contraception
advertisement

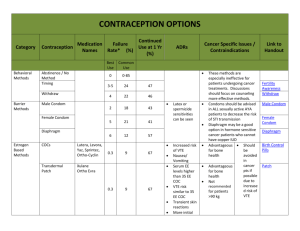
Contraception David Blair Toub, M.D. Dept. of Obstetrics and Gynecology Pennsylvania Hospital Methods Oral Contraceptive Pills (OCP’s) Depo-Provera, Norplant Intrauterine Device (IUD) Male / Female Condom Diaphragm Emergency Contraception (EC) Efficacy (modified from trussell, et. al 1990) Failure Rate (Percent) During First Year of Use 6 6 5 4 3 3 2 2 0.8 0.5 1 0.3 0.1 0 Spermicides Comb. OCP's Prog. OCP's Diaphragm Condom DepoProvera 0.04 Cu-T380A Norplant 0.2 TL Hormonal Contraception: Combination OCP’s Contain Synthetic Estrogen/Progestin Modern E2 Dosage ≤ 50 Mcg Despite Diversity, Side Effects and Efficacies Similar Requires Patient Compliance May Be Monophasic or Triphasic Combination OCP’s: Mechanism of Action Suppresses LH / FSH Release (E2 FSH, P LH) Progestin Thickens Cervical Mucus and Alters Endometrium Major Effect Is Anovulation and Impairment of Sperm Transport and Oöcyte Implantation Combination OCP’s: Additional Benefits Menstrual Regulation Decreased Risk of Anemia Ovarian, Endometrial CA: Risk Lower PID Risk Prevention of Benign Breast Disease Combination OCP’s: Side Effects Breakthrough Bleeding (≤ 25%) Amenorrhea Breast Tenderness, Nausea H/A (+/–) ?HTN ?Weight Gain Combination OCP’s: Risks Thromboembolism (≥ 35 yo, Smoker) MI (Smokers Only): – < 15 cig/day: 3X Risk – > 15 cig/day : 21X Risk Liver Adenomas (Very Rare) Depo-Provera: Inhibits Ovulation 150 mg q3months (14 day grace period) Delayed Ovulation After Discontinuation Main Side-Effects: – Amenorrhea – AUB – Weight Gain – Hair Loss Norplant: Implantable for ≤ 5 Years Similar Side Effects as Depo-Provera Avg. Yearly Failure Rate: 0.8/100 (Increases : > 2/100 after 5 years) Occasionally Difficult to Remove Barrier Methods: Diaphragm: High Failure Rates – Must Remain in ~6 Hrs post-coitus – Best if Combined with Spermicide – UTI Potential Condom: STD Protection, Inconsistent Use by Men Female Condom: Cumbersome, Learning Curve Today Sponge: As seen on Seinfeld IUD: Overview ParaGard (CuT380A), Progestasert Very Effective (~ TL), Reversable Risks OVERBLOWN Monogamy Essential, However Does Not Protect Against STD’s Can Remain for ≤ 10 Years IUD: Mechanisms of Action NOT ABORTIFACIENT!!!!!!!! Prevents Conception: – Sperm Transport Inhibited – Sperm Survival / Capacitation Diminished Prevents Implantation: hCG Levels = 0 IUD: Work-up History: STD’s, Sexual History, Ectopic PEx: Size / Configuration of Uterus Cervical Cultures, Pap Counseling IUD: Contraindications Lack of Monogomy, High Risk for STD’s Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Current Pelvic Infection (GC, Chl) Actinomyces on Pap ???Nulliparity Pregnancy Wilson’s Dz, Cu Allergy (both rare) IUD: Complications PID: Usually 20 Insertional Contamination – Unproven Role for Prophylactic ABx Hypermenorrhea Expulsion Perforation (< 0.1%) Failure: IUD Should be Removed ??Ectopic Emergency Contraception IUD, OCP’s Specific OCP Regimens Given ≤ 72 Hours After Unprotected Intercourse ~ 75% Effective Yuzpe Method: Ovral 2 tabs po now and 2 tabs 120 later May Cause Nausea Consider Dispensing at Yearly Visit Special Circumstances Postpartum/Postabortion: – IUD, Progestins, Combination OCP’s* Anticonvulsant/Antibiotic Use: – TCN Probably OK – Most Anticonvulsants Impair Efficacy of Hormonal Contraceptives * may affect lactation before milk flow established Summary A Limited, but Diverse Range of Contraceptive Options Exist in the USA Barrier Methods Tend to Have Higher Failure Rates than Hormonal Methods and the IUD The IUD is Underutilized All Methods have Risks and May Not be Appropriate for all Patients