PARAM Padma SuperComputer Vishal Bakshi Aditya Polumetla
advertisement

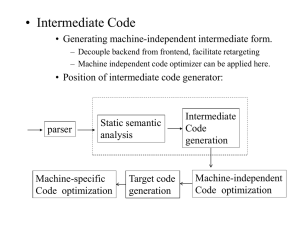
PARAM Padma SuperComputer Vishal Bakshi Aditya Polumetla Topics ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Introduction Specifications Machine Architecture Microkernel Architecture PARAMNet II System Software Applications on PARAM PARAM ● ● ● ● ● ● PARAM – PARAllel Machine Developed by Center for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) India PARAM Padma is the latest in the line of PARAM series after PARAM 8000, PARAM 9000 and PARAM 10000 Introduced in 2003 Its a next generation high performance scalable computing cluster PARAM Padma's theoretical peak performance of complete configuration is 1.13 TFlops PARAM Padma PARAM Padma Configuration Specifications Compute Nodes: • • • • 248 Power 4 1 Ghz processors 54 4-way SMP and 1 32-way SMP (Symmetric MultiProcessing) configuration OS – AIX / LINUX AIX (Advanced Interactive eXecutive) is a IBM's UNIX operating system Aggregate Memory of 0.5 TeraBytes Specifications continued Network: • • PARAMNet II (primary) GigaByte Ethernet (backup) File Servers: • • • • 24 UltraSparc-III 900MHz processors 6 4-way SMP configuration OS – Solaris File System – QFS (Quantitative File System) Specifications continued External Storage: • • Storage array 5 TeraBytes Tape Library 12 TeraBytes System Software: • • C-DAC's HPCC Suite of System Software It provides a high flexible software environment for the cluster PARAM Padma System Layout PARAM Machine Architecture PARAM Machine Architecture continued Cluster Personality - Data Link Provider Interface (DLPI) driver allows mapping of common network protocols to the underlying network MPP (Massively Parallel Processor) Personality - Architecture allows microkernel to be loaded on compute nodes - implements custom designed Concurrent Runtime Environment (CORE) - Standard message passing interface 1. Parallel Virtual Machine (PVM) • PARAS Microkernel Architecture • Message for high MPP • Supports multiple tasks with a paged virtual memory space • Multiple threads of execution within each task • Message based interprocess communication • Communication between tasks by message passing • Location independent interprocess communication supported by port abstraction PARAS Microkernel Architecture continued • Services: - An executive which schedules priority based threads - Location transparent interprocess communication mechanism - Simple virtual memory model - Low kernel hardware supervisor PARAS Microkernel – Block Diagram Microkernel Architecture PARAS service request dispatcher routes all requests to appropriate service provides • • Resource Managers - Process Manager - Virtual Memory Manager - Inter-Process Communication (IPC) Manager Microkernel Abstractions • Five basic abstractions supported - Tasks - Threads - Ports - Messages - Regions Operating Environment Operating Environment continued • Components of Operating Environment - Partition Manager: global resource manager and management of that partition's resources - Process Server: Spawning tasks on a node and provides remote system call interface - Microkernel File System Server: to serve UNIX file system calls - Name Server: provides port naming services to user application PARAMNet II • Developed by C-DAC • System Area Network (SAN) switch to interconnect the nodes of the system • Provides a low latency and high bandwidth interconnect • data rate @ 2.5 Gigabits/sec • message latency of 10 µ sec • switch latency of 0.5 µ sec PARAMNet II continued Major components are 1. 8 / 16-port SAN switch 2. Network Interface Card (NIC) with CCP-III (C-DAC Co-Processor) communication coprocessor 3. Application Programming Interface (C-VIPL) C-DAC's Virtual Interface Provider Library PARAMNet II – SAN Switch • Non-blocking crossbar based architecture • 2.5 Gbps full duplex bandwidth per port • Distributed schedulers allow individual routing tables per port, allowing for any network topology • More than 8 / 16 ports supported using multi-level switching • Ethernet based management interface allows for remote access and control of multiple switches PARAMNet II – SAN Switch continued Virtual channel based routing with 1 KB buffering per port each at input and output • • Interval routing scheme based on 32-bit header (16-bit routing information) • Group adaptive routing based on LRU algorithm to ensure uniform bandwidth distribution in a group • Point-to-point flow control with pause and resume token PARAMNet II - NIC Provides interface to SANSW8 (8 port ) and SANSW16 (16 port) PARAMNet II switch • • Supports for connection oriented and connectionless protocols • Can be configured for other protocols • Capable of performing I/O from paged virtual memory PARAMNet II – NIC continued Support for up to 1024 connections and up to 1024 completion queues • • Support for different page sizes • Packetization and reassembly done in hardware • Error detection and recovery done in hardware • Latency of 10 µ sec PARAMNet II - C-VIPL PARAMNet II – C-VIPL continued C-VIPL is an application programming interface for PARAMNet II • • Major feature – Thread safe implementation • Supports AIX, Linux, Solaris and Windows OS System Level Block diagram for PARAMNet II System Level Block diagram for PARAMNet II continued PARAMNet II network comprises of N hosts connected in non-blocking fat tree topology • • For more than 8 / 16 hosts multiple SANSW8 / SANSW16 are required • As switch latency is low multiple levels of switches have less latency PARAM Padma and PARAMNet II PARAM Padma has 12 PARAMNet II switches connected to two-level configuration to form 64 node CLOS network • • CLOS Network: multi-stage network topology that provides alternate paths between input and output making it possible to eliminate the blocking that occurs in other networks • Latency associated with packet routing are small for a non -blocking topology HPCC Software HPCC software on the PARAM Padma provides a high performance flexible software environment HPCC Software continued • HPCC Software consists of -program development tools - system management tools - software engineering tools • Provides low overhead for communication • Optimized Message Passing Interface (MPI) Parallel file system with MPI-IO interface to enable applications to scale on large cluster HPCC Software continued C-FPS is a client-server and user level parallel file system that addresses high I/O throughput requirements • • The Fortran programming environment consists of - Fortran 90 compiler, - parallelizing compiler for Fortran 77/90 for SMP - integrated development environment and Fortran 77 to Fortran 90 converter HPCC Software continued The DIViA debugging environment comprises of a coherent set of tools that help programmers in debugging parallel programs • • PARMON the system management tool, enables the administrator to monitor activities and resource utilization of various cluster components • RMS resource management tool enables users to optimally schedule jobs across the cluster nodes Storage Architecture Storage is provided by Storage array and Tape library • • Storage Area Network • PARAM Padma has a network centric storage architecture • Storage capacity of 5 TB scalable to 22 TB • Use of Fibre Channel Arbitration Loop (FC-AL) technology to interconnect storage subsystems Applications on PARAM Padma • Bioinformatics - stimulations of large bio molecules - analysis of large databases for studying functions of genes • Computational Structural Mechanics - fracture analysis - stress analysis - visualization for structural and fluid mechanics - study of thin walled structures Applications on PARAM Padma contt • Seismic Data Processing - for oil and natural gas exploration • Computational Chemistry - calculation of electronic structure and properties of molecules - molecular dynamics simulation • Computational Fluid Dynamics - simulation of external and internal flows - simulation of hypersonic flows References 1. http://cdac.in/html/parampma.asp 2.A Microkernel Based Operating System for PARAM 9000, Mohan Ram, N et al, CDAC 1995 3. PARAM Padma – A Teraflops Computing System And High Performance Computing in India, Purohit, S.K., CDAC, 2003 4.Current State and Future Trends in High Performance Computing & Communications (HPCC) Research in India, Sinha, P.K. et al, 10th IEEE Internaltional Workshop on FTDCS 2004. 5.Overview of recent supercomputers, Aad J. van der