Embryology lecture HUMN110. Development in second week
advertisement

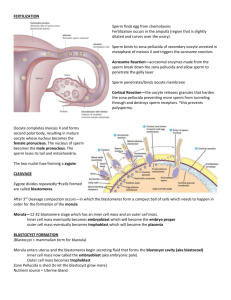
Dr. FARHAT AAMIR Lecturer of Anatomy and Embryology Objectives a)Discuss the changes and formation of bilayer differentiation of trophoblast b)Describe lacunar phase of trophoblast and formation of primitive yolk sac c)Discuss the developmental change in trophoblast and blastocyst in day 11 and 12 of gestation d)Describe the formation of definitive yolk sac, chorionic cavity and chorionic plate e)Discuss Abnormal Implantation DAY 8 - The blastocyst is formed of trophoblast inner cell mass and blastocyst cavity. It is partially embedded in the endometrial stroma. A - The trophoblast in the area over the embryoblast, has differentiated into 2 layers: 1. An inner layer of mononucleated cells: The cytotrophoblast. 2. An outer multinucleated zone without definite cell boundaries: The syncytiotrophoblast. - Mitotic figures are found in the cytotrophoblast: So cells in the cytotrophoblast divide and migrate into the syncytiotrophoblast, where they fuse and lose their individual cell membranes. - Mitotic figures are not found in the syncytiotrophoblast. B - Cells of the inner cell mass is differentiated into 2 layers: 1. A layer of small cuboidal cells: Adjacent to the blastocyst cavity, known as the hypoblast layer. 2. A layer of high columnar cells: Adjacent to the amniotic cavity, the Epiblast layer. - Together, the 2 layers form a flat disc. - At the same time: A small cavity appears within the Epiblast and it enlarges to become the amniotic cavity. - Epiblast cells adjacent to cytotrophoblast layer called Amnioblasts. Amnioblasts with the rest of the Epiblast they line the amniotic cavity. - The endometrial stroma: Adjacent to the site of implantation is edematous and highly vascular. The large, tortuous glands secretes abundant glycogen and mucus. DAY 9 The blastocyst: It is more deeply embedded in the endometrium and the penetration defect in the epithelium is closed by fibrin clot. 1. At the embryonic pole of trophoblast: It shows progress in the development and multiple vacuoles appear in the syncytium. The vacuoles fuses to form large lacunae and this phase is known as (lacunar stage). 2. At the abembryonic pole of trophoblast: - Flattened cells originating from the hypoblast to form thin membrane called the exocoelomic membrane that lines the inner surface of the cytotrophoblast. - This membrane together with the hypoblast, forms the lining of the exocoelomic cavity, or primitive yolk sac. DAYS 11 AND 12 The blastocyst: It is completely embedded in the endometrial stroma and the surface epithelium covers the original defect in the uterine wall. 1. At the embryonic pole: The trophoblast is characterized by lacunar spaces in the syncytium that forms intercommunicating network. - Cells of the syncytiotrophoblast penetrates the endothelial lining of the maternal capillaries. - These capillaries are congested, dilated and known as sinusoids. - The lacunae become continuous with the sinusoids and maternal blood enters the lacunar system to share in the uteroplacental circulation. - At the abembryonic pole: - A new population of cells derived from the yolk sac cells appears between the cytotrophoblast and the exocoelomic cavity. - These cells forms the extraembryonic mesoderm that fills all of the space between the trophoblast externally and the amnion and exocoelomic membrane internally. - Large cavities develops in extraembryonic mesoderm then fuses to form the extraembryonic or chorionic cavity . - This space surrounds the primitive yolk sac and amniotic cavity, except where the germ disc is connected to the trophoblast by the connecting stalk. - The extraembryonic mesoderm lining the cytotrophoblast and amnion is called the extraembryonic somatic mesoderm. - The lining covering the yolk sac is known as the extraembryonic splanchnic mesoderm. - Growth of the bilaminar disc is relatively slow compared with that of the trophoblast. DAY 13 - The surface defect in the endometrium has usually healed. - Bleeding occurs at the site of implantation as a result of increased blood flow into the lacunar spaces. - The trophoblast is characterized by villous structure: Cells of the cytotrophoblast proliferate locally and penetrate into the syncytiotrophoblast to form primary villi. - The hypoblast produces additional cells that migrates inside the exocoelomic membrane. - These cells proliferate and gradually form new cavity within the exocoelomic cavity called secondary yolk sac or definitive yolk sac. - The yolk sac is much smaller than the original exocoelomic cavity or primitive yolk sac. - The extraembryonic coelom expands to form chorionic cavity. - The extraembryonic mesoderm lining the cytotrophoblast is known as the chorionic plate. - The extraembryonic mesoderm traverse the chorionic cavity at the connecting stalk (Future umblical cord). Clinical application Normal site of implantation: The blastocyst implants along the anterior and posterior wall of the body of the uterus. Abnormal site of implantation: A. Intrauterine: Outside the normal site of implantation as Placenta Previa: 1. Complete Placenta Previa. 2. Partial Placenta Previa. 3. Marginal Placenta Previa. 4. Low lying Placenta Previa. B. Extra uterine (Ectopic pregnancy): Outside the uterine cavity. 1. In the fallopian tube: It represent 95% of Ectopic pregnancy. 2. In the ovary. 3. Abdominal cavity.