the cells that are produced by MEIOSIS. • Sex cells • Gametes 4. Contrast • Cells produced by mitosis have the SAME # of chromosomes as the cells parent cell. Cells produced my created by mitosis and meiosis have HALF the # of chromosomes as the parent cell meiosis. • Cells that are produced by mitosis are GENETICALLY identical to the parent cell. Cells produced by meiosis are NOT genetically identical to the parent cells. 5. Contrast somatic cells and gametes. • Somatic cells are BODY cells. Gametes are SEX cells. • Somatic cells are produced during MITOSIS. Gametes are produced during MEIOSIS. Let’s Review! 1.How many parents are required for asexual and sexual reproduction? Asexual 1, Sexual 2 2.Compare the offspring's’ genetic information for asexual and sexual reproduction. Asexual offspring is genetically identical to parents Sexual offspring is not genetically identical to parents 3. Identify the two types of cells found in the body and the type of cell division used to produce or replicate them. Somatic cells/ body cells mitosis Gametes meiosis Let’s Review! 4. Compare the daughter cells to the parent cells for mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis daughter cells have SAME # of chromosomes as original cells (genetically identical) Meiosis daughter cells have HALF the # of chromosomes as original cells 5. Why does the chromosome number divide in half during meiosis? Sperm and egg cell join together to create an embryo. Which statement best describes what happens when someone receives a vaccination? 1. The ability to fight disease will increase due to antibodies received from the pathogen. 2. The ability to fight disease caused by the pathogen will increase due to antibody production. 3. The ability to produce antibodies will decrease after the vaccination. 4. The ability to resist most types of diseases will increase. Which activity is NOT a function of white blood cells in response to a pathogen? 1. engulfing these bacteria 2. producing antibodies to act against this type of bacteria 3. preparing for future invasions of this type of bacteria 4. speeding transmissions of nerve impulses to detect these bacteria The immune system of humans may respond to chemicals on the surface of a pathogen by 1. releasing hormones that break down these chemicals 2. synthesizing antibodies that mark these organisms to be destroyed 3. secreting antibiotics that attach to these organisms 4. altering a DNA sequence in these organisms Vaccinations help prepare the body to fight invasions of a specific pathogen by 1. inhibiting antigen production 2. stimulating antibody production 3. inhibiting white blood cell production 4. stimulating red blood cell production Which phrase does not describe a way the human body responds to fight disease? (1) destruction of infectious agents by white blood cells (2) production of antibodies by white blood cells (3) increased production of white blood cells (4) production of pathogens by white blood cells The type of immunity in which antibodies and memory cells are produced is called 1. temporary immunity 2. active immunity 3. passive immunity 4. long-term immunity The type of immunity in which antibodies are received from another source is called 1. temporary immunity 2. active immunity 3. passive immunity 4. long-term immunity A person with AIDS is likely to develop infectious diseases because the virus that causes AIDS (1) destroys cancerous cells (2) damages the immune system (3) increases the rate of antibody production (4) increases the rate of microbe destruction Infectious diseases are caused by 1. deficiencies in the diet 2. allergies 3. microscopic organisms that can be transmitted from one organism to another 4. malfunctioning organs