TAP 534- 2: Making PET scans Making PET scans
advertisement
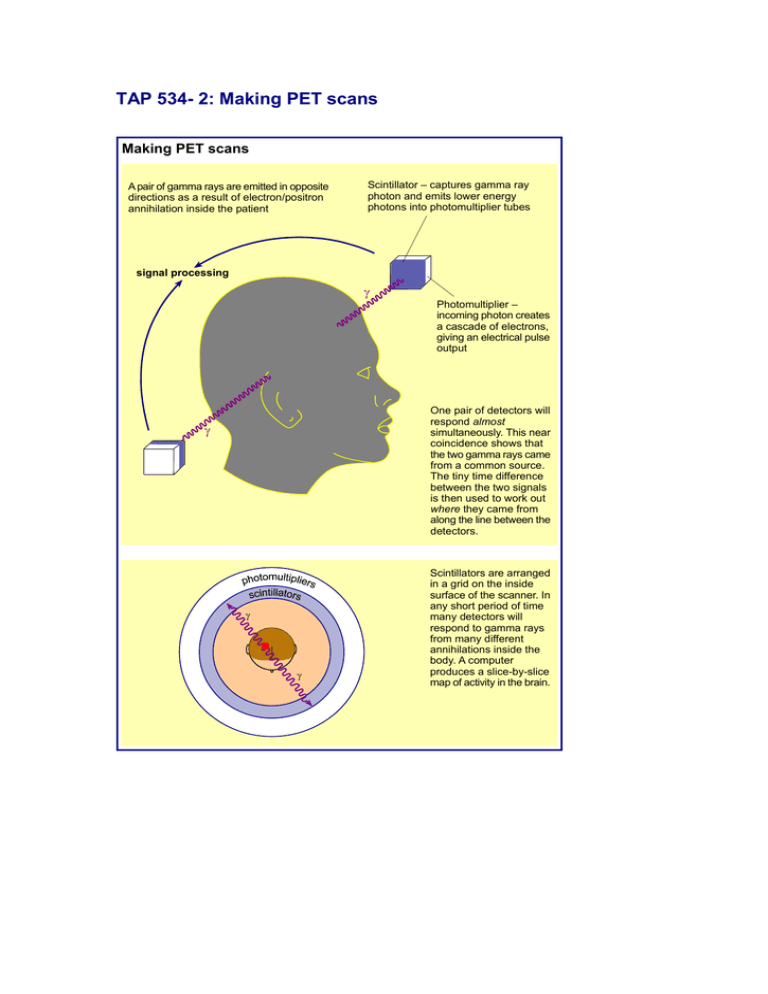
TAP 534- 2: Making PET scans Making PET scans A pair of gamma rays are emitted in opposite directions as a result of electron/positron annihilation inside the patient Scintillator – captures gamma ray photon and emits lower energy photons into photomultiplier tubes signal processing Photomultiplier – incoming photon creates a cascade of electrons, giving an electrical pulse output One pair of detectors will respond almost simultaneously. This near coincidence shows that the two gamma rays came from a common source. The tiny time difference between the two signals is then used to work out where they came from along the line between the detectors. Scintillators are arranged in a grid on the inside surface of the scanner. In any short period of time many detectors will respond to gamma rays from many different annihilations inside the body. A computer produces a slice-by-slice map of activity in the brain. Practical advice This diagram is reproduced here so that you can discuss it with your class. External reference This activity is taken from Advancing Physics chapter 17, 20O











