Bacterial Genetics
advertisement

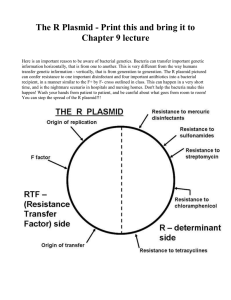
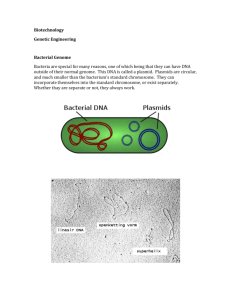
Bacterial Genetics Plasmids Characters Extra-chromosomal circular double stranded DNA molecules. They are dispensable as they are Not necessary for bacterial life. Capable of autonomous replication (independent of the bacterial chromosome). Multiple copies of the same plasmid may be present in the same bacterial cell. Different types of plasmids may co-exist within the same bacterial cell. Types According to transmissibility between the bacterial cells: Conjugative plasmids (transmissible) Non-conjugative plasmids (non-transmissible) Large Usually small 1-2 (stringent) 10-60 (relaxed) Present Absent Contain tra gene Yes No Sex pilus formation Yes No By conjugation By the help of a conjugative plasmid Common in Gram –Ve bacilli Common in Gram +Ve cocci Item Size Copy number Fertility factor (F factor) Transfer among bacteria Host bacteria Functions F- factor plasmid F-factor mediates gene transfer by conjugation. R- factor plasmid These plasmids carry genes encoding antibiotic resistance. These plasmids are usually conjugative. Virulence Plasmids may carry genes that produce toxins which are virulence factors of pathogenic bacteria. Production of bacteriocins Plasmids may carry genes that produce bacteriocins. Bacteriocins or colicins are bactericidal substances produced by certain strains of bacteria and kill other strains of the same or closely related species. Production of antibiotics Plasmids in some bacteria carry genes that produce antibiotics. For example: antibiotic production by streptomyces bacteria. Transposons Characters Fragments of extra-chromosomal DNA. Move inside the bacterial cell by transposition. Move from one location on the bacterial chromosome to another location. Or between the chromosome and plasmid and the reverse. Thus, transposons are called jumping genes. Structure Inverted repeat Transposase gene Repressor gene Inverted repeat Antibiotic resistance gene Transposon is formed of 4 domains: 1) Inverted repeat at each end. 2) Transposase gene: produce the enzyme responsible for excision and integration of the transposon. 3) Respressor gene: regulates domains 2 and 4. 4) Gene coding for: Antibiotic resistance OR Toxin production Insertion sequence o Simple type of transposon. o Carries only the genetic information for its excision and integration. o No antibiotic resistance gene. BEST WISHES