SixSigma[1]
advertisement
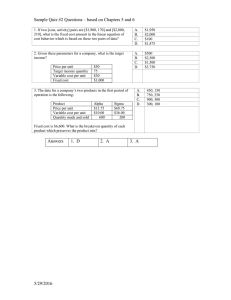
![SixSigma[1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/015258178_1-51e7e9353766c3c214ad38ec0815b258-768x994.png)
Six Sigma By Cathy Hiatt Boise State University October 9, 2001 Overview: • • • • Six Sigma Defined The Statistical Tools of Six Sigma The Components of Six Sigma Corporations practicing Six Sigma and a specific success story • An exercise opportunity • Summary Six Sigma Defined: Quality management program developed by Motorola in the 1980s. Management philosophy focused on business process improvements to: • Eliminate waste, rework, and mistakes • Increase customer satisfaction • Increase profitability and competitiveness Statistical measure to objectively evaluate processes. GOAL: Reach Six Sigma Quality Six Sigma List some ways this program can be used in your organization. The Statistical Tools of Six Sigma: The Statistical Tools of Six Sigma: The Statistical Tools of Six Sigma Another way to look at it: 1. Clearly define the customer’s explicit requirements--CTQ 2. Count the number of defects that occur. 3. Determine the yield-- percentage of items without defects. 4. Use the conversion chart to determine DPMO and Sigma. Sigma Conversion Table: If your yield is: Your DPMO is: Your Sigma is: 30.9% 690,000 1.0 62.9% 308,000 2.0 93.3 66,800 3.0 99.4 6,210 4.0 99.98 320 5.0 99.9997 3.4 6.0 The Components of Six Sigma: • People Power • Process Power People Power: Executive Leader Champion/Sponsor Master Black Belt Black Belt Green Belt Green Belt Green Belt Executive Leader Roles: • High Level Executive committed to Six Sigma Success • Knowledgeable in Six Sigma Process • Assign key individuals to the Champion/Sponsor Position. Champion/Sponsor Roles: • High Level Executive • Oversee the Black Belt positions • Provide resources to complete the job • Assist Black Belts to select projects • Benchmark with other organizations Master Black Belt Roles: • Resource for the Black Belts-experts on the mathematical theory of statistical methods • Experts on the Six Sigma process • Works with the Champion/Sponsor to select projects. Black Belt Roles: • • • • Leaders of the Six Sigma process Management and technical skills Bring the project vision to reality Solely dedicated to Six Sigma Program • Oversee Green Belts Green Belt Roles: • Project Leaders • Support the Black Belt to complete the project Process Power: DMAIC—Five Step Process Define Control Improve Measure Analyze Define: • Clearly identify the problem • Utilize numerical definition • Focus on process that creates the problem not on the outcome Measure: • Benchmark • Capability of a given process • Focus on CTQ Analyze: • Current process results • What is possible compared to what the competition is doing Improve: • Implement changes • Be creative to find new ways to do things better, cheaper, or faster Control: • Lock in successes • Implement measures to keep variables within the new operating limits Corporations Practicing Six Sigma: • • • • • General Electric Motorola Allied Signal Sony Polaroid Specific Success Story: GE • 1995 Operating margin—13.5% • 1998 Operating margin—16.7% • Result: $600million bonus “The most important initiative GE has ever undertaken” --Jack Welch, CEO General Electric Exercise You have just completed all your training sessions for the valued Black Belt role. Currently your organization is operating at a 2 sigma level and your Champion wants this to improve using the Six Sigma process. It seems that although production is high, the defect levels are too high for the production of your leading line of products, Sticky Buns. This has significantly cut into profits almost to the point of dropping the line. Customer surveys indicate there is a demand for Sticky Buns so you are handed the challenging task of improving this process using the Six Sigma DMAIC approach. Summary: • Management philosophy of quality • Statistical target of six sigma or 3.4 defects in one million opportunities • Components of Six Sigma are people power and process power – Executive Leader, Champion, Master Black Belt, Black Belt, and Green Belt – Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control • Customer focus Bibliography • • • Chowdhury, S. The Power of Six Sigma. Chicago: Dearborn Trade, 2001 Pande, P. S., Neuman, R. P., Cavanaugh, R. R. The Six Sigma Way How GE, Motorola, and Other Top Companies Are Honing Their Performance. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2000 Normal Distribution Bell Curve: Six Sigma IT Concepts Kurt Haubner HomePage: http://www.sixsigma.de/english/images/sixsigma/gauss_kurve.gif • Six Sigma Process Graph: http://www.isixsigma.com/me/six_sigma/