Viral infections
advertisement

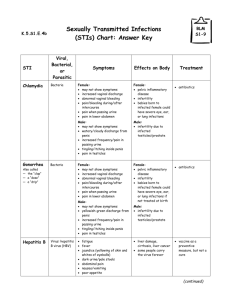
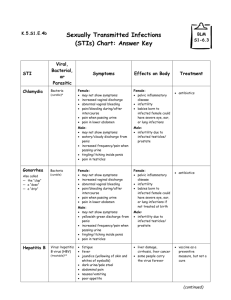
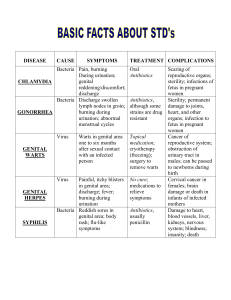
Viral skin infections Herpes simplex • Caused by herpes virus hominis, DNA virus. • HSV I: mostly oral, transmitted by saliva • HSV II: mostly genital transmitted by sex Virus entry ͢ attacks primary infection ͢ latent infection ͢ recurrent Clinical features Primary type I: usually affects children ●Usually asymptomatic ● Few Symptomatic ͢ heals within 2 weeks ͢ gingivostomatitis-vesicles and erosions, keratitis ͢ Whitlow, infection of the finger mostly in children, transmitted from oral lesion due to finger sucking. Primary type II: genital vesicles and painful erosions Recurrent attacks (type I): Herpes labilais or cold sore: Recurrent vesicles, then pustules and erosions in the lips and near skin Ppt. factors: sunlight, menstruation, viral and bacterial infections. Recurrent attack usually last for 1 week. Recurrent type II: Recurrent genital ulcers affecting the penis, vulva, vagina and anus. Type II recur more frequent than type I It is a common STD It represents a bad stigma with guilt feeling because of its persistence for many years. Complications • Meningitis • Encephalitis • Disseminated inf. • Secondary impetigo • Corneal ulceration Treatment Primary: ●Mild cases: rest, symptomatic, acyclovir 200mg 5 times daily for 10 days. ●Disseminated inf. In immunocompromised : intravenous acyclovir 510mg/ kg 8 hourly ●Recurrent attacks: suppressive therapy, Acyclovir 400mg twice daily Acyclovir not eradicates the HSV from the ganglia, but decrease the recurrence Varicella zoster • Caused by reactivation of V-Z virus acquired from previous chicken pox inf. • V-Z virus latent in the cranial or dorsal root ganglia, its reactivation herpes zoster at the dermatome of corresponding nerve • Usually its risk increase with age and low immunity Clinical features • Unilateral dermatomal pain for 3-5 days, then vesicles appear and then ulcerations. Last 2-6 weeks according to the age. Duration increases with age. Sites of involvement: thoracic, cervical, trigeminal, lumbosacral Complications • Secondary bact. Inf. • Corneal ulceration in ophthalmic zoster • Motor nerve involvement • Post herpetic neuralgia Treatment • Mild cases: rest, symptomatic • Severe cases, opthalmic zoster, low immunity acyclovir within 2-3 days Viral warts • Cause: HPV, more than 60 subtypes • Transmission: direct contact and sex. • Usually affects young people • Immune deficiency predispose to extensive warts • Type 16 and 18 cause cervical ca. Clinical features • Common warts ( verruca vulgaris): single or multiple papules with rough surface. Usually affect the hands, but can appear anywhere. • Plantar warts: rough slightly raised papules. • Plane warts: slightly raised skin colored- grey- pink smooth papules. Face and hands • Anogenital warts (condylomata acuminata): affects skin and mucous membrane of the genital area. Papillomatous or cauliflower lesions It is similar to condylomata lata which are flat papules representing secondary syphilis Treatment • Local therapy: *Keratolytics: 12-20% salicylic acid * Caustic agents: TCA for genital warts * cytotoxics: ●5-FU for plane warts. ●podophylline for genital warts * Surgical: curretage, electrocautery, cryotherapy * immunomodulators: imiquimod for plane and genital warts * Retinoic acid: for plane warts Systemic therapy • For extensive warts • Zinc sulfate, BCG vaccine, retinoids. Pox virus infections Molluscum contagiosum * Pox virus, transmitted by direct contact and sex * Clinical features: I.P. 2-6 weeks *Shiny white or pink papule with central punctum in some cases. * Usually disease of children, especially affects the face. * In adults involvement of the genital area indicates STD. Treatment • Squeezing, curretage, cryotherapy, cautery, phenol puncture, retinoic acid Orf • Caused by parapox v. • Transmitted from sheep. • I.P. 5-6 days • Firm papule then pustular nodule • Clear in about 1 month spontaneously. • No treatment required. Measles • Paramyxovirus, droplet transmission. • I.P. 10 days • Catarrhal stage:2 days of fever, running nose, red eyes, then photophobia and koplik’s spots • Days 3-4 maculopap. rash • Days 6-7 days fever and rash decrease Complications • Pneumonia, keratitis, otitis media, encephilitis, weight loss Treatment Symptomatic, antibiotics for secondary bact. Inf. Rubella (German measles) • Caused by toga virus, droplet inf. • I.P. 18 days. • Less severe than measles, trivial in children, more sever in adults. • Prodromal symptoms with suboccipital LAP • Fine maculopap. Rash Varicella • V-Z virus. • Prodromal symptoms • Pink papules ͢vesicles ͢ pustules ͢ crusted erosions • Cetripetal distribution • Treatment: sympotmatic, acyclovir for adults, severe cases and immunocompramised AIDS • Caused by HIV, which target the CD4 T cells • Skin manifestations of AIDS *Tumors: kaposi sarcoma, extensive with systemic involvement * Dermatitis: seborrheic derm. * Infections: opportunistic inf. ex candidiasis, severe HSV and HZV.