6-1
Market Potential and Sales
Forecasting
Chapter 06
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2008 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Forecasts versus Potential
6-3
Five major uses of potential estimates
To make entry/exit decisions
To make resource level decisions
To make location and other
resource allocation decisions
To set objectives and evaluate
performance
As an input to forecasts
6-4
Deriving Potential Estimates
6-5
Useful Sources for Potential Estimates
Government Sources
Trade Associations
Private Companies
Financial and Industry Analysts
Popular Press
The Internet
6-6
New or Growing Product Potential
Relative Advantage
Compatibility
Risk
6-7
Methods of Estimating Market and
Sales Potential
Determine who are the potential
buyers or users of the product
Determine how many are in each
potential group of buyers defined by
step 1
Estimate the purchasing or usage
rate
6-8
Market Potential: Electric Coil
6-9
Uses of Sales Forecasts
To answer “what if” questions
To help set budgets
To provide a basis for a monitoring
system
To aid in production planning
By financial analysts to value a
company
6-10
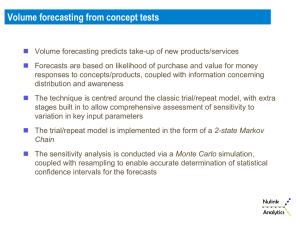
Scenario-Based Forecasts
6-11
Judgment-based Forecasting Methods
Naïve extrapolation
Sales force composite
Jury of expert opinion
Delphi method
Electronic Markets
6-12
Summary of Forecasting Methods
6-13
Graphical Eyeball Forecasting
6-14
Customer-Based Methods
Market Testing
Situations in which potential
customers are asked to respond to a
product or product concept
Market Surveys
A form of primary market research in
which potential customers are asked
to give some indication of their
likelihood of purchasing a product
6-15
Time-Series Forecasting Methods
Moving Averages
Exponential Smoothing
Regression Analysis
6-16
Potential Customers by Industry and
Size
6-17
Sample Data
6-18
Times-Series Extrapolation
6-19
Time-Series Regression Example
6-20
Trial over Time for a New Product
6-21
Model-Based Methods
Regression analysis
Leading indicators
Econometric models
6-22
Forecasting Method Usage
6-23
Use of New-Product Forecasting
Techniques by All Responding Firms
6-24
Developing Regression Models
Plot sales over time
Consider the variables that are
relevant to predicting sales
Customer status and traits
“Our” marketing programs
Competitive behavior
General environment
Collect data
Analyze the data
6-25
Cereal Sales Data (monthly)
6-26
Cereal Data
6-27
Cereal Data Correlation Matrix*
6-28
Regression Results: Cereal Data*
6-29
Format for Reporting a Regression
Model Based Forecast
6-30
The Impact of Uncertain Predictors on
Forecasting
6-31