U.RADHAKRISHNAN.M.P.T
advertisement
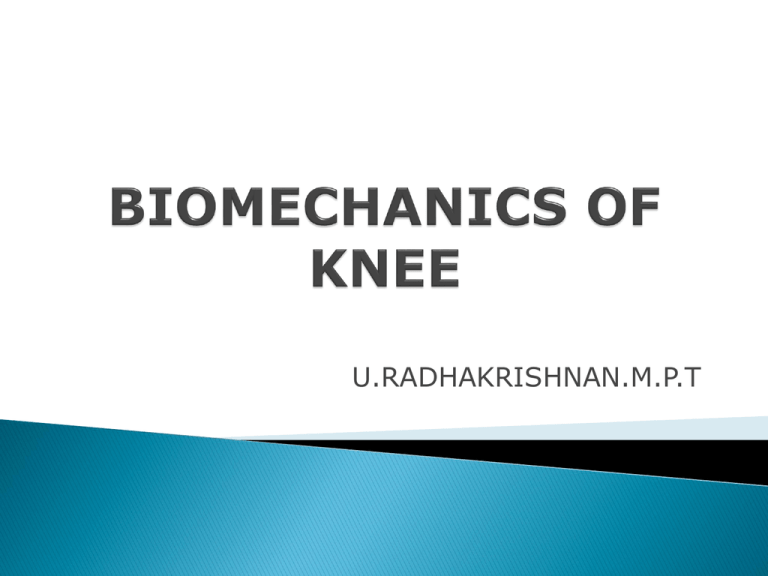
U.RADHAKRISHNAN.M.P.T Knee Joint produces Functional shortening and Lengthening of extremity Knee complex plays a major role in supporting the body in Dynamic and Static situation The Knee complex is composed of TIBIOFEMORAL JOINT PATELLOFEMORAL JOINT ARTICULATION: ON DISTAL FEMUR-----Convex,Asymmetric,Medial and Lateral condyle ON PROXIMAL TIBIA------Concave,Asymmetric,Medial and Lateral Plateau The FEMORAL CONDYLES are twice as large as length of TIBIAL CONDYLES Fibrocartilaginous Joint Disc Medial and Lateral Menisci---asymmetric The two ends are called horns Coronary ligament attaches the Menisci to Tibial plateau Transverse ligament joins the two Menisci Medial Menisci is more fixed and attached to capsule and Medial collateral ligament. They are less mobile and prone to injury Stability & Mobility Function STABILITY: Deepens articular surface Keeps the joint surface tight Distribute the load MOBILITY: Reduces friction Joint capsule encloses Tibiofemoral and Patellofemoral Joint. It is large,lax,with many folds The deep folds of capsule forms the Bursae Suprapatellar Bursae Prepatellar Bursae Infrapatellar Bursae Subpopleteal Bursae Gastrocnemius Bursae INTRACAPSULAR LIGAMENT ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT: Extends superiorly and posteriorly attached to posterior part of inner aspect of Lateral condyle of Femur.It is more prone for injury eg. Foot ball players POSTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT: Extends superiorly and anteriorly to attach to anterior portion of inner aspect of Medial femoral condyle MEDIAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENT:(TIBIAL) Extends from medial Femoral condyle to medial part of proximal Tibia,attaches with medial meniscus LATERALCOLLATERALLIGAMENT:(FIBULAR) Extends from Lateral Femoral condyle to head of Fibula STABILITY LIGAMENTS MUSCLES MEDIAL STABILITY MEDIAL COLLATERAL SEMIMEMBRANOSUS LATERAL STABILITY LATERAL COLLATERAL POPLITEUS.IT BAND ANTERIOR STABILITY ANTERIOR CRUCIATE QUADRICEPS, PATELLA POSTERIORSTABILITY POSTERIOR CRUCIATE BICEPS FEMORIS,POPLITEUS ANTEROMEDIAL MEDIAL COLLATERAL,ANTERI OR CRUCIATE QUADRICEPS ANTERIOLATERAL LATERAL COLLATERAL,POSTER IOR CRUCIATE POSTERIOR MEDIAL OBLIQUE POPLITEAL LIGAMENT SEMIMEMBRANOSUS POSTERIOR LATERAL ARCUATE POPLITEAL POPLITEUS A Line runs along the shaft of the Femur and shaft of Tibia they form angle of 170 to 175 degree When the angle is less than 165 degree an abnormal condition called GENU VALGUM, The medial aspect of knee is subjected to distraction force When the angle is more than 180 degree an abnormal condition called GENU VARUM The medial aspect of knee is subjected to Increase compression loading FLEXION- EXTENSION Saggital plane,Mediolateral axis ROTATION Transverse plane,vertical axis Flexion active range is 120 degree restricted by contact of posterior muscle,active insufficiancy passive range is 130 degree During complete Extension, the Tibial tubercle locks in to intercondylar fossa of Femur, it is the closed packed position. ROTATION: It is not possible when knee in full Extension as ligaments are taught When Knee in 90 degree Flexion---Rotation is possible, Lateral rotation is 40 degree and Medial rotation is 30 degree ABDUCTION can be done passively FLEXION AND EXTENSION: During Flexion from full Extension Femoral condyles roll in an posterior direction with sliding anteriorly.In First part of Flexion consist of Rolling and spinning During Extension from full Flexion Femoral condyles roll in an anterior direction with sliding posteriorly.In last few degrees of Extension Femoral condyles Roll and Spin on Tibia Pure Rolling will move condyles out The spin of Femur in last few degree of Extension causes a Medial rotation of Femur on Tibia will keep joint in closed packed position, so Femoral rotation is called LOCKING or SCREW HOME MECHANISM.The Knee is Unlocked by Lateral rotation of Femur In open Kinematic chain Tibia laterally rotates on Femur during last few degrees of Extension to produce LOCKING.Unlocking by Medial rotation. EXTENSORS QUADRICEPS The efficiency of Quadriceps depends on PATELLA,it increases the moment arm Supports the body weight Resist the force of gravity FLEXORS HAMSTRINGS Work more effectively in Knee if they are lengthened over a Flexed hip MEDIAL MENISCUS INJURY: More common,it is fixed, attached to capsule ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY: More common in foot ball players GENU VALGUM/GENU VARUM PREPATELLAR BURSITIS: Inflammation of Prepatellar bursae,common in workers who kneel and work Patella is the largest sesamoid bone ARTICULATION: Patella is attached to the patellar surface on distal Femur. During Flexion , from Full Extension patella slides downwards and rest in intercondylar notch During Extension,from Full Flexion patella slides upwards QUADRICEPS ANGLE( Q ANGLE ): The angle formed by resultant vector of Quadriceps and the pull of ligamentum patella It is found by drawing two lines 1.From ASIS to midpoint of Patella 2.From Tibial tubercle to midpoint of Patella The normal angle is 15 degree When the angle is large -----Lateral pull on patella is increased. PATELLA ALTA: High riding of patella(elevation),there is lateral stress to patella and instability. CONDROMALACIA PATELLA: Softening of articular cartilage of Patellofemoral joint. Later stage fibrillation and thining of cartilage occurs and subchondral bone exposed.