ch 4 summary
advertisement

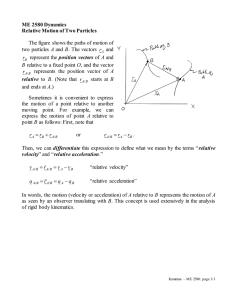
Chapter 4 summary Position vector: ( 𝑟⃗ =𝑥𝑖̂ + 𝑦𝑗̂ + 𝑧𝑘̂ ) Displacement : change in position vector ( ∆𝑟⃗ =∆𝑥𝑖̂ + ∆𝑦𝑗̂ + ∆𝑧𝑘̂ ) ∆𝑟⃗ Average velocity ( 𝑣⃗ avg = Instantaneous velocity ( 𝑣 Average velocity ( 𝑎 ⃗ avg = Instantaneous acceleration (a = ∆𝑡 ) 𝑑𝑟⃗ = 𝑑𝑡 ) ⃗⃗ ∆𝑣 ∆𝑡 ) ⃗⃗ 𝑑𝑣 𝑑𝑡 ) Exercises: 1. Find the position vector ( 2m ,-1m,-3m ) 2. A particle moves through displacement [(2𝑚)𝑖̂ + (6𝑚 )𝑗̂ − (4𝑚)𝑘̂] in (2 s ) find the average velocity ?? 3. The x and y component of an object moving in xy plane are given as( x=2t3 – 2t2 +t) m and (y=3t2+2t) m determine :at ( t=2 s) The position vector Velocity vector Acceleration vector 4. At t=0 the velocity of a particle is measured to be 3 m/s along the negative y- axis and its acceleration is a=( 2𝑖̂ − 4𝑗̂) (m/s2) Find the velocity vector as a function of time ?? Projectile motion : A projectile is : A particle moving in the x-y plane Have an initial velocity It have the free fall acceleration (g) Projectile motion : the motion of a projectile Vi x = vi cos 𝜃 ( =)ثابته ال تتغير طوال فترة الحركةvx at any time Vi y = vi sinθ Range : horizontal distance (R) R= 𝑣𝑖 2 𝑠𝑖𝑛 2𝜃 𝑔 Maximum range at ( 𝜃= 45°) R max= 𝑣𝑖 2 𝑔 Maximum height ( H = (𝑣𝑖 sin 𝜃)2 2𝑔 أو يمكن استخدام قوانين الحركة: Vertical( ↓)حركة عمودية لألسفل Vertical( ↑)حركة عمودية لألعلى Vf = vi+ gt Vf = vi- gt 𝟏 ∆𝒚 =vi t + 𝟐gt2 Vf2 = vi2+ 2g ∆𝒚 𝟏 ∆𝒚 =𝟐( vf+ vi ) t 𝟏 ∆𝒚 =vi t - 𝟐gt2 Vf2 = vi2- 2g ∆𝒚 𝟏 ∆𝒚 =𝟐( vf+ vi ) t Thrown horizontally ( = 𝜃 )قذف افقيا0 عند اقصى ارتفاعvy =0 لكن vx لها قيمة وهي نفسها السرعة السينية االبتدائية في حركة المقذوفات االلتزام بأمثلة الكتاب: مالحظة Uniform circular motion : it travels around a circle path the tangential velocity of a particle has constant magnitude and change direction continuously . the center petal acceleration has constant magnitude and towards at the center of the circle the velocity and acceleration are perpendicular to each other a= 𝑣2 𝑟 a=center petal acceleration(m/s2) v=velocity (m/s) r= radius (m) ( ) نصف القطر period of revolution : the time taken to complete one revolution 2𝜋𝑟 𝜏= 𝑣 Frequency :the number of revolution per second 1 𝑓= 𝜏 𝑓= 𝑣 2𝜋𝑟