DETERMINING THE LOCATION OF THE NORTHRIDGE BLIND FAULT
advertisement
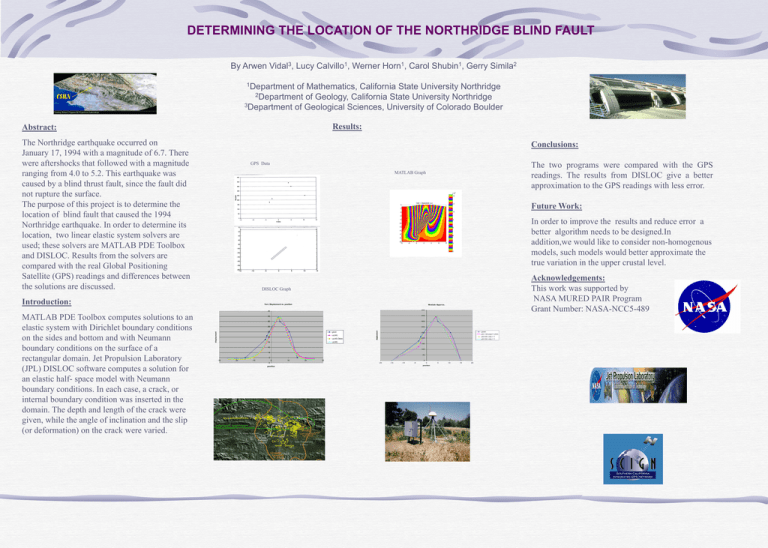
DETERMINING THE LOCATION OF THE NORTHRIDGE BLIND FAULT By Arwen 3 Vidal , Lucy 1 Calvillo , Werner 1 Horn , Carol 1 Shubin , Gerry 2 Simila 1Department of Mathematics, California State University Northridge 2Department of Geology, California State University Northridge 3Department of Geological Sciences, University of Colorado Boulder Results: Abstract: The Northridge earthquake occurred on January 17, 1994 with a magnitude of 6.7. There were aftershocks that followed with a magnitude ranging from 4.0 to 5.2. This earthquake was caused by a blind thrust fault, since the fault did not rupture the surface. The purpose of this project is to determine the location of blind fault that caused the 1994 Northridge earthquake. In order to determine its location, two linear elastic system solvers are used; these solvers are MATLAB PDE Toolbox and DISLOC. Results from the solvers are compared with the real Global Positioning Satellite (GPS) readings and differences between the solutions are discussed. Conclusions: MATLAB Graph Future Work: In order to improve the results and reduce error a better algorithm needs to be designed.In addition,we would like to consider non-homogenous models, such models would better approximate the true variation in the upper crustal level. Acknowledgements: This work was supported by NASA MURED PAIR Program Grant Number: NASA-NCC5-489 DISLOC Graph Introduction: Vert. Displacm ent vs. position M atlab Approx. 450 45 400 35 350 30 300 given uz(44) 20 uz(45) Disloc displacement 40 25 displacment MATLAB PDE Toolbox computes solutions to an elastic system with Dirichlet boundary conditions on the sides and bottom and with Neumann boundary conditions on the surface of a rectangular domain. Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) DISLOC software computes a solution for an elastic half- space model with Neumann boundary conditions. In each case, a crack, or internal boundary condition was inserted in the domain. The depth and length of the crack were given, while the angle of inclination and the slip (or deformation) on the crack were varied. The two programs were compared with the GPS readings. The results from DISLOC give a better approximation to the GPS readings with less error. GPS Data given 250 phi =40,s lip=1.25m phi=40, s lip = 1 200 phi=42, s lip = 1 uz(46) 15 150 10 100 5 50 0 -30 -20 -10 0 -5 position 10 20 30 0 -20 -15 -10 -5 0 position 5 10 15 20