Lesson 3 - Graphs of Functions
advertisement

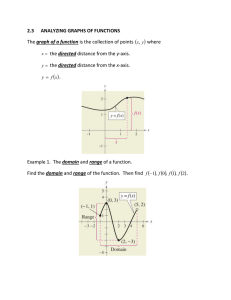
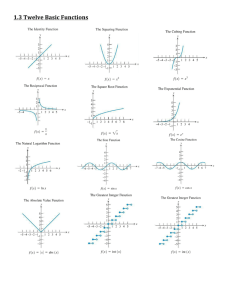
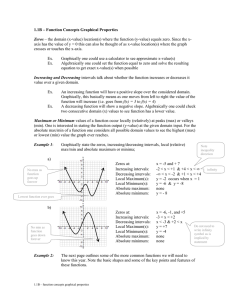
Graphs of Functions Lesson 3 Warm Up – Perform the Operations and Simplify 4 a. 12 x2 3 x b. 2 2 x x 20 x 4 x 5 2 x 3 11x 2 6 x x 10 c. 2 5x 2 x 5x 3 x7 x7 d. 2x 9 2x 9 4 a. 12 x2 Solution 4 12 x2 12x 2 4 x2 x2 12 x 24 4 x2 12 x 20 x2 3 x b. 2 2 x x 20 x 4 x 5 x Solution x 5x 4 x 5x 1 3 x 1 x x 4 x 5x 4x 1 3 3x 3 x 2 4 x x 5x 4x 1 x x3 x 5x 4x 1 2 2 x 3 11x 2 6 x x 10 c. 2 5x 2 x 5x 3 Solution 2 x 3 11x 2 6 x x 10 2 5x 2 x 5x 3 x 2 x 2 11x 6 x 10 2 x 1x 3 5x x2 x 1 x 6 x 10 5 x2 x 1 x 3 x 6 x 10 5 x 3 x7 x7 d. 2x 9 2x 9 Solution x7 x7 2x 9 2x 9 x 7 2x 9 2x 9 x 7 x7 x7 Domain & Range of a Function What is the domain of the graph of the function f? A : 1,4 Domain & Range of a Function What is the range of the graph of the function f? 5,4 Domain & Range of a Function Find f 1 and f 2. f 1 5 f 2 4 Let’s look at domain and range of a function using an algebraic approach. Then, let’s check it with a graphical approach. Find the domain and range of f x x 4. Algebraic Approach The expression under the radical can not be negative. Therefore, x 4 0. Domain A: x 4 Since the domain is never negative the or range is the set of all nonnegative real 4, numbers. A: y 0 or 0, Range Find the domain and range of f x x 4. Graphical Approach Increasing and Decreasing Functions The more you know about the graph of a function, the more you know about the function itself. Consider the graph on the next slide. Falls from x = -2 to x = 0. Is constant from x = 0 to x = 2. Rises from x = 2 to x = 4. Ex: Find the open intervals on which the function is increasing, decreasing, or constant. Increases over the entire real line. Ex: Find the open intervals on which the function is increasing, decreasing, or constant. INCREASING : ,1 and 1, DECREASING : 1,1 Ex: Find the open intervals on which the function is increasing, decreasing, or constant. INCREASING : ,0 CONSTANT : 0,2 DECREASING : 2. Relative Minimum and Maximum Values The point at which a function changes its increasing, decreasing, or constant behavior are helpful in determining the relative maximum or relative minimum values of a function. General Points – We’ll find EXACT points later…… Approximating a Relative Minimum Example: Use a GDC to approximate the relative minimum of the function given by f x 3x 4 x 2. 2 f x 3x 4 x 2. 2 Put the function into the “y = “ the press zoom 6 to look at the graph. Press trace to follow the line to the lowest point. Example Use a GDC to approximate the relative minimum and relative maximum of the function given by f x x x. 3 Solution Relative Minimum (-0.58, -0.38) Solution Relative Maximum (0.58, 0.38) Step Functions and Piecewise-Defined Functions Because of the vertical jumps, the greatest integer function is an example of a step function. Let’s graph a PiecewiseDefined Function Sketch the graph of 2 x 3, x 1 f x x 4, x 1 Notice when open dots and closed dots are used. Why? Even and Odd Functions Graphically Algebraically Let’s look at the graphs again and see if this applies. Graphically ☺ ☺ Example Determine whether each function is even, odd, or neither. Algebraic Graphical – Symmetric to Origin Algebraic Graphical – Symmetric to yaxis Algebraic Graphical – NOT Symmetric to origin OR y-axis. You Try Is the function f x x Even, Odd, of Neither? Solution f x x Symmetric about the y-axis.