Algebra II 3rd 6 Weeks IPG
advertisement

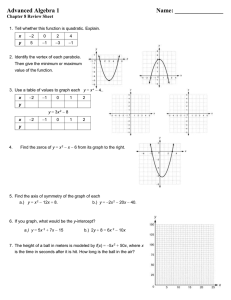
Austin ISD Instructional Planning Guide – Mathematics 3rd Six Weeks IPG – Nov. 10 - Dec. 17 (25 days; 2 days for 6 weeks review/test and 4 days for Final Exams) ©2009 Austin ISD Algebra II Discipline Based Concept Pacing: 25 days Concept description: Quadratic functions can be represented in different ways, and students should be able to translate among and make connections between the various representations. Unit: Quadratics Unit Pacing: 25 days Unit Overarching Unit Vocabulary: Quadratic functions have many applications in business models and science, and can also be used to determine the path of an object that is thrown or projected. Idea Discipline Based Concept: Quadratic Functions Unit Guiding Questions Arc Guiding Questions Quadratic and square root functions Foundations for Functions Strand What are some real-world applications of quadratic functions? How can factoring, graphing, completing the square, and the quadratic formula be used to solve quadratic equations and inequalities? How are solutions to quadratic equations and inequalities represented in tables, graphs, and equations? How are the different representations connected? What are the similarities or differences between solving quadratic equations and solving quadratic inequalities? Arc : Quadratic Functions and Transformations In what ways is the quadratic function similar to linear functions? How are they different? How does the symbolic notation of quadratic transformations (horizontal shifts) connect to the graph? How does the standard form compare to the vertex form of a quadratic function? How can the standard and vertex forms of a quadratic function be used to graph the function? TEKS Knowledge & Skill Student Expectation 2A.1The student uses properties and attributes of functions and applies functions to problem situations 2A.1B The student is expected to collect and organize data, make and interpret scatter plots, fit the graph of a function to the data, interpret the results, and proceed to model, predict, and make decisions and critical judgments. 2A.6 The student understands that quadratic functions can be represented in different ways and translates among their various representations. 2A.6B The student is expected to relate representations of quadratic functions, such as algebraic, tabular, graphical, and verbal descriptions. 2A.8: The student formulates equations and inequalities based on quadratic functions, uses a variety of methods to solve them, and analyzes the solutions in terms of the situations. 2A.8A The student is expected to analyze situations involving quadratic functions and formulate quadratic equations or inequalities to solve problems. TAKS OBJ Resource Time/ Pace Teacher Tools Intended Learning: Students will be able to use quadratic functions to model data and use quadratic models to analyze and make predictions. Team Pattern Challenge Holt 5.8 Curve Fitting with Quadratic Models (for regression and practice) 90 min. Essential Questions: What are types of patterns can be modeled by quadratic functions? How do you connect the pattern in a geometric model to a rule for the pattern? What is the difference in the regression equation when a linear regression is chosen instead of quadratic for a set of data? How does one choose between which regression is appropriate for a set of data? Vocabulary: quadratic model, quadratic regression MAlg2_3rdIA1a=lesson plan MAlg2_3rdIA1a_TeamRoles MAlg2_3rdIA1a_TeamPatternChallenge= Pattern Challenge Activity TEXTEAMS: Algebra II Part 2 ETQ: Ensuring Teacher Quality AA: Algebra II Assessments MAP: Maximizing Algebra II Performance SATEC: San Antonio Technology in Education Coalition Page 1 of 5 ACM: Accelerated Curriculum for Mathematics Algebra II ©2009 Austin ISD Quadratic and square root functions Algebra and Geometry Quadratic and square root functions Strand Austin ISD Instructional Planning Guide – Mathematics 3rd Six Weeks IPG – Nov. 10 - Dec. 17 (25 days; 2 days for 6 weeks review/test and 4 days for Final Exams) TEKS Knowledge & Skill Student Expectation 2A.7 The student interprets and describes the effects of changes in the parameters of quadratic functions in applied and mathematical situations. 2A.7A The student is expected to use characteristics of the quadratic parent function to sketch the related graphs and connect between the y = ax2 + bx + c and the y = a (x - h)2 + k symbolic representations of quadratic functions. 2A.7B The student is expected to use the parent function to investigate, describe, and predict the effects of changes in a, h, and k on the graphs of y = a (x - h)2 + k form of a function in applied and purely mathematical situations. 2A.6 The student understands that quadratic functions can be represented in different ways and translates among their various representations. 2A.4 The student connects algebraic and geometric representations of functions. 2A.6B The student is expected to relate representations of quadratic functions, such as algebraic, tabular, graphical, and verbal descriptions. TAKS OBJ Time/ Pace DL: Shapes of Quadrilaterals 5 (Alg1) Holt 5-1 Using Transformations to Graph Quadratic Functions (for practice/homework) 90 min. MAlg2_3rdIA1b1=lesson plan MAlg2_3rdIA1b1_ Shapes of Quadratics MAlg2_3rdIA1b1_ShapesofQuadratics_Lesson_Guide MAlg2_3rdIA1b1_ShapesofQuadratics_Record_sheet MAlg2_3rdIA1b1_ShapesofQuadratics_Task 2A.4A The student is expected to identify and sketch graphs of parent functions, including linear (f(x) = x), quadratic (f(x) = x2), exponential (f(x) = ax), and logarithmic (f(x) = logax) functions, absolute value of x (f(x) = |x|), square root of x (f(x) = √x), and reciprocal of x (f(x) = 1/x); Closing distance Grade 11 Lesson 8 Graphs, Transformations, and Solving Equations MAlg2_3rdIA1b2=lesson plan 45 min. MAlg2_3rdIA1b2_StuPgs Intended Learning: Students use the properties of quadratic functions to identify similarities and differences between the standard and vertex forms of quadratic functions and translate between the forms. 2A.7B 2A.6B (Alg1) 2A.4A MAlg2_3rdIA1b2_matching cards MAlg2_3rdIA1b2_QuadQuiz 2A.7 2A.4 Essential Questions: How does the value of a affect the appearance and location of the graph? How does the value of the constant term c or k affect the appearance and location of the graph? How do h & k affect the appearance and location of the graph? How can you tell from the equation whether a quadratic function has a maximum or minimum point on the graph? Does the graph of every quadratic function have a yintercept? How can you determine the y-intercept by looking at the equation? Vocabulary: Vertex, Minimum , Maximum, quadratic function, parabola, vertex form, standard form 2A.7A 2A.6 Teacher Tools Intended Learning: Students will transform quadratic functions and investigate the changes of a, h, and k in vertex form. 5 Algebra and Geometry Resource Algebra II Holt 5.2 Properties of Quadratic Functions in Standard Form 90 min. Essential Questions: What applications use quadratic functions and how do parabolas model real-life situations? What is the significance of the vertex and roots of a parabola in real-life applications? What causes the parabola to change direction? How do h & k effect the position of the parabola? Vocabulary: axis of symmetry, standard form, minimum value, maximum value, vertex form MAlg2_3rdIA1c=lesson MAlg2_3rdIA1c_warm_up_trans MAlg2_3rdIA1c_alternate_opener_transp MAlg2_3rdIA1c_Equation_Plotter_R&A2 MAlg2_3rdIA1c_InvestigateTransQuadFuncs MAlg2_3rdIA1c_a2_ch05_02ppt = Holt 5.2 PowerPoint MAlg2_3rdIA1c_tx_practice_b TEXTEAMS: Algebra II Part 2 ETQ: Ensuring Teacher Quality AA: Algebra II Assessments MAP: Maximizing Algebra II Performance SATEC: San Antonio Technology in Education Coalition Page 2 of 5 ACM: Accelerated Curriculum for Mathematics Algebra II Austin ISD Instructional Planning Guide – Mathematics 3rd Six Weeks IPG – Nov. 10 - Dec. 17 (25 days; 2 days for 6 weeks review/test and 4 days for Final Exams) ©2009 Austin ISD Algebra II Discipline Based Concept Pacing: 25 days Concept description: Quadratic functions can be represented in different ways, and students should be able to translate among and make connections between the various representations. Unit: Quadratics Unit Pacing: 25 days Unit Overarching Unit Vocabulary: Quadratic Functions have many applications in business models and science, and can also be used to determine the path of an object that is thrown or projected. Idea Discipline Based Concept: Quadratic Functions Unit Guiding Questions Arc Guiding Questions Foundations for Functions Strand What are some real-world applications of quadratic functions? How can factoring, graphing, completing the square, and the quadratic formula be used to solve quadratic equations and inequalities? How are solutions to quadratic equations and inequalities represented in tables, graphs, and equations? How are the different representations connected? What are the similarities or differences between solving quadratic equations and solving quadratic inequalities? Arc : Solving Quadratic Equations and Inequalities How is solving quadratic equations similar to or different from solving quadratic inequalities? What are the connections between the factors, solutions, intercepts, and zeroes of quadratic equations? How do you determine the solution to a quadratic equation or inequality from a graph? How are solutions of quadratic equations related to geometric applications? TEKS Knowledge & Skill 2A.2 The student understands the importance of the skills required to manipulate symbols in order to solve problems and uses the necessary algebraic skills required to simplify algebraic expressions and solve equations and inequalities in problem situations. Student Expectation Quadratic and Square Root Functions Resource Time/ Pace 2A.8C The student is expected to compare and translate between algebraic and graphical solutions of quadratic equations. Teacher Tools Intended Learning: Students will be able to use quadratic functions to model real-world situations such as the height of a football, baseball, soccer ball or some other type of object that is thrown or dropped. 2A.2A The student is expected to use tools including factoring and properties of exponents to simplify expressions and to transform and solve equations. 2A.8A 2A.8 TAKS OBJ Essential Questions: Holt 5.3 Solving Quadratic Equations by Graphing and Factoring 90 min. How can a student graph and/or factor quadratic equations to solve equations? What determines the solution(s) to quadratic equations when graphing? What determines the solution(s) when factoring? What is the significance of finding the zeros of a function? What form represents a quadratic equation? Vocabulary: Zero of a function, Root of a Function, Binomial, Trinomial, Solutions MAlg2_3rdIA2a= lesson 2A.8D The student is expected to solve quadratic equations and inequalities using graphs, tables, and algebraic methods. 2A.6 2A.6C The student is expected to determine a quadratic function from its roots (real and complex) or a graph. MAlg2_3rdIA2a_Tech_Lab5_3 MAlg2_3rdIA2a_AccCurr_factors MAlg2_3rdIA2a_Roots_Graphically MAlg2_3rdIA2a_homework TEXTEAMS: Algebra II Part 2 ETQ: Ensuring Teacher Quality AA: Algebra II Assessments MAP: Maximizing Algebra II Performance SATEC: San Antonio Technology in Education Coalition Page 3 of 5 ACM: Accelerated Curriculum for Mathematics Algebra II ©2009 Austin ISD Algebra & Geometry Strand TEKS Knowledge & Skill 2A.5 The student knows the relationship between the geometric and algebraic descriptions of conic sections. Foundations for Functions 2A.8 2A.2 2A.2 Quadratic and square root functions 2A.6 Austin ISD Instructional Planning Guide – Mathematics 3rd Six Weeks IPG – Nov. 10 - Dec. 17 (25 days; 2 days for 6 weeks review/test and 4 days for Final Exams) Student Expectation TAKS OBJ Resource Time/ Pace Teacher Tools Intended Learning: Students will solve quadratic equations in order to find the time needed for water to fall from the top of a waterfall. 2A.5E The student is expected to use the method of completing the square. Holt 5.4 Completing the Square 90 min. 2A.8D 2A.2A 2A.2A 2A.2B The student is expected to use complex numbers to describe the solutions of quadratic equations. 2A.6A The student is expected to determine the reasonable domain and range values of quadratic functions, as well as interpret and determine the reasonableness of solutions to quadratic equations and inequalities. 2A.6B Intended Learning: Students will be introduced to quadratic functions that have no real zeros. Holt 5.5 Complex Numbers and Roots 90 min. 2A.8 2A.8D Review and Quiz 2A.8B The student is expected to analyze and interpret the solutions of quadratic equations using discriminants and solves quadratic equations using the quadratic formula. Essential Questions: How does the solution method of completing the square differ from solving by graphing and factoring quadratic equations? What is the importance of using square roots when completing the square? Why is it important to use perfect squares when completing the square? Vocabulary: Completing the Square MAlg2_3rdIA2b= lesson MAlg2_3rdIA2b_algebra_tiles MAlg2_3rdIA2b_completing_square MAlg2_3rdIA2b_problem_solving MAlg2_3rdIA2b_practice_b 2A.8A 2A.8 Algebra II 45 min. Essential Questions: How can the complex number be used when solving a quadratic function? What occurs when a quadratic equation has no real solution? What form and for what purpose is the complex number “i” used in solving quadratic equations? In complex numbers, which is the complex part and which is the real part? Vocabulary: Imaginary unit, imaginary number, complex numbers, real part, imaginary part, complex conjugate. MAlg2_3rdIA2c= lesson MAlg2_3rdIA2c_warm up activity MAlg2_3rdIA2c_alternate_exploration_trans MAlg2_3rdIA2c_engagement activity MAlg2_3rdIA2c_graphic_organizer_trans MAlg2_3rdIA2c_lesson_quiz_trans Review and Quiz over solving by graphing and factoring and completing the square. Complex numbers and roots may be included at the teacher’s discretion. Intended Learning: This method will allow students how to solve quadratic equations written in standard form. Holt 5.6 The Quadratic Formula 90 min. Essential Questions: How is the discriminant used when determining the type of solution for a quadratic equation? The values of “a”, “b”, and “c” play what role in a quadratic equation when written in standard form? What must occur before using the Quadratic Formula if an equation is written in vertex form? What is the role of the discriminant and for what purpose does it play when solving a quadratic equation? TEXTEAMS: Algebra II Part 2 ETQ: Ensuring Teacher Quality AA: Algebra II Assessments MAP: Maximizing Algebra II Performance SATEC: San Antonio Technology in Education Coalition Page 4 of 5 ACM: Accelerated Curriculum for Mathematics Algebra II ©2009 Austin ISD Strand TEKS Knowledge & Skill Quadratic and square root functions 2A.8 Austin ISD Instructional Planning Guide – Mathematics 3rd Six Weeks IPG – Nov. 10 - Dec. 17 (25 days; 2 days for 6 weeks review/test and 4 days for Final Exams) Student Expectation Resource Time/ Pace Vocabulary: Discriminant MAlg2_3rdIA2d= lesson MAlg2_3rdIA2d_SolvingQuadraticEqsA MAlg2_3rdIA2d_Quadratic_formula MAlg2_3rdIA2d_Exploring_the_Discriminant MAlg2_3rdIA2d_Quiz_Finding_Roots MAlg2_3rdIA2d_homework 2A.8A Intended Learning: The student will learn how tour companies and other businesses use quadratic inequalities to make predictions of profits. 2A.8B Holt 5.7 Solving Quadratic Inequalities 2A.6A 90 min. 2A.2 Teacher Tools 2A.8D The student is expected to solve quadratic equations and inequalities using graphs, tables, and algebraic methods. 2A.8D 2A.6 TAKS OBJ Algebra II 2A.2A Essential Questions: Why is there a procedure in place for solving quadratic inequalities? What are the rules to determine the appropriate portion of a parabola to be graphed? When is the boundary of a parabola dashed or solid? How do you find critical values? Which x-values are tested in the original inequality? How can you determine which intervals belong to the solution set of an inequality? Vocabulary: Quadratic inequality in two-variables MAlg2_3rdIA2e= lesson MAlg2_3rdIA2e_warm_up_trans MAlg2_3rdIA2e_alternate_exploration_trans MAlg2_3rdIA2e_engagement activity MAlg2_3rdIA2e_Additional Clarifying Activity MAlg2_3rdIA2e_additional_examples_trans MAlg2_3rdIA2e_graphic_organizer_trans MAlg2_3rdIA2e_lesson_quiz_trans TEXTEAMS: Algebra II Part 2 ETQ: Ensuring Teacher Quality AA: Algebra II Assessments MAP: Maximizing Algebra II Performance SATEC: San Antonio Technology in Education Coalition Page 5 of 5 ACM: Accelerated Curriculum for Mathematics Algebra II