Lab6_Slides
advertisement

CS110
Programming 1
Lab
1
CS110
Functions
return_typefunction_name( parameter list )
{
body of the function
}
2
CS110
Functions
The parts of a function:
- type is the type of the value returned by the function.
- name is the identifier by which the function can be called.
- parameters (as many as needed):
• parameter consists of a type followed by an identifier
• each parameter being separated from the next by a comma
- statements is the function's body. It is a block of statements
surrounded by braces { }
3
CS110
Function Arguments
While calling a function, there are two ways that arguments
can be passed to a function:
Call by value: This method copies the actual value of an
argument into the formal parameter of the function.
Call by reference: This method copies the reference of an
argument into the formal parameter.
4
CS110
Call by value Ex.
int addition (int a, int b)
{
int r;
r=a+b;
return r;
}
int main ()
{
int z;
z = addition (5,3);
cout<<"The result is "<< z;
}
5
CS110
Call by reference Ex.
int addition (int a, int b)
{
int r;
r=a+b;
return r;
}
int main ()
{
int z, a=5,b=3;
z = addition (a,b);
cout<<"The result is "<< z;
}
6
CS110
Math Operations in C++:
C++ math libraries accessed by
including<cmath>header file.
#include<cmath>
7
CS110
Math Operations in C++:
• Sin-compute sine function
•Pow-raise to power function
• Sqrt-compute a square root value
• Floor-round down value
•Abs-compute absolute value
8
CS110
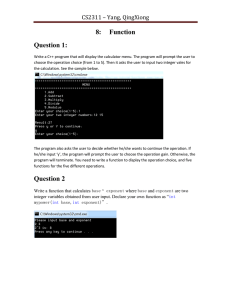
Question
Write the two functions :
• integerPower( int base, int exponent ) that returns
the value of base exponent. For example,
integerPower( 3, 4 ) = 3 * 3 * 3 * 3.
(the function should use while or for loop ).
•integerSqrt(int num):
That returns square of number.
9
CS110