Oceans - MCQ topic quiz - Lesson element (DOC, 396KB) Updated 29/03/2016
advertisement

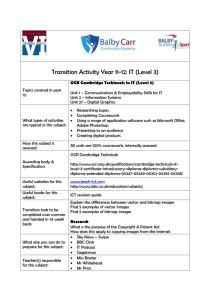
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) topic quiz Oceans Instructions and answers for teachers These instructions cover the student activity section which can be found on page 9. This Lesson Element supports OCR A Level Chemistry B (Salters). When distributing the activity section to the students either as a printed copy or as a Word file you will need to remove the teacher instructions section. The Activity This Lesson Element is a teaching and learning resource containing 10 multiple choice questions (MCQs) on the theme of oceans. Some questions might require synoptic thinking, using knowledge and ideas from various topics across the full A Level content. This resource can be used to test and consolidate understanding at the end of a topic or to revisit and refresh knowledge at a later point in the course. Learning Outcomes This Lesson Element relates to the specification learning outcomes O(b), O(d), O(e), O(f), O(h), O(i), O(l), O(m), O(n). Introduction Multiple choice questions allow rapid coverage of a wide range of sub-topics. Contrary to a widespread belief among students, multiple choice questions are not necessarily easy – they can be easy, moderate or difficult. The questions are written so that the incorrect answers are plausible distractors based on common errors or misconceptions. The questions in this quiz cover topics mainly from specification sections: Oceans. Version 1 1 © OCR 2016 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) topic quiz - answers 1. Which statement about the greenhouse effect is true? A Absorption of infrared radiation causes homolytic fission and creates radicals. Infrared energy is not of a high enough frequency to cause electron excitation or photolysis. B Oxygen molecules do not absorb infrared radiation. Correct answer: Oxygen does not have a dipole moment and so does not absorb infrared radiation. C Greenhouse gases reflect infrared Greenhouse gases do not reflect; the radiation back to the Earth’s molecules absorb infrared radiation and then surface, trapping the heat. re-emit it in all directions, resulting in some going back towards the Earth’s surface. D Solar energy reaches the Earth mainly as infrared radiation. Most solar energy reaches the Earth’s surface as UV and visible light. Your answer Version 1 2 B © OCR 2016 2. The boiling points of some hydrocarbons are listed below. Name and formula of hydrocarbon Propane, C3H8 Butane, C4H10 Pentane, C5H12 Hexane, C6H14 Boiling point / K 231 273 309 342 What is the correct order for the standard entropy for these hydrocarbons, from lowest to highest? A butane, propane, hexane, pentane The learner has placed the molecules in order of decreasing, rather than increasing molar entropy. B hexane, pentane, butane, propane The learner has simply placed the molecules in order of decreasing size. C pentane, hexane, propane, butane Correct answer: Liquids have lower molar entropies than gases. If the molecule is in the same state then the larger molecule has the greater entropy as it has a greater number of energy levels. D propane, butane, pentane, hexane The learner has assumed that molar entropy increases with molecular size (true) but has not taken into account their state at room temperature. Your answer Version 1 3 C © OCR 2016 3. surrS for a reaction is –16.5 J mol–1 K–1 at 298 K. What is the value of the enthalpy change for this reaction? A –55.4 kJ mol–1 The learner has performed the same mistake as in D but has also neglected to change the sign of their answer. B –4.92 kJ mol–1 The learner has forgotten that the sign of surrS is always opposite to the sign of H. C +4.92 kJ mol–1 Correct answer: Rearranging the equation gives H = –surrS × T; the answer is then divided by 1000 to give the answer in kJ mol–1. D +55.4 kJ mol–1 The learner has not correctly rearranged the equation. They have divided –surrS by 298 and multiplied by 1000 (as if surrS and H were interchangeable). Your answer 4. Which species is the conjugate base of the acid HSO3–? A H2SO4 This is not related to the HSO3– ion at all, and is simply a more familiar molecule. B H2SO42– Here the learner has added OH– to the ion, thinking of acid behaviour as a molecule that reacts with hydroxide ions rather than producing H+. C H2SO3 This is the conjugate acid of the ion. D SO32– Correct answer: This is the species formed when the ion acts as an acid (proton donor). Your answer Version 1 C 4 D © OCR 2016 5. Which statement is true of buffer solutions? A A buffer does not change in pH when small amounts of acid or alkali is added. This is a common misconception – the pH will always change, but only very slightly. B An acidic buffer is a mixture of a weak acid and a solution of its salt. Correct answer: These are the core components of an acidic buffer, providing a ‘reservoir’ of HA and A– to allow the equilibrium position to shift in response to changes in H+ concentration. C All buffers are acidic. Buffers can also be alkaline if they are made from a combination of a weak base and its salt. D The pH of a buffer depends only on the ratio of its components’ concentrations. If this statement specified room temperature, it would be true; however the pH of any buffer solution also depends on temperature as this will affect the value of Ka and thus the equilibrium position. Your answer 6. What is the hydroxide ion concentration in a solution for which pH = 4? A 1010 mol dm–3 Incorrect rearrangement of the Kw equation ([OH–] = [H+]/Kw). B 10–4 mol dm–3 The learner has worked out the hydrogen ion concentration. C 10–10 mol dm–3 Correct answer: Correct rearrangement of the Kw equation gives [OH–] = Kw/[H+]. D 10–18 mol dm–3 Incorrect rearrangement of the Kw equation ([OH–] = Kw × [H+]). Your answer Version 1 B 5 B © OCR 2016 7. Calcium phosphate is a sparingly soluble solid. The equation for the dissolving process is shown below: Ca3(PO4)2(aq) 3Ca2+(aq) + 2PO43–(aq) What are the units for the solubility product, Ksp, for this process? A mol4 dm–12 The learner has multiplied the concentration terms on the right but has divided them by a concentration term from the left hand side for the solid calcium phosphate. B mol5 dm–15 Correct answer: Ksp = [Ca2+]3[PO43–]2 so the units are calculated by (mol dm–3)5. C mol5 dm–15 s–1 The learner is confusing equilibrium constants with rate constants and so has included a time component. D it has no units The learner is perhaps confused about the nature of heterogeneous equilibrium constants and has taken the fact that the left hand side is not included in the equation as meaning the constant has no units. Your answer 8. Which of the following processes is associated with hydH? A XY(s) X+(aq) + Y–(aq) This is the solH. The two processes have similar names and are thus often confused. B X+(s) X+(aq) The state symbols here are incorrect. The learner has not taken into account the energy required to break the ion away from the lattice. C XY(s) X+(g) + Y–(g) This is the reverse of the lattice enthalpy. D X+(g) X+(aq) Correct answer: This is the energy released upon hydration of a gaseous ion. Your answer Version 1 B 6 D © OCR 2016 9. An experiment was carried out to determine the standard enthalpy change of solution for a compound which readily dissolves at room temperature. During the dissolving process a decrease in temperature was recorded. What can be assumed from these results? A The compound dissolves more readily at lower temperatures. The dissolving process is endothermic, therefore surrS is negative. Since surrS = –H/T, it follows that surrS will become more negative at lower temperatures, making totS more negative and dissolving less likely to be spontaneous. B The dissolving process has a positive surrS. If the process is endothermic then surrS will be negative. C The dissolving process has a positive sysS. Correct answer: If the compound readily dissolves at room temperature then totS must be positive. Since surrS is negative it follows that sysS must be positive to compensate. D The process has a high activation energy. Nothing can be ascertained about the activation energy as this will only affect the rate of dissolving. The learner is associating an endothermic reaction with a high activation energy. Your answer Version 1 7 C © OCR 2016 10. The pH of an acidic buffer solution can be calculated from rearrangement of the Ka equation below: Ka = [H+][A–]/[HA] Which statement(s) is/are true for this calculation? Statement 1: The exact concentrations of A– and HA do not need to be known, only their molar ratio. Statement 2: The pH will also be dependent on temperature. Statement 3: It can be approximated that [H+] = [A–] A 1, 2 and 3 Statement 3 is not true for a buffer solution, only for a weak acid alone. In a buffer solution a significant quantity of the anion is added to the mixture. B only 1 and 2 Correct answer: The pH depends on the ratio of salt/acid and the Ka; the Ka is also dependent on temperature. C only 2 and 3 The learner does not appreciate that the units for A– and HA cancel out in the equation and so a simple molar ratio is sufficient to carry out the calculation. D only 1 The learner has forgotten that Ka is only constant at a given temperature. Your answer B This resource has been produced as part of our free Chemistry teaching and learning support package. All the Chemistry teaching and learning resources, including delivery guides, topic exploration packs, lesson elements and more are available on the qualification webpages. If you are looking for examination practice materials, you can find Sample Assessment Materials (SAMs) and a link to the Practice Papers on the qualification webpages: Chemistry A, Chemistry B. We’d like to know your view on the resources we produce. By clicking on ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ you can help us to ensure that our resources work for you. When the email template pops up please add additional comments if you wish and then just click ‘Send’. Thank you. If you do not currently offer this OCR qualification but would like to do so, please complete the Expression of Interest Form which can be found here: www.ocr.org.uk/expression-of-interest OCR Resources: the small print OCR’s resources are provided to support the teaching of OCR specifications, but in no way constitute an endorsed teaching method that is required by the Board, and the decision to use them lies with the individual teacher. Whilst every effort is made to ensure the accuracy of the content, OCR cannot be held responsible for any errors or omissions within these resources. © OCR 2016 - This resource may be freely copied and distributed, as long as the OCR logo and this message remain intact and OCR is acknowledged as the originator of this work. OCR acknowledges the use of the following content: n/a Please get in touch if you want to discuss the accessibility of resources we offer to support delivery of our qualifications: resources.feedback@ocr.org.uk Version 1 8 © OCR 2016 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) topic quiz Oceans Learner Activity 1. Which statement about the greenhouse effect is true? A Absorption of infrared radiation causes homolytic fission and creates radicals. B Oxygen molecules do not absorb infrared radiation. C Greenhouse gases reflect infrared radiation back to the Earth’s surface, trapping the heat. D Solar energy reaches the Earth mainly as infrared radiation. Your answer 2. The boiling points of some hydrocarbons are listed below. Name and formula of hydrocarbon Propane, C3H8 Butane, C4H10 Pentane, C5H12 Hexane, C6H14 Boiling point / K 231 273 309 342 What is the correct order for the standard entropy for these hydrocarbons, from lowest to highest? A butane, propane, hexane, pentane B hexane, pentane, butane, propane C pentane, hexane, propane, butane D propane, butane, pentane, hexane Your answer Version 1 9 © OCR 2016 3. surrS for a reaction is –16.5 J mol–1 K–1 at 298 K. What is the value of the enthalpy change for this reaction? A –55.4 kJ mol–1 B –4.92 kJ mol–1 C +4.92 kJ mol–1 D +55.4 kJ mol–1 Your answer 4. Which species is the conjugate base of the acid HSO3–? A H2SO4 B H2SO42– C H2SO3 D SO32– Your answer 5. Which statement is true of buffer solutions? A A buffer does not change in pH when small amounts of acid or alkali are added. B An acidic buffer is a mixture of a weak acid and a solution of its salt. C All buffers are acidic. D The pH of a buffer depends only on the ratio of its components’ concentrations. Your answer Version 1 10 © OCR 2016 6. What is the hydroxide ion concentration in a solution for which pH = 4? A 1010 mol dm–3 B 10–4 mol dm–3 C 10–10 mol dm–3 D 10–18 mol dm–3 Your answer 7. Calcium phosphate is a sparingly soluble solid. The equation for the dissolving process is shown below: Ca3(PO4)2(aq) 3Ca2+(aq) + 2PO43–(aq) What are the units for the solubility product, Ksp, for this process? A mol4 dm–12 B mol5 dm–15 C mol5 dm–15 s–1 D it has no units Your answer 8. Which of the following processes is associated with hydH? A XY(s) X+(aq) + Y–(aq) B X+(s) X+(aq) C XY(s) X+(g) + Y–(g) D X+(g) X+(aq) Your answer Version 1 11 © OCR 2016 9. An experiment was carried out to determine the standard enthalpy change of solution for a compound which readily dissolves at room temperature. During the dissolving process a decrease in temperature was recorded. What can be assumed from these results? A The compound dissolves more readily at lower temperatures. B The dissolving process has a positive surrS. C The dissolving process has a positive sysS. D The process has a high activation energy. Your answer 10. The pH of an acidic buffer solution can be calculated from rearrangement of the Ka equation below: Ka = [H+][A–]/[HA] Which statement(s) is/are true for this calculation? Statement 1: The exact concentrations of A– and HA do not need to be known, only their molar ratio. Statement 2: The pH will also be dependent on temperature. Statement 3: It can be approximated that [H+] = [A–] A 1, 2 and 3 B only 1 and 2 C only 2 and 3 D only 1 Your answer Version 1 12 © OCR 2016