Course Plan 176 Aftab.doc
advertisement

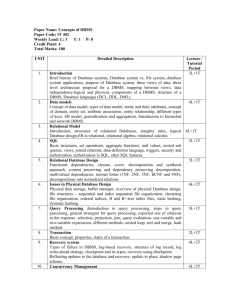
COURSE PLAN COMPUTER INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY CIT176 INTRODUCTION TO DATABASE CONTENT INSTRUCTOR’S DETAILS 1 COURSE SCHEDULE 1 SYNOPSIS 2 LEARNING OUTCOMES 2 COURSE OUTLINE 2 WEEKLY PLAN 3 ASSESSMENT BREAKDOWN & POLICY 5 ATTENDANCE POLICY 5 REFERENCES 6 INSTRUCTOR’S DE TAILS Name: Aftab Alam Abdussami Office: Room 201/1B, Computer Information Technology Section, 1st Floor, Jeddah Community College. Telephone No: 2870026 Ext. 513 E-mail: alamaft@gmail.com COURSE SCHEDULE Day Sat/Mon Wed Time 1000 - 1100 1000 - 1200 Room 006A 006A SYNOPSIS This course explains the key concepts used in database systems and demonstrates the features of a Database management software. The course will discuss the different types of commercial database systems and will explain the concepts used to design a database. Also this course will teach how to implement a database using the relational DBMS. The course also illustrates the usage of database management systems . LEARNING OUTCOMES After completing the course, students should be able to: Identify the various types of database management programs and database users. Describe the main features, advantages and limitations of a DBMS. Understand database system concepts and architecture Design a database Using ER model and Map it to a relational schema Describe relational model concepts, constraints and operations Operate the database program and the microcomputer on which it runs, at an elementary level. Create database tables, add, delete and update records within the database files. Use a full complement of database commands and selection tools. Access multiple tables simultaneously. Create and use database queries using various operators Create reports to display stored information COURSE OUTL INE Chapter 1 Database and Database Users 2 Database System Concept and Architecture 3 Data Modeling Using Entity Relationship Model 4 The Relational Data Model and Relational Database Constraints 5 Relational Database Design by ER-to- Topics Introduction Characteristics of the database Approach Actors on the scene Workers behind the scene Advantages of Using the DBMS Approach A brief history of Database Applications When not to Use a DBMS Data Models, Schemas and Instances Three Schema Architecture and Data Independence Database Languages and Interfaces DBMS Component Modules and System Utilities Client/Server and Centralized architectures for DBMS Classification of Database Management System Using High-Level Conceptual Data Models for Database Design An example of Database Application Entity Types, Entity Sets, Attributes, and Keys Relationship Types, Relationship Sets, Roles, and Structural Constraints Weak Entity Types ER Diagrams, Naming Conventions and Design Issues Relational Model Concepts Relational Model Constraints and Relational database Schemas Update Operations and Dealing with Constraint Violations Relational Database Design Using ER-to-Relational Mapping H 1 Relational Mapping 6 SQL Basic Queries 7 Spreadsheet Basics 8 Microsoft Access basics SQL Data definition and Data Types Basic Queries in SQL Insert, Delete, and Update statements in SQL Introduction to Microsoft Excel Working with Microsoft Excel Working with Microsoft Excel Charts Introduction to Microsoft Access Create the Database using Microsoft Access Import structures and data from external sources Refine the Database and Create Relationships and set the relationship constraints TOTAL WEEKLY PLAN *CAClass Assignment Dates Wk Ch Sept 10 1 2 Assignments Introduction to the Course 1 Sept 17 Introduction Characteristics of the database Approach Forum F1 Assignment CA1 3 1 Sept 25 4 2 5 2 6 3 7 3 8 3 9 4 10 4 Oct 01 Oct 08 Oct 15 Oct 22 Oct 29 12 Nov 19 Nov **LALab Assignment Topic Actors on the scene Workers behind the scene Advantages of Using the DBMS Approach A brief history of Database Applications When not to Use a DBMS Assignment LA1 Data Models, Schemas and Instances Three Schema Architecture and Data Assignment LA2 Independence Database Languages and Interfaces DBMS Component Modules and System Utilities Quiz Q1[ch1,2] Client/Server and Centralized architectures for DBMS Assign CA2 Classification of Database Management System Using High-Level Conceptual Data Models for Database Design An example of Database Application Assignment LA3 Entity Types, Entity Sets, Attributes, and Keys Revision & Midterm I (Chapter 1 & 2) Relationship Types, Relationship Sets, Roles, Quiz Q2(Ch3) and Structural Constraints Review Exam-I Weak Entity Types ER Diagrams, Naming Conventions and Design Exam-I[CH1,2,3] Issues Review Chapter 3 Assignment LA4 Relational Model Concepts Relational Model Constraints and Relational Forum F2 database Schemas Assignment CA3 Update Operations and Dealing with Constraint Violations Assignment CA4 Remarks: Due Date 6 Dates Wk Ch 11 5 26 Nov 12 5 Dec 3 13 Topic Assignments Relational Database Design Using ER-toRelational Mapping Remarks: Due Date Quiz Q3[CH4] Assignment LA5 Relational Database Design Using ER-toRelational Mapping 6 SQL Data definition and Data Types Basic Queries in SQL Insert, Delete, and Update statements in SQL Revision & Midterm II(Chapter 3,5,7) 14 7 Introduction to Microsoft Excel Dec 17 Working With Microsoft Excel Design a database- Course Project 15 7 Working with MS Excel Charts Dec 24 Review Project P176 Assignment CA5 Quiz Q4[CH5] Dec 10 16 8 17 8 Dec 31 Jan 7 Jan 14 18 Review Exam-II Project P176 Exam-II[CH3,4,5] Quiz Q5[CH6,7] Review P176 Review P176 Introduction to Microsoft Access Create the Database using Microsoft Access Quiz Q6[CH8] Create Relationships and set constraints Import Structures and data from External sources Overall Review Export database and data from Excel to Access and vice versa Review for Final Exam FINAL EXAMINATION ASSESSMENT BREAKDOWN & POLICY Students’ assessments in this course are based on the following: 1) Carry Marks Assignments Mid-Semester Examination 2) 10% 40% Quizzes 10% Forums 5% Final Examination Total 35 % 100 % Carry marks will be given before or on Week 7. ATTENDANCE POLICY Attendance is mandatory. Instructor is required to keep attendance records and report absences. Due to the interactive nature of this course, attendance is an essential part of the educational experience. JCC expects students to exercise good judgment regarding attendance. Students accept full responsibility for ensuring that work does not suffer from absence. Punctuality is important. The instructor MAY NOT ALLOW student(s) to enter the classroom if he/she is a habitual latecomer. Students with ZERO absence will be upgraded to the next grade, if passed. Registration to a course and dropping procedure is a student’s responsibility The proof of registration should be shown in the first class The students are expected to be in class from the beginning of class. Proof of valid reasons for absences will be verified by authority after receiving DN Those who come in the class within 10 minutes are considered LATE After ten (10) minutes the students are marked absent After three weeks equivalent absence, a grade of “DN” (Denied) will be issued It's responsibility of the student to keep the record of his absences. Electronic devices must be turned off during all class and Lab times. Otherwise he may be asked to leave class and will be marked absent. STUDENT'S RESPONSIBI LITY Students accept full responsibility for ensuring that work does not suffer from absence. The devices in the Lab must not be used for any other activities and/or in any other ways than that which is explained by the instructor Students are required to bring pen, notebook, textbook, one flash memory (min 20 MB) in the class During tests no external devices are allowed. SPECIAL ACCOMMODATIO NS If there is any student in this class who has special needs because of learning disabilities or other disabilities, please discuss these needs with your instructor or please contact Course Coordinator. REFERENCES Main Reference 1. 2. 3. 4. Fundamentals of Database Systems 4th edition by Elmasri and Navathe, ISBN: 0-321-20448-4 Absolute Beginner’s Guide to Databases by John V. Petersen (QUE) Access Database Design and Programming, Steven Roman (O’REILLY) Online resources http://emestest.kau.edu.sa