: Institution Academic Department :
advertisement

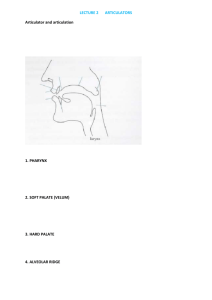
Institution: College of Sciences an Humanitarian Studies in Al Ghat Academic Department : English Department Programme : Bachelor of English Course : Linguistics -1- (320 Eng.) Course Coordinator : Samah Abdel-Karim Ibrahim Programme Coordinator : Dr. Mohanad Sabha Course Specification Approved Date : …./ … / …… H A. Course Identification and General Information Linguistics -1Course Code: 320 Eng. 1. 1 - Course title : 2. Credit hours : Three hours 3 - Program(s) in which the course is offered: Bachelor of English 4 – Course Language : English 5 - Name of faculty member responsible for the course: Samah Abdel Karim Ibrahim 3 level \ 2nd year 2. 6 - Level/year at which this course is offered : 7 - Pre-requisites for this course (if any) : Not found. 8 - Co-requisites for this course (if any) : Not found 9 - Location if not on main campus : )College of Sciences an Humanitarian Studies in Al Ghat( 10 - Mode of Instruction (mark all that apply) A - Traditional classroom What percentage? / 100 % B - Blended (traditional and online) What percentage? ……. % D - e-learning What percentage? ……. % E – Correspondence What percentage? ……. % F - Other What percentage? ……. % Comments : ........................................................................................................... B Objectives What is the main purpose for this course? 1. Summary of the main learning outcomes for students enrolled in the course. After completing the course, students should be able to: 1. Define basic concepts in the major areas of linguistics: phonetics, phonology, morphology, syntax and semantics. 2. Define the field of ‘linguistics’. 3. Describe English sounds using phonological terminology 4. Transcribe simple words . 5. Differentiate between some similar concepts: phonology/phonetics, phoneme/allophone, morpheme/allomorph, derivational/inflectional morphemes, deep structure/surface structure, etc. 6. Explain phonological processes egaP2 fO 9 7. State phonological processes using phonological rules 8. Perform morphological analysis of words 9. Explain basic principles of the various syntactic theories. 10. Perform syntactic analysis of sentences using tree diagram and transformational rules 11. Identify basic principles underlining some semantic theories. 12. Explain the various theories of meaning. Briefly describe any plans for developing and improving the course that are being implemented : Use of www.wiki.com and www.moodle.com and http://el.ksu.edu.sa for writing C. Course Description 1. Topics to be Covered List of Topics Introduction + registry week I. Introduction: A. What is Linguistics? B. Some general principles in linguistics II. Phonetics and Phonology: A. Sounds of English and phonemic symbols 1. Consonants: description and classification 2. Vowels: description and classification 3. Transcription of words B. Structural phonology: phonemes, allophones, and minimal pairs C. Generative phonology: 1. Major class features 2. Phonological rules III. Morphology: A. Definition of morpheme; types of morphemes, problems in morphological analysis B. Morphemes and allomorphs C. Morphological analysis of words IV. Syntax: A. The sentence as a unit of syntactic analysis: Definitions of the sentences in the various approaches to syntax B. Traditional Grammar C. Structural syntax D. Transformational-generative syntax: competence / performance, egaP3 fO 9 No. of Weeks 1 week 1 week Contact Hours 3 hrs 3 hrs 5 weeks 15 hrs 2 weeks 6 hrs 3 weeks 9 hrs phrase structure rules. V. Semantics: A. Meaning of words: 1. sense /reference B. semantic rules C. Lexical relations Review 2 weeks 6 hrs 1 week 3 hrs 2. Course components (total contact hours and credits per semester): Lecture Tutorial Laboratory Practical Other: Total Contact Hours 35 ............ ............ 10 ............ 45 Credit 35 ............ ............ 10 ............ 45 3. Additional private study/learning hours expected for students per week. 3 4. Course Learning Outcomes in NQF Domains of Learning and Alignment with Assessment Methods and Teaching Strategy: NQF Learning Domains And Course Learning Outcomes 1.0 Knowledge 1. The basic concepts in linguistics, 1.1 definitions and application. 1.2 2. The nature of the discipline of linguistics, its branches. egaP4 fO 9 Course Teaching Strategies Course Assessment Methods Lectures Class participation Class discussions/teaching students to think independently and engage in group discussions Quizzes NQF Learning Domains And Course Learning Outcomes 1.3 3. Introducing the different components of grammar: a. phonology: definitions of relevant concepts and terms, description of sounds. Course Teaching Strategies Course Assessment Methods Individual meetings with Midterms students/ encouragement of students to discuss paper topics outside the Final exam class room with the instructor b. phonetics: phonetic symbols c. morphology: what is morphology; types of morphemes; morphological analysis d. syntax: introducing the various syntactic theories; syntactic analysis of sentences e. semantics: different theories of meaning 2.0 Cognitive Skills 2.1 The ability to apply different linguistic rules to different contexts and patterns. Lectures/teaching students how to think Oral presentation of language and deal with it objectively and descriptively. 2.2 The ability to answer applications Ask students in class to assignments and make use of the information bring examples from from primary and secondary sources. languages other than class discussion English, Arabic for example. This enables them to apply the analytic tools learned on new data. 2.3 To gain sufficient knowledge and skill to enable them to perform simple linguistic analysis at various levels: sounds, words, phrases and sentences. 3.0 Interpersonal Skills & Responsibility egaP5 fO 9 Give assignments where In term & final exams they have to solve problems based on theoretical knowledge gained. NQF Learning Domains And Course Learning Outcomes 3.1 Students can participate in class discussion and express their concerns. Course Teaching Strategies Course Assessment Methods Encourage the Allot marks for students to take class participation. responsibility for their own learning. 3.2 Students can complete assignments in due time. 3.3 Students work in group to discuss assignments. Encourage students to Instructor’s assessment of ask questions. students’ performance and seriousness during assignments and class discussion Monitor the Give assignments . students’ cooperation in the group assignments/projects 4.0 Communication, Information Technology, Numerical 4.1 The ability to use good English to . Encourage students demonstrate their knowledge. to make extensive use of the material on the Allot marks for the use of web-based material in students' presentations. web. 4.2 The use of the internet websites to look up information for the assignments. 5.0 Psychomotor 5.1 Not Applicable Provide feedback to Allot marks for extra information the students on their the students get from the web and language in the present in class in assignments/projects. the discussion. Not Applicable Not Applicable 5. Schedule of Assessment Tasks for Students During the Semester: Assessment task egaP6 fO 9 Week Due Proportion of Total Assessment 1 First Mid-term Week 7 20 % 2 Second Mid- term Week 13 20 % 3 Quizzes and assignments throughout 10 % 4 Final exam End of term 50 % D. Student Academic Counseling and Support Arrangements for availability of teaching staff for individual student consultations and academic advice. (include amount of time teaching staff are expected to be available each week) 6 hours per week E. Learning Resources 1. List Required Textbooks : Lobeck, A. (2010). Linguistics for everyone. Wadsworth Cengage Learning. 2. List Essential References Materials : a. Winkler, E. G. (2007). Understanding language. London: Continuum. Crane, Ben et al. (1984). Introduction to Linguistics. b. Fromkin, V, R. Rodman & N. Hyams. (2007). An Introduction to Language, Eighth Edition. Boston: Thompson Wordsworth. c. Yule, G. (2006). The Study of Language, Third Edition. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. d. McGregor, W. (2009). Linguistics: An Introduction. Continuum International Publishing Group. e. Crystal, D. (2003). The Cambridge Encyclopedia of the English Language, Second Edition. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. F. Facilities Required 1. Accommodation Lecture rooms should be large enough to accommodate the number of registered students 2. Computing resources egaP7 fO 9 Laptop computer - projector system 3. Other resources None G Course Evaluation and Improvement Processes 1 Strategies for Obtaining Student Feedback on Effectiveness of Teaching: 1. 1. The feed-back from the in-terms and quizzes increases instructor’s awareness of the weak and strong points of the class 2. End of term college evaluation of course by students 3. Throughout-the-term debriefing in class of students and teacher regarding what went well and what could have gone better. 2 Other Strategies for Evaluation of Teaching by the Program/Department Instructor : Peer evaluation to give instructor objective feedback on some elements of delivery of the course. 3 Processes for Improvement of Teaching : 1. Training sessions 2. Workshops to facilitate the exchange of experiences amongst faculty members 3. Discussion of challenges in the classroom with colleagues 4. Encouragement of faculty members to attend professional development conferences 5. Keep up to date with pedagogical theory and practice 6. Set goals for achieving excellence in teaching at the beginning of each new semester after reviewing last semester’s teaching strategies and results. 7. Regular meetings with the coordinators and other instructors of the course to exchange ideas and discuss ideas and problems. 4. Processes for Verifying Standards of Student Achievement 1. Check marking of a sample of examination papers by another faculty member. 2. Regular meetings with the coordinator and other instructors to exchange samples of exam papers to verify standards of students’ achievement. egaP8 fO 9 3. Students who believe they are under graded can have their papers checked by a second reader 5 Describe the planning arrangements for periodically reviewing course effectiveness and planning for improvement : 1. Compare syllabi and course description with other universities (including those on the net). 2. Regular meetings with the coordinators and other instructors to discuss improvement. 3. Have a curriculum review committee to review the curriculum periodically and suggest improvements. Course Specification Approved Department Official Meeting No ( ….. ) Date … / …. / ….. H Name : Course’s Coordinator Samah Abdel-Karim Ibrahim Signature : Date : egaP9 fO 9 ........................... …./ … / …… H Department Head Name : Dr.Mohanad Sabha .......................... Signature : …./ … / …… H Date :