C15: Our Solar System Exoplanets
advertisement
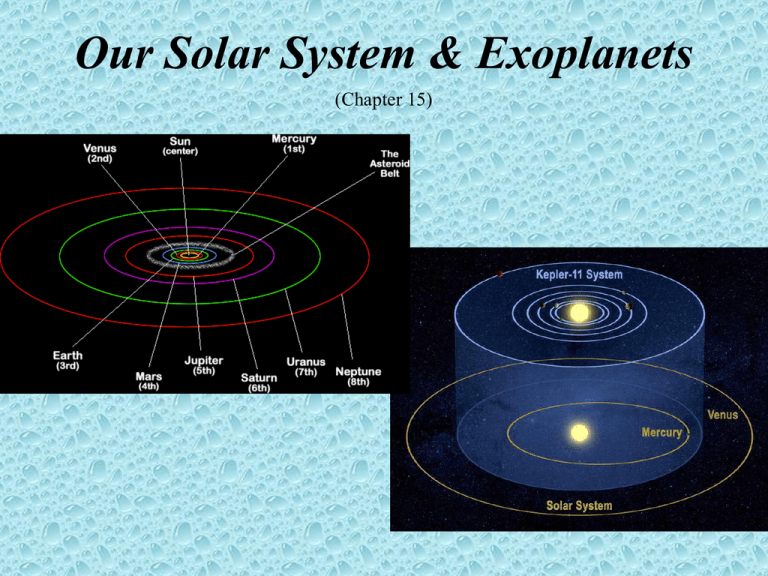
Our Solar System & Exoplanets (Chapter 15) Student Learning Objectives • Identify and locate objects in our solar system • Describe planet formation processes • Explain how exoplanets are found. What are the main characteristics of our solar system? All of the objects in our solar system formed at about the same time. 4.5 Billion Years Ago Objects in our solar system revolve and rotate counterclockwise as viewed from above Venus rotates backwards Uranus rotates on its side Our Solar System Our solar system has one star, the Sun. Planets orbit the Sun. Moons orbit the planets. Dwarf planets orbit the Sun. Asteroids and Comets orbit the Sun. Practice 1) How many stars are within our solar system? 2) How many moons do you think there are in our solar system? 3) List the planets in order from the Sun outward. What is the process of planet formation? Planets form in a disk of rotating gas and dust surrounding a forming star. Solar Nebula Theory Condensation Accretion Planetesimals Proto-planets Planets Two Zones develop during the condensation phase. Near & Far from Sun Metals Far from Sun Ices Iron Water Methane Ammonia Silicates Original Cloud Spins Faster As It Contracts Flattened Disk Of Planets 2nd Stage Planet Formation Migration Differentiation Atmosphere Clearing of the Nebula Bombardment Atmosphere & Leftovers Atmospheres form on some solid planets. Outgassing/Volcanism Gravity Comet Impacts Leftover planetesimals become moons, asteroids, & comets. Large planets capture atmosphere. Phobos Practice 1) Why is the motion of objects in our solar system relatively uniform? 3) What two factors determine whether a planet has an atmosphere? 2) What determines the two zones? 4) Why does Earth have an abundance of oxygen? How do astronomers search for extra-solar planets? Gravity Eclipses Microlensing Direct Imaging http://kepler.nasa.gov/ http://planetquest.jpl.nasa.gov/ (number of exoplanets) Gravitational Wobble Gravity causes a star to wobble. The wobble causes a Doppler Effect. Transits Transits cause some starlight to be eclipsed. http://kepler.nasa.gov/Mission/discoveries/ Microlensing Light follows the curvature of space. Direct Imaging Space telescopes "see" planets Gemini Planet Imager Beta Pictoris b is a giant planet – several times larger than Jupiter – and is approximately ten million years old. (January 2014) Direct Image of an Exo-planet 155 LY Away by David Dickinson May 14, 2014 1st Habitable Zone planet observed (2010) Question: What is the Habitable Zone? Kepler 11 NASA's Kepler Mission Discovers a World Orbiting 2 Stars (September 2011) Kepler 16 NASA's Kepler Telescope Discovers First Earth-Size Planet in Habitable Zone (April 2014) Practice Astronomers are searching for planets around stars like our Sun. Why?