Assignment 1 - Student Version.doc
advertisement

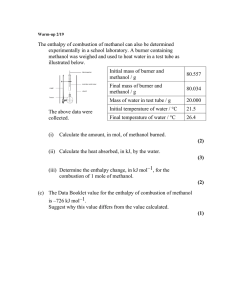
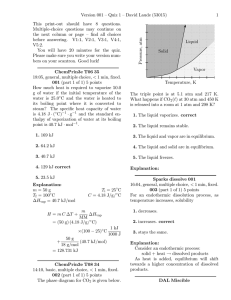
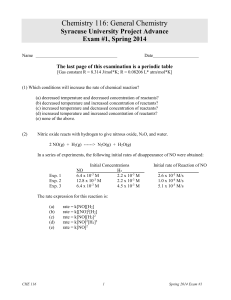
Assignment Problem 1. Solutions of methanol and propanol obey Raoult’s law. At 40 oC, the vapor pressures of pure methanol and pure propanol are 303 and 44.6 torr, respectively. What is the composition of a methanol-propanol solution that has a vapor pressure of 275 torr at 40oC? Problem 2. When a 4.00-g sample of a molecule was dissolved in 30.0 g carbon tetrachloride (CCl4), the boiling point of this solution was determined to be 79.85oC. Calculate the molar mass of the molecule. For CCl4, the boiling point constant is 5.03 oC/m and the boiling point of pure CCl4 is 76.50 oC. Problem 3. An increase of 10 K in temperature doubles the rate of a reaction. What must the activation energy be for this statement to be true for a temperature increase from 20°C to 30°C? Problem 4. A general reaction written as A + 2B C + 2D is studied and yields the following data Experiment 1 2 3 [A]0 (mol/L) 0.16 0.16 0.08 [B]0 (mol/L) 0.15 0.30 0.30 Initial -[A]/t (mol/L·s) 0.08 0.32 0.08 a. What is the rate law for this reaction? b. What is the magnitude of the rate constant for the reaction? c. What are the units for the rate constant for this reaction? d. What is the order of this reaction? Problem 5. A mixture of 0.100 mol of NO, 0.0500 mol of H2, and 0.100 mol of H2O is placed in a 1.00-L vessel. The following equilibrium is established: 2NO(g) + 2H2 (g) N2(g) + 2H2O(g) At equilibrium [NO] = 0.0620 M. Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of H2, N2, and H2O.