Chapter 6 Photosynthesis.doc
advertisement

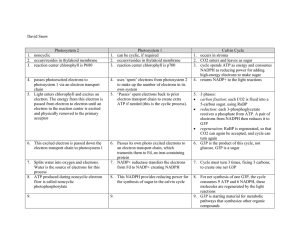
Chapter 6 Photosynthesis Sunlight energyfood energy Plants and algae are autotrophs They just need CO2 and light to make food Key to the first steps in photosynthesis are pigments Light is part of the electromagnetic spectrum Low energy/high wavelength/low frequency High energy/ low wavelength/high frequency InfraredROYGBIVUltraviolet When pigments absorb light, they get charged up (reduced) 6H20 + 6CO2 6O2 + C6H12O6 Low energy high energy Endergonic 1) Light dependent reactions (require light) Sunlight energy electron carriers (reduced molecules) ATP and NADPH 2) Light independent reactions (require CO2) Electron carriers sugar molecules Chloroplasts contain stacks of thylakoids; stacks are called grana. More thylakoids=more photosynthesis. Photosystem II Energy from sunlight is used to make P680 a very powerful reducing agent, powerful enough to reduce water H2O oxygen + hydrogen Electrons are removed from water (low energy state); raised to a high level of energy Electrons flow down electron transport chain, Energy is used to make ATP (high energy) Photosystem I Takes sunlight energy, raises electron energy again, electrons flow down a second electron transport chain, energy used to NADP+NADPH NADPH (reduced, high energy) Light independent reactions (Calvin Cycle) ATP + NADPH + CO2 G3P (very small, 3 carbon sugar) Sometimes the Calvin Cycle is delayed following the Light Dependent Reactions.