Cu-Ni-PGE Mineralization of MLI
advertisement
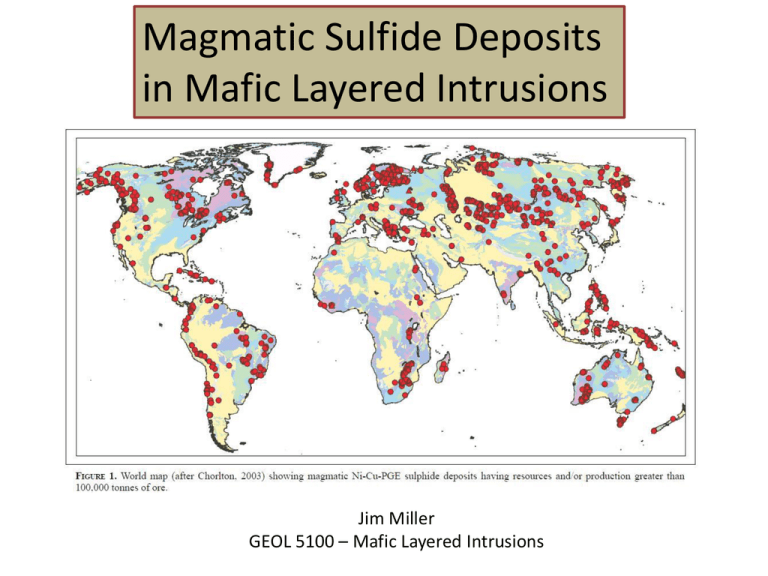
Magmatic Sulfide Deposits in Mafic Layered Intrusions Jim Miller GEOL 5100 – Mafic Layered Intrusions PGE-dominant Deposits Ni-Cu Sulfidedominant Deposits Two Major Groups of Magmatic Sulfide Deposits Naldrett, 2010 Ni-Cu Sulfide Deposits STAGES IN THE LIFE OF A MAGMATIC SULFIDE DEPOSIT Naldrett, 2010 Ni-Cu Sulfide Deposits Partial Melting of the Mantle Adiabatic Rise of Magmas Amount of metals taken up by the magma depends on degree of melting SCSS (sulfide concentration at sulfide saturation) increases with decreasing pressure resulting in sulfide-undersaturated magmas in the upper crust Normal Range of Mantle Melting Crust Mantle Naldrett, 2010 Mavrogenes and O’Neill, 2010 Ni-Cu Sulfide Deposits Contamination by sulfur-bearing country rocks is CRITICAL to formation of magmatic sulfide. Other factors lowering the sulfide carrying capacity of magma, thus promoting sulfide liquation: • Increased Si contamination • Decreased Fe content • Oxidation • Decreased Temperature Mavrogenes and O’Neill, 2010 Lescher and Barnes, 2009 Ni-Cu Sulfide Deposits Metal Tenor of Sulfides controlled by R-factor = Wt% silicate magma/Wt% sulfide liquid and Recharge leading to Upgrading Naldrett, 2010 Li, 2009 Dominant Mineralogy of Magmatic Cu-Ni Sulfide Deposits Po - Pyrrhotite – FeS1-x Cp - Chalcopyrite - CuFeS2 Pn - Pentlandite - (Fe,Ni)9S8 Cb - Cubanite – CuFe2S3 Tk - Talnahkite – Cu9(Fe,Ni)8S16 Bn - Bornite - Cu5FeS4 Cc - Chalcocite - Cu2S Co - Cobaltite - CoAsS Platinum Group Elements (PGE) Platinum Group Minerals (PGM) Metal Alloys or PGEs complexed with Bi, As, Sb, Sn, Pb, Te, IPGEs Follows Ni PPGEs Follows Cu Precious Metal Minerals PMM Name Formula Total # Sulfide Host Mineral Total PMM In Sulfide cp pn cb po tn bn Kotulskite Pd(Bi,Te)1-2 15 8 8 0 0 0 0 0 Froodite PdBi2 11 10 3 6 1 0 0 0 Naldrettite Pd2Sb 3 3 3 0 0 0 0 0 Paolovite Pd2Sn 83 68 45 10 7 4 1 1 Sobolevskite PdBi 2 2 1 0 0 0 1 0 Sperrylite PtAs2 26 22 13 5 3 1 0 0 Stibiopalladinite Pd5Sb2 11 5 4 1 0 0 0 0 Taimyrite (Pd,Pt,Cu)3Sn 2 2 2 0 0 0 0 0 Telluropalladinite Pd9Te4 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 93 68 31 24 3 4 3 3 Undetermined PGM Silver sulfide AgS 16 11 7 3 1 0 0 0 Empressite AgTe 2 2 1 0 0 1 0 0 Hessite Ag2Te 3 3 1 1 1 0 0 0 Electrum AuAg 62 22 12 3 3 3 1 0 Gold Au 17 7 3 1 0 3 0 0 347 234 135 54 19 16 6 4 67% 57% 23% 8% 7% 3% 2% TOTALS % PMM study of NorthMet ore, Cervin, 2011 Ni-Cu Sulfide Deposits Fractionation of Sulfide Liquid MSS –mono-sulfide solution (Fe,NiS) With IPGEs Exsolves to Po + Pn Kullerud (1976) ISS : intermediate sulfide solution (Fe,CuS) Exsolves to Cp-Cb Holwell (2010) Types of Ni-Cu Sulfide Deposits Naldrett, 2010 Eckstrand and Hulbert, 2007 Types of Ni-Cu Sulfide Deposits Naldrett, 2010 Li, 2009 Types of Ni-Cu Sulfide Deposits Naldrett, 2010 Oovoid Ore Body, Voisey’s Bay Types of Ni-Cu Sulfide Deposits Types of Ni-Cu Sulfide Deposits Eckstrand and Hulbert, 2007 Li, 2009 Types of Ni-Cu Sulfide Deposits Duke Island from Ripley, 2009 PGE-dominant Deposits PGE-dominant Deposits PGE-dominant Deposits Comparison of Attributes of Skaergaard-type and Classic PGE Reefs Skaergaard-type PGE Reefs Classic PGE Reefs Tectonic Setting Plume-influenced continental rifts, occur as subvolcanic intrusions Unclear, occur as large, isolated intrusions within Precambrian cratons Age Mesoproterozoic and younger Neoarchean to Paleoproterozoic Parent Magma Aluminous, olivine tholeiite (E-MORB) High-Cr/Mg/Si boninite/komatiite (U-type) with aluminous tholeiite (A-type) Host Rock Gabbroic to ferrogabbroic cumulates (Pl+CpxOxOl); some associated with layering. Pyroxenitic to noritic cumulates; locally associated with chromitite layers, early anorthositic cumulates, and pegmatite. Sulfide Composition of Mineralized Intervals Cu/Ni >100 (closed systems) Cu/Ni = 0.3-5.0 (open systems) Precious Metal Ratios of Mineralized Intervals Pt/Pd = 7 – 0.1 Pt/Pd = 2.5 - 0.2 Pt+Pd/Au = 1 - 10 Pt+Pd/Au > 10 Stratigraphic Distribution of 1 Peak Concentrations Pt / Pd Au Pd / Pt / Au Pt + Pd Cu (Ni) Au Pt + Pd / Ni Cu Au Examples Closed systems - Skaergaard, Sonju Intrusion, New Haven diabase ( below, coincident with, / or) Cu/Ni >1 (open systems) Lake Open systems- Layered Series at Duluth, Kap Edvard Holm Complex, Lake Owen Intrusion, Freetown Complex, Muskox Intrusion, Rincón del Tigre Complex Bushveld Complex, Stillwater Complex, Great Dyke, Munni Munni Complex, Jimberlana Intrusion, Penikat, Portimo and other Fennoscandian intrusions, Rum Intrusion, Muskox Intrusion, Rincón del Tigre Complex Based on data from this study; Arnason and Bird, 2000; Prendergast, 2000; Andersen et al., 1998; Lee, 1996; Bird et al., 1995; Barnes and Francis, 1995; Barnes et al., 1990; Gottfried et al., 1990; Naldrett and Wilson, 1990; Naldrett, 1989b. PGE-dominant Deposits PGE-dominant Deposits Classic PGE reefs involve a mix of ultramafic (U-type) and tholeiitic (T-type) magmas. Reef occurrences commonly occur near the mixed interface. Mineral Norms of Parental Magmas Naldrett, 2010 PGE-dominant Deposits Naldrett, Li, Mungall, Barnes, Maier, .... Boudreau PGE-dominant Deposits Hydromagmatic Model of Boudreau Boudreau, 2009 PGE-dominant Deposits The Cu/Pd Ratio A monitor of sulfide saturation DPd (Sulf/Sil) = ≥ 105 DCu (Sulf/Sil) = 500-1000 DNi (Sulf/Sil) = 300-500 DNi (Ol/Sil) = 2-15 --Pt+Pd --Cu --Ni PGE-dominant Deposits Metal Offsets PGE-dominant Deposits Metal Offsets Kinetic Model (Mungall, 2002) Partitioning controlled more by kinetic effects rather than equilibrium Effective R-factor proportional to diffusivity of metal in silicate melt Other factors: • Size of the sulfide droplets • Duration of that sulfide is in contact with silicate • Viscosity of silicate magma PGE-dominant Deposits Dsulf/sil~105 Dsulf/sil~102 PGE-dominant Deposits Bushveld Complex PGE-dominant Deposits Bushveld Complex PGE-dominant Deposits Bushveld Complex PGE-dominant Deposits Stillwater Complex, Montana - JM Reef Li et al., 2010 PGE-dominant Deposits Stillwater Complex, Montana Cooper, 2009 PGE-dominant Deposits Great Dyke, Zimbabwe Barnes and Maier, 2010 PGE-dominant Deposits Great Dyke, Zimbabwe Li et al., 2010 PGE-dominant Deposits Munni Munni Intrusion Western Australia FennoScandian Intrusions Finnish PGE Reefs SJ Reef