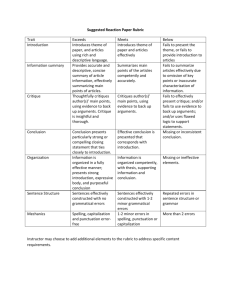
Specialty Area Matrix (K-12) 2011
advertisement

Appendix B Curriculum Crosswalk For Educational Administration: Superintendent Fall 2011 Missouri State University Educational Administration: Superintendent Listing-Link of Program Syllabi Conceptual Framework 1-10 EAD 850 Politics in Education EAD 858 School Personnel Administration EAD 862 Superintendency EAD 863 Curriculum Design and Evaluation EAD 864 School and Community Relations EAD 865 School Law EAD 866 Public School Finance EAD 867 School Plant Planning and Maintenance EAD 782 Onsite Internship (Superintendency) EAD 895 Research in Administrative Practices EAD 860 Field Study Standard 1A 1B 1C 1D 1E 2A 2B MOSTEP 1.3.1 1.3.5 1.3.1 1.3.1 1.3.1 1.3.1 1.3.2 1.3.2 C. F. 1, 6, 10 1, 6, 10 1, 6, 10 1, 6, 10 1, 6, 10 2, 3 2, 3 850 858 862 SPECIALIST LEVEL 864 865 866 863 867 782 895 860 KT CT 2C 2D 3A 3B 3C 4A 4B 4C 5A 5B 5C 6A 6B 6C 1.3.2 1.3.3 1.3.5 1.3.2 1.3.2 1.3.3 1.3.3 1.3.6 1.3.3 1.3.3 1.3.4 1.3.6 1.3.4 1.3.3 1.3.4 1.3.2 1.3.5 1.3.2 1.3.5 1.3.3 1.3.5 1.3.3 1.3.5 1.3.6 1.3.6 1.3.6 2, 3 2, 3 4, 5, 7 4, 5, 7 8, 10 6, 8, 9 6, 8, 9 6, 8, 9 Knowledge/Content Skill 1-10 8, 10 8, 10 1-10 1-10 4, 5, 7 Missouri State University Conceptual Framework Our General Learning Outcomes The curricula of professional education programs at Missouri State University reflect our commitment to these beliefs. Further, they reflect and are aligned with the professional standards specified by state, national, and professional accreditation organizations. Our initial and advanced programs are designed to develop candidate knowledge, skills, and dispositions associated with successful professional educational practice. Missouri State professional education graduates will demonstrate competence in: 1. Foundations: knowledge of the historical development of the profession, and foundational issues and arguments underlying its practices, as well as understanding of the importance of integrated learning across disciplines. 2. Subject Matter: knowledge of subject matter discipline content and the ability to integrate content with pedagogy appropriate to the candidate's field of study. 3. Learning and Development: knowledge of human development and motivation, theories of learning, pedagogy and assessment. 4. Reflective skills: communication skills, critical and creative thinking abilities and other skills crucial to reflective decision- making. 5. Technology: knowledge and skills in the use of technology appropriate to the candidate's field of study. 6. Professional Skills: the practical abilities to implement the skills, techniques, and strategies associated with student learning and development in the educational context in which they practice. 7. Assessment Skills: the skills to conduct valid and reliable assessments of their students' learning, and use that assessment to improve learning and development for their students. 8. Dispositions: the intellectual, social, ethical, and other personal attributes and beliefs previously ascribed to reflective decision- makers in a variety of professional settings, including a commitment to their own lifelong learning and professional development. 9. Diversity: the ability to skillfully facilitate and promote the learning of all students, including those from diverse cultural, racial and economic backgrounds, and those with disabilities. 10. Collaboration and Leadership: the ability and skills to foster and maintain collaborative, empowering relationships with other professionals within schools and the community. The Assessment of General Learning Outcomes Candidate attainment of the general learning outcome competencies is continuously assessed and evaluated using multiple data sources. These outcome based assessment systems include, but are not limited to, standardized testing procedures, traditional classroom-based testing, observations, research and conceptual papers, portfolios and related performance assessments. Individual departments responsible for specific programs that lead to certification develop assessment plans and procedures unique to their specific discipline area. These procedures are in alignment with our Conceptual Framework, national standards of various learned societies, NCATE standards and the program accreditation standards of the Missouri Department of Elementary and Secondary Education. Standard 1.0: Candidates who complete the program are educational leaders who have the knowledge and ability to promote the success of all students by facilitating the development, articulation, implementation, and stewardship of a school or district vision of learning supported by the school community. Specialist Crosswalk Conceptual Framework: 1. Foundations: knowledge of the historical development of the profession, and foundational issues and arguments underlying its practices, as well as understanding of the importance of integrated learning across disciplines. 6. Professional Skills: the practical abilities to implement the skills, techniques, and strategies associated with student learning and development in the educational context in which they practice. 10. Collaboration and Leadership: the ability and skills to foster and maintain collaborative, empowering relationships with other professionals within schools and the community. Elements Meets Standards for School District Leadership Mo STEP 1.3 EAD Course Strands A. Develop a Vision 1. Candidates develop and demonstrate the skills needed to work with a board of education to facilitate the development of a vision of learning for a school district that promotes the success of all students. 1.3.1 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by facilitating the development, articulation, implementation, and stewardship of a vision of learning that is shared and supported by the school community. 1.1 Facilitate the development and implementation of a shared vision and strategic plan for the school or district that focuses on teaching and learning (e.g. cultivate group norms, influence institutional culture, and affirm core values.). 2. Candidates base development of the vision on Rubric Fails to develop and implement a shared vision for a school or district and has no understanding of cultural groups, institutional culture and core values. Has the understanding of the development of a shared vision but does not understand the culture of the building/district and its core values. Has developed and implemented a shared vision and strategic plan that has included the cultural audiences, institutional culture and core values. relevant knowledge and theories applicable to school-level leaders applied to a school district context. 3. Candidates use data-based research strategies to create a vision that takes into account the diversity of learners in a district. 4. Candidates demonstrate knowledge of ways to use a district’s vision to mobilize additional resources to support the vision. Understands the needs for and the process of collaboratively developing a vision and mission based on student learning and relevant demographic data pertaining to students and their families 11.7 Develop appropriate procedures and relationships for working with local governing boards. Unable to develop procedures and relationships for working with local governing boards. Develops inappropriate procedures and relationships for working with local governing boards. Develops appropriate procedures and relationships for working with local governing boards. 1.3.5 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by acting with integrity, fairness, and in an ethical manner. 1.5 Identify and critique several theories of leadership and their application to various school environments. Fails to identify and critique leadership theories and their application to the school environment. Identifies theories of leadership but fails to critique theories and apply them to the school environment. Identifies and shows ability to continuously critique theories of leadership and their application to the school environment. Demonstrates understanding of the purpose of education and the role of leadership in modern society 11.3 Define and relate the general characteristics of internal and external political systems as they apply to school settings. Fails to define and relate the general characteristics of internal and external political systems as they apply to school settings. Inconsistently defines and relates the general characteristics of internal and external political systems as they apply to school settings. Defines and relate the general characteristics of internal and external political systems as they apply to school settings. B. Articulate a Vision 1. Candidates demonstrate the ability to articulate the components of this vision for a district and the leadership processes necessary to implement and support the 1.3.1 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by facilitating the development, articulation, implementation, and stewardship 2.2 Use qualitative and quantitative data to inform decisions, to plan and assess school programs, to design accountability systems, to plan for school improvement, and to develop and conduct research. Does not use qualitative and quantitative data to make informed decisions. Uses qualitative and quantitative data to make decisions, but fails to apply data to all areas and conduct research. Uses qualitative and quantitative data to inform decisions, to plan and assess school programs, to design accountability systems, to plan for school improvement, and to develop and conduct research. 8.2 Acquire and manage financial and material assets, and capital goods and services, allocating resources according to district or school priorities (e.g. property, plant, equipment, transportation, and food service.). Does not acquire and manage financial and material assets, and capital goods and services. Acquires and manages financial and material assets and capital goods and services but fails to allocate these resources according to the district or school priorities. Acquires and manages financial and material assets, and capital goods and services, allocating resources according to district or school priorities (e.g. property, plant, equipment, transportation, and food service.). 7.2 Use appropriate written, verbal, and nonverbal communication in a variety of situations. Does not have appropriate written, verbal, and nonverbal communication skills. Has written, verbal, and nonverbal communication skills but fails to use them in a variety of situations. Uses appropriate written, verbal, and nonverbal communication in a variety of situations. vision. 2. Candidates explain how data-based research strategies and strategic planning processes that focus on student learning help develop a vision, drawing on relevant information sources such as student assessment results, student and family demographic data, and an analysis of community needs. 3. Candidates demonstrate the ability to communicate the vision to school boards, staff, parents, students, and community members through the use of symbols, ceremonies, of a vision of learning that is shared and supported by the school community. Recognizes the need to communicate and models the vision and mission to all stakeholders through varied means (symbols, ceremonies, stories, etc.) 7.3 Apply appropriate communications strategies (e.g. identifying audiences, determining messages selecting transmission mediums, identifying reaction of receivers, soliciting responses, etc.). Fails to apply appropriate communications strategies. Inconsistently applies communications strategies. Applies appropriate communications strategies. 10.2 Articulate the district’s or school’s vision, mission and priorities to the community and media, and build community support for district or school priorities and programs (e.g. form collaborative relationships with businesses, citizen groups, neighborhood associations, social Fails to articulate the district's or school's vision, mission and priorities to the community and media. Articulates the district's or school's vision, mission and priorities to the community and media but fails to build community support. Articulates the district’s or school’s vision, mission and priorities to the community and media, and builds community support for district or school priorities and programs. stories, and other activities. service agencies, parent organizations, advocacy groups, universities, and religious institutions, etc.). 2.1 Conduct needs assessment by collecting information on the students; on staff and the school environment; on family and community values, expectations and priorities; and on national and global conditions affecting schools. Fails to conduct needs assessment. Conducts needs assessment but fails to collect information on all areas. Conducts needs assessment by collecting information on students; on staff and the school environment; on family and community values, expectations and priorities; and on national and global conditions affecting schools. 2.2 Use qualitative and quantitative data to inform decisions, to plan and assess school programs, to design accountability systems, to plan for school improvement, and to develop and conduct research. Does not use qualitative and quantitative data to make informed decisions. Uses qualitative and quantitative data to make decisions, but fails to apply data to all areas and conduct research. Uses qualitative and quantitative data to inform decisions, to plan and assess school programs, to design accountability systems, to plan for school improvement, and to develop and conduct research. 7.2 Use appropriate written, verbal, and Does not have appropriate written, Has written, verbal, and nonverbal Uses appropriate written, verbal, and nonverbal communication in a variety of situations. verbal, and nonverbal communication skills. communication skills but fails to use them in a variety of situations. nonverbal communication in a variety of situations. 7.3 Apply appropriate communications strategies (e.g. identifying audiences, determining messages selecting transmission mediums, identifying reaction of receivers, soliciting responses, etc.). Fails to apply appropriate communications strategies. Inconsistently applies communications strategies. Applies appropriate communications strategies. 10.1 Analyze community and district power structures, and identify major opinion leaders and their relationships to school goals and programs. Fails to analyze community and district power structures. Analyzes community and district power structures but fails to identify their relationships to school goals and programs. Analyzes community and district power structures, and identify major opinion leaders and their relationships to school goals and programs. 10.4 Involve family and community in appropriate policy development, program planning, Fails to involve family and community in appropriate policy development, Inconsistently involves family and community in appropriate policy development, Involves family and community in appropriate policy development, program planning, C. Implement a 1. Candidates demonstrate the Vision ability to plan programs to motivate staff, students, and families to achieve a school district’s vision. 2. Candidates design researchbased processes to effectively implement a district vision throughout an entire school district and community. 1.3.1 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by facilitating the development, articulation, implementation, and stewardship of a vision of learning that is shared and supported by the school community. and assessment processes. program planning, and assessment processes. program planning, and assessment processes. and assessment processes. 10.5 Develop an effective and interactive staff communications plan and public relations program. Has no staff communications plan or public relations program. Has an ineffective staff communications plan and public relations program. Develops an effective and interactive staff communications plan and public relations program. 1.2 Use motivational theory to create conditions that motivate staff, students and families to achieve the school’s vision (e.g. facilitate collegiality and teamwork, arrange significant work, encourage challenging standards, provide autonomy, support innovation, delegate responsibility, develop leadership in others, provide leadership opportunities, recognize and reward effective performance, provide knowledge of results, provide coaching and mentoring, gain Insufficient skills to motivate staff, students and families to achieve a school mission and does not have the knowledge and strategies to implement a school vision. Has the ability to motivate staff, students and families, but lacks abilities to engage colleagues in one or more of the skills areas necessary to fully achieve the mission. Has the ability utilize multiple (9 or more) strategies to create conditions to motivate staff, students and families to achieve the school vision. resources, serve as a role model.). Uses the vision and mission to shape programs, actions, & plans 1.4 Initiate, manage, and evaluate the change process. Fails to demonstrate an understanding of the change process. Has the ability to initiate, manage, or evaluate change, but fails to implement all three aspects in the change process. Fully understands and implements the initiation, management and evaluation of the change process. 10.4 Involve family and community in appropriate policy development, program planning, and assessment processes. Fails to involve family and community in appropriate policy development, program planning, and assessment processes. Inconsistently involves family and community in appropriate policy development, program planning, and assessment processes. Involves family and community in appropriate policy development, program planning, and assessment processes. 1.1 Facilitate the development and implementation of a shared vision and strategic plan for the school or district that focuses on teaching and learning (e.g. cultivate group norms, influence institutional culture, and affirm core values.). Fails to develop and implement a shared vision for a school or district and has no understanding of cultural groups, institutional culture and core values. Has the understanding of the development of a shared vision but does not understand the culture of the building/district and its core values. Has developed and implemented a shared vision and strategic plan that has included the cultural audiences, institutional culture and core values. D. Steward a Vision 1. Candidates demonstrate the ability to align and, as necessary, redesign administrative policies and practices required for full implementation of a district vision. 2. Candidates understand the theory and research related to organizational and educational leadership and engage in the collection, organization, and analysis of a variety of 2.2 Use qualitative and quantitative data to inform decisions, to plan and assess school programs, to design accountability systems, to plan for school improvement, and to develop and conduct research. Does not use qualitative and quantitative data to make informed decisions. Uses qualitative and quantitative data to make decisions, but fails to apply data to all areas and conduct research. Uses qualitative and quantitative data to inform decisions, to plan and assess school programs, to design accountability systems, to plan for school improvement, and to develop and conduct research. 1.3.1 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by facilitating the development, articulation, implementation, and stewardship of a vision of learning that is shared and supported by the school community. 1.1 Facilitate the development and implementation of a shared vision and strategic plan for the school or district that focuses on teaching and learning (e.g. cultivate group norms, influence institutional culture, and affirm core values.). Fails to develop and implement a shared vision for a school or district and has no understanding of cultural groups, institutional culture and core values. Has the understanding of the development of a shared vision but does not understand the culture of the building/district and its core values. Has developed and implemented a shared vision and strategic plan that has included the cultural audiences, institutional culture and core values. Clearly articulates objectives & strategies and the means by which 6.1 Establish operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, utilizing practical Fails to establish operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals. Establishes operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, but fails to utilize Establishes operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, utilizing practical information, including student performance data, required to assess progress toward a district’s vision, mission, and goals. those objectives & strategies will be monitored and evaluated applications of organizational theories. Identifies and draws upon existing resources 6.3 Implement appropriate management techniques and group processes to define roles, assign functions, delegate effectively, and determine accountability for attaining goals. Understands the need and processes for regularly and collaboratively monitoring, evaluating, and revising the vision, mission, and implementation of plans based on student-learning data practical applications of organizational theories. applications of organizational theories. Fails to implement appropriate management techniques and group processes. Inadequately implements appropriate management techniques and group processes, neglecting one or more of the following areas: definition of roles, assignment of functions, effective delegation, and determination of accountability for attaining goals. Fully and appropriately implements management techniques and group processes to define roles, assign functions, delegate effectively, and determine accountability for attaining goals. 6.4 Monitor and assess the progress of activities, making adjustments and formulating new action steps as necessary. Fails to monitor and asses the progress of activities and make adjustments as necessary. Monitors and assesses the progress of activities, but fails to make adjustments and formulate new action steps when necessary. Monitors and assesses the progress of activities, making adjustments and formulating new action steps as necessary. 1.5 Identify and critique several theories of leadership and their application to various school environments. Fails to identify and critique leadership theories and their application to the school environment. Identifies theories of leadership but fails to critique theories and apply them to the school environment. Identifies and shows ability to continuously critique theories of leadership and their application to the school environment. 1. Candidates E. Promote demonstrate the Community Involvement in ability to bring the Vision together and communicate effectively with stakeholders within the district and the larger community concerning implementation and realization of the vision. 1.3.1 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by facilitating the development, articulation, implementation, and stewardship of a vision of learning that is shared and supported by the school community. 6.1 Establish operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, utilizing practical applications of organizational theories. Fails to establish operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals. Establishes operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, but fails to utilize practical applications of organizational theories. Establishes operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, utilizing practical applications of organizational theories. 1.2 Use motivational theory to create conditions that motivate staff, students and families to achieve the school’s vision (e.g. facilitate collegiality and teamwork, arrange significant work, encourage challenging standards, provide autonomy, support innovation, delegate responsibility, develop leadership in others, provide leadership opportunities, recognize and reward effective performance, provide knowledge Insufficient skills to motivate staff, students and families to achieve a school mission and does not have the knowledge and strategies to implement a school vision. Has the ability to motivate staff, students and families, but lacks abilities to engage colleagues in one or more of the skills areas necessary to fully achieve the mission. Has the ability utilize multiple (9 or more) strategies to create conditions to motivate staff, students and families to achieve the school vision. of results, provide coaching and mentoring, gain resources, serve as a role model.). Recognizes everyone’s contributions to implementing the vision and mission 7.3 Apply appropriate communications strategies (e.g. identifying audiences, determining messages selecting transmission mediums, identifying reaction of receivers, soliciting responses, etc.). Fails to apply appropriate communications strategies. Inconsistently applies communications strategies. Applies appropriate communications strategies. 10.2 Articulate the district’s or school’s vision, mission and priorities to the community and media, and build community support for district or school priorities and programs (e.g. form collaborative relationships with businesses, citizen groups, neighborhood associations, social Fails to articulate the district's or school's vision, mission and priorities to the community and media. Articulates the district's or school's vision, mission and priorities to the community and media but fails to build community support. Articulates the district’s or school’s vision, mission and priorities to the community and media, and builds community support for district or school priorities and programs. service agencies, parent organizations, advocacy groups, universities, and religious institutions, etc.). Standard 1.0 Narrative Explanation: Standard addresses the need to prepare educational leaders who value and are committed to educating all students to become successful adults. Each educational leader is responsible for creating and articulating a vision of high standards for learning within the school or district that can be shared by all employees and is supported by the broader school-community of parents and citizens. This requires that educational leaders be willing to examine their own assumptions, beliefs, and practices; understand and apply research; and foster a climate of continuous improvement among all members of the educational staff. Such educational leaders will commit themselves to high levels of personal and organizational performance in order to ensure implementation of this vision of learning. Examples of Promising Practices for Candidate Performance Activities: vision statement for a school or district, share it with the executive team in the central office or with a site-based management team, and demonstrate how stakeholders were involved in the development. e required to collect, interpret, and analyze school data. The analysis should reflect the candidate’s understanding of the school’s vision and mission statement, the level of involvement and actual contributions of the school community, and recommendations for inclusion in the school improvement plan. beginning on page 25 of the Instructions to Implement Standards for Advanced Programs in Educational Leadership document. Conceptual Framework: 2. Subject Matter: knowledge of subject matter discipline content and the ability to integrate content with pedagogy appropriate to the candidate's field of study. 3. Learning and Development: knowledge of human development and motivation, theories of learning, pedagogy and assessment. Standard 2.0: Candidates who complete the program are educational leaders who have the knowledge and ability to promote the success of all students by promoting a positive school culture, providing an effective instructional program, applying best practice to student learning, and designing comprehensive professional growth plans for staff. Elements Meets Standards for School District Leadership Mo STEP 1.3 EAD Course Strands A. Promote Positive School Culture 1. Candidates develop a sustained approach to improve and maintain a positive district culture for learning that capitalizes on multiple aspects of diversity to meet the learning needs of all students. 1.3.2 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by advocating, nurturing, and sustaining a school culture and instructional program conducive to student learning and staff professional 3.1 Create with teachers, parents and students a positive school culture that promotes learning; (e.g. holds high expectations, focuses on accomplishments and recognition, and promotes a supportive climate.). Rubric Fails to create a positive school culture that promotes learning. Creates a positive school culture that promotes learning but does not involve teachers, parents and students. Creates with teachers, parents and students a positive school culture that promotes learning. growth. B. Provide Effective Instructional Program 1. Candidates can demonstrate an understanding of a variety of instructional research methodologies and can analyze Demonstrates the ability to create and regularly assess the effectiveness of a school culture and climate in which students and staff feel valued and important, in which responsibilities, contributions, and accomplishments of students and staff are acknowledged and celebrated, in which life-long learning is encouraged and modeled, in which high expectations are held for self, students, and staff 7.4 Promote multicultural awareness, gender sensitivity, and racial and ethnic appreciation. Lacks awareness of multicultural awareness, gender sensitivity, and racial and ethnic appreciation. Limited promotion of multicultural awareness, gender sensitivity, and racial and ethical appreciation. Consistently promotes multicultural awareness, gender sensitivity, and racial and ethnic appreciation. 1.3.2 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by advocating, 1.5 Identify and critique several theories of leadership and their application to various school environments. Fails to identify and critique leadership theories and their application to the school environment. Identifies theories of leadership but fails to critique theories and apply them to the school environment. Identifies and shows ability to continuously critique theories of leadership and their application to the school environment. the comparable strengths and weaknesses of each method. 2. Candidates are able to use qualitative and quantitative data, appropriate research methods, technology, and information systems to develop a longrange plan for a district that assesses the district’s improvement and accountability systems. 3. Candidates demonstrate the ability to use and promote technology and information systems to enrich district curriculum and instruction, monitor instructional practices, and provide nurturing, and sustaining a school culture and instructional program conducive to student learning and staff professional growth. Demonstrates the ability to create and regularly assess the effectiveness of a school culture and climate in which students and staff feel valued and important, in which responsibilities, contributions, and accomplishments of students and staff are acknowledged and celebrated, in which life-long learning is encouraged and modeled, in which high expectations are held for self, 3.4 Design curricula with consideration for philosophical, sociological, and historical foundations, democratic values, and the community’s values goals, social needs and changing conditions. Does not design curricula with consideration for philosophical, sociological, and historical foundations, democratic values, and the community’s values goals, social needs and changing conditions. Designs curricula without consideration for all of the following areas: philosophical, sociological, and historical foundations, democratic values, and the community’s values goals, social needs and changing conditions. Designs curricula with consideration for philosophical, sociological, and historical foundations, democratic values, and the community’s values goals, social needs and changing conditions. assistance to administrators who have needs for improvement. 4. Candidates demonstrate the ability to allocate and justify resources to sustain the instructional program. students, and staff Recognizes the need for promoting professional development focused on student learning and consistent with school vision and goals, high expectations, and an attitude that everyone can succeed 3.5 Align curricular goals and objectives with instructional goals and objectives and desired outcomes when developing scope, sequence, balance, etc. Fails to align curricular goals and objectives with instructional goals and objectives and desired outcomes. Partially aligns curricular goals and objectives with instructional goals and objectives and desired outcomes Aligns curricular goals and objectives with instructional goals and objectives and desired outcomes when developing scope, sequence, balance, etc. 2.2 Use qualitative and quantitative data to inform decisions, to plan and assess school programs, to design accountability systems, to plan for school improvement, and to develop and conduct research. Does not use qualitative and quantitative data to make informed decisions. Uses qualitative and quantitative data to make decisions, but fails to apply data to all areas and conduct research. Uses qualitative and quantitative data to inform decisions, to plan and assess school programs, to design accountability systems, to plan for school improvement, and to develop and conduct research. 3.3 Base curricular decisions on research, applied theory, informed practice, the recommendations of learned societies, Does not base curricular decisions on research, applied theory, informed practice, and the recommendations of learning Makes curricular decisions without considering and applying all of the following areas: research, applied theory, informed Bases curricular decisions on research, applied theory, informed practice, the recommendations of learned societies, and state and federal policies and mandates (e.g. cognitive development, human development, learning styles, contemporary methodologies, content priorities, special needs legislation on topics such as least restrictive environment, etc.). societies, and state and federal policies and mandates. practice, the recommendations of learned societies, and state and federal policies and mandates. and state and federal policies and mandates. 3.6 Develop with others curriculum and instruction appropriate for varied teaching and learning styles and specific student needs based on gender, ethnicity, culture, social class and exceptionalities. Does not develop curriculum and instruction that is appropriate for varied teaching and learning styles and specific student needs. Develops curriculum and instruction appropriate for varied teaching and learning styles but fails to take into consideration specific student needs based on gender, ethnicity, culture, social class and exceptionalities. Develops with others curriculum and instruction appropriate for varied teaching and learning styles and specific student needs based on gender, ethnicity, culture, social class and exceptionalities. 3.8 Use various staffing patterns, student grouping plans, class scheduling forms, school organizational structures, and Does not use resources to support various teaching strategies and desired student outcomes. Uses limited resources to support various teaching strategies and desired student outcomes. Uses various staffing patterns, student grouping plans, class scheduling forms, school organizational structures, and facilities design processes, to support various teaching strategies and desired student outcomes. facilities design processes, to support various teaching strategies and desired student outcomes. 6.4 Monitor and assess the progress of activities, making adjustments and formulating new action steps as necessary. Fails to monitor and asses the progress of activities and make adjustments as necessary. Monitors and assesses the progress of activities, but fails to make adjustments and formulate new action steps when necessary. Monitors and assesses the progress of activities, making adjustments and formulating new action steps as necessary. 9.2 Apply and assess current technologies for school management and business procedures. Lacks awareness of current technologies for school management and business procedures. Limited awareness of current technologies for school management and business procedures. Applies and fully assesses current technologies for school management and business procedures. 4.1 Work with faculty and other stakeholders to identify needs for professional development, to organize, facilitate, and evaluate professional development programs, to integrate district and school priorities, to build Fails to work with faculty and other stakeholders. Works with faculty and other stakeholders but fails to address all of the following areas: identifying needs for professional development, organizing, facilitating and evaluating professional development Works with faculty and other stakeholders to do all of the following: identify needs for professional development, to organize, facilitate, and evaluate professional development programs, to integrate district and school faculty as resource, and to ensure that professional development activities focus on improving student outcomes. programs, integrating district and school priorities, building faculty as resource, and ensuring that professional development activities focus on improving student outcomes. priorities, to build faculty as resource, and to ensure that professional development activities focus on improving student outcomes. 9.1 Use technology, telecommunications and information systems to enrich curriculum and instruction (e.g. CAI systems, CD ROM retrieval systems, on-line networks, distance learning, interactive video, etc.). Does not use technology, telecommunications and information systems to enrich curriculum and instruction. Inconsistently uses technology, telecommunications and information systems to enrich curriculum and instruction. Uses technology, telecommunications and information systems to enrich curriculum and instruction (e.g. CAI systems, CD ROM retrieval systems, on-line networks, distance learning, interactive video, etc.). 9.2 Apply and assess current technologies for school management and business procedures. Lacks awareness of current technologies for school management and business procedures. Limited awareness of current technologies for school management and business procedures. Applies and fully assesses current technologies for school management and business procedures. 9.3 Develop and monitor long range plans for school and district technology and information Has no long range plans for school and district technology and information Develop a long range plan for school district technology and information systems but fail to Develops and monitors long range plans for school and district technology and information systems, making C. Apply Best Practice to Student Learning 1. Candidates demonstrate the ability to facilitate and engage in activities that use best practices and sound educational research to improve instructional programs. 2. Candidates demonstrate an ability to assist 1.3.2 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by advocating, nurturing, and sustaining a school culture and instructional program conducive to student learning and staff systems, making informed decisions about computer hardware and software, and about staff development, keeping in mind the impact of technologies on student outcomes and school operations. decisions. implement and monitor the plan. informed decisions about computer hardware and software, and about staff development, keeping in mind the impact of technologies on student outcomes and school operations. 8.1 Identify and analyze the major sources of fiscal and non-fiscal resources for schools and school districts. Lacks awareness of the major sources of fiscal and nonfiscal resources for schools and school districts. Limited awareness of the major sources of fiscal and non-fiscal resources for schools and school districts. Fully identifies and analyzes the major sources of fiscal and non-fiscal resources for schools and school districts. 3.2 Develop collaboratively a learning organization that supports instructional improvement, builds an appropriate curriculum, and incorporates best practice. Fails to develop a collaborative learning organization that supports instructional improvement, curriculum, and best practices. Develops a learning organization that fails to do one or more of the following: support instructional improvement, build appropriate curriculum, or incorporate best practices. Develops collaboratively a learning organization that supports instructional improvement, builds an appropriate curriculum, and incorporates best practice. school and district personnel in understanding and applying best practices for student learning. 3. Candidates understand and can apply human development theory, proven learning, and motivational theories, and concern for diversity to the learning process. 4. Candidates understand how to use appropriate research strategies to profile student performance in a district and analyze differences among subgroups. professional growth Is able and inclined to promote and facilitate a learning environment in which diversity is viewed as an asset, in which every student is provided multiple opportunities to learn, in which technologies are used in teaching and learning 3.3 Base curricular decisions on research, applied theory, informed practice, the recommendations of learned societies, and state and federal policies and mandates (e.g. cognitive development, human development, learning styles, contemporary methodologies, content priorities, special needs legislation on topics such as least restrictive environment, etc.). Does not base curricular decisions on research, applied theory, informed practice, and the recommendations of learning societies, and state and federal policies and mandates. Makes curricular decisions without considering and applying all of the following areas: research, applied theory, informed practice, the recommendations of learned societies, and state and federal policies and mandates. Bases curricular decisions on research, applied theory, informed practice, the recommendations of learned societies, and state and federal policies and mandates. 3.8 Use various staffing patterns, student grouping plans, class scheduling forms, school organizational structures, and facilities design processes, to support various teaching strategies Does not use resources to support various teaching strategies and desired student outcomes. Uses limited resources to support various teaching strategies and desired student outcomes. Uses various staffing patterns, student grouping plans, class scheduling forms, school organizational structures, and facilities design processes, to support various teaching strategies and desired student outcomes. and desired student outcomes. 5.1 Apply the principles of student growth and development to the learning environment and the educational program. Does not apply the principles of student growth and development to the learning environment and educational program. Inadequately applies the principles of student growth and development to the learning environment and educational program. Applies the principles of student growth and development to the learning environment and the educational program. 2.3 Engage staff in an ongoing study of current best practices and relevant research and demographic data, and analyze their implications for school improvement. Does not engage the staff in ongoing study of current best practices and relevant research. Engages staff in an ongoing study of current best practices but does not analyze their implications and apply this information for school improvement. Engages staff in an ongoing study of current best practices and relevant research and demographic data, and analyze their implications for school improvement. 5.1 Apply the principles of student growth and development to the learning environment and the educational program. Does not apply the principles of student growth and development to the learning environment and educational program. Inadequately applies the principles of student growth and development to the learning environment and educational program. Applies the principles of student growth and development to the learning environment and the educational program. 1.5 Identify and critique several theories of Fails to identify and critique leadership theories and their Identifies theories of leadership but fails to critique Identifies and shows ability to continuously leadership and their application to various school environments. application to the school environment. theories and apply them to the school environment. critique theories of leadership and their application to the school environment. 3.9 Assess student progress using a variety of appropriate techniques. Fails to assess student progress. Assesses student progress using limited techniques. Assesses student progress using a variety of appropriate techniques. 5.1 Apply the principles of student growth and development to the learning environment and the educational program. Does not apply the principles of student growth and development to the learning environment and educational program. Inadequately applies the principles of student growth and development to the learning environment and educational program. Applies the principles of student growth and development to the learning environment and the educational program. 2.1 Conduct needs assessment by collecting information on the students; on staff and the school environment; on family and community values, expectations and priorities; and on national and global conditions affecting schools. Fails to conduct needs assessment. Conducts needs assessment but fails to collect information on all areas. Conducts needs assessment by collecting information on students; on staff and the school environment; on family and community values, expectations and priorities; and on national and global conditions affecting schools. D. Design Comprehensive Professional Growth Plans 1. Candidates demonstrate knowledge of adult learning strategies and the ability to apply technology and research to professional development design focusing on authentic problems and tasks, mentoring, coaching, conferencing, and other techniques that promote new knowledge and skills in the workplace. 2. Candidates demonstrate the ability to use observations and collaborative reflection to help form comprehensive professional growth plans with district and school personnel. 3. Candidates develop personal professional 1.3.2 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by advocating, nurturing, and sustaining a school culture and instructional program conducive to student learning and staff professional growth 3.7 Utilize a variety of supervisory models to improve teaching and learning (e.g. clinical, developmental, cognitive and peer coaching, as well as applying observation and conferencing skills.). Fails to utilize a varied of supervisory models to improve teaching and learning. Utilizes one or very few supervisory models to improve teaching and learning. Utilizes a variety of supervisory models to improve teaching and learning. Recognizes the need for promoting professional development focused on student learning and consistent with school vision and goals, high expectations, and an attitude that everyone can succeed 4.1 Work with faculty and other stakeholders to identify needs for professional development, to organize, facilitate, and evaluate professional development programs, to integrate district and school priorities, to build faculty as resource, and to ensure that professional development Fails to work with faculty and other stakeholders. Works with faculty and other stakeholders but fails to address all of the following areas: identifying needs for professional development, organizing, facilitating and evaluating professional development programs, integrating district and school priorities, building Works with faculty and other stakeholders to do all of the following: identify needs for professional development, to organize, facilitate, and evaluate professional development programs, to integrate district and school priorities, to build faculty as resource, and to ensure that professional growth plans that reflect commitment to life-long learning and best practices. activities focus on improving student outcomes. faculty as resource, and ensuring that professional development activities focus on improving student outcomes. development activities focus on improving student outcomes. 4.2 Apply adult learning strategies to professional development, focusing on authentic problems and tasks, and utilizing mentoring, coaching, conferencing and other techniques to ensure that new knowledge and skills are practiced in the workplace. Does not focus on professional development and implementing new knowledge and stills in the workplace. Focuses on adult learning strategies and new knowledge and skills but does not apply this knowledge to the workplace. Applies adult learning strategies to professional development, focusing on authentic problems and tasks, and utilizing mentoring, coaching, conferencing and other techniques to ensure that new knowledge and skills are practiced in the workplace. 7.5 Apply counseling and mentoring skills, and utilize stress management and conflict management techniques. Fails to apply counseling and mentoring skills or utilize stress management and conflict management techniques. Limited application of counseling and mentoring skills and little or no utilization of stress management and conflict management techniques. Appropriately and consistently applies counseling and mentoring skills and fully utilizes stress management and conflict management techniques. 9.1 Use technology, telecommunications and information systems to enrich curriculum and instruction (e.g. Does not use technology, telecommunications and information systems to enrich curriculum and Inconsistently uses technology, telecommunications and information systems to enrich curriculum and Uses technology, telecommunications and information systems to enrich curriculum and instruction (e.g. CAI systems, CD ROM retrieval systems, on-line networks, distance learning, interactive video, etc.). instruction. instruction. CAI systems, CD ROM retrieval systems, on-line networks, distance learning, interactive video, etc.). 9.2 Apply and assess current technologies for school management and business procedures. Lacks awareness of current technologies for school management and business procedures. Limited awareness of current technologies for school management and business procedures. Applies and fully assesses current technologies for school management and business procedures. 9.3 Develop and monitor long range plans for school and district technology and information systems, making informed decisions about computer hardware and software, and about staff development, keeping in mind the impact of technologies on student outcomes and school operations. Has no long range plans for school and district technology and information decisions. Develop a long range plan for school district technology and information systems but fail to implement and monitor the plan. Develops and monitors long range plans for school and district technology and information systems, making informed decisions about computer hardware and software, and about staff development, keeping in mind the impact of technologies on student outcomes and school operations. 3.2 Develop collaboratively a learning organization that supports instructional improvement, Fails to develop a collaborative learning organization that supports instructional improvement, Develops a learning organization that fails to do one or more of the following: support instructional improvement, build Develops collaboratively a learning organization that supports instructional improvement, builds an appropriate curriculum, and incorporates best practice. curriculum, and best practices. appropriate curriculum, or incorporate best practices. builds an appropriate curriculum, and incorporates best practice. 3.7 Utilize a variety of supervisory models to improve teaching and learning (e.g. clinical, developmental, cognitive and peer coaching, as well as applying observation and conferencing skills.). Fails to utilize a varied of supervisory models to improve teaching and learning. Utilizes one or very few supervisory models to improve teaching and learning. Utilizes a variety of supervisory models to improve teaching and learning. 4.1 Work with faculty and other stakeholders to identify needs for professional development, to organize, facilitate, and evaluate professional development programs, to integrate district and school priorities, to build Fails to work with faculty and other stakeholders. Works with faculty and other stakeholders but fails to address all of the following areas: identifying needs for professional development, organizing, facilitating and evaluating professional development Works with faculty and other stakeholders to do all of the following: identify needs for professional development, to organize, facilitate, and evaluate professional development programs, to integrate district and school faculty as resource, and to ensure that professional development activities focus on improving student outcomes. programs, integrating district and school priorities, building faculty as resource, and ensuring that professional development activities focus on improving student outcomes. priorities, to build faculty as resource, and to ensure that professional development activities focus on improving student outcomes. 4.4 Formulate and implement a selfdevelopment plan, endorsing the value of career-long growth, and utilizing a variety of resources for continuing professional development. Fails to formulate and implement a self-development plan, endorsing the values of careerlong growth, and utilizing a variety of resources for continuing professional development. Formulates a selfdevelopment plan, endorsing the value of career-long growth, and utilizing a variety of resources for continuing professional development, but fails to implement this plan. Formulates and implement a selfdevelopment plan, endorsing the value of career-long growth, and utilizing a variety of resources for continuing professional development. 4.5 Identify and apply appropriate policies, criteria and processes for the recruitment, selection, induction compensation and separation of personnel, with attention to issues of equity and diversity. Fails to use appropriate policies, criteria, and processes for the recruitment, selection, induction, compensation, and separation of personnel. Identify and applies appropriate policies, criteria and processes for the recruitment, selection, induction, compensation, and separation of personnel but pays no attention to issues of equity and diversity. Identifies and applies appropriate policies, criteria and processes for the recruitment, selection, induction compensation and separation of personnel, with attention to issues of equity and diversity. Standard 2.0 Narrative Explanation: Standard addresses the need for educational leaders to position teaching and learning at the focal point of schools. It accepts the proposition that all students can learn and that student learning is the fundamental purpose of schools. To this end, educational leaders are responsible for ensuring that decisions about curriculum, instructional strategies (including instructional technology), assessment, and professional development are based on sound research, best practice, school and district data, and other contextual information and that observation and collaboration are used to design meaningful and effective experiences that improve student achievement. Educational leaders must capitalize on diversity to create a school culture that promotes respect and success for all students. All members of the school community should have confidence in the integrity of the decision-making process for school improvement and the appropriateness of that process, thus ensuring dignity and respect for all. Successful educational leaders must be able to identify, clarify, and address barriers to student learning and communicate the importance of developing learning strategies for diverse populations. In addition, this standard requires that educational leaders be learners who model and encourage life-long learning. They should establish a culture of high expectations for themselves, their students, and their staff. Candidates preparing to lead schools or districts must be able to assess the culture and climate on a regular basis. They must also understand the importance of supervision and be able and willing to evaluate teacher and staff performance using a variety of supervisory models. Examples of Promising Practices for Candidate Performance Activities: Candidates are required to organize and lead parent and teacher focus groups about high-stakes testing and alternative methods of measuring student performance. Candidates are required to present a multimedia report to a community forum about the latest instructional technologies, including the use of the web and teaching strategies. Additional activities can be found beginning on page 25 of the Instructions to Implement Standards for Advanced Programs in Educational Leadership document. Conceptual Framework: 4. Reflective skills: communication skills, critical and creative thinking abilities and other skills crucial to reflective decision-making. 5. Technology: knowledge and skills in the use of technology appropriate to the candidate's field of study. 7. Assessment Skills: the skills to conduct valid and reliable assessments of their students' learning, and use that assessment to improve learning and development for their students. Standard 3.0: Candidates who complete the program are educational leaders who have the knowledge and ability to promote the success of all students by managing the organization, operations, and resources in a way that promotes a safe, efficient, and effective learning environment. Elements Meets Standards for School District Leadership Mo STEP 1.3 EAD Course Strands A. Manage the Organization 1. Candidates demonstrate the ability to use research-based knowledge of learning, teaching, student development, organizational development, and data management to optimize learning for all students. 1.3.2 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by advocating, nurturing, and sustaining a school culture and instructional program conducive to student learning and staff professional growth 2.1 Conduct needs assessment by collecting information on the students; on staff and the school environment; on family and community values, expectations and priorities; and on national and global conditions affecting schools. 2. Candidates focus on effective organization of fiscal, human, . Rubric Fails to conduct needs assessment. Conducts needs assessment but fails to collect information on all areas. Conducts needs assessment by collecting information on students; on staff and the school environment; on family and community values, expectations and priorities; and on national and global conditions affecting schools. and material resources, giving priority to student learning and safety, and demonstrating an understanding of district budgeting processes and fiduciary responsibilities. 3. Candidates demonstrate an ability to manage time effectively and to deploy financial and human resources in a way that promotes student achievement. 4. Candidates demonstrate the ability to organize a district based on indicators of equity, effectiveness, and efficiency and can apply legal principles that promote educational equity. 1.3.3 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by ensuring management of the organization, operations, and resources for a safe, efficient, and effective learning environment. 2.2 Use qualitative and quantitative data to inform decisions, to plan and assess school programs, to design accountability systems, to plan for school improvement, and to develop and conduct research Does not use qualitative and quantitative data to make informed decisions. Uses qualitative and quantitative data to make decisions, but fails to apply data to all areas and conduct research. Uses qualitative and quantitative data to inform decisions, to plan and assess school programs, to design accountability systems, to plan for school improvement, and to develop and conduct research. Uses effective problemframing, problem-solving, conflictresolution, group process, consensus building, and communication skills to identify, confront, and resolve problems and opportunities in a timely manner. 3.9 Assess student progress using a variety of appropriate techniques. Fails to assess student progress. Assesses student progress using limited techniques. Assesses student progress using a variety of appropriate techniques. Exhibits the ability to manage and regularly 4.3 Apply effective job analysis procedures, Fails to apply effective job analysis Inconsistently applies effective job analysis Applies effective job analysis procedures, 5. Candidates demonstrate an understanding of how to apply legal principles to promote educational equity and provide safe, effective, and efficient facilities. assess and evaluate the effectiveness of operational systems and procedures designed to maximize opportunities for successful learning and the attainment of school’s vision and goals. supervisory techniques and performance appraisal for instructional and non-instructional staff. procedures, supervisory techniques and performance appraisal for instructional and non-instructional staff. procedures, supervisory techniques and performance appraisal for instructional and non-instructional staff. supervisory techniques and performance appraisal for instructional and non-instructional staff. 1.3.5 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by acting with integrity, fairness, and in an ethical manner. 6.1 Establish operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, utilizing practical applications of organizational theories. Fails to establish operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals. Establishes operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, but fails to utilize practical applications of organizational theories. Establishes operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, utilizing practical applications of organizational theories. Demonstrates the ability to serve as a role model through such actions as accepting responsibility for 8.1 Identify and analyze the major sources of fiscal and non-fiscal resources for schools and school districts. Lacks awareness of the major sources of fiscal and nonfiscal resources for schools and school districts. Limited awareness of the major sources of fiscal and non-fiscal resources for schools and school districts. Fully identifies and analyzes the major sources of fiscal and non-fiscal resources for schools and school districts. school operations, opening the school to public scrutiny, considering the impact of one’s administrative practices on others, treating people fairly, equitably, and with dignity and respect, protecting the rights and confidentiality of students and staff, and using the influence of office to enhance educational programs rather than for personal gain. 8.2 Acquire and manage financial and material assets, and capital goods and services, allocating resources according to district or school priorities (e.g. property, plant, equipment, transportation, and food service.). Does not acquire and manage financial and material assets, and capital goods and services. Acquires and manages financial and material assets and capital goods and services but fails to allocate these resources according to the district or school priorities. Acquires and manages financial and material assets, and capital goods and services, allocating resources according to district or school priorities (e.g. property, plant, equipment, transportation, and food service.). 8.3 Develop an efficient budget planning process that is driven by district and school priorities and involves staff and community. Unable to develop an efficient budget planning process. Develops an efficient budget planning process but fails to involve staff and community and focus on district and school priorities.1 Develops an efficient budget planning process that is driven by district and school priorities and involves staff and community. 8.4 Perform budget management functions including financial planning, monitoring, cost control, expenditures accounting, and cash flow management. Fails to perform necessary budget management functions. Performs budget management functions but does not include financial planning, monitoring, cost control, expenditures accounting, and cash flow management. Performs budget management functions including financial planning, monitoring, cost control, expenditures accounting, and cash flow management. B. Manage Operations 4. Candidates create a plan for involving stakeholders in aligning 1.3.2 A school administrator is an educational leader who 8.4 Perform budget management functions including financial planning, monitoring, cost control, expenditures accounting, and cash flow management. Fails to perform necessary budget management functions. Performs budget management functions but does not include financial planning, monitoring, cost control, expenditures accounting, and cash flow management. Performs budget management functions including financial planning, monitoring, cost control, expenditures accounting, and cash flow management. 4.5 Identify and apply appropriate policies, criteria and processes for the recruitment, selection, induction compensation and separation of personnel, with attention to issues of equity and diversity. Fails to use appropriate policies, criteria, and processes for the recruitment, selection, induction, compensation, and separation of personnel. Identify and applies appropriate policies, criteria and processes for the recruitment, selection, induction, compensation, and separation of personnel but pays no attention to issues of equity and diversity. Identifies and applies appropriate policies, criteria and processes for the recruitment, selection, induction compensation and separation of personnel, with attention to issues of equity and diversity. 5.3 Develop and administer policies that provide a safe school environment and promote student health and welfare. Does not develop policies that provide a safe school environment and promote student health and welfare. Develops and administers policies that provide a safe school environment but does not focus on promoting student health and welfare. Develop and administer policies that provide a safe school environment and promote student health and welfare. 6.3 Implement appropriate management techniques and group processes to Fails to implement appropriate management techniques and Inadequately implements appropriate management techniques and Fully and appropriately implements management techniques and resources and priorities to maximize ownership and accountability. 5. Candidates can use appropriate and effective needs assessment, research-based data, and group process skills to build consensus, communicate, and resolve conflicts in order to align resources with the district vision. 6. Candidates develop an effective and interactive staff communication plan for integrating district’s schools and divisions. 7. Candidates develop a plan to promote and support community collaboration among district promotes the success of all students by advocating, nurturing, and sustaining a school culture and instructional program conducive to student learning and staff professional growth. define roles, assign functions, delegate effectively, and determine accountability for attaining goals. group processes. group processes, neglecting one or more of the following areas: definition of roles, assignment of functions, effective delegation, and determination of accountability for attaining goals. group processes to define roles, assign functions, delegate effectively, and determine accountability for attaining goals. Demonstrates the ability to develop pupil personnel programs to meet the needs of students and their families 10.5 Develop an effective and interactive staff communications plan and public relations program. Has no staff communications plan or public relations program. Has an ineffective staff communications plan and public relations program. Develops an effective and interactive staff communications plan and public relations program. Bases curricular, co-curricular, and extra-curricular decisions on a variety of information sources, including research, teachers’ expertise, the recommendations of learned societies 11.3 Define and relate the general characteristics of internal and external political systems as they apply to school settings. Fails to define and relate the general characteristics of internal and external political systems as they apply to school settings. Inconsistently defines and relates the general characteristics of internal and external political systems as they apply to school settings. Defines and relate the general characteristics of internal and external political systems as they apply to school settings. personnel. 1.3.3 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by ensuring management of the organization, operations, and resources for a safe, efficient, and effective learning environment. 2.1 Conduct needs assessment by collecting information on the students; on staff and the school environment; on family and community values, expectations and priorities; and on national and global conditions affecting schools. Fails to conduct needs assessment. Conducts needs assessment but fails to collect information on all areas. Conducts needs assessment by collecting information on students; on staff and the school environment; on family and community values, expectations and priorities; and on national and global conditions affecting schools. Uses effective problemframing, problem-solving, conflictresolution, group process, consensus building, and communication skills to identify, confront, and resolve problems and opportunities in a timely manner. Understands the 2.4 Analyze and interpret educational data, issues, and trends for boards, committees, and other groups, outlining possible actions and their implications. Fails to analyze and interpret educational data, issues, and trends and their application with boards, committees and other groups. Analyzes and interprets educational data, issues, and trends but fails to outline possible actions and their implications. Analyzes and interprets educational data, issues, and trends for boards, committees, and other groups, outlining possible actions and their implications. need to create and maintain a safe, clean, and aesthetically pleasing school environment Understands the need to create and maintain a safe, clean, and aesthetically pleasing school environment Exhibits the ability to manage and regularly assess and evaluate the effectiveness of operational systems and procedures designed to maximize opportunities for successful learning and the attainment of school’s vision and goals. 7.3 Apply appropriate communications strategies (e.g. identifying audiences, determining messages selecting transmission mediums, identifying reaction of receivers, soliciting responses, etc.). Fails to apply appropriate communications strategies. Inconsistently applies communications strategies. Applies appropriate communications strategies. Exhibits the ability to ensure the school plant, equipment, and support systems operate safely, efficiently, and effectively 7.5 Apply counseling and mentoring skills, and utilize stress management and conflict management techniques. Fails to apply counseling and mentoring skills or utilize stress management and conflict management techniques. Limited application of counseling and mentoring skills and little or no utilization of stress management and conflict management techniques. Appropriately and consistently applies counseling and mentoring skills and fully utilizes stress management and conflict management techniques. 1.3.6 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by understanding, responding to, and influencing the larger political, social, economic, legal, and cultural context. 4.3 Apply effective job analysis procedures, supervisory techniques and performance appraisal for instructional and non-instructional staff. Fails to apply effective job analysis procedures, supervisory techniques and performance appraisal for instructional and non-instructional staff. Inconsistently applies effective job analysis procedures, supervisory techniques and performance appraisal for instructional and non-instructional staff. Applies effective job analysis procedures, supervisory techniques and performance appraisal for instructional and non-instructional staff. Understands the need and processes necessary to create and maintain a school environment that operates on behalf of students and 7.2 Use appropriate written, verbal, and nonverbal communication in a variety of situations. Does not have appropriate written, verbal, and nonverbal communication skills. Has written, verbal, and nonverbal communication skills but fails to use them in a variety of situations. Uses appropriate written, verbal, and nonverbal communication in a variety of situations. 7.3 Apply appropriate communications strategies (e.g. Fails to apply appropriate communications Inconsistently applies communications Applies appropriate communications strategies. their families C. Manage Resources 4. Candidates use problemsolving skills and knowledge of strategic, long-range, and operational planning 1.3.3 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by ensuring identifying audiences, determining messages selecting transmission mediums, identifying reaction of receivers, soliciting responses, etc.). strategies. strategies. 10.5 Develop an effective and interactive staff communications plan and public relations program. Has no staff communications plan or public relations program. Has an ineffective staff communications plan and public relations program. Develops an effective and interactive staff communications plan and public relations program. 4.3 Apply effective job analysis procedures, supervisory techniques and performance appraisal for instructional and non-instructional staff. Fails to apply effective job analysis procedures, supervisory techniques and performance appraisal for instructional and non-instructional staff. Inconsistently applies effective job analysis procedures, supervisory techniques and performance appraisal for instructional and non-instructional staff. Applies effective job analysis procedures, supervisory techniques and performance appraisal for instructional and non-instructional staff. 1.3 Frame, analyze, and resolve problems using appropriate problem-solving techniques and decision-making skills (e.g. identify Lacks the ability to adequately resolve problems and make appropriate decisions. Has the ability to solve problems but does so without utilizing problemsolving techniques and decisionmaking skills. Has the ability to frame, analyze and resolve problems using appropriate problem-solving techniques and decisions-making (including applications of technology) in the effective, legal, and equitable use of fiscal, human, and material resource allocation that focuses on teaching and learning. 5. Candidates creatively seek new resources to facilitate learning. 6. Candidates apply an understanding of school district finance structures and models to ensure that adequate financial resources are allocated equitably for the district. 7. Candidates apply and assess current technologies for management, business management of the organization, operations, and resources for a safe, efficient, and effective learning environment. problem, seek and analyze problem factors, collect and organize relevant information, identify causes, seek creative solutions, apply ethical standards, determine best solution with others when appropriate. skills. Uses knowledge of learning, teaching, and student development to inform management decisions 8.1 Identify and analyze the major sources of fiscal and non-fiscal resources for schools and school districts. Lacks awareness of the major sources of fiscal and nonfiscal resources for schools and school districts. Limited awareness of the major sources of fiscal and non-fiscal resources for schools and school districts. Fully identifies and analyzes the major sources of fiscal and non-fiscal resources for schools and school districts. Aligns and manages time and resources (financial, human, and material) to maximize attainment of organizational goals 8.2 Acquire and manage financial and material assets, and capital goods and services, allocating resources according to district or school priorities (e.g. property, plant, equipment, transportation, and Does not acquire and manage financial and material assets, and capital goods and services. Acquires and manages financial and material assets and capital goods and services but fails to allocate these resources according to the district or school priorities. Acquires and manages financial and material assets, and capital goods and services, allocating resources according to district or school priorities (e.g. property, plant, equipment, transportation, and procedures, and scheduling. food service.). food service.). 1.3.5 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by acting with integrity, fairness, and in an ethical manner. 8.4 Perform budget management functions including financial planning, monitoring, cost control, expenditures accounting, and cash flow management. Fails to perform necessary budget management functions. Performs budget management functions but does not include financial planning, monitoring, cost control, expenditures accounting, and cash flow management. Performs budget management functions including financial planning, monitoring, cost control, expenditures accounting, and cash flow management. Demonstrates values, beliefs, and attitudes that inspire others to higher levels of performance and that reveal an appreciation for and sensitivity to the prevailing values of the diverse school community 9.2 Apply and assess current technologies for school management and business procedures. Lacks awareness of current technologies for school management and business procedures. Limited awareness of current technologies for school management and business procedures. Applies and fully assesses current technologies for school management and business procedures. 3.6 Develop with others curriculum and instruction appropriate for varied teaching and learning styles and specific student needs based on gender, ethnicity, culture, social class and exceptionalities. Does not develop curriculum and instruction that is appropriate for varied teaching and learning styles and specific student needs. Develops curriculum and instruction appropriate for varied teaching and learning styles but fails to take into consideration specific student needs based on gender, ethnicity, culture, social class and exceptionalities. Develops with others curriculum and instruction appropriate for varied teaching and learning styles and specific student needs based on gender, ethnicity, culture, social class and exceptionalities. 9.1 Use technology, telecommunications and information systems to enrich curriculum and instruction (e.g. CAI systems, CD ROM retrieval systems, on-line networks, distance learning, interactive video, etc.). Does not use technology, telecommunications and information systems to enrich curriculum and instruction. Inconsistently uses technology, telecommunications and information systems to enrich curriculum and instruction. Uses technology, telecommunications and information systems to enrich curriculum and instruction (e.g. CAI systems, CD ROM retrieval systems, on-line networks, distance learning, interactive video, etc.). 8.1 Identify and analyze the major sources of fiscal and non-fiscal resources for schools and school districts. Lacks awareness of the major sources of fiscal and nonfiscal resources for schools and school districts. Limited awareness of the major sources of fiscal and non-fiscal resources for schools and school districts. Fully identifies and analyzes the major sources of fiscal and non-fiscal resources for schools and school districts. 8.2 Acquire and manage financial and material assets, and capital goods and services, allocating resources according to district or school priorities (e.g. property, plant, equipment, transportation, and food service.). Does not acquire and manage financial and material assets, and capital goods and services. Acquires and manages financial and material assets and capital goods and services but fails to allocate these resources according to the district or school priorities. Acquires and manages financial and material assets, and capital goods and services, allocating resources according to district or school priorities (e.g. property, plant, equipment, transportation, and food service.). Standard 3.0 Narrative Explanation: Standard addresses the need to enhance student learning through effective, efficient, and equitable utilization of resources. Educational leaders must use their knowledge of organizations to create a learning environment conducive to the success of all students. Proper allocation of resources such as personnel, facilities, and technology 8.3 Develop an efficient budget planning process that is driven by district and school priorities and involves staff and community. Unable to develop an efficient budget planning process. Develops an efficient budget planning process but fails to involve staff and community and focus on district and school priorities.1 Develops an efficient budget planning process that is driven by district and school priorities and involves staff and community. 8.4 Perform budget management functions including financial planning, monitoring, cost control, expenditures accounting, and cash flow management. Fails to perform necessary budget management functions. Performs budget management functions but does not include financial planning, monitoring, cost control, expenditures accounting, and cash flow management. Performs budget management functions including financial planning, monitoring, cost control, expenditures accounting, and cash flow management. 9.2 Apply and assess current technologies for school management and business procedures. Lacks awareness of current technologies for school management and business procedures. Limited awareness of current technologies for school management and business procedures. Applies and fully assesses current technologies for school management and business procedures. are essential to creating an effective learning environment. Resource management decisions should give priority to teaching, student achievement, and student development. Also, operational procedures and policies must be established to maintain school safety and security and to strengthen the academic environment. All management decisions, including those regarding human resources, fiscal operations, facilities, legal issues, time management, scheduling, technology, and equipment, should be based on sound organizational practice. Educational leaders must monitor and evaluate operational systems to ensure that they enhance student learning and reflect the school’s and district’s accountability to the community. Skills in job analysis, supervision, recruitment, selection, professional development, and appraisal of staff positions, as well as an understanding of relevant collective bargaining agreements, strengthen the ability to use personnel resources. Effective educational leaders define job roles, assign tasks, delegate appropriately, and require accountability. They also actively seek additional sources of financial, human, and physical support. They involve stakeholders to ensure that management and operational decisions take into consideration the needs of multiple constituencies while at the same time focusing the entire community on student achievement as the ultimate goal. To include stakeholders in management decisions, educational leaders must be competent in conflict resolution, consensus building, group processes, and effective communication. Examples of Promising Practices for Candidate Performance Activities: Candidates are required to conduct a cost-benefit analysis of a school or district instructional improvement plan. Candidates are required to analyze the school/district budget and identify how specific budget allocations support the school improvement plan/district strategic plan. Additional activities can be found beginning on page 25 of the Instructions to Implement Standards for Advanced Programs in Educational Leadership document. Standard 4.0: Candidates who complete the program are educational leaders who have the knowledge and ability to promote the success of all students by collaborating with families and other community members, responding to diverse community interests and needs, and mobilizing community resources. Conceptual Framework: 8. Dispositions: the intellectual, social, ethical, and other personal attributes and beliefs previously ascribed to reflective decision-makers in a variety of professional settings, including a commitment to their own lifelong learning and professional development. 10. Collaboration and Leadership: the ability and skills to foster and maintain collaborative, empowering relationships with other professionals within schools and the community. Elements Meets Standards for School District Leadership Mo STEP 1.3 EAD Course Strands A. Collaborate 9. Candidates demonstrate the ability to facilitate the planning and implementation of programs and services that bring together the resources of families and the community to positively affect student learning. 1.3.2 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by advocating, nurturing, and sustaining a school culture and instructional program conducive to student learning and staff professional growth. 3.1 Create with teachers, parents and students a positive school culture that promotes learning; (e.g. holds high expectations, focuses on accomplishments and recognition, and promotes a supportive climate). Fails to create a positive school culture that promotes learning. Creates a positive school culture that promotes learning but does not involve teachers, parents and students. Creates with teachers, parents and students a positive school culture that promotes learning. Understands and exhibits the inclination to promote and use a variety of methods for assessing student and staff performance 3.2 Develop collaboratively a learning organization that supports instructional improvement, builds an appropriate curriculum, and incorporates best practice. Fails to develop a collaborative learning organization that supports instructional improvement, curriculum, and best practices. Develops a learning organization that fails to do one or more of the following: support instructional improvement, build appropriate curriculum, or incorporate best practices. Develops collaboratively a learning organization that supports instructional improvement, builds an appropriate curriculum, and incorporates best practice. with Families and Other Community Members 10. Candidates demonstrate an ability to use public information and research-based knowledge of issues and trends to collaborate with community members and community organizations to have a positive affect on student learning. 11. Candidates apply an Rubric understanding of community relations models, marketing strategies and processes, data driven decisionmaking, and communication theory to craft frameworks for school, business, community, government, and higher education partnerships. 12. Candidates demonstrate an ability to develop and implement a plan for nurturing relationships with community leaders and reaching out to different business, religious, political, and service organizations to strengthen programs and support district goals. 1.3.3 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by ensuring management of the organization, operations, and resources for a safe, efficient, and effective learning environment. 6.1 Establish operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, utilizing practical applications of organizational theories. Fails to establish operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals. Establishes operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, but fails to utilize practical applications of organizational theories. Establishes operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, utilizing practical applications of organizational theories. Demonstrates the ability and inclination to involve stakeholders in decisions and shares responsibility to maximize ownership and accountability. 10.4 Involve family and community in appropriate policy development, program planning, and assessment processes. Fails to involve family and community in appropriate policy development, program planning, and assessment processes. Inconsistently involves family and community in appropriate policy development, program planning, and assessment processes. Involves family and community in appropriate policy development, program planning, and assessment processes. 1.3.4 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by collaborating 10.6 Utilize and respond effectively to electronic and printed news media. Fails to utilize and respond to electronic and printed news media. Ineffectively utilizes and responds to electronic and printed news media. Utilizes and responds effectively to electronic and printed news media. 13. Candidates demonstrate the ability to involve community members, groups, and other stakeholders in district decisionmaking, reflecting an understanding of strategies to capitalize on the district’s integral role in the larger community. 14. Candidates develop a plan to collaborate with community agencies to integrate health, social, and other services in the schools to address student and family conditions that affect learning. 15. Candidates develop a plan for community relations that effects knowledge of effective media with families and community members, responding to diverse community interests and needs, and mobilizing community resources Collaboratively develops and implements a comprehensive community relations plan that uses information about family and community concerns, expectations, and needs; that identifies and nurtures relationships with community leaders; and that involves a variety of outreach activities in which the school and community 3.2 Develop collaboratively a learning organization that supports instructional improvement, builds an appropriate curriculum, and incorporates best practice. Fails to develop a collaborative learning organization that supports instructional improvement, curriculum, and best practices. Develops a learning organization that fails to do one or more of the following: support instructional improvement, build appropriate curriculum, or incorporate best practices. Develops collaboratively a learning organization that supports instructional improvement, builds an appropriate curriculum, and incorporates best practice. relations and that models effective media relations practices. 16. Candidates develop a plan that supports the involvement of families in the education of their children that reinforces for district staff a belief that families have the best interests of their children in mind. serve one another as resources. Demonstrates a commitment to high visibility, active involvement, and communication with the larger community 10.1 Analyze community and district power structures, and identify major opinion leaders and their relationships to school goals and programs. Fails to analyze community and district power structures. Analyzes community and district power structures but fails to identify their relationships to school goals and programs. Analyzes community and district power structures, and identify major opinion leaders and their relationships to school goals and programs. Understands how to establish partnerships with area businesses, institutions of higher education, and community youth and family service groups to help the school solve problems and achieve goals 6.2 Apply a systems perspective, viewing schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. Does not view schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. Views schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments but fails to apply this knowledge. Applies a systems perspective, viewing schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. Understands the necessity of using public resources and funds appropriately and wisely 10.1 Analyze community and district power structures, and identify major opinion leaders and their relationships to school goals and programs. Fails to analyze community and district power structures. Analyzes community and district power structures but fails to identify their relationships to school goals and programs. Analyzes community and district power structures, and identify major opinion leaders and their relationships to school goals and programs. . Models community collaboration for staff and provides opportunities for everyone to develop collaborative skills 10.3 Communicate effectively with various cultural, ethnic, racial, and special interest groups in the community Fails to communicate effectively with various cultural, ethnic, racial, and special interest groups in the community. Inconsistently communicates with various cultural, ethnic, racial, and special interest groups in the community. Communicates effectively with various cultural, ethnic, racial, and special interest groups in the community. 1.3.6 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by understanding, responding to, and influencing the larger political, social, economic, legal, and cultural context. 5.4 Address student and family conditions affecting learning by collaborating with community agencies to integrate health, social, and other services for students. Fails to collaborate with community agencies to address student and family conditions affecting learning. Addresses student and family conditions affecting learning, but fails to integrate health, social and other services for students by collaborating with community agencies. Addresses student and family conditions affecting learning by collaborating with community agencies to integrate health, social, and other services for students. Can maintain open lines of communication and ongoing dialog with diverse community 10.1 Analyze community and district power structures, and identify major opinion leaders and their relationships to school goals and Fails to analyze community and district power structures. Analyzes community and district power structures but fails to identify their relationships to school goals and programs. Analyzes community and district power structures, and identify major opinion leaders and their relationships to school goals and groups and decision-makers concerning trends, issues, and potential changes in the environment within which the school operates programs. programs. 5.4 Address student and family conditions affecting learning by collaborating with community agencies to integrate health, social, and other services for students. Fails to collaborate with community agencies to address student and family conditions affecting learning. Addresses student and family conditions affecting learning, but fails to integrate health, social and other services for students by collaborating with community agencies. Addresses student and family conditions affecting learning by collaborating with community agencies to integrate health, social, and other services for students. 5.5 Plan and manage activity programs to fulfill student developmental, social, cultural, athletic, leadership and scholastic needs; working with staff, students, families, and community. Does not plan and manage activity programs to fulfill student needs. Plans but ineffectively manages activity programs that fully meet student developmental, social, cultural, athletic, leadership and scholastic needs; working with staff, students, families, and community. Fully plans and manages activity programs to fulfill student developmental, social, cultural, athletic, leadership and scholastic needs; working with staff, students, families, and community. 10.2 Articulate the district’s or school’s vision, mission and priorities to the community and media, and build community support for district or Fails to articulate the district's or school's vision, mission and priorities to the community and media. Articulates the district's or school's vision, mission and priorities to the community and media but fails to build community support. Articulates the district’s or school’s vision, mission and priorities to the community and media, and builds community support for district or school priorities and programs (e.g. form collaborative relationships with businesses, citizen groups, neighborhood associations, social service agencies, parent organizations, advocacy groups, universities, and religious institutions, etc.). school priorities and programs. 10.6 Utilize and respond effectively to electronic and printed news media. Fails to utilize and respond to electronic and printed news media. Ineffectively utilizes and responds to electronic and printed news media. Utilizes and responds effectively to electronic and printed news media. 3.2 Develop collaboratively a learning organization that supports instructional improvement, builds an appropriate curriculum, and incorporates best practice. Fails to develop a collaborative learning organization that supports instructional improvement, curriculum, and best practices. Develops a learning organization that fails to do one or more of the following: support instructional improvement, build appropriate curriculum, or incorporate best practices. Develops collaboratively a learning organization that supports instructional improvement, builds an appropriate curriculum, and incorporates best practice. B. Respond to Community Interests and Needs 5. Candidates facilitate and engage in activities that reflect an ability to inform district decision-making by collecting and organizing formal and informal information from multiple stakeholders. 6. Candidates develop a plan to promote maximum involvement with, and visibility within the community. 7. Candidates demonstrate the ability to interact effectively with individuals and groups that 10.4 Involve family and community in appropriate policy development, program planning, and assessment processes. Fails to involve family and community in appropriate policy development, program planning, and assessment processes. Inconsistently involves family and community in appropriate policy development, program planning, and assessment processes. Involves family and community in appropriate policy development, program planning, and assessment processes. 1.3.4 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by collaborating with families and community members, responding to diverse community interests and needs, and mobilizing community resources 6.1 Establish operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, utilizing practical applications of organizational theories. Fails to establish operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals. Establishes operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, but fails to utilize practical applications of organizational theories. Establishes operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, utilizing practical applications of organizational theories. Understands how to establish partnerships with area businesses, institutions of higher education, and community youth and family 10.3 Communicate effectively with various cultural, ethnic, racial, and special interest groups in the community. Fails to communicate effectively with various cultural, ethnic, racial, and special interest groups in the community. Inconsistently communicates with various cultural, ethnic, racial, and special interest groups in the community. Communicates effectively with various cultural, ethnic, racial, and special interest groups in the community. reflect conflicting perspectives. 8. Candidates demonstrate the ability to effectively and appropriately assess, research, and plan for diverse district and community conditions and dynamics and capitalize on the diversity of the community to improve district performance and student achievement. 10. Candidates develop a plan to advocate for students with special and exceptional needs. service groups to help the school solve problems and achieve goals Recognizes and values diversity, as evidenced in equitable treatment of all community stakeholders even when the values and opinions of individuals and groups may conflict 5.5 Plan and manage activity programs to fulfill student developmental, social, cultural, athletic, leadership and scholastic needs; working with staff, students, families, and community. Does not plan and manage activity programs to fulfill student needs. Plans but ineffectively manages activity programs that fully meet student developmental, social, cultural, athletic, leadership and scholastic needs; working with staff, students, families, and community. Fully plans and manages activity programs to fulfill student developmental, social, cultural, athletic, leadership and scholastic needs; working with staff, students, families, and community. 10.3 Communicate effectively with various cultural, ethnic, racial, and special interest groups in the community. Fails to communicate effectively with various cultural, ethnic, racial, and special interest groups in the community. Inconsistently communicates with various cultural, ethnic, racial, and special interest groups in the community. Communicates effectively with various cultural, ethnic, racial, and special interest groups in the community. 10.4 Involve family and community in appropriate policy development, program planning, and assessment processes. Fails to involve family and community in appropriate policy development, program planning, and assessment Inconsistently involves family and community in appropriate policy development, program planning, and assessment Involves family and community in appropriate policy development, program planning, and assessment processes. processes. processes. 5.2 Develop with the counseling and teaching staff a full program of student advisement, counseling, and guidance services. Fails to develop a program of student advisement, counseling, and guidance services. Develops an incomplete program of student advisement, counseling, and guidance services. Uses the resources of the counseling and teaching staff to help develop a full program of student advisement, counseling, and guidance services. 7.1 Use appropriate interpersonal skills (e.g. exhibiting sensitivity, showing respect and interest, perceiving needs and concerns, showing tact, exhibiting consistency and trustworthiness, etc.). Lacks appropriate interpersonal skills. Inconsistently uses appropriate interpersonal skills. Uses appropriate interpersonal skills. 7.3 Apply appropriate communications strategies (e.g. identifying audiences, determining messages selecting transmission mediums, identifying reaction of receivers, soliciting responses, etc.). Fails to apply appropriate communications strategies. Inconsistently applies communications strategies. Applies appropriate communications strategies. 10.3 Communicate effectively with various cultural, ethnic, racial, and special interest groups in the community. Fails to communicate effectively with various cultural, ethnic, racial, and special interest groups in the community. Inconsistently communicates with various cultural, ethnic, racial, and special interest groups in the community. Communicates effectively with various cultural, ethnic, racial, and special interest groups in the community. 6.1 Establish operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, utilizing practical applications of organizational theories. Fails to establish operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals. Establishes operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, but fails to utilize practical applications of organizational theories. Establishes operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, utilizing practical applications of organizational theories. 10.3 Communicate effectively with various cultural, ethnic, racial, and special interest groups in the community. Fails to communicate effectively with various cultural, ethnic, racial, and special interest groups in the community. Inconsistently communicates with various cultural, ethnic, racial, and special interest groups in the community. Communicates effectively with various cultural, ethnic, racial, and special interest groups in the community. 5.2 Develop with the counseling and teaching staff a full program of student advisement, counseling, and guidance services. Fails to develop a program of student advisement, counseling, and guidance services. Develops an incomplete program of student advisement, counseling, and guidance services. Uses the resources of the counseling and teaching staff to help develop a full program of student advisement, counseling, and guidance services. C. Mobilize Community Resources 4. Candidates demonstrate an understanding of and ability to use community resources, including youth services that enhance student achievement, to solve district problems and accomplish district goals. 5. Candidates develop a plan to offer district resources to the community to solve issues of joint concern. 6. Candidates demonstrate an understanding of ways to use public resources and funds appropriately and effectively to encourage communities to provide new resources to address emerging student problems. 1.3.4 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by collaborating with families and community members, responding to diverse community interests and needs, and mobilizing community resources 5.5 Plan and manage activity programs to fulfill student developmental, social, cultural, athletic, leadership and scholastic needs; working with staff, students, families, and community. Does not plan and manage activity programs to fulfill student needs. Plans but ineffectively manages activity programs that fully meet student developmental, social, cultural, athletic, leadership and scholastic needs; working with staff, students, families, and community. Fully plans and manages activity programs to fulfill student developmental, social, cultural, athletic, leadership and scholastic needs; working with staff, students, families, and community. Collaboratively develops and implements a comprehensive community relations plan that uses information about family and community concerns, expectations, and needs; that identifies and nurtures relationships 6.1 Establish operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, utilizing practical applications of organizational theories. Fails to establish operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals. Establishes operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, but fails to utilize practical applications of organizational theories. Establishes operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, utilizing practical applications of organizational theories. with community leaders; and that involves a variety of outreach activities in which the school and community serve one another as resources. Understands the necessity of using public resources and funds appropriately and wisely 8.1 Identify and analyze the major sources of fiscal and non-fiscal resources for schools and school districts. Lacks awareness of the major sources of fiscal and nonfiscal resources for schools and school districts. Limited awareness of the major sources of fiscal and non-fiscal resources for schools and school districts. Fully identifies and analyzes the major sources of fiscal and non-fiscal resources for schools and school districts. 8.2 Acquire and manage financial and material assets, and capital goods and services, allocating resources according to district or school priorities (e.g. property, plant, equipment, transportation, and food service.). Does not acquire and manage financial and material assets, and capital goods and services. Acquires and manages financial and material assets and capital goods and services but fails to allocate these resources according to the district or school priorities. Acquires and manages financial and material assets, and capital goods and services, allocating resources according to district or school priorities (e.g. property, plant, equipment, transportation, and food service.). 8.4 Perform budget management functions including financial planning, monitoring, cost control, expenditures accounting, and cash flow management. Standard 4.0 Narrative Explanation: Standard addresses the fact that cooperation among schools, the district, and the larger community is essential to the success of educational leaders and students. Educational leaders must see schools as an integral part of the larger community. Collaboration and communication with families, businesses, governmental agencies, social service organizations, the media, and higher education institutions are critical to effective schooling. The ability to analyze emerging issues and trends that might affect schools and districts enables educational leaders to plan effective instructional programs and school services. Effective and appropriate communications, coupled with the involvement of families and other stakeholders in decisions, helps to ensure continued community support for schools. Seeing families as partners in the education of their youngsters, and believing that families have the best interests of Fails to perform necessary budget management functions. Performs budget management functions but does not include financial planning, monitoring, cost control, expenditures accounting, and cash flow management. Performs budget management functions including financial planning, monitoring, cost control, expenditures accounting, and cash flow management. their children in mind, encourages educational leaders to involve them in decisions at the school and district levels. Family and student issues that negatively affect student learning must be addressed through collaboration with community agencies that can integrate health, social, and other services. Such collaboration relies on good relationships with community leaders and outreach to a wide array of business, religious, political, and service agencies. Providing leadership to programs serving all students, including those with special and exceptional needs, further communicates to internal and external audiences the importance of diversity. To work with all elements of the community, educational leaders must recognize, value, and communicate effectively with various cultural, ethnic, racial, and special interest groups. Modeling community collaboration for staff and then offering opportunities for staff to develop collaborative skills maximizes positive interactions between schools and the community. Examples of Promising Practices for Candidate Performance Activities: Candidates are required to develop and present a plan recommending alignment of social service agency programs with school improvement needs. Candidates are required to identify at least five key community leaders in a school community, justify why each was selected, and identify their roles or potential roles in school improvement in the district. A confidential analysis of this power structure is shared with the superintendent or board of education. Additional activities can be found beginning on page 25 of the Instructions to Implement Standards for Advanced Programs in Educational Leadership document. Conceptual Framework: 6. Professional Skills: the practical abilities to implement the skills, techniques, and strategies associated with student learning and development in the educational context in which they practice. 8. Dispositions: the intellectual, social, ethical, and other personal attributes and beliefs previously ascribed to reflective decision-makers in a variety of professional settings, including a commitment to their own lifelong learning and professional development. 9. Diversity: the ability to skillfully facilitate and promote the learning of all students, including those from diverse cultural, racial and economic backgrounds, and those with disabilities. Standard 5.0: Candidates who complete the program are educational leaders who have the knowledge and ability to promote the success of all students by acting with integrity, fairly, and in an ethical manner. Elements Meets Standards for School District Leadership A. Acts with 2. Candidates demonstrate a respect for the rights of others with regard to Integrity Mo STEP 1.3 EAD Course Strands 1.3.2 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the 1.7 Manifest a professional code of ethics and values. Rubric Has no professional code of ethics and values. Actions fail to reflect student's professional code of ethics and values Always acts in accordance with professional code of ethics and values. confidentiality and dignity and engage in honest interactions. success of all students by advocating, nurturing, and sustaining a school culture and instructional program conducive to student learning and staff professional growth Treats everyone with fairness, dignity, and respect 1.3.3 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by ensuring management of the organization, operations, and resources for a safe, efficient, and effective learning environment Understands and 7.1 Use appropriate interpersonal skills (e.g. exhibiting sensitivity, showing respect and interest, perceiving needs and concerns, showing tact, exhibiting consistency and trustworthiness, etc.). Lacks appropriate interpersonal skills. Inconsistently uses appropriate interpersonal skills. Uses appropriate interpersonal skills. expresses the need to maintain confidentiality and privacy of school records B. Acts Fairly 2. Candidates demonstrate the ability to combine impartiality, sensitivity to student diversity, and ethical considerations in their interactions with others. 1.3.2 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by advocating, nurturing, and sustaining a school culture and instructional program conducive to student learning and staff professional growth 1.7 Manifest a professional code of ethics and values. Has no professional code of ethics and values. Actions fail to reflect student's professional code of ethics and values Always acts in accordance with professional code of ethics and values. Treats everyone with fairness, dignity, and respect 7.1 Use appropriate interpersonal skills (e.g. exhibiting sensitivity, showing respect and interest, perceiving needs and concerns, showing tact, exhibiting consistency and trustworthiness, Lacks appropriate interpersonal skills. Inconsistently uses appropriate interpersonal skills. Uses appropriate interpersonal skills. etc.). 1.3.5 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by acting with integrity, fairness, and in an ethical manner. 7.4 Promote multicultural awareness, gender sensitivity, and racial and ethnic appreciation. Lacks awareness of multicultural awareness, gender sensitivity, and racial and ethnic appreciation. Limited promotion of multicultural awareness, gender sensitivity, and racial and ethical appreciation. Consistently promotes multicultural awareness, gender sensitivity, and racial and ethnic appreciation. Demonstrates values, beliefs, and attitudes that inspire others to higher levels of performance and that reveal an appreciation for and sensitivity to the prevailing values of the diverse school community 11.5 Make decisions based on the moral and ethical implications of policy options and political strategies. Fails to base decisions on the moral and ethical implications of policy options and political strategies. Inconsistently bases decisions on the moral and ethical implications of policy options and political strategies. Consistently makes decisions based on the moral and ethical implications of policy options and political strategies. Demonstrates the ability to serve as a role model through such actions as accepting responsibility for school operations, opening the school to public scrutiny, considering the impact of one’s administrative practices on others, treating people fairly, equitably, and with dignity and respect, protecting the rights and confidentiality of students and staff, and using the influence of office to enhance educational programs rather than for personal gain. Recognizes the need and desire to fulfill legal and contractual obligations C. Acts 2. Candidates make and 1.3.5 A school administrator is 1.7 Manifest a professional code Has no professional code of ethics and Actions fail to reflect student's Always acts in accordance with Ethically explain decisions based upon ethical and legal principles. an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by acting with integrity, fairness, and in an ethical manner. of ethics and values. values. professional code of ethics and values professional code of ethics and values. Possesses and reflects upon a personal and professional code of ethics and expects others in the school community to behave ethically and with integrity 7.2 Use appropriate written, verbal, and nonverbal communication in a variety of situations. Does not have appropriate written, verbal, and nonverbal communication skills. Has written, verbal, and nonverbal communication skills but fails to use them in a variety of situations. Uses appropriate written, verbal, and nonverbal communication in a variety of situations. Demonstrates the ability to serve as a role model through such actions as accepting responsibility for school operations, opening the school to public scrutiny, considering the 11.5 Make decisions based on the moral and ethical implications of policy options and political strategies. Fails to base decisions on the moral and ethical implications of policy options and political strategies. Inconsistently bases decisions on the moral and ethical implications of policy options and political strategies. Consistently makes decisions based on the moral and ethical implications of policy options and political strategies. impact of one’s administrative practices on others, treating people fairly, equitably, and with dignity and respect, protecting the rights and confidentiality of students and staff, and using the influence of office to enhance educational programs rather than for personal gain. Recognizes the need and desire to fulfill legal and contractual obligations Standard 5.0 Narrative Explanation: Standard addresses the educational leader’s role as the "first citizen" of the school/district community. Educational leaders should set the tone for how employees and students interact with one another and with members of the school, district, and larger community. The leader’s contacts with students, parents, and employees must reflect concern for others as well as for the organization and the position. Educational leaders must develop the ability to examine personal and professional values that reflect a code of ethics. They must be able to serve as role models, accepting responsibility for using their position ethically and constructively on behalf of the school/district community. Educational leaders must act as advocates for all children, including those with special needs who may be underserved. Examples of Promising Practices for Candidate Performance Activities: Candidates are required to develop a code of ethics using personal platforms, professional leadership association examples, and a variety of additional source documents focusing on ethics. Candidates are required to conduct a self-analysis of a transcript of a speech delivered to a community organization and look for examples of integrity, fairness, and ethical behavior. Additional activities can be found beginning on page 25 of the Instructions to Implement Standards for Advanced Programs in Educational Leadership document. Conceptual Framework: Refer to numbers 1-10 on Pages 3 and 4 above. Standard 6.0: Candidates who complete the program are educational leaders who have the knowledge and ability to promote the success of all students by understanding, responding to, and influencing the larger political, social, economic, legal, and cultural context. Elements Meets Standards for School District Leadership A. Understand 9. Candidates demonstrate the ability to use appropriate research methods, theories, and concepts to improve district operations. the Larger Context 10. Candidates demonstrate an understanding of the complex causes of poverty and other disadvantages and their effects MoSTEP 1.3 EAD Course Strands Rubric 1.3.5 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by acting with integrity, fairness, and in an ethical manner. 1.4 Initiate, manage, and evaluate the change process. Fails to demonstrate an understanding of the change process. Has the ability to initiate, manage, or evaluate change, but fails to implement all three aspects in the change process. Fully understands and implements the initiation, management and evaluation of the change process. Recognizes and respects the legitimate authority of others 1.5 Identify and critique several theories of leadership and their application to various school Fails to identify and critique leadership theories and their application to the school Identifies theories of leadership but fails to critique theories and apply them to the school Identifies and shows ability to continuously critique theories of leadership and their application to the on families, communities, children, and learning. 11. Candidates demonstrate an understanding of the policies, laws, and regulations enacted by local, state, and federal authorities affecting a specific district. 12. Candidates can explain the system for financing public schools and its effects on the equitable distribution of educational opportunities within a district. 13. Candidates can explain their familiarity with political leaders at the local, state, and national level. 14. Candidates can apply an environments. environment. environment. school environment. Recognizes the need and desire to fulfill legal and contractual obligations 11.6 Analyze the major philosophical tenets of contemporary intellectual movements and analyze their effect on school contexts (e.g. critical theory, feminism, poststructuralism, fundamentalism, etc.). Fails to analyze the major philosophical tenets of contemporary intellectual movements. Analyzes the major philosophical tenets of contemporary intellectual movements but fails to analyze their effect on school contexts. Analyzes the major philosophical tenets of contemporary intellectual movements and analyzes their effect on school contexts. 1.3.6 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by understanding, responding to, and influencing the larger political, social, economic, legal, and cultural context. 1.6 Act with a reasoned understanding of major historical, philosophical, ethical, social and economic influences affecting education in a democratic society. Does understand education in a democratic society and its relationship to historical, philosophical, ethical, social and economic influences. Understands education in a democratic society and its relationship to historical, philosophical, ethical, social and economic influences, but does not act with these influences in mind. Understands education in a democratic society and its relationship to historical, philosophical, ethical, social and economic influences and acts with these influences in mind. Understands the need and processes necessary to 6.2 Apply a systems perspective, viewing schools as interactive internal Does not view schools as interactive internal systems operating within external Views schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments but Applies a systems perspective, viewing schools as interactive internal systems operating understanding of how specific laws at the local, state, and federal level affect school districts and residents. 15. Candidates espouse positions in response to proposed policy changes that would benefit or harm districts and explain how proposed policies and laws might improve educational and social opportunities for specific communities. create and maintain a school environment that operates on behalf of students and their families systems operating within external environments. environments. fails to apply this knowledge. within external environments. 7.4 Promote multicultural awareness, gender sensitivity, and racial and ethnic appreciation. Lacks awareness of multicultural awareness, gender sensitivity, and racial and ethnic appreciation. Limited promotion of multicultural awareness, gender sensitivity, and racial and ethical appreciation. Consistently promotes multicultural awareness, gender sensitivity, and racial and ethnic appreciation. 6.2 Apply a systems perspective, viewing schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. Does not view schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. Views schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments but fails to apply this knowledge. Applies a systems perspective, viewing schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. 11.1 Apply knowledge of federal and state constitutional, statutory and regulatory provisions and judicial decisions governing education. Has little or no knowledge of federal and state constitutional, statutory and regulatory provisions and judicial decisions governing education. Does not apply knowledge of federal and state constitutional, statutory and regulatory provisions and judicial decisions governing education. Applies knowledge of federal and state constitutional, statutory and regulatory provisions and judicial decisions governing education. 11.2 Apply knowledge of common law and contractual requirements and procedures in an educational setting (e.g. tort liability, contract administration, formal hearings. No knowledge of common law and contractual requirements and procedures in an educational setting. Does not apply knowledge of common law and contractual requirements and procedures in an educational setting. Applies knowledge of common law and contractual requirements and procedures in an educational setting. 11.4 Describe the processes by which federal, state, district, and schoolsite policies are formulated, enacted, implemented and evaluated, and develop strategies for influencing policy development. Cannot describe the process by which federal, state, district, and schoolsite policies are formulated, enacted, implemented and evaluated. Can describe the process by which federal, state, district, and schoolsite policies are formulated, enacted, implemented and evaluated, but fails to develop strategies for influencing policy development. Describes the processes by which federal, state, district, and schoolsite policies are formulated, enacted, implemented and evaluated, and develops strategies for influencing policy development. 4.6 Negotiate and manage effectively collective bargaining or written agreements. Does not negotiate and manage collective bargaining or written agreements. Ineffectively negotiates and manages collective bargaining or written agreements. Negotiates and manages effectively collective bargaining or written agreements. 6.2 Apply a systems perspective, viewing schools as Does not view schools as interactive internal systems operating Views schools as interactive internal systems operating within external Applies a systems perspective, viewing schools as interactive internal interactive internal systems operating within external environments. within external environments. environments but fails to apply this knowledge. systems operating within external environments. 7.2 Use appropriate written, verbal, and nonverbal communication in a variety of situations. Does not have appropriate written, verbal, and nonverbal communication skills. Has written, verbal, and nonverbal communication skills but fails to use them in a variety of situations. Uses appropriate written, verbal, and nonverbal communication in a variety of situations. 8.1 Identify and analyze the major sources of fiscal and non-fiscal resources for schools and school districts. Lacks awareness of the major sources of fiscal and nonfiscal resources for schools and school districts. Limited awareness of the major sources of fiscal and non-fiscal resources for schools and school districts. Fully identifies and analyzes the major sources of fiscal and non-fiscal resources for schools and school districts. 6.2 Apply a systems perspective, viewing schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. Does not view schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. Views schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments but fails to apply this knowledge. Applies a systems perspective, viewing schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. 7.2 Use appropriate written, verbal, and nonverbal communication in a variety of situations. Does not have appropriate written, verbal, and nonverbal communication skills. Has written, verbal, and nonverbal communication skills but fails to use them in a variety of situations. Uses appropriate written, verbal, and nonverbal communication in a variety of situations. 6.2 Apply a systems perspective, viewing schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. Does not view schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. Views schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments but fails to apply this knowledge. Applies a systems perspective, viewing schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. 11.1 Apply knowledge of federal and state constitutional, statutory and regulatory provisions and judicial decisions governing education. Has little or no knowledge of federal and state constitutional, statutory and regulatory provisions and judicial decisions governing education. Does not apply knowledge of federal and state constitutional, statutory and regulatory provisions and judicial decisions governing education. Applies knowledge of federal and state constitutional, statutory and regulatory provisions and judicial decisions governing education. 11.2 Apply knowledge of common law and contractual requirements and procedures in an educational setting (e.g. tort liability, contract administration, formal hearings. No knowledge of common law and contractual requirements and procedures in an educational setting. Does not apply knowledge of common law and contractual requirements and procedures in an educational setting. Applies knowledge of common law and contractual requirements and procedures in an educational setting. 11.4 Describe the processes by which federal, state, Cannot describe the process by which federal, state, Can describe the process by which federal, state, Describes the processes by which federal, state, district, and schoolsite policies are formulated, enacted, implemented and evaluated, and develop strategies for influencing policy development. district, and schoolsite policies are formulated, enacted, implemented and evaluated. district, and schoolsite policies are formulated, enacted, implemented and evaluated, but fails to develop strategies for influencing policy development. district, and schoolsite policies are formulated, enacted, implemented and evaluated, and develops strategies for influencing policy development. 4.6 Negotiate and manage effectively collective bargaining or written agreements. Does not negotiate and manage collective bargaining or written agreements. Ineffectively negotiates and manages collective bargaining or written agreements. Negotiates and manages effectively collective bargaining or written agreements. 6.2 Apply a systems perspective, viewing schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. Does not view schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. Views schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments but fails to apply this knowledge. Applies a systems perspective, viewing schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. 7.3 Apply appropriate communications strategies (e.g. identifying audiences, determining messages selecting transmission mediums, Fails to apply appropriate communications strategies. Inconsistently applies communications strategies. Applies appropriate communications strategies. identifying reaction of receivers, soliciting responses, etc.). B. Respond to the Larger Context 2. Candidates develop a plan to engage students, parents, members of the school board, and other community members in advocating for adoption of improved policies and laws. 3. Candidates apply their understanding of the larger political, social, economic, legal, and cultural context to develop activities and policies that benefit their district and its students. 4. Candidates develop a plan to communicate regularly with all 1.3.6 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the success of all students by understanding, responding to, and influencing the larger political, social, economic, legal, and cultural context. 6.1 Establish operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, utilizing practical applications of organizational theories. Fails to establish operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals. Establishes operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, but fails to utilize practical applications of organizational theories. Establishes operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, utilizing practical applications of organizational theories. Can maintain open lines of communication and ongoing dialog with diverse community groups and decision-makers concerning trends, issues, and potential changes in the environment within which the 10.2 Articulate the district’s or school’s vision, mission and priorities to the community and media, and build community support for district or school priorities and programs (e.g. form collaborative relationships with businesses, citizen groups, neighborhood associations, social Fails to articulate the district's or school's vision, mission and priorities to the community and media. Articulates the district's or school's vision, mission and priorities to the community and media but fails to build community support. Articulates the district’s or school’s vision, mission and priorities to the community and media, and builds community support for district or school priorities and programs. segments of the district community concerning trends, issues, and policies affecting the district. school operates service agencies, parent organizations, advocacy groups, universities, and religious institutions, etc.). Demonstrates the ability to ensure that the school community works within the framework of policies, laws, and regulations enacted by local, state, and federal authorities 6.2 Apply a systems perspective, viewing schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. Does not view schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. Views schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments but fails to apply this knowledge. Applies a systems perspective, viewing schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. 7.4 Promote multicultural awareness, gender sensitivity, and racial and ethnic appreciation. Lacks awareness of multicultural awareness, gender sensitivity, and racial and ethnic appreciation. Limited promotion of multicultural awareness, gender sensitivity, and racial and ethical appreciation. Consistently promotes multicultural awareness, gender sensitivity, and racial and ethnic appreciation. 6.1 Establish operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, utilizing practical applications of organizational theories. Fails to establish operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals. Establishes operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, but fails to utilize practical applications of organizational theories. Establishes operational plans and processes to accomplish strategic goals, utilizing practical applications of organizational theories. C. Influence the Larger Context 5. Candidates demonstrate an understanding of how to develop lines of 1.3.6 A school administrator is an educational leader who promotes the 6.2 Apply a systems perspective, viewing schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. Does not view schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. Views schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments but fails to apply this knowledge. Applies a systems perspective, viewing schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. 7.2 Use appropriate written, verbal, and nonverbal communication in a variety of situations. Does not have appropriate written, verbal, and nonverbal communication skills. Has written, verbal, and nonverbal communication skills but fails to use them in a variety of situations. Uses appropriate written, verbal, and nonverbal communication in a variety of situations. 7.3 Apply appropriate communications strategies (e.g. identifying audiences, determining messages selecting transmission mediums, identifying reaction of receivers, soliciting responses, etc.). Fails to apply appropriate communications strategies. Inconsistently applies communications strategies. Applies appropriate communications strategies. 4.6 Negotiate and manage effectively collective bargaining or written agreements. Does not negotiate and manage collective bargaining or written agreements. Ineffectively negotiates and manages collective bargaining or written agreements. Negotiates and manages effectively collective bargaining or written agreements. communication with local, state, and federal authorities and actively advocate for improved policies, laws, and regulations affecting a specific district, both directly and through organizations representing schools, educators, or others with similar interests. 6. Candidates advocate for policies and programs that promote equitable learning opportunities and success for all students, regardless of socioeconomic background, ethnicity, gender, disability, or other individual characteristics. success of all students by understanding, responding to, and influencing the larger political, social, economic, legal, and cultural context. Understands how to shape public policy in ways designed to provide quality education for students 6.2 Apply a systems perspective, viewing schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. Does not view schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. Views schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments but fails to apply this knowledge. Applies a systems perspective, viewing schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. 7.2 Use appropriate written, verbal, and nonverbal communication in a variety of situations. Does not have appropriate written, verbal, and nonverbal communication skills. Has written, verbal, and nonverbal communication skills but fails to use them in a variety of situations. Uses appropriate written, verbal, and nonverbal communication in a variety of situations. 7.3 Apply appropriate communications strategies (e.g. identifying audiences, determining messages selecting transmission mediums, Fails to apply appropriate communications strategies. Inconsistently applies communications strategies. Applies appropriate communications strategies. identifying reaction of receivers, soliciting responses, etc.). 10.1 Analyze community and district power structures, and identify major opinion leaders and their relationships to school goals and programs. Fails to analyze community and district power structures. Analyzes community and district power structures but fails to identify their relationships to school goals and programs. Analyzes community and district power structures, and identify major opinion leaders and their relationships to school goals and programs. 11.4 Describe the processes by which federal, state, district, and schoolsite policies are formulated, enacted, implemented and evaluated, and develop strategies for influencing policy development. Cannot describe the process by which federal, state, district, and schoolsite policies are formulated, enacted, implemented and evaluated. Can describe the process by which federal, state, district, and schoolsite policies are formulated, enacted, implemented and evaluated, but fails to develop strategies for influencing policy development. Describes the processes by which federal, state, district, and schoolsite policies are formulated, enacted, implemented and evaluated, and develops strategies for influencing policy development. 6.2 Apply a systems perspective, viewing schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. Does not view schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. Views schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments but fails to apply this knowledge. Applies a systems perspective, viewing schools as interactive internal systems operating within external environments. 7.4 Promote multicultural awareness, gender sensitivity, and racial and ethnic appreciation. Standard 6.0 Narrative Explanation: Standard addresses the need for educational leaders to understand and be able to operate within the larger context of the community and beyond, which affects opportunities for all students. Educational leaders must respond to and influence this larger political, social, economic, and cultural context. Of vital importance is the ability to develop a continuing dialogue with economic and political decision makers concerning the role of schools and to build collaborative relationships that support improved social and educational opportunities for children. Educational leaders must be able to participate actively in the political and policy-making context in the service of education, including proactive use of the legal system to protect students’ rights and improve students’ opportunities. Examples of Promising Practices for Candidate Performance Activities: Candidates are required to interview state legislators and/or lobbyists and present a report about Lacks awareness of multicultural awareness, gender sensitivity, and racial and ethnic appreciation. Limited promotion of multicultural awareness, gender sensitivity, and racial and ethical appreciation. Consistently promotes multicultural awareness, gender sensitivity, and racial and ethnic appreciation. the state’s strategies used to influence change. Candidates are required to participate in a simulated public debate about the pros and cons of selected international educational practices compared to practices in the United States. Additional activities can be found beginning on page 25 of the Instructions to Implement Standards for Advanced Programs in Educational Leadership document.