Lecture Slide Week 6.ppt
advertisement

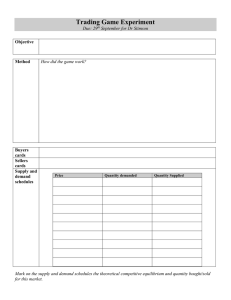
ECON107 Principles of Microeconomics Week 6 SEPTEMBER 2013 Chapter-3 1 6w/9/2013 Dr. Mazharul Islam 3 6w/9/2013 Market Equilibrium Dr. Mazharul Islam 3 Lesson Objectives Define market and market equilibrium Explain how demand and supply determine prices and quantities bought and sold Use the demand and supply model to make predictions about changes in prices and quantities 6w/9/2013 Dr. Mazharul Islam 4 MARKETS DEFINED POTENTIAL BUYERS POTENTIAL SELLERS MARKETS 6w/9/2013 Dr. Mazharul Islam 5 Market A set of arrangements through which buyers and sellers carry out exchange at mutually agreeable terms. It determine prices and quantities of goods and services by bringing together two sides of exchange demand and supply. Markets are often physical places, such as supermarkets, shopping malls etc. Market also include other mechanisms by which buyers and sellers communicate, like radio television advertisement, telephones etc. There are two types of market in the economy. These are Product market and Resource market. 6w/9/2013 Dr. Mazharul Islam 6 Market Equilibrium Market equilibrium refers a situation in which the supply of an item is exactly equal to its demand. Since there is neither surplus nor shortage in the Market. The equilibrium price is the price at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. The equilibrium quantity is the quantity bought and sold at the equilibrium price. 6w/9/2013 Dr. Mazharul Islam 7 Market Demand and Supply CORN OIL CORN OIL P $5 4 3 2 1 QD 10 20 35 55 80 MARKET x 200 DEMAND B 2,000 U Y E R S 4,000 7,000 11,000 16,000 P QS $5 4 3 2 1 EQUILIBRIUM 6w/9/2013 MARKET 60 50 35 20 5 x 200 SUPPLY S 12,000 E L L E 10,000 7,000 4,000 1,000 R S Dr. Mazharul Islam 8 Market Demand and Supply CORN MARKET P QD $5 2,000 4 4,000 3 7,000 2 11,000 1 16,000 P CORN MARKET P Q 4 Market Clearing Equilibrium 3 2 1 o 6w/9/2013 S $5 $5 4 3 2 1 S 12,000 10,000 7,000 4,000 1,000 D 2 4 6 7 8 10 12 14 16 Q (in thousand) Dr. Mazharul Islam 9 Market Demand and Supply CORN MARKET P QD $5 2,000 4 4,000 3 7,000 2 11,000 1 16,000 P Surplus $5 S P Q At a $4 price 4 more is being supplied than 3 demanded 2 1 o 6w/9/2013 CORN MARKET $5 4 3 2 1 S 12,000 10,000 7,000 4,000 1,000 D 2 4 6 7 8 10 12 14 16 Q (in thousand) Dr. Mazharul Islam 10 Market Demand and Supply CORN MARKET P QD $5 2,000 4 4,000 3 7,000 2 11,000 1 16,000 P S $5 CORN MARKET P Q 4 At a $2 price more is being 3 demanded than supplied 2 Shortage 1 o 6w/9/2013 $5 4 3 2 1 S 12,000 10,000 7,000 4,000 1,000 D 2 4 6 8 101112 14 16 Q (in thousand) Dr. Mazharul Islam 11 Market Demand and Supply P CORN MARKET P QD $5 2,000 4 4,000 3 7,000 2 11,000 1 16,000 $5 Surplus CORN MARKET S P Q (put downward pressure on the price) 4 $5 4 3 2 1 3 2 Shortage 1 ( Create market pressure for a higher price) o 6w/9/2013 2 4 6 7 8 101112 14 16 S 12,000 10,000 7,000 4,000 1,000 D Q (in thousand) Dr. Mazharul Islam 12 Changes in Equilibrium Once a market reaches equilibrium, that price and quantity will prevail until one of the determinants of demand or supply changes. A change in any one of these determinants will usually change equilibrium price and quantity in a predictable way 6w/9/2013 Dr. Mazharul Islam 13 Changes in Equilibrium An increase in demand will cause an increase in the equilibrium price and quantity of a good. The increase in demand causes excess demand at the initial price. Excess demand will cause the price to rise, and as price rises producers are willing to sell more, thereby increasing output. 6w/9/2013 Dr. Mazharul Islam 14 Changes in Equilibrium A decrease in demand will cause a reduction in the equilibrium price and quantity of a good. The decrease in demand causes excess supply at the initial price. Excess supply will cause price to fall, and as price falls producers are willing to supply less of the good, thereby decreasing output 6w/9/2013 Dr. Mazharul Islam 15 Changes in Equilibrium An increase in supply will cause a reduction in the equilibrium price and an increase in the equilibrium quantity of a good. The increase in supply creates an excess supply at the initial price. Excess supply causes the price to fall and quantity demanded to increase. 6w/9/2013 Dr. Mazharul Islam 16 Changes in Equilibrium An decrease in supply will cause an increase in the equilibrium price and a decrease in the equilibrium quantity of a good. The decrease in supply creates an excess demand at the initial price. Excess demand causes the price to rise and quantity demanded to decrease. 6w/9/2013 Dr. Mazharul Islam 17 Changes in Equilibrium 6w/9/2013 Dr. Mazharul Islam 18 Changes in Equilibrium S = D P , Q unchanged 6w/9/2013 Dr. Mazharul Islam 19 Changes in Equilibrium 6w/9/2013 Dr. Mazharul Islam 20 Changes in Equilibrium S = D P (unchanged) , Q 6w/9/2013 Dr. Mazharul Islam 21 Summary Change in Demand Change in Supply Demand increases Supply increases Supply decreases Equilibrium price change is indeterminate. Demand decreases Equilibrium price falls. Equilibrium quantity increases. Equilibrium quantity change is indeterminate. Equilibrium price rises. Equilibrium price change is indeterminate. Equilibrium quantity change is indeterminate. Equilibrium quantity decreases. 6w/9/2013 Dr. Mazharul Islam 22 Now it’s over for today. Do you have any question? 5w/9/2013 Dr. Mazharul Islam