Ice Ages of the Pleistocene Epoch
advertisement

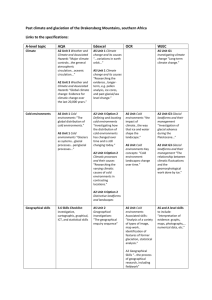
Earth History GEOL 2110 The Pleistocene Epoch The Ice Age Major Concepts • The gradual cooling evident in the mid to late Cenozoic reached a critical threshold which triggered extensive glaciation around 1.8 Ma. • Causes for this general cool down are not generally agreed upon but seem to be related to the dispersal and enlargement of the continents (relative to ocean areas) and thermal isolation of the polar regions. • Multiple cycles of advance and retreat (with periods of about 100,000 yrs most recently) appear to be related to earth’s orbital motions (orbital eccentricity & axial wobble. • These glacial cycles have had a profound global effect on climate, sea level changes, land elevation, distribution of lakes and rivers, and the ecology of the land. The Great Cenozoic Cool Down Thermal Threshold Recognition of Continental Glaciation Drift, Erratics, and Moraines • Hutton (1795) suggests Alpine glaciers more extensive than today • Esmark (1824) first to propose continental glaciation of N Europe • Venetz-Sitten & de Charpentier (1830) confirm Alpine glaciers extended to the Swiss Plain Louis Agazzi – Father of Continental Glaciation Theory (1840) The Swiss-born naturalist came to the U.S. in the mid1800’s and founded the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard. Ichthyologist, paleontologist, geologist, Agassiz mounted the first significant scientific expedition on Lake Superior in the summer of 1848, delivering 12 papers describing his findings at the first annual meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science that fall. Louis Agassiz (1807-1873) The Last Peak of Glaciation 20,000ybp Continental Shelves Exposed Tropical Belt Shrinks, but same climate Siberian Desert The Last Peak of Glaciation 20,000ybp Continental Shelves Exposed Missouri and Ohio – Pro-glacial Drainage Pathways of Glacial Meltwaters Semi-arid desert - Loess Effects of Glaciation Isostatic Rebound Effects of Glaciation Sea Level Change Minimum – 140m Maximum + 65m Effects of Glaciation Sea Level Change River Terraces Develop as Base Levels Drop in Steps Effects of Glaciation Large Meltwater Lakes Ice Dam Lava Dam Potholes Channeled Scablands of the Columbia Plateau Carved 18,000ybp by catastrophic outletting of Glacial Lake Missoula. Water velocities likely topped 50 mph Effects of Glaciation Large Meltwater Lakes Effects of Glaciation Wind-blown Silt - Loess Loess Hills of Western Iowa Palouse Loess of Southeastern Washington Dating Glacial Episodes Techniques: C14 isotopic dating (<80,000y) Fission Track in obsidian K-Ar isotopic dating (>100,000y) Th-Pr dating of clays (<300,000) The Current Glacial Stratigraphy Correlating Glacial Episodes Correlating Glacial Episodes Ice Cores from Greenland and Antarctica Correlating Glacial Episodes Ice Cores from Greenland and Antarctica Correlating Glacial Episodes Lake Sediment Cores Greenland ice core warm Piston Coring cold North Atlantic sediment core Ice rafted debris % cold water foram species Last 650,000 yrs of Glacial Cycles Antarctic Record 380! Current CO2 level Why the Cycles? Possible Factors • Changes in Solar Radiation Can’t Test • Orbital Effects • Changes in Atmospheric Transparency • Changes in Reflectivity – Albedo • Paleogeographic Controls of Climate • Changes to Ocean Currents Volcanism not apparently more prevalent in Pleistocene Why the Cycles? Orbital Effects Milankovitch Cycles Why the Cycles? Orbital Effects What Brought us to the Thermal Threshold? Thermal Threshold What Brought us to the Threshold? Changes in Reflectivity - Albedo •Land more reflective than Oceans •Land area has been growing •Land getting higher – more cloud cover •Ice caps increase albedo - feedback What Brought us to the Threshold? Changes in Paleogeography The Thermohaline Conveyer Belt Brings warm waters to the Arctic The Younger Dryas Small Scale (1,000 y) Cycles Fresh Meltwaters Shut Down the Conveyor Catastrophic Glacial Calving Next Lecture The Pleistocene Epoch The Ice Age in Minnesota Read MN at a Glance – Quaternary Geology