Improving Compliance with Surviving Sepsis Goals
advertisement

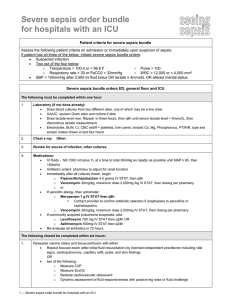
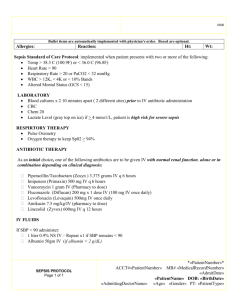
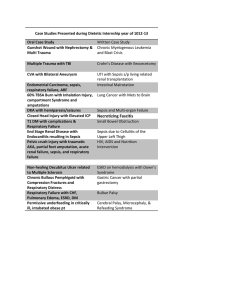
Improving Compliance with Surviving Sepsis Goals Bela Patel, MD Tammy Campos RN Lillian Kao MD Sepsis • • • • 10th most common cause of death in US Leading cause of death in ICU 17 billion dollars/year Sepsis is the body’s response to infection – Severe sepsis: multiple organ dysfunction – Septic shock: hypotension – Septicemia: bloodstream infection • Estimated 800,000 cases of severe sepsis per year in the US • Rate increasing by 1.5% per year – estimated additional 1 million cases by 2020 Incidence of Severe Sepsis & Septic Shock 800,000 600,000 Severe sepsis 800,000 400,000 Septic shock 400,000 200,000 Deaths from septic shock 200,000 0 Approximate Cases/Year Projected Incidence of Severe Sepsis Severe Sepsis Cases US Population Sepsis Cases 1,600,000 500,000 1,400,000 400,000 1,200,000 1,000,000 300,000 800,000 200,000 600,000 400,000 100,000 200,000 2001 2025 Year Angus DC, et al. Crit Care Med. 2001. 2050 Total U.S. Population/1,000 600,000 1,800,000 Severe Sepsis: Incidence and Mortality Incidence Mortality 250000 250 Deaths/Year Cases/100,000 300 200 150 200000 150000 100000 100 50000 50 0 0 AIDS Breast Cancer 1st MI Severe Sepsis AIDS Breast Cancer AMI Severe Sepsis Sepsis and Mortality • Mortality 30-50% • 1,400 people per day worldwide die from sepsis • The 28-day mortality rate from sepsis is similar to 1960’s rates for acute myocardial infarction • Surviving Sepsis Campaign – Goal of 25% reduction in mortality by 2009 – Potential lives saved in US: 50,000/ year – Potential lives saved in world: 1,100,000/ year Sepsis Bundles • Bundle: group of interventions when performed together result in better outcomes than each individually • Sepsis Resuscitation Bundle: Evidencebased goals that must be completed within 6 hours for patients with severe sepsis, septic shock and/or lactate > 4 mmol/L • Sepsis Management Bundle: completion of tasks by 24 hours after presentation Resuscitation Bundle 1. Serum lactate measured 2. Blood cultures prior to antibiotic administration 3. Broad-spectrum antibiotics administered Within 3 hours of ED arrival or 1 hour non-ED admission 4. Treat hypotension with fluids +/vasopressors Initial minimum of 20 mL/kg of crystalloid Vasopressors to keep MAP > 65 mm Hg 5. Persistant hypotension Maintain central venous pressure > 8 mm Hg Central venous O2 saturation (Scvo2) > 70% Resuscitation Bundle Rivers E et al. NEJM 2001. Importance of Early Goal-Directed Therapy NNT to prevent 1 event (death) = 6-8 Mortality (%) 60 50 Standard therapy EGDT 40 30 20 10 0 In-hospital mortality (all patients) 28-day mortality 60-day mortality Rivers E, Nguyen B, Havstad S, et al.. N Engl J Med 2001; 345:1368-1377 Management Bundle 1. Administration of low dose steroids in septic shock per ICU policy. 2. Administration of drotrecogin alfa by a standard ICU policy. 3. Glycemic control > lower limit of normal but < 180 mg/dl 4. Maintenance of inspiratory plateau pressure < 30 cm H2O in mechanically ventilated patients. MICU – ED collaboration • The Medical ICU – 16 bed unit that admits approximately 1100 patients per year. – Chief diagnoses include septicemia, respiratory failure, renal failure, and multisystem organ failure secondary to multiple co-morbid conditions • The Emergency Department – Level 1 Trauma Center – 65,000 annual visits Aims To increase mean overall compliance with the Sepsis Resuscitation within 6 hours of arrival from <5% to ≥ 50% within 6 months. To achieve an absolute reduction in mortality in septic MICU patients and decrease length of stay for these patients. Measures of Success • Increased compliance with the individual SRB elements within 6 hours of arrival • Increased compliance with all 6 SRB elements for each patient within 6 hours of arrival • Decreased mortality for sepsis patients • Decreased cost per case • Decreased length of stay What’s so hard? Bundle Compliance for Severe Sepsis Equipment/ Supplies People Lab results not available on computer Drugs and fluids not available in Pyxis Lack of buy-in from key people Bundle increases workload Lack of education about potential to improve outcome Competing tasks deemed more important by residents and nurses ScVO2 catheters not placed prior to ICU transfers from floor Nurses, Residents sidetracked by other patients MICU residents fail to recognize need for intervention Failure of EC residents to identify sepsis Lab tests not ordered in timely way MICU resident unaware that sepsis protocols I nitiated in EC Delay of transfer from EC to MICU of up to 6 hours Residents unaware of change in patient’s condition Protocol not automated -dependent on residents ordering appropriately Lack of standardization delays key interventions Policy, Procedure Communication Non-compliance with resuscitation bundle for severe sepsis Nurses unaware of residents orders How should we do it? Process Map DIAGNOSIS OF SEPSIIS REQUIRING ICU ADMISSION EC DIRECT MICU ADMISSION FLOOR RRT BLOOD CULTURES LACTATE ABG EGDT SEPSIIS NURSE SCREENING TOOL CONFIRM SEPIS ICU TEAM RESIDENT FELLOW ATTENDING 24 HOUR BUNDLE 6 HOUR BUNDLE STEROIDS DROTRECOGIN ALPHA LACTATE BLOOD CX GLYCEMIC CONTROL AB WITHIN 1 HOUR POLICY FOLLOWED PLATEAU PRESSURE HYPOTENSION NO YES EGDT ScVO2.>70 NO MONITOR AND GUIDE TREATMENT BLOOD DOBUTAMINE CONTACT MICU MD Where do we start? Percent Incorrect per Bundle Item 400 100 60 200 40 100 0 C2 C3 Percent Cum % 20 ScVO2 97.2 25.7 25.7 CVP >8 81.0 21.4 47.1 Antibiotics Fluids/Vaso 65.4 59.0 17.3 15.6 64.4 80.0 Lactat e Blood Cultures 40.4 35.2 10.7 9.3 90.7 100.0 0 Percent 80 300 Interventions: Education • Education of multidisciplinary staff including nurses, physicians, nutritionists, respiratory therapists on the resuscitation bundle • National experts invited to provide optimal dialogue for change • Interdepartmental meetings for team building • Sepsis screen checklist placed in each chart for physician screening • Appointed unit champions to assure education was available 24/7 in the ICU and EC • Implemented standardized Sepsis Order Sets to improve compliance • Posted compliance rates in the unit for staff and MDs to see • Posted posters explaining process in ICUs for staff reference Interventions: Tools Interventions: Monitors • Daily audit rounds sheet to track bundle compliance for the physician team • Bundle compliance review regularly in multidisciplinary team meetings • Daily nursing manager rounds to assure bundle compliance • Routine feedback to the EC – Decrease time to initiation of bundle elements – Decrease time to transfer to ICU Interventions: Work Flow • Implemented mini-RCA process to review all failures • Decreased time to central line placement via Clinical Skills Center at UT and ultrasound placement education • Decreased EC to ICU delays with collaborative workflow changes • Transitioned Rapid Response Team (RRT) nurses to incorporate sepsis screening and resuscitation outside of the ICU • Decreased pharmacy time by limiting drug options • Added additional drugs to the Pyxis to assure rapid access • Decreased time to blood transfusion via standardization of order on the sepsis order sets Lactate Blood Cultures Antibiotics Fluids/Vaso CVP >8 ScVO2 Aug-09 Jul-09 Jun-09 May-09 Apr-09 Mar-09 Feb-09 Jan-09 Dec-08 Nov-08 Oct-08 Sep-08 Aug-08 Jul-08 Jun-08 May-08 Apr-08 Mar-08 Feb-08 Jan-08 Dec-07 Nov-07 Oct-07 Sep-07 Aug-07 Jul-07 Jun-07 May-07 Apr-07 Mar-07 Feb-07 Jan-07 Dec-06 Nov-06 Oct-06 Sep-06 Aug-06 Outcomes: Bundle Compliance with Bundle Elements 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Aug-06 Sep-06 Oct-06 Nov-06 Dec-06 Jan-07 Feb-07 Mar-07 Apr-07 May-07 Jun-07 Jul-07 Aug-07 Sep-07 Oct-07 Nov-07 Dec-07 Jan-08 Feb-08 Mar-08 Apr-08 May-08 Jun-08 Jul-08 Aug-08 Sep-08 Oct-08 Nov-08 Dec-08 Jan-09 Feb-09 Mar-09 Apr-09 May-09 Jun-09 Jul-09 Aug-09 Per Cent Compliance Outcomes: 6 of 6 Overall Compliance Patients Who Received 6 of 6 -- Goal 50% 80 60 40 20 0 Outcomes: Mortality Sepsis -Illness Risk 4- Mortality Rate Reduction Jan 04 to Dec 06 Jan-04 EGDT Jan-07- began Jan-07 1.0 UCL=0.887 Proportion 0.8 0.6 _ P=0.398 0.4 0.2 0.0 LCL=0 1 8 15 22 29 Tests performed with unequal sample sizes 36 43 50 57 64 Outcomes: Mortality Sepsis Illness Risk 3 Mortality Reduction EGDT - began Jan - 07 29 1 Jan-04 1.0 Proportion 0.8 0.6 UCL=0.473 0.4 0.2 _ P=0.102 0.0 LCL=0 1 6 11 16 21 26 Tests performed with unequal sample sizes 31 36 41 46 51 Outcomes: Mortality Mortality Rates APR-DRG 720 Septicemia 49% 40% 33 total lives 14% 19% Reduction 10% 26% Reduction Illness Risk 4 Illness Risk 3 Before After Outcomes: LOS, Cost •There has been a $1200 cost per case reduction in direct costs for a total savings of $525,600 based on 440 cases between January 2007 and July 2009. Conclusion • With focused effort, we were able to improve both compliance with individual bundle components and with patients receiving all 6 within 6 hours of arrival. In addition mortality rates, cost per case and length of stay decreased. • This methodology is readily transferrable to additional ICUs and to community hospitals using existing protocols. Acknowlegements • UT Divisions of Critical Care, Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine • UT Department of Emergency Medicine • MHH ICU Nursing Staff • UT-MHH Academy of Patient Safety & Effectiveness • MD Anderson Cancer Center