Cell Membrane
advertisement

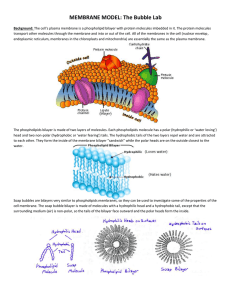
Cell Membrane: Gateway to the World Three Components: Phospholipid Bilayer, Integral Proteins, Glycolipids/Glycoproteins Physpholipid Bilayer: Two layers of lipid molecules consisting of a hydrophobic tail and a hydrophilic head. Hydrophilic head: made of phosphate and glycerol, water-liking Hydrophobic tail: made of lipids, water-disliking Integral Proteins: Two Types: o Protein Channels: allow large molecules like glucose access to the cell. o Protein Pumps: pump charged ions across the membrane to maintain homeostasis Glycolipids/Glycoproteins: complex sugar molecule found on the exterior of the cell, help the cell membrane to recognize and communicate with other cells Functions: Barrier between interior and exterior of the cell Supports the cell Protects the cell The glucose compounds serve as chemical identification markers (cell adhesion, cell communication, recognition) Allows certain molecules in and restricts other molecules (semi-permeable)