Chem 1405 Chapter 1b.doc
advertisement

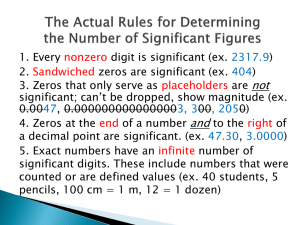
1405 - CHAPTER 1b SCIENTIFIC MEASUREMENTS Precision and Accuracy: Precision is a measure of how closely individual measurements agree with one another. Accuracy refers to how closely individual measurements agree with the correct or true value. Significant figures: They are used to represent the accuracy of a given number. The number of significant figures is equal to the number of digits that are certain and the one that is uncertain. Rules for assigning significant figures 1. All non-zero digits are significant 2. Trailing zeros in a decimal number are significant. 3. Zeros within two non-zero digits are significant. 4. Zeros before the first non-zero digit are not significant. 5. A number ending in zero with no decimal point is ambiguous. For such number, we should use the scientific notation to decide the number of significant figures. Q: Find the number of significant figures in the following 0.0945, 83.22, 0.000550, 105 km, 2001 kg, 0.30050, 21.2m, 453.39 g, 25.9000 g, 20, 100 m. Rounding off. Rule 1. If the digit following the last digit to be retained is less than five, drop the other digits and leave the last digit unchanged. Rule 2. If the digit following the last digit to be retained is 5 or more than five, the last digit to be retained is increased by one unit and drop the other digits. Scientific Notation or Exponential Notation: Writing the numbers using coefficient and exponential factor Rules: 1. For a number greater than one, the decimal is moved to the left to create a coefficient between 1 and 10. Assign a suitable exponential factor using a suitable positive power of 10, which is equal to the number of places the decimal point moved. 2. For a number less than 1, the decimal is moved to the right to create a coefficient between 1 and 10. Assign a suitable exponential factor using a suitable negative power of 10, which is equal to the number of places the decimal point moved. Q: Change into scientific notation: 38, 548 kg, 3847 g, 0.00839, 0.0000568, 87000 yrs, 0.097 sec. Addition, Subtraction, multiplication and division in scientific notation For addition and subtraction modify the numbers such that the exponents are equal. For multiplication, multiply the coefficients and add the exponents. For division, divide the coefficients and subtract the exponents of 10 in the denominator from the exponents of 10 in the numerator. Q. Perform the following calculations. 1. 4.18 x 10-2 + 2.86 x 10-3 2. 5.693 x 10-4 – 3.21 x 10-5 3. Multiply 4.6 x 103 by 2.6 x 10-2 4. Divide 3.45 x 104 by 7.2 x 10-2 Calculation based on significant figures. Rules: 1. In addition or subtraction the final result should be reported to the least number of decimal places as the number with minimum # of decimal places. Q. Perform the following calculations to the correct number of significant figures. a) 35.52+10.3 b) 3.56-0.021 2.In multiplication or division the result should be reported to the minimum number of significant figures as the number with least # of significant figures. Q. Perform the following calculations to the correct number of significant figures. a) 6.26 x 5.8 b) 5.27/12 3.If some exact number is involved the calculation, the result is limited to the number of digits in the other number 11 apples x 0.250g Q: Make the following conversions using the correct significant figures. 4.18 gal to mL, 250 lb to kg, 2.95 ounces to mg, Unit Equations and Unit Factors A unit equation is a simple statement of two equivalent quantities. 1 dollar = 10 dimes 1yard = 36 inches A unit conversion factor is a ratio of two equivalent quantities 1 dollar 10 dimes 36 inches 1 yard The percent concept A percent is the amount calculated out of 100. One quantity x 100% Total sample =%