Cardiovascular Fitness
advertisement
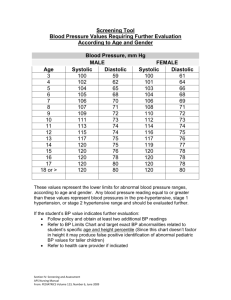
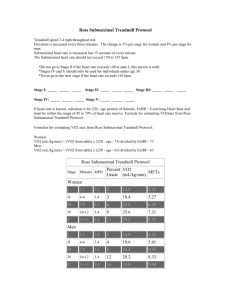
Assessing Cardiorespiratory Endurance A Fitness Indicator Determination of Fitness Level Everyone possesses some degree of cardiorespiratory endurance (CRE) CRE=a health associated component that relates to the ability of circulatory and respiratory systems to supply fuel during sustained physical activity and to eliminate fatigue products after supplying fuel. VO2 max VO2 max is the most commonly used index to assess CRE Definition - The largest amount of oxygen that an individual can utilize during strenuous exercise to complete exhaustion Has become the accepted measure of CRE VO2 max Units – liters/minute or ml/minute (absolute) – ml/kg/min (relative to body weight) – ml/kg of FFM/min (relative to FFM) Range 15 (sedentary with disease) to 75 (young endurance runner) ml/kg/min Women about 10-20% lower than men Methods of Determining VO2 max Submaximally Maximally GXT Graded Exercise Testing - GXT (incremental increases in workload) General Guidelines – measure the subject’s HR and BP and RPE at regular intervals (near the end of each stage [HR, BP, RPE] or every minute [HR]) – if HR does not reach steady state during the stage extend stage 1 minute GXT General Guidelines – All testing begins with a 2-3 min warm-up – Cool- down at a low intensity for at least 4 minutes - continue measuring HR, BP and RPE – increase intensity in .5-2 MET increments – closely observe subject for contraindications Submaximal Protocols Oxygen consumption for any given WL does not vary between subjects The slope of the line is about the same for any two given subjects The rate of increase in O2 consumption with increasing WL does not vary between subjects Bruce Treadmill Protocol 5. Stage 1 – Increase grade to 10% – 3 minutes long – Measure HR at end of each minute and BP at end of each stage Bruce Treadmill Protocol 6. The objective is to reach a steady state HR between 115 and 155 bpm (usually occurs during the first 6 minutes of exercise or by the end of the 2nd stage) – Page 98 guidelines 7. Once subject reaches proper HR terminate the test at the end of that stage Bruce Treadmill Protocol 8. Reduce treadmill speed to 1.7mph and 5% grade and cool-down for 4 minutes. 9. VO2 is estimated from the last minute of a fully completed stage Treadmill Protocol 10. Calculate VO2 from the gender specific equations Males – VO2=SMVO2 [(HRmax-61)/(HRSM-61)] Females – VO2=SMVO2[(HRmax-72)/(HRSM-72)] – SMVO2 = submaximal VO2 from table or ACSM equations – HRSM = submax HR from test Modified Bruce Protocol Start at 1.7 mph, 0% grade or at 1.7 mph and 5% grade (used on diseased and elderly populations) Treadmill Protocol Protocols should be individualized Test time should ideally be 8-12min Increments of 10-15 W/min or 1-3%/min grade can be used for the elderly Maximal Protocols Field Tests 4. 12 minute run 5. 1.5 mile run 6. Rockport Walking Test Normal Responses to GXT 1. Systolic BP increases in direct proportion to increasing WL 2. HR increases linearly with WL 3. Diastolic BP changes very little 4. Shortened QT Interval 5. Reduced R-wave amplitude 6. Positive upslope of ST segment Abnormal responses to GXT 1. ST segment depression 2. Increased R-wave amplitude 3. V-tach 4. Multiform PVC’s 5. Failure of HR to rise with WL 6. Failure of systolic to rise 7. Systolic and diastolic greater than 250 or 120 Test Termination 1. Have reached a pre-determined endpoint Absolute 1. Suspicion of myocardial infarction 2. Moderate to severe angina 3. Drop in Systolic BP with increasing Workload (>20) Absolute 4. Arrhythmias 5. Pale or cold and clammy skin 6. Severe shortness of breath 7. Dizzy, blurred vision, or confusion 8. Patient requests stop 9. V-tach or multiform PVC’s 10. ST segment depression Absolute 11. Excessive rise in BP (systolic >250; diastolic >120) 12. Failure of HR to increase Relative 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. ECG changes from baseline Chest pain that is increasing Wheezing Leg cramps High Systolic/Diastolic Less serious arrhythmias Less severe shortness of breath Advantages of Submaximal Testing 1. Safer 2. Controlled pace (motivation not a factor) 3. Not population specific (no pacing advantage) 4. Quick assessment 5. Cost effective Advantages of Submaximal Testing 6. Don’t need highly trained personnel 7. Can do mass testing 8. No physician supervision required (if symptom and disease free) Disadvantages of Submaximal Testing 1. VO2 max is not directly measured (error rate of 10-20%) 2. Don’t get a measure of true maximal HR – estimates of max HR using 220-age can vary by +15 bpm for individuals of the same age Advantages and Disadvantages of a Maximal Test Advantages 1. More accurate Disadvantages 1. Motivation is a factor 2. More risk involved 3. Time 4. Cost of equipment (if using metabolic cart)