war n peace 1 2 eng
advertisement

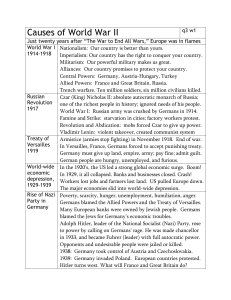
C. Why did World War II break out two decades after World War I? World War I ended in November 1918. Germany, as well as Austria-Hungary, Turkey1 and Bulgaria2, had been defeated by a worldwide combination of allies including Britain, France and the United States. Peace treaties were then signed with the defeated countries in 1919-1920. In the two decades that followed, the Powers tried to avoid the possibility of another war, but they failed. World War II broke out in 1939. 1. Did World War I sow the seed for World War II? a. Which country suffered the most in the peace treaties of 1919-1920? Study Sources A and B. Source A Key terms of Treaty of Versailles 1 2 War Guilt Clause – Article 231: Germany had to accept full responsibility for the war. Reparations: Germany had to pay £6,600 million for the damage caused by the war. Military terms: Germany was forbidden to have tanks, submarines or air force. The navy could only have 6 battleships. The army was limited to 100,000 men. There was to be no conscription. The Rhineland was demilitarized. Germany was not allowed to place any troops in the Rhineland. The Allies were to keep an army of occupation on the west bank of the Rhine for fifteen years. All Germany’s colonies in Africa were given to Britain, France or South Africa. The League of Nations was to be set up to keep international peace. Turkey: The Ottoman Empire was dissolved after World War I and Turkey was formed. Bulgaria: It became fully independent from Ottoman Empire in 1908. 1 The following map shows the territory lost of Germany under the Treaty of Versailles. <http://www.johndclare.net/peace_treaties4.htm> Source B The peace treaties signed with the other defeated states. Turkey Treaty of Sevres 1920 Most of Turkey’s land in Europe was taken away. Greece gained Austria Treaty of St Germanin 1919 Hungary and Austria became separate and independent states. Territories were given up to Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia, Poland and Italy. Armed forces were reduced. Austria had to pay reparations. Austria was not allowed to unite with Germany (Anschluss). Eastern Thrace and Smyrna. The Turkish Empire was broken up. France and Britain governed the land from the Turkish Empire as mandates on behalf of the League of Nations. The Turkish Straits were put under the control of the League of Nations. Turkey was occupied by French, British and Italian troops. 2 Hungary Treaty of Trianon 1920 Hungary had to pay reparations. Army was limited to 35,000. Hungary had to hand over war criminals. Lands were given to Romania, Czechoslovakia and Yugoslavia. Bulgaria Treaty of Neuilly 1919 Lands were given to Yugoslavia and Greece Bulgaria had to pay repaations Army was limited to 20,000. Refer to the maps below, can you identify the major territorial changes in Europe before and after World War I? Europe 1914 Europe 1919 http://www.nationalarchives.gov.uk/ pathways/firstworldwar/maps/europ e1914.htm http://www.nationalarchives.gov.uk /pathways/firstworldwar/maps/euro pe1919.htm 3 Refer to Sources A and B. Which country suffered the most in the settlement of World War I, as shown in Sources A and B? The table below will help you to find out the answer. Put a ‘√’ against the country that had to accept the treaty term stated on the left. Treaty terms Austria-H Bulgaria Hungary Germany Turkey ungary Loss of territory Reduction in armed forces Reparations War guilt Which country suffered the most? Personal Opinion (Teachers can request students to explain their choices.) b. Was the settlement of World War I able to keep peace? Study Sources C, D, E and F. Source C The following cartoon was published in Britain in 1919. The ‘Tiger’ is meant to represent Clemenceau, the Prime Minister of France. The child in the cartoon is labeled ‘1940 Class’, that is, those who would be the soldiers of 1940. http://www.sirbernardlovell.s-gloucs.sc h.uk/learningcentre/history/20century/v ersailles.jpg 4 Source D The following comment on the Treaty of Versailles was written by a British historian in 1966. The greatest weakness of the Treaty was that it did not end the German ‘menace’ by means of the punishment clauses. The German empire was left basically intact. Although Germany did lose some territories, by far the major part of its strength (land, population and resources) was untouched. Source E The following shows how a German newspaper, Deutsche Zeitung, announced the news of the Treaty of Versailles in June 1919. Vengeance! German nation! Today in the Hall of Mirrors the disgraceful treaty is being signed. Do not forget it. The German people will, with unceasing work, press forward to reconquer the place among nations to which it is entitled. Then will come vengeance for the shame of 1919. Source F The editor of the a British newspaper, Daily Graphic, 5 July 1919, wrote the following Nobody involved is completely satisfied – not those who wish to punish the evildoers and least of all, of course, the evildoers. The Germans may even treat the Peace Treaty as another Scrap of Paper. 5 Refer to Sources C, D, E and F i) Which source(s) show(s) that the settlement would possibly arouse resentment among Germans? Explain your answer. Source Explanati on C Students should explain according to the information given in Source C. (e.g.: the crying child without clothing represented Germany, he would take revenge on the victors. As shown in the cartoon, the child was labeled “1940 class”, meaning that the child would be the soldier of 1940. And it predicted a future war.) E Germany might re-conquer the lost territories. F The “evildoers” were not satisfied with the treaty. The evildoers were the Germans ii) Which source(s) show(s) that the settlement with Germany was not harsh enough? Explain your answer. Source D Explanation As the Versailles Settlement did not weaken Germany enough, her ambition was not suppressed. The major part of her strength was untouched. iii) Some people consider that the Treaty of Versailles was too harsh to Germany. The Germans became very resentful and determined to re-gain what they had lost. This sowed the seed for World War II. Which source(s) show(s) the impacts of the settlement of World War I in this aspect? Impact Source(s) The settlement caused ill feelings of the Germans who tried to revenge C, E & F by starting another war. The punishment was not effective. Germany was not weakened and could expand again. 6 D 2. Was Hitler to blame for World War II? Besides the legacy of World War I, World War II was also caused by several other factors. It has been usually believed that Hitler caused World War II. However, should he be totally responsible? Was he assisted by circumstances? a. Why did the Germans expand in the 1930s? Study Sources A, B, C and D. Source A The following shows the Dow Jones Industrial (the US share market) Average Year-end close 1919– 1933. http://www.shambhala.org/business/goldocean/causde p.html Source B The impact of the Wall Street Crash in 1929 on world economy and on Germany. Wall Street shares collapsed. This sparked off the Great Depression. American firms and banks went bankrupt. American trade declined and loans to Europe dried up. European firms went bankrupt. Europeans and Americans could not afford to buy raw materials. European governments tried to raise money through high import duties. World trade collapsed. Unemployment spread worldwide. Hunger marches took place. Support for extremist political parties grew. The Great Depression attacked Germany harder than any other European country because the German economic recovery depended chiefly on loans provided by the powers, especially the United States. These powers were also facing serious economic problems, so Germany could receive no more financial help. This worsened German’s economy. For everyday life of Americans during the Great Depression, please refer to <http://encarta.msn.com/media_461556531_761584403_-1_1/WPA_Workers.html> 7 Source C The poster below was published in Germany by the Nazi Party in 1932. The slogan says, ‘Our last hope – Hitler’. <http://academic.brooklyn.cuny.edu/history/core/pi cs/0255/img0029.htm> Hitler made promises to satisfy the needs of most Germans and gained their support. For example, he gained the support from workers and the unemployed by promising them employment and security for. He promised to rearm the country and thus gained support from former soldiers and army officers. He promised to abolish the Versailles Treaty. Germans believed that Hitler was a strong leader who could solve the economic problems. Source D The following shows the relationship between German unemployment and Nazi vote share. http://econ161.berkeley.edu/TCEH/Slo uch_Purge15.html 8 Put arrows to link up the following bubbles, which explain how the general desire of the Germans made expansion inevitable. Serious economic problems in Germany The Great Depression The Germans wanted a strong man as their leader. Hitler rose to power in Germany. Expansion b. Why was so little done to stop Hitler’s aggression? World War II broke out in September 1939 when Hitler invaded Poland. Why was so little done by other countries to stop Hitler’s aggression? Study Sources A and B. Source A The following speech was made in 1938 by Neville Chamberlain (the British Prime Minister from 1937 to 1940) after he had promised to give the Sudetenland (See Source B) to Germany in the Munich Conference. He wanted to avoid war by giving Hitler everything he demanded. This policy was known as appeasement. My good friends, this is the second time in our history that there has come back from Germany to Downing Street peace with honour. I believe it is peace in our time. Hitler would not deceive a man he respected. I have established an influence over Hitler who can now be trusted. 9 Source B Hitler violated the Treaty of Versailles and rearmed Germany. In 1936, he reclaimed the Rhineland demilitarized zone from French control. France was in particular position to act but did not do so fearing war. Austria was traditionally and culturally bound to Germany. In 1938 Hitler annexed Austria to Germany which again violated the Treaty of Versailles. In 1939, Hitler wanted to take over Sudetenland from Czechoslovakia. In the Munich Conference, the European countries scarified the interest of Czechoslovakia in exchange for a promise from Hitler that this would be the end of his expansion. Neville Chamberlain, Prime Minister of Britain, declare “Peace in our time”. Weeks later Hitler annexed the rest of Czechoslovakia by force violating the Munich Pact. On 1 September 1939, Germany invaded Poland. At this point, Hitler could not be ignored and Britain and France declared war on Germany on 3 Septermber 1939. Refer to Sources A and B i) Does Source B show that the view of Chamberlain as shown in Source A was right? Give evidence from Source B to support your answer. Suggested answer: No. Students should support their answer with evidence about Hitler’s expansion from Source B. ii) What was the responsibility of Chamberlain and Hitler for causing World War II, as reflected in Sources A and B? Responsibility for causing World War II Chamberlain His appeasement policy encouraged Hitler’s expansion. Hitler Germany’s territorial expansion threatened peace in Europe. This initiated other countries to join World War II. 10 3. How did the war become worldwide? World War II was the most destructive war in history. The Second World War started with the German invasion of Poland. At first, it was a European war between the Axis (Germany, Italy, Japan) and the Allies (Britain and France). It was not until 1941 when the Soviet Union and United States were driven into the warfare that the European war really developed into a global war. When and why did the USA join World War II? In 1941, after the Pearl Harbour Attack Reference: Steven Waugh. Essential Modern World History. UK.: Nelson Thornes, 2001. Christopher Culpin. Making History (New Edition): World History from 1914 to the Present. London: Collins Educational, 1997. 11