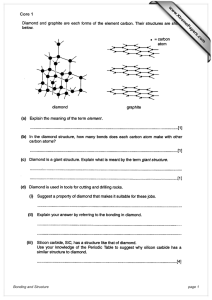
Chemical Basis of Life
advertisement

Chemical Basis of Life Chemistry • Matter is made up of separate chemical components. – Chemistry = Interactions between atoms/molecules. • Biological function begins at the chemical level. – Hierarchical interactions add function. – Ex. Photosynthesis Sub-cellular concepts • • • • Matter Elements Atoms Natural elements – – – – 92 About 25 essential for life H,O,N,C = 96% of human body Trace elements Periodic Table of Elements Atomic Structure • 3 Basic subatomic particles. – Proton – Electron – Neutrons • Atomic Number • Atomic Mass • Compounds Isotopes • Atoms representing different forms of the same element. • Same number of Protons, but different mass – Different number of neutrons • Radioactive Isotopes Electrons • Arranged in shells • Valence • Reactivity • Molecules Molecular Structure • Structural formula • Ball and stick Chemical Bonding – Ionic Bonds • Form between Ions of opposite charge • NaCl – One atom gives up e- (cation). – One atom recieves e- (anion). – Results in filled outer shells for both. Chemical Bonding – Ionic Bonds Chemical Bonding – Covalent Bonds • Result from electron sharing. – 1 or more pairs of outer shell electrons. – Number of possible bonds = number needed to fill outer shell. Chemical Bonding – Hydrogen Bonds • Attraction between the (+) and (-) ends of a water molecule • Weak bonds • Hydrogen = positive end • Oxygen = negative end Water • Polar molecule – Electronegativity – Polar covalent bonds • Cohesion • Adhesion • Resistant to temperature change More Definitions • Solutions – Solvent – Solute • Aqueous solution = Water is the solvent – Water = Universal solvent – Results from the Polarity pH • Potential hydrogen. • H2O dissociates into H+ and OH- (hydroxide) ions. – Acids – Bases • pH scale pH Scale Chemical Reactions • Processes producing chemical changes in matter. – Reactants – Products • Matter cannot be created or destroyed • Energy flow Types of Chemical Reactions • Synthesis – Ex. A + B => AB • Decomposition – Ex. AB => A + B • Exchange – Ex. AB + CD => AC + BD • Oxidation-Reduction (redox) – Ex. C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP