unit 11
advertisement

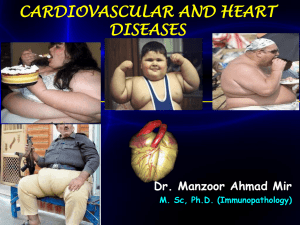
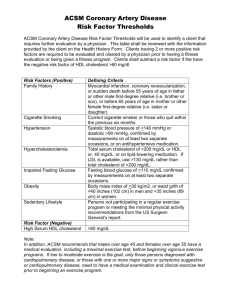
Alterations in the Cardiovascular System DR. MOHAMED SEYAM NORMAL CIRCULATION What is Atherosclerosis what is coronary artery disease? Over time, fatty deposits called plaque build up within the artery walls. The artery becomes narrow. This is atherosclerosis •When this occurs in the coronary arteries, heart does not get sufficient blood, the condition is called coronary artery disease, or coronary heart disease Cardiovascular Disorders: Major cardiovascular disorders include atherosclerosis, stroke, heart attack, aneurysm, and hypertension. Atherosclerosis: Atherosclerosis is due to a build-up of fatty material (plaque), mainly cholesterol, under the inner lining of arteries. The plaque can cause a thrombus (blood clot) to form. The thrombus can dislodge as an embolus and lead to thromboembolism . Stroke, Heart Attack, and Aneurysm: Stroke: A cerebrovascular accident , or stroke , results when an embolus lodges in a cerebral blood vessel or a cerebral blood vessel bursts; a portion of the brain dies due to lack of oxygen. A myocardial infarction , or heart attack , occurs when a portion of heart muscle dies due to lack of oxygen. Angina pectoris: It is the partial blockage of a coronary artery causes angina pectoris , or chest pain. Aneurysm: An aneurysm is a ballooning of a blood vessel, usually in the abdominal aorta or arteries leading to the brain. Death results if the aneurysm is in a large vessel and the vessel bursts. Atherosclerosis and hypertension weaken blood vessels over time, increasing the risk of aneurysm. SYMPTOMS OF A HEART ATTACK Discomfort, pressure, heaviness, pain in the chest, Discomfort radiating to the back, jaw, throat, or arm. Sweating, nausea, vomiting, or dizziness. Extreme weakness, anxiety, or shortness of breath. Rapid or irregular heartbeats. During a heart attack, symptoms typically last 30 minutes or longer and are not relieved by rest or oral medications. Initial symptoms may start as a mild discomfort that progresses to significant pain. people with diabetes have a heart attack without having any symptoms, which is known as a "silent" myocardial infarction (MI). Hypertension: Hypertension About 20% of Americans suffer from hypertension (high blood pressure). Hypertension is present when systolic pressure is 140 or greater or diastolic pressure is 100 or greater; diastolic pressure is emphasized when medical treatment is considered. A genetic predisposition for hypertension occurs in those who have a gene that codes for angiotensinogen , a powerful vasoconstrictor. Cardiovascular Disorders Pulmonary heart disease, a failure of the right side of the heart. Hereditary heart disease, heart disease caused by unavoidable genetic factors Hypertensive heart disease, heart disease caused by high blood pressure, especially localised high blood pressure Inflammatory heart disease, heart disease that involves inflammation of the heart muscle and/or the tissue surrounding it. Valvular heart disease, heart disease that affects the valves of the heart. Venous thrombosis, Varicose veins and Lymphedema Venous thrombosis, This is the formation of a blood clot (thrombus) in a vein. This condition may damage the vein and its valves. In addition, clots that break off and travel in the bloodstream can lodge in the lungs, a condition known as pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis and stroke. Varicose veins, This is a condition in which the veins become twisted and enlarged. The veins are usually located on the backs of the calves or on the inside of the legs, from the groin to the ankle. The veins appear blue because they contain less oxygen. Lymphedema, This is an obstruction of the lymphatic vessels. It results in an excessive build-up of fluid, which can cause swelling and pain. It can be caused by infections, trauma, tumours, surgery and radiation treatment. Arrhythmia / Dysrhythmia Heart block / Atrio ventricular block: Failure of conduction of impulses through the A.V.Node. Damage to the S.A.Node causes week impulses failing to reach the ventricles. Cardiac pacemaker establishes normal rhythm. It is a small, battery-operated electronic device. It is inserted under the skin. It has leads that travel through a large vein to the heart, where the wires are anchored, which send the electrical impulses to the heart. What Increases Risk? You can’t help it ! Age: Men > 45; Women > 55 You can !! High Cholesterol Smoking High Blood Pressure Sex Race Diabetes Family History Obesity Alcohol Physical Inactivity Good Cholesterol vs. Bad Cholesterol LDL cholesterol is known as bad cholesterol. It has a tendency to increase risk of heart disease HDL cholesterol is known as the good cholesterol. Higher in women, increases with exercise LDL cholesterol is a major component of the plaque that clogs arteries HDL cholesterol helps carry some of the bad cholesterol out of arteries. Obesity People who are overweight (10-30 % more than their normal body weight) Obese have 2 to 6 times the risk of developing heart disease Normal Waist-Hip Ratio < 0.85 for women; < 0.95 for men Pears and Apples Pear-shaped paunch store fat on the hips and thighs, just below the surface of the skin. Apple-shaped paunch store body fat around the abdomen and chest, surrounding internal organs Apple- shaped are at a higher risk Cigarette Smoking Increases blood pressure •Decreases HDL •Damages arteries and blood cells •Increases heart attacks •Cigarette smoke contains more than 4,000 chemicals, and 200 of these chemicals are poisonous Diabetes At any given cholesterol level, diabetic persons have a 2 or 3 x higher risk of heart attack or stroke A diabetic is more likely to die of a heart attack than a non-diabetic ~80% Diabetics die from heart disease Risk of sudden death from a heart attack for a diabetic is the same as that of someone who has already had a heart attack. Preventing Heart Disease Rule #1 Look before your eat Limit your intake of foods high in calories and low in nutrition, including foods like soft drinks, candy, junk food Limit foods high in saturated fat, trans- fat and cholesterol Eat less than 6 gms of salt a day Have no more than1-2 alcoholic drink a day if you are a regular drinker Foods rich in Cholesterol and Saturated fats – Egg Yolk – Fatty meat & organ meat( Liver) – Butter chicken / Batter fried fish ! – Milk fat – Desi Ghee, Butter, Cheese, Malai, Rabri, Khurchan, Doda, Ice Cream, full cream milk, – Hidden Fat like Bakery biscuits, Patties (!), Cakes, Pastries, Preventing Heart Disease Rule #2 Exercise Maintain a level of physical activity that keeps you fit and matches the calories you eat Serves several functions in preventing and treating those at high risk Reduces incidence of obesity Increases HDL Lowers LDL and total cholesterol Helps control diabetes and hypertension Exercise significantly reduces the chances of diabetes and stroke With regular exercise, blood pressure in those with hypertension is reduced by as much as 20mms Hg Rule # 3 Stop Smoking NOW The risk of heart attack starts decreasing within 24 hours of quitting smoking, within 1 year of quitting, CHD risk decreases significantly, within 2 years it reaches the level of a non-smoker Smell and taste improve within days Within three months of quitting, the smokers' cough disappears in most people Controlling Blood Pressure Adults should have their blood pressure checked at least once every two years, as there are no symptoms to tell if you have high blood pressure Optimal levels : 120 /80 mm Hg If high Modify your lifestyle – Diet, Weight, Exercise, Salt restriction Adhere to the prescribed medication without fail, to decrease chances of getting heart disease – Do not stop your medicines without consulting your doctor, even if the blood pressure becomes normal