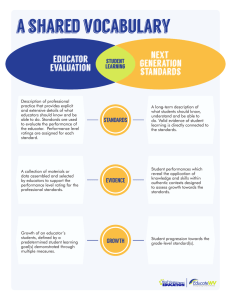
CURIN 850 Course Grade Rubric
advertisement
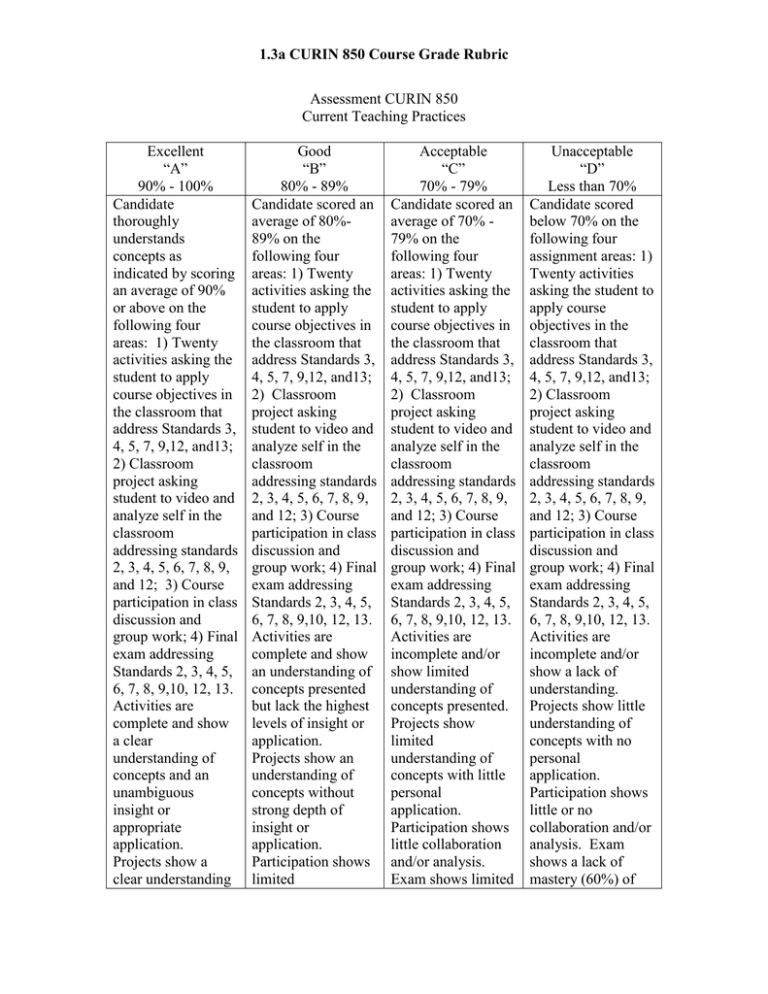
1.3a CURIN 850 Course Grade Rubric Assessment CURIN 850 Current Teaching Practices Excellent “A” 90% - 100% Candidate thoroughly understands concepts as indicated by scoring an average of 90% or above on the following four areas: 1) Twenty activities asking the student to apply course objectives in the classroom that address Standards 3, 4, 5, 7, 9,12, and13; 2) Classroom project asking student to video and analyze self in the classroom addressing standards 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, and 12; 3) Course participation in class discussion and group work; 4) Final exam addressing Standards 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,10, 12, 13. Activities are complete and show a clear understanding of concepts and an unambiguous insight or appropriate application. Projects show a clear understanding Good “B” 80% - 89% Candidate scored an average of 80%89% on the following four areas: 1) Twenty activities asking the student to apply course objectives in the classroom that address Standards 3, 4, 5, 7, 9,12, and13; 2) Classroom project asking student to video and analyze self in the classroom addressing standards 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, and 12; 3) Course participation in class discussion and group work; 4) Final exam addressing Standards 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,10, 12, 13. Activities are complete and show an understanding of concepts presented but lack the highest levels of insight or application. Projects show an understanding of concepts without strong depth of insight or application. Participation shows limited Acceptable “C” 70% - 79% Candidate scored an average of 70% 79% on the following four areas: 1) Twenty activities asking the student to apply course objectives in the classroom that address Standards 3, 4, 5, 7, 9,12, and13; 2) Classroom project asking student to video and analyze self in the classroom addressing standards 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, and 12; 3) Course participation in class discussion and group work; 4) Final exam addressing Standards 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,10, 12, 13. Activities are incomplete and/or show limited understanding of concepts presented. Projects show limited understanding of concepts with little personal application. Participation shows little collaboration and/or analysis. Exam shows limited Unacceptable “D” Less than 70% Candidate scored below 70% on the following four assignment areas: 1) Twenty activities asking the student to apply course objectives in the classroom that address Standards 3, 4, 5, 7, 9,12, and13; 2) Classroom project asking student to video and analyze self in the classroom addressing standards 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, and 12; 3) Course participation in class discussion and group work; 4) Final exam addressing Standards 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,10, 12, 13. Activities are incomplete and/or show a lack of understanding. Projects show little understanding of concepts with no personal application. Participation shows little or no collaboration and/or analysis. Exam shows a lack of mastery (60%) of 1.3a CURIN 850 Course Grade Rubric of concepts and a strong depth of insight or application. Participation shows collaboration and/or analysis. Exam shows nearly full mastery (90%) of objectives. collaboration and/or analysis. Exam shows partial mastery (80%) of objectives. mastery (70%) of objectives. objectives. Standard #13 The educator is a reflective practitioner who uses an understanding of historical, philosophical, and social foundations of education to guide educational practices. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Synthesize the history of effective teaching research. Identify key changes occurring in American society that have directly affected the education system. Identify key paradigm shifts occurring in American education. Recognize diversity in the American classroom. Identify the significant indicators of an “at-risk child” as illustrated in research. Standard #9 The educator is a reflective practitioner who continually evaluates the effects of his or her choices and actions on others (students, parents, and other professionals in the learning community), actively seeks out opportunities to grow professionally, and participates in the school improvement process (Kansas Quality Performance Accreditation [QPA]). 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Identify the fundamental beliefs and correlates of the Effective Schools movement and evaluate a school based on the criteria. Explore various beliefs about education and state a personal philosophy towards teaching. Identify the fundamental beliefs and components in Outcomes Based Education (OBE) and evaluate a school based on the criteria. Evaluate various school mission statements and exit outcomes and state a personal preference. Synthesize the accreditation process associated with Kansas Quality Performance Accreditation (QPA). Outline the key concepts associated with "No Child Left Behind" legislation. Standard #7 The educator plans effective instruction based upon the knowledge of all students, community, subject matter, curriculum outcomes, and current methods of teaching reading. 12. 13. 14. 15. Understand the variables that affect teacher planning and describe the basic components of a lesson plan. Write cognitive, affective and psychomotor objectives using taxonomies. Use the Internet to acquire lesson and/or unit plans. Distinguish various models of lesson planning and write several lesson plans based on specific models. Standard #4 The educator understands and uses a variety of appropriate instructional strategies to develop various kinds of students' learning including critical thinking, problem solving, and reading. Identify, define and use the eight phases of Madeline Hunter’s Direct Instruction model to develop a lesson plan. Explain the Science of Teaching by describing specific teacher actions that affect student achievement regardless of grade level – Pygmalion behaviors, high time-on-task, scaffolding, organization, and questioning. 18. Identify specific biases and teacher behaviors that affect student achievement. 19. Identify specific questioning behaviors that affect student achievement. 20. Explain the major elements and precepts of Mastery Learning. 16. 17. Standard #6 The educator uses a variety of effective verbal and non-verbal communication techniques to foster active inquiry, collaboration, and supportive interaction in the classroom. 21. Explain the Art of Teaching by describing specific nonverbal teacher actions that impact student motivation, identifying specific novel and vivid communication techniques that gain and keep attention, and illustrating how a humorous learning environment impacts learning. 22. Recognize the human characteristics of an effective teacher as defined in today's research. 23. Associate the domains and effects of nonverbal communication into the art of teaching. 24. Outline several benefits and strategies to use humor in the classroom. Standard #3 The educator demonstrates the ability to provide different approaches to learning and creates instructional opportunities that are equitable, that are based on developmental levels, and that are adapted to diverse learners, including those with exceptionalities. 25. Identify and define the major intelligences identified by Howard Gardner. 1.3a CURIN 850 Course Grade Rubric 26. 27. 28. Explore his/her own multiple intelligence by creating a personal intelligence profile. Use each of the multiple intelligences in planning a lesson. Give examples of how different student learning styles can be accommodated in lesson planning, instruction, classroom management, and assessment. Standard #2 The educator demonstrates an understanding of how individuals learn and develop intellectually, socially, and personally and provides learning opportunities that support this development. 29. 30. 31. 32. Define cooperative learning and synthesize the benefits as illustrated in the research. List developmentally appropriate social skills to be taught through cooperative learning activities. Identify particular team recognitions that support positive interdependence and individual accountability. Explain the steps and strategies employed in STAD, TGT, and Jigsaw. Standard #5 The educator uses an understanding of individual and group motivation and behavior to create a learning environment that encourages positive social interaction, active engagement in learning, and self-motivation. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. Examine the basic elements and critical components of effective classroom management plan as illustrated in today's research. Describe various procedures and routines that should be established to provide an environment conducive to learning. Differentiate the basic orientations in contemporary management systems such as Canter’s Assertive Discipline and Glaser’s Choice Theory. Describe the teacher actions that help maintain an effective classroom management system. Develop a personal classroom management plan by listing developmentally appropriate rules and consequences. Develop an individual student management plan that identifies the observable misbehavior, proposing the possible unmet needs being manifested, and the various teacher actions that could be tried to correct behavior and structure self-motivation. Standard #8 The educator understands and uses formal and informal assessment strategies to evaluate and ensure the continual intellectual, social, and other aspects of personal development of all learners. 39. 40. 41. Describe the key elements in an effective assessment system that assesses student learning and communicates to students and parents. Describe various performance assessment techniques and identify the benefits of alternative assessment. List possible structures for portfolio assessment. Standard #10 The educator fosters collegial relationships with school personnel, parents, and agencies in the larger community to support all students' learning and well being. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. Identify methods of developing professional communication between the home and school. Follow the steps in conducting a two-way parent teacher conference and use effective techniques in handling difficult parents. Reflect upon the importance of mentoring and creating a collegial culture for early career professionals. Identify key components in effective early career / mentoring programs. Describe the process and portfolio focus in National Board Certification. Standard #12 The educator understands the role of technology in society and demonstrates skills using instructional tools and technology to gather, analyze, and present information, enhance instructional practices, facilitate professional productivity and communication, and help all students use instructional technology effectively. 47. Use the Internet to assess curriculum, acquire lesson plans, develop individual student management plans, and research instructional practices and issues. 48. Using a recorded teaching episode, reflect upon the effectiveness of his/her teaching.