CURIN 878
advertisement

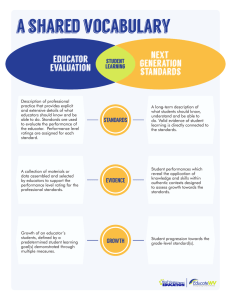
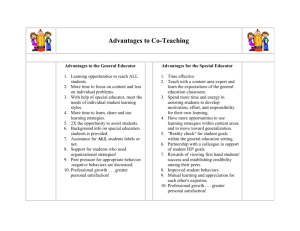
CURIN 878-01 Assessment for Effective Teaching Course Syllabus Instructor: Dr. Ray Willard Hughes Hall, Rm. 117D Dept. of Curriculum and Instruction Pittsburg State University Office – (620) 235 - 4491 rwillard@pittstate.edu Dates: Spring 2009 Place: Hughes Hall Credit: 3 hours, graduate Course Description: The three (3) hour course will examine the current research on effective assessment in terms of methodologies and perspectives. It will explore state and national assessment directions, classroom evaluation systems, test construction and interpretation, performance and portfolio assessments, as well as various assessment techniques that meet or accommodate diverse intelligences and learning needs. Course Texts: Optional Text: Popham, James. Classroom Assessment: What Teachers Need to Know. Boston: Allyn and Bacon, 2002. Required: Internet Research Course Objectives: As a result of the study of CURIN 878, the student should be able to; Standard #13 – The educator is a reflective practitioner who uses an understanding of historical, philosophical, and social foundations of education to guide educational practices. 1. Synthesize the history of educational testing. 2. Identify key changes occurring in American society that has directly affected educational assessment. 3. Recognize key paradigm shifts occurring in the assessment of student learning. Standard #9 – The educator is a reflective practitioner who continually evaluates the effects of his or her choices and actions on others (students, parents, and other professionals in the learning community), actively seeks out opportunities to grow professionally, and participates in the school improvement process (Kansas Quality Performance Accreditation [QPA]). 4. Distinguish the key components associated with “Frequent Monitoring” in the Effective Schools research and evaluate a school based on the criteria. 5. Distinguish the key components associated with “Criteria Reference Testing” in Outcomes Based research and evaluate a school based on the criteria. 6. Outline the key assessment components associated with “no Child Left Behind” legislation (NCLB). 7. Synthesize the testing structure associated Kansas Quality Performance Accreditation (QPA) and how the concept of meeting Adequate Yearly Progress (AYP) affects individual Kansas schools. 8. Synthesize the testing structure associated with the Missouri Assessment Program (MAP) and how the concept of meeting Adequate Yearly Progress (AYP) affects individual Kansas schools. Standard #12 – The educator understands the role of technology in society and demonstrates skills using instructional tools and technology to gather, analyze, and present information, enhance instructional practices, facilitate professional productivity and communication, and help all students use instructional technology effectively. 9. Use an electronic record-keeping program to maintain a classroom assessment system. 10. Use the Internet to acquire assessment rubrics and various assessment tools. 11. Illustrate how numerous instructional curriculums use technology to assess, analyze, and report student progress. 12. Appreciate how a Teacher Work Sample will be used to facilitate professional productivity. Standard #7 – The educator plans effective instruction based upon the knowledge of all students, community, subject matter, curriculum outcomes, and current methods of teaching reading. 13. Understand the variables that affect student assessment and describe the basic components of an effective evaluation system. 14. Write cognitive, affective and psychomotor objectives that reflect the curriculum outcomes as well as the classroom assessment system. 15. Name the types and state the purposes of various standardized tests. 16. Overview the primary student assessment information found in various national and state tests. 17. Understand how to use standardized tests to enhance instructional practices. Standard #3 – The educator demonstrates the ability to provide different approaches to learning and creates instructional opportunities that are equitable, that are based on developmental levels, and that are adapted to diverse learners, including those with exceptionalities. 18. Identify and define the major intelligences identified by Howard Gardner and develop multiple intelligence assessment plans for various content related lessons. 19. Identify specific questioning behaviors that can assess student learning as well as affect student achievement. 20. Explain and put into practice the major elements and precepts of re-teaching, retesting, and enrichment found in Mastery Learning. 21. Design appropriate assessment accommodations and modifications for students with special needs. 22. Design appropriate assessment techniques for English Language Learners. Standard #2 – The educator demonstrates an understanding of how individuals learn and develop intellectually, social, and personally and provides learning opportunities that support this development. 23. Appreciate how various standardized tests are used to provide feedback on student intellectual, aptitude, or achievement development. 24. Comprehend how raw scores, percentiles, and stanines are used to measure individual development. 25. Understand how reliability, validity, and bias affect testing. 26. Use character, value, or attitudinal inventories to assess student social development. 27. Assess appropriate social objectives in a cooperative learning activity. Standard #5 – The educator uses an understanding of individual and group motivation and behavior to create a learning environment that encourages positive social interaction, active engagement in learning, and self-motivation. 28. Examine the basic elements and critical components of an effective classroom assessment plan that motivates success. 29. Describe various games, activities, and questioning techniques that help create an assessment environment conductive to learning. 30. Depict specific teacher actions that help prepare and maintain an effective classroomtesting atmosphere. 31. Develop a personal classroom assessment system. Standard #8 – The educator understands and uses formal and informal assessment strategies to evaluate and ensure the continual intellectual, social, and other aspects of personal development of all learners. 32. Describe the key components involved in T/F, multiple-choice, completion, short answer, and essay assessment. 33. Name various formal and informal performance assessments and how they are used to evaluated intellectual, social and attitudinal development of students. 34. List possible structures and display formats for portfolio assessment. 35. Develop and use rubrics to evaluate performance and portfolio artifacts. Standard #10 – The educator fosters collegial relationships with school personnel, parents, and agencies in the larger community to support all students’ learning and well-being. 36. Identify methods of communicating student performance between the home and school. 37. Describe the process and portfolio assessment focus in National Board Certification and appreciate how it is used to increase a teacher’s effectiveness in teaching. Course Requirements: 1. Attendance and Activity Participation Each student will be responsible for reading the required readings, visiting Internet sites, and for participating in class activities and discussions. Each student will be expected to participate in a cooperative learning group that will stay together throughout the term of the course and participate in a number of class activities. 2. Class Activities Each student will complete various class activities from a list of options and individualize them to his/her own teaching situation. The grade will be dependent on how many of these projects are successfully completed. The points awarded are as follows: 5 projects = 25 4 projects = 20 3 projects = 15 2 projects = 10 1 project = 5 3. Research Project Each student will construct a classroom assessment system, portfolio plan, or performance assessment that can be used in the classroom. 4. Final Exam At the end of the course an exam will review the student’s level of application for each of the major objectives of the course. Each student will use his or her cooperative group to prepare for the exam. Course Evaluation: 1. 2. 3. 4. Class attendance and activity participation Class Activities Research Project Final Exam 25% 25% 25% 25%