EE2003 Circuit Theory Chapter 19 Two-Port Networks
advertisement

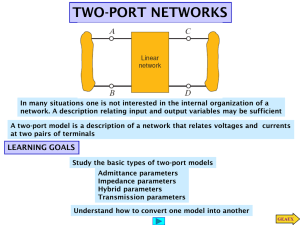
EE2003 Circuit Theory Chapter 19 Two-Port Networks Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Two Port Networks Chapter 19 19.1 19.2 19.3 19.4 19.5 Introduction Impedance parameters z Admittance parameters y Hybrid parameters h Transmission parameters T 2 19.1 Introduction (1) What is a port? It is a pair of terminals through which a current may enter or leave a network. 3 19.1 Introduction (2) One port or two terminal circuit Two port or four terminal circuit • It is an electrical network with two separate ports for input and output. • No independent sources. 4 19.2 Impedance parameters (1) Assume no independent source in the network V1 z11I1 z12I 2 V2 z 21I1 z 22I 2 V1 z11 z12 I1 V z z I z 2 21 22 2 I1 I 2 where the z terms are called the impedance parameters, or simply z parameters, and have units of ohms. 5 19.2 Impedance parameters (2) z11 V1 I1 and z 21 I 2 0 V2 I1 I 2 0 z11 = Open-circuit input impedance z21 = Open-circuit transfer impedance from port 1 to port 2 z12 V1 I2 and I1 0 z 22 V2 I2 z12 = Open-circuit transfer impedance from port 2 to port 1 z22 = Open-circuit output impedance I1 0 6 19.2 Impedance parameters (2a) z11 z12 V1 I1 V1 I2 and z 21 I 2 0 and I1 0 z 22 V2 I1 I 2 0 V2 I2 I1 0 •When z11 = z22, the two-port network is said to be symmetrical. •When the two-port network is linear and has no dependent sources, the transfer impedances are equal (z12 = z21), and the twoport is said to be reciprocal. 7 19.2 Impedance parameters (3) Example 1 Determine the Z-parameters of the following circuit. I1 V1 60 40 Answer: z 40 70 I2 z11 V2 z12 V1 I1 V1 I2 and z 21 I 2 0 and I1 0 z 22 V2 I1 I 2 0 V2 I2 I1 0 z11 z12 z z 21 z 22 8 19.3 Admittance parameters (1) Assume no independent source in the network I1 y11V1 y12V2 I 2 y 21V1 y 22V2 I1 y11 y12 V1 V1 I y y V y V 2 21 22 2 2 where the y terms are called the admittance parameters, or simply y parameters, and they have units of Siemens. 9 19.3 Admittance parameters (2) y11 I1 V1 and y 21 V2 0 I2 V1 V2 0 y11 = Short-circuit input admittance y21 = Short-circuit transfer admittance from port 1 to port 2 y12 I1 V2 and V1 0 y 22 I2 V2 y12 = Short-circuit transfer admittance from port 2 to port 1 y22 = Short-circuit output admittance V1 0 10 19.3 Admittance parameters (3) Example 2 Determine the y-parameters of the following circuit. I2 I1 y11 V1 I1 V1 and y 21 V2 0 I2 V1 V2 0 I2 V2 V1 0 V2 y12 0.75 0.5 S 0.5 0.625 Answer: y I1 V2 and V1 0 y 22 y11 y12 y S y 21 y 22 11 19.3 Admittance parameters (4) Example 3 Determine the y-parameters of the following circuit. I1 y11V1 y12V2 I1=i V1 0.15 0.05 y Answer: 0.25 0.25 S I 2 y 21V1 y 22V2 I2 Apply KVL V2 V1 8I1 2(I1 I 2 ) V2 4(2i I 2 ) 2(I1 I 2 ) I1 0.15V1 0.05V2 I 2 0.25V1 0.25V2 12 19.4 Hybrid parameters (1) Assume no independent source in the network V1 h11I1 h12V2 I 2 h 21I1 h 22V2 V1 h11 h12 I1 I1 h I h 2 21 h 22 V2 V2 where the h terms are called the impedance parameters, or simply h parameters, and each parameter has different units, refer above. 13 19.4 Hybrid parameters (2) Assume no independent source in the network V h 11 1 I1 I h 21 2 I1 V2 0 V2 0 h11= short-circuit input impedance () V1 h12 V2 H2 = short-circuit forward current gain h 22 I2 V2 I1 0 I1 0 H12 = open-circuit reverse voltage-gain H22 = open-circuit output admittance (S) 14 19.4 Hybrid parameters (3) Example 4 Determine the h-parameters of the following circuit. I1 I2 V1 I1 h11 V1 V2 h12 4Ω 23 Answer: h 2 1 9 S 3 V1 V2 and h 21 V2 0 and I1 0 h 22 I2 I1 V2 0 I2 V2 I1 0 h11Ω h12 h h h S 22 21 15 19.5 Transmission parameters (1) Assume no independent source in the network V1 AV2 BI 2 I1 CV2 DI 2 V1 A B V2 V2 I C D I T I 2 1 2 where the T terms are called the transmission parameters, or simply T or ABCD parameters, and each parameter has different units. 16 19.5 Transmission parameters (2) V A 1 V2 I C 1 V2 A=open-circuit voltage ratio I2 0 I 2 0 C= open-circuit transfer admittance (S) V1 B I2 D I1 I2 V2 0 B= negative shortcircuit transfer impedance () V2 0 D=negative shortcircuit current ratio 17 19.5 Transmission parameters (3) Example 5 Determine the T-parameters of the following circuit. V1 AV2 BI 2 I1 CV2 DI 2 V1 V2 Apply KVL V1 10I1 20(I1 I 2 ) V2 3I1 20(I1 I 2 ) Answer: 1.765 15.294Ω T 0.059S 1.176 30 260 V2 I2 17 17 1 20 I1 V2 I 2 17 17 V1 18 19.5 Transmission parameters (4) Example 6 The ABCD parameters of the two-port network below are 4 T= 0.1S 20Ω 2 The output port is connected to a variable load for maximum power transfer. Find RL and the maximum power transferred. I1 V1 Answer: VTH = 10V V; RL = 8; Pm = 3.125W. I2 V2 19