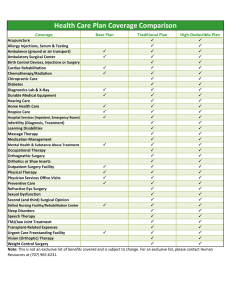
Service Descriptions Goals and Objectives
advertisement

Service Descriptions Goals and Objectives PGY 3 (1 month ENT) To expose the first year plastic surgery resident to general otorhinolaryngology. This will allow our residents to develop knowledge and skills in nasoendoscopy, assessment of the Head & Neck cancer patient, pediatric ENT, management of emergent airway situations, and evaluation and treatment of speech and airway passage pathology. This rotation will allow a greater exposure to facial injuries and fractures, furthering our remedy of marginal facial fracture exposure including zygomatic maxillary, orbital complex and nasal/septal fractures. A. Medical Knowledge* Goal: The resident will achieve a detailed knowledge of the evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment of a variety of disease processes of the head and neck. The resident will be exposed to patients with both medical and surgical emergencies and will become comfortable with the initial evaluation and stabilization of patients. Objectives: 1. Discuss the diagnosis and treatment of patients with ENT emergencies, including: a. b. c. d. e. f. g. epistaxis acute pharyngitis sinusitis otitis media and externa foreign bodies in the ears, nose, and throat acute epiglottis airway obstruction 2. Draw the anatomy of the head and neck with attention to the upper aerodigestive tract. 3. Discuss the physiology of the upper aerodigestive tract. 4. Discuss the management of various infections of the head and neck and the associated complications. 5. Recite the methods of evaluating the head and neck, including endoscopic procedures. 6. Discuss the pathogenesis and common presentations of head and neck malignancies. 7. List the staging systems for head and neck malignancies. 8. Discuss the techniques of evaluation and treatment of metastatic carcinoma in the neck. 9. Discuss the adjuvant therapeutic treatment available for treatment of patients with head and neck malignancies. B. 10. Discuss the options for head and neck reconstruction after extirpative surgery. 11. List the common nonmalignant and malignant diseases of the parotid gland and their treatment. 12. Discuss the common disease entities affecting the facial nerve, including Bell’s palsy. 13. Describe the static and dynamic reconstructive procedures for facial nerve reanimation. 14. Discuss the physiology of the nose, with attention to the nasal cycle, internal nasal valve physiology, and the effect of anatomy on air flow. 15. Discuss the anatomic relationship of the facial nerve with attention to the facial planes. 16. Discuss the branches of the external carotid artery and their courses. 17. Discuss the courses and relationships of the cranial nerves. Patient Care Goal: The resident will provide patient care that is compassionate, appropriate, and effective for the treatment of head and neck problems. Objectives C. 1. Perform a comprehensive head and neck examination including endoscopy. 2. Treat patients with Bell’s palsy. 3. Participate in extirpative surgery of head and neck malignancies including neck dissections. 4. Participate in head and neck reconstructive surgery following extirpative cancer resections. 5. Participate in static and dynamic facial nerve reconstructions. 6. Participate in tracheostomy procedures. 7. Participate in the treatment of airway obstruction. 8. Manage the postoperative care of patients undergoing head and neck extirpative and reconstructive surgery. 9. Become comfortable with nasal exams using a nasal speculum. 10. Manage patients with epistaxis, and become comfortable with nasal packing. Practice Based Learning and Improvement Goal: The resident will investigate and evaluate his or her own patient care practices, appraise and assimilate scientific evidence, and improve patient care practices. Objectives D. 1. Uses information technology to prepare for cases, using in the OR the knowledge of current modalities of care and the scientific evidence for that care. 2. Routinely analyzes the effectiveness of own practices in caring for head and neck surgery patients. 3. Improves own practices in the care of patients by integrating appropriately gathered data and feedback. 4. Educates medical students and other healthcare professionals in the practices of head and neck surgery. 5. Functions independently with graduated advancement and appropriate faculty supervision. 6. Uses library sources to perform research and perform literature searches. 7. Understands the principles of clinical research and the application of biostatistics. Interpersonal and Communication Skills Goal: The resident will demonstrate interpersonal and communication skills that result in effective information exchange and teaming with patients, their families, and professional associates. Objectives E. 1. Educates patients and families in follow-up strategies and rehabilitation for head and neck surgery patients. 2. Demonstrates compassion for patients and families undergoing head and neck surgery. 3. Provides adequate counseling and informed consent to patients. 4. Listens to patients and their families. 5. Assimilates data and information provided by other members of the head and neck cancer team. 6. Charts and records accurate information. 7. Educates patients and families of skin damage, cancerous and pre-cancerous lesions. System Based Practice Goal: The resident will demonstrate an awareness of and responsiveness to the larger context and system of health care and the ability to effectively call on system resources to provide care that is of optimal value. Objectives 1. Coordinates all aspects of the preoperative and postoperative care and rehabilitation of head and neck surgery patients. 2. Creates a cost-effective, focused work-up of diagnostic testing. 3. Advocates for head and neck cancer patients within the health care system. 4. Refers head and neck patients to the appropriate practitioners and agencies. 5. Facilitates the timely discharge and/or placement of head and neck surgery patients 6. Learns to coordinate the admission of patients and communicate with primary care physicians, inpatient house staff, and consultants. 7. Directs the total care of head and neck patients by partnering with the following: a. b. c. d. e. f. F. cancer surgeons reconstructive surgeons radiation oncologists medical oncologists nutritionalists social workers Professionalism Goal: The resident will demonstrate a commitment to carrying out professional responsibilities, adherence to ethical principles, and sensitivity to a diverse patient population. Objectives 1. Develops a sensitivity of the unique stresses placed on families under care for head and neck surgery . 2. Exhibits an unselfish regard for the welfare of head and neck surgery patients. 3. Demonstrates firm adherence to a code of moral and ethical values. 4. Is respectful to patients and their families especially in times of stress to the family unit. 5. Respects and appropriately integrates other members of the head and neck surgery health care team. 6. Provides appropriately prompt head and neck consultations when requested. 7. Demonstrates sensitivity to the individual patient’s profession, life goals, and cultural background as they apply to surgery. 8. Is reliable, punctual, and accountable for own actions in the OR and clinic. 9. Understands the concepts of autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, justice, and respect for life. 10. Maintains patient confidentiality. PGY 3 (1 month Orthopedic Surgery) To expose the first year plastic surgery resident to general orthopedic patient care. This will allow our resident to develop knowledge and skills in evaluating patients with all extremity trauma, spine procedures, joint replacement, orthopedic tumor management, application of rigid fixation (external and internal) for long bone fractures, assessment of radiographic fracture findings, and rehabilitation of the debilitated patient with extremity problems. Also, the resident will develop knowledge and skills in evaluating patients with musculoskeletal neoplasms and become familiar with multiple therapeutic approaches and diagnostic tools. Further, this month will help reinforce the importance of a multidisciplinary team approach to the patient with complex spine and extremity problems. A. Medical Knowledge* Goal: The resident will achieve a detailed knowledge of the evaluation and management of orthopedic patients. Objectives: B. 1. Discuss the basic science component of fracture and soft tissue injury and healing. 2. Discuss the concepts of internal fixation and its influences on fracture healing. 3. List the classification and terminology of open and closed fractures. 4. Discuss the acute management of open and closed fractures. 5. Recite the criteria for the diagnosis of compartment syndrome. 6. Discuss the soft tissue management in open fractures. 7. Discuss the diagnosis and management of malunions, nonunions, and osteomyelitis. 8. Discuss the diagnosis and management of the common soft tissue and bony tumors affecting the musculoskeletal system. Patient Care Goal: The resident will provide patient care that is compassionate, appropriate, and effective for the treatment of orthopedic care. Objectives 1. Participate in the management of skeletal trauma. 2. Learn and participate in splinting and casting techniques. C. 3. Diagnose and treat compartment syndrome. 4. Participate with graduated surgical independence in the open reduction and internal fixation of fractures. 5. Participate with graduated surgical independence in the closed reduction and external fixation of fractures. 6. Participate in the care of acute hand injuries. 7. Attends the sarcoma multi-disciplinary conference. Practice Based Learning and Improvement Goal: The resident will investigate and evaluate his or her own patient care practices, appraise and assimilate scientific evidence, and improve patient care practices. Objectives D. 1. Uses information technology to prepare for surgical cases, bringing to the OR the knowledge of current modalities of care and the scientific evidence for that care. 2. Routinely analyzes the effectiveness of own practices in caring for orthopedic patients. 3. Improves own practices in the care of orthopedic patients by integrating appropriately gathered data and feedback. 4. Educates medical students and other healthcare professionals in the practices of orthopedic surgery. 5. Functions independently with graduated advancement and appropriate faculty supervision. 6. Uses library sources to perform research and perform literature searches. 7. Understands the principles of clinical research and the application of biostatistics. Interpersonal and Communication Skills Goal: The resident will demonstrate interpersonal and communication skills that result in effective information exchange and teaming with patients, their families, and professional associates. Objectives 1. Educates patients and families in post operative and rehabilitative strategies for trauma patients. 2. Demonstrates compassion for patients and families afflicted with trauma. 3. Provides adequate counseling and informed consent to patients. 4. Listens to patients and their families. E. 5. Assimilates data and information provided by other members of the health care team. 6. Charts and records accurate information. System Based Practice Goal: The resident will demonstrate an awareness of and responsiveness to the larger context and system of health care and the ability to effectively call on system resources to provide care that is of optimal value. Objectives 1. Coordinates all aspects of the rehabilitation of the orthopedic surgery patient. 2. Direct the rehabilitation of orthopedic surgery patients by partnering with the following: a. b. c. d. e. F. physical Therapy occupational Therapy PRM physicians social workers nutritionalists 3. Demonstrates knowledge of cost-effective orthopedic care. 4. Advocates for orthopedic surgery patients within the health care system. 5. Refers orthopedic patients to the appropriate practitioners and agencies. 6. Facilitates the timely discharge of orthopedic surgery patients. 7. Works with paramedical professionals in the pre-hospital care of trauma patients. Professionalism Goal: The resident will demonstrate a commitment to carrying out professional responsibilities, adherence to ethical principles, and sensitivity to a diverse patient population. Objectives 1. Develops a sensitivity of the unique stresses placed on families under care for traumatic orthopedic injuries. 2. Exhibits an unselfish regard for the welfare of orthopedic surgery patients. 3. Demonstrates firm adherence to a code of moral and ethical values. 4. Is respectful to hand patients and their families, especially in times of trauma and stress to the family unit. 5. Respects and appropriately integrates other members of the orthopedic surgery team. 6. Provides appropriately prompt consultations when requested. 7. Demonstrates sensitivity to the individual patient’s profession, life goals, and cultural background as they apply to orthopedic care. 8. Is reliable, punctual, and accountable for own actions in the OR and clinic. 9. Understands the concepts of autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, justice, and respect for life. 10. Maintains patient confidentiality. PGY 3 Anesthesia (1 month) To expose our 3rd year residents to the field of anesthesia and management of the patient pre-op and intra-op. This rotation will also allow residents to become familiar with the most advanced methods of airway control, anesthetic agents and intra-operative strategies for managing the critically ill patient. Throughout the month, the 3rd year resident will be embedded into and receive mentorship from a board certified anesthesiologist and her/his team. A. Medical Knowledge Goal: The resident will achieve a detailed knowledge of the techniques and practice of anesthesia. Objectives: B. 1. Discuss the preoperative anesthesia evaluation, including the identification of risk factors (i.e. chronic lung disease, cervical spine disorder) that is critical to the formulation of a safe anesthetic plan. 2. Discuss the appropriate use of regional vs. general anesthesia for a given patient and given procedure. 3. Discuss the indications and contraindications of basic anesthesia pharmacology. 4. Outline the appropriate NPO guidelines for adult and pediatric patients. 5. List the indications for and relative contraindications against regional anesthesia. 6. Describe the common postoperative pain management modalities, including epidural anesthesia. 7. Discuss the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management of pain syndromes. Patient Care Goal: The resident will provide patient care that is compassionate, appropriate, and effective for the treatment of surgical problems. Objectives 1. Participate in the induction, administration, and emergence of general anesthesia. 2. Participate in the administration of regional anesthesia, including: a. b. c. 3. spinal anesthesia epidural anesthesia regional blocks Perform intraoperative monitoring of patients under anesthesia. 4. Manage the complications of general and regional anesthesia. 5. Perform effective airway management skills, including: a. b. c. d. C. mask ventilation endotracheal intubation laryngeal mask airway oral and nasal airways 6. Become certified in CPR and ACLS. 7. Maintain an airway in an anesthetized, spontaneously ventilating healthy patient. 8. Perform laryngoscopy and oral intubation in anesthetized patients. 9. Set-up and check all necessary anesthesia equipment for a surgical procedure. 10. Perform arterial catheterization. 11. Perform central venous catheterization. 12. Perform upper extremity and lower extremity regional anesthesia. 13. Participate in the post anesthesia care unit management of patients, including ventilatory support, pain management, blood pressure control, fluid management, monitoring and appropriate time of discharge. Practice Based Learning and Improvement Goal: The resident will investigate and evaluate his or her own patient care practices, appraise and assimilate scientific evidence, and improve patient care practices. Objectives 1. Uses information technology to prepare for cases, bringing to the OR the knowledge of current modalities of care and the scientific evidence for that care. 2. Routinely analyzes the effectiveness of own practices in caring for surgery patients. 3. Improves own practices in the care of patients by integrating appropriately gathered data and feedback. 4. Educates medical students and other healthcare professionals in the practices of surgery. 5. Functions independently with graduated advancement and appropriate faculty supervision. 6. Uses library sources to perform research and literature searches. 7. Understands the principles of clinical research and the application of biostatistics. D. Interpersonal and Communication Skills Goal: The resident will demonstrate interpersonal and communication skills that result in effective information exchange and teaming with patients, their families, and professional associates. Objectives E. 1. Educates patients and families in post anesthesia care. 2. Demonstrates compassion for patients and families. 3. Provides adequate counseling and informed consent to patients. 4. Listens to patients and their families. 5. Assimilates data and information provided by other members of the health care team. 6. Charts and records accurate information. System Based Practice Goal: The resident will demonstrate an awareness of and responsiveness to the larger context and system of health care and the ability to effectively call on system resources to provide care that is of optimal value. Objectives F. 1. Coordinates all aspects of the post anesthetic care for patients. 2. Demonstrates knowledge of cost-effective anesthetic care. 3. Advocates for patients within the health care system. 4. Refers patients to the appropriate practitioners and agencies. 5. Facilitates the timely discharge of same day surgery patients. 6. Works with primary care physicians, and other consultants such as cardiologists, toward the safe administration of anesthesia. Professionalism Goal: The resident will demonstrate a commitment to carrying out professional responsibilities, adherence to ethical principles, and sensitivity to a diverse patient population. Objectives 1. Develops a sensitivity of the unique stresses placed on families under care for surgical diagnoses. 2. Exhibits an unselfish regard for the welfare of surgical patients. 3. Demonstrates firm adherence to a code of moral and ethical values. 4. Is respectful to patients and their families especially in times of stress to the family unit. 5. Respects and appropriately integrates other members of the health care team. 6. Provides appropriately prompt hand consultations when requested. (Should ‘hand’ be here?) 7. Demonstrates sensitivity to the individual patient’s profession, life goals, and cultural background as they apply to health care. 8. Is reliable, punctual, and accountable for own actions in the OR and clinic. 9. Understands the concepts of autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, justice, and respect for life. 10. Maintains patient confidentiality. Plastic Surgery Residency Overview The plastic surgery residency commences at PGY 4 and completes at PGY 6. Each residency year, each resident spends two months rotating on each of the four primary services. The University of Chicago Medical Center is the location of three primary services organized by sub-specialty focus (Gold, Red, and Blue) and the Northshore Medical Center is the location of the fourth primary service. For the remaining four months of the year each resident is rotating through 3 additional services (‘Hand’, ‘Cosmetic’, ‘Lutheran General Hospital’) in equal time throughout the three years of residency. Plastic Surgery Resident Years (PRSY) PSRY 1 (PGY-4) PSRY 2 (PGY-5) PSRY 3 (PGY-6) Plastic Surgery U of C Gold Service The U of C Gold service will expose to the evaluation and treatment of general plastic and reconstructive surgery issues with a primary focus on, breast reconstruction. The full complement of breast reconstructive management as well as aesthetic surgery of the face and trunk will be provided. The faculties of the U of C Gold Service are Julie Park and David Song. The PSRY 1 (PGY 4) resident will be introduced to the basic principles of breast reconstruction and aesthetic surgery. Diagnosis of conditions and complications as well as a focus of the engaging the multi-disciplinary team for treating breast cancer will be the instruction focus. The second year plastic surgery resident should have a working knowledge of the service and thus will be an integral member contributing to the diagnosis, assessment, surgical plan and care of the patient. Further, a disposition for each patient will be formulated by the second year resident with faculty oversight. The second year resident should also gain the skills necessary to understand and perform the index operations that the Gold service faculty engages in. A thorough knowledge base of breast reconstruction and breast plastic surgery and aesthetic surgery should be developed by the second year resident, and the assessment of that knowledge will be based on the following. The third year plastic surgery resident (chief resident) should demonstrate competence in breast reconstruction and breast plastic surgery and aesthetic surgery. With supervision, the third year resident should be able to diagnose, plan, execute and care for the breast reconstructive and aesthetic patients on the Gold service. Upon completion of the rotation, the third year resident should be able to demonstrate the skills and techniques required to practice safely and independently based upon the following parameters. A. Medical Knowledge Goal: The resident will achieve a detailed knowledge of the evaluation and management of the breast patient. I: 1. Discusses the evaluation, diagnosis, and surgical care of the breast mass. 2. Describes the evaluation of non-palpable breast abnormalities 3. Discusses the appropriate use of mammography, ultrasound, fine needle aspiration, and stereotactic biopsies 4. Discusses the preoperative staging of breast cancer. 5. Recites the use of preoperative chemotherapy and radiation therapy for breast cancer. 6. Describes the indication for operative management of breast disease, and selection of appropriate surgical procedures. 7. Discusses the adjuvant treatment regimens and indications for their use in breast cancer. 8. Describes the treatment of advanced breast cancer. 9. Recites the screening for breast cancer. 10. Discusses the genetic predisposition to breast cancer and prophylactic mastectomy. Microsurgery Goal: The resident will demonstrate knowledge of the principles of microsurgery, and master basic microsurgery techniques, including microneural repair and microvascular anastomosis. Objectives: 1. Explains the use of the operating microscope and the technical aspects of microvascular anastomosis (artery and vein) and microneural repair. 2. Discerns the indications for, the contraindications to, and the techniques for accomplishing replantation of amputated parts. Recognize the techniques of monitoring the success of replantation. 3. Discusses the varying types of blood supply to discrete units of tissue (including arterialized flap, musculocutaneous flap, fasciocutaneous flap). 4. Lists the terms and types of free tissue flaps – skin, skin/muscle, skin/muscle/bone, skin/tendon, muscle alone. 5. Lists in detail the anatomy for harvesting the most common flaps, including latissimus dorsi, rectus abdominis, radial forearm. 6. Discerns the indications for harvesting various flaps and matching donor sites to specific recipient site needs. 7. Discusses radiologic techniques for evaluation of both donor and recipient sites. 8. Discusses the mechanisms and consequences of the no-reflow phenomenon; knows how to treat a failing flap. 9. Discusses the technologic, pharmacologic and physiologic principles of postoperative monitoring of free flaps. 10. Recites the basic physiology of nerve injury (axontomesis, neurotomesis, neuropraxia, Wallerian degeneration) and of nerve healing. 11. Draws the intraneural anatomy and anatomic relationships of structures of the major peripheral nerves. 12. Explains the principles of repair of nerve injury including need for nerve grafting, the anatomy of nerve graft donor sites, and the physiology, timing and techniques of primary, delayed primary and late nerve repair. 13. Discusses the principles and techniques of hematologic manipulation of abnormal vascular flow characteristics. 14. Discusses the technical aspects of microsurgery including: a. b. c. d. 15. II: microscopes – principles, usage sutures – types, indications\ microvascular coupling devices suturing techniques Discusses the use of electrophysiologic tools in the evaluation of nerve injury (EMG, NCS). Implants/Biomaterials Goal: The resident will demonstrate knowledge of both biology and physiology of various implant materials, including bone, cartilage, and alloplasts. Objectives: 1. Identifies the local wound factors which influence bone graft survival. III: 2. Discusses the biologic differences between vascularized and non-vascularized bone grafts. 3. Recites the influence of perichondrial and scoring on the warping of cartilage grafts. 4. Discusses the various types of breast implants and the factors involved in implant choice, including surface content characteristics; is aware of the issues regarding silicone and is able to discuss these with a patient. 5. Discerns the effects of breast implant surface characteristics on formation of capsular contracture. 6. Discusses the various injectable materials for subcutaneous filling and the principles of their use. 7. Discusses the processes of bone repair: incorporation, osteoconduction and osteoinduction. 8. Discusses the difference in incorporation between cortical and cancellous bone grafts and membranous and endochondral autografts. 9. Explains the immunology of bone and cartilage transplantation. 10. Lists the chemistry and biocompatibility of the commonly implanted biomaterials, including silicone, methyl methacrylate, hydroxyapatite, tricalcium phosphate and proplast. 11. Describe the factors involved in the choice of implant materials for varying reconstructive problems. 12. Discusses the chemistry and biocompatibility of commonly injected materials including: collagen (bovine and human), fat, and others. Special Techniques Goal: The resident will demonstrate knowledge of the principles of a variety of special techniques in plastic surgery, including liposuction, tissue expansion, laser treatments and dermabrasion, and utilize the techniques effectively in appropriate clinical scenarios. Objectives: 1. Discusses the basic principles, the common techniques and the instrumentation of suction lipectomy, including tumescence, standard and ultrasonic liposuction. 2. Recites the indications and for contraindications to suction lipectomy, and be familiar with the principles of patient assessment; recognizes the limitations of liposuction. 3. Explains the preoperative, intraoperative and postoperative management of the patient undergoing suction lipectomy; be familiar with the complications of liposuction and their management. 4. Discusses the physiologic principles of tissue expansion. IV: 5. Discriminates the various techniques for tissue expansion and be familiar with the differing expansion devices. 6. Discusses the principles of management of patients undergoing tissue expansion; recognizes and treats the complications of tissue expansion. 7. Discusses the physiologic and pathologic principles of dermabrasion, chemical peel and laser resurfacing; recognize the differences between the techniques and the indications for choice between the techniques. 8. Recites the principles of pre- and postoperative management of patients undergoing facial resurfacing; recognizes the complications of the technique and its management. 9. Explains the pharmacologic aspects and the techniques of chemical peel. 10. Discriminates the biophysical properties of commonly used lasers, and chooses different lasers for different types of problems. 11. Discusses the indications for and contraindications to laser treatments and techniques of laser use, and the various complications of laser therapy and their treatment. Medicolegal and Psychiatric Aspects of Plastic Surgery Goal: The resident will demonstrate a clear understanding of medicolegal and psychiatric aspects of plastic surgery practice, regularly obtain informed consent from patients, and perform a basic psychological evaluation when appropriate. Objectives: 1. Discusses the medical and legal perspectives of the contractual agreement between a physician and his/her patient. 2. Discerns the concepts of informed consent and implied guarantee. 3. Discusses the role of the medical record as a legal document. 4. Discerns the impact physical deformity can have on patients and their families. 5. Discusses techniques to explore the motivations of patients seeking cosmetic surgery, and how to distinguish acceptable, unacceptable, and pathological motivations. 6. Recites the legal and ethical ways to sever the physician/patient relationship. 7. Discusses the various types of malpractice insurance. 8. Discusses the basic principles of risk management. 9. Lists the psychiatric and psychological treatment options for patients with physical deformities and their families. 10. Discusses the strategies to effectively treat the dissatisfied patient/family. B. Patient Care Goal: The resident will provide patient care that is compassionate, appropriate, and effective for the treatment of reconstructive surgery. Objectives: 1. Performs reconstructive surgery on the trunk, breast, and abdomen with increasing independence and surgical responsibility. 2. Participates in treatment of patients with malignancy of the trunk, thorax and abdominal wall. 3. Participates in the surgical management of thoracic and abdominal wall reconstruction with graduated independence, including: a. b. c. d. e. 4. reconstruction following sternal dehiscence and/or infection reconstruction after tumor resection utilizing flaps and grafts reconstruction of radiation injury of the thorax and trunk abdominal wall fascial reconstruction abdominal wound dehiscences and hernias utilizing prosthetic material, grafts, separation of parts Participates in surgical and nonsurgical management of pressure sores including: a. b. c. d. e. f. etiology and staging prevention nonsurgical considerations and management, including patient compliance pressure sore surgery utilizing local flaps, muscle and myocutaneous flaps, and distant flaps complications of surgery rehabilitation 5. Participates in the surgical care of common developmental breast anomalies, with graduated surgical independence, including amastia, Poland’s syndrome, asymmetry, ectopic mammary tissue, virginal hypertrophy, and gynecomastia. 1. Participates in the full spectrum of reconstructive surgery after breast carcinoma, including procedures on the opposite breast; participates in long-term treatment and follow-up of these patients. 2. Evaluates and treats patients with premalignant diseases of the breast, including prophylactic mastectomy in selected patients. 3. Evaluates and surgically treats patients with gynecomastia. 9. Participates in breast reconstruction following mastectomy, including: a. b. c. d. e. f. tissue expanders implants flaps nipple reconstruction other procedures including tattooing management of contralateral breast. C. 10. Participates in the evaluation and treatment of patients with post surgical breast deformities. 11. Participates in the evaluation of patients with developmental breast abnormalities and performs diagnostic studies; interacts with appropriate consultants in allied areas. 12. Performs perioperative care and surgery on patients with developmental and acquired breast abnormalities, including breast hypertrophy, asymmetry, tubular deformity, and Poland’s syndrome. 13. Critically analyzes patients with developmental chest wall deformities for aesthetic and functional reconstruction. 14. Participates in reconstructive surgery on patients with developmental chest deformities. 15. Participates in the surgical care of posterior trunk lesions, including meningomyelocele, sacrococcygeal teratomas, etc. 16. Evaluates and participates in the multispecialty surgical evaluation of patients with congenital deformities of the posterior trunk. 17. Participates in the reconstruction of posterior trunk congenital defects. 18. Participates in the surgical care of congenital abdominal wall deformities such as gastroscesis, prune belly, and omphalocele. 19. Participates in the evaluation and surgical planning (in concert with other surgical specialists) of congenital abdominal wall deformities. Practice Based Learning and Improvement Goal: The resident will investigate and evaluate his or her own patient care practices, appraise and assimilate scientific evidence, and improve patient care practices. Objectives 1. Uses information technology to prepare for cases, bringing to the OR the knowledge of current modalities of care and the scientific evidence for that care. 2. Routinely analyzes the effectiveness of own practices in caring for surgery patients. 3. Improves own practices in the care of patients by integrating appropriately gathered data and feedback. 4. Educates medical students and other healthcare professionals in the practices of oral and maxillofacial surgery. 5. Functions independently with graduated advancement and appropriate faculty supervision. 6. Uses library sources to perform research and literature searches. 7. Understands the principles of clinical research and the application of biostatistics. D. Interpersonal and Communication Skills Goal: The resident will demonstrate interpersonal and communication skills that result in effective information exchange and teaming with patients, their families, and professional associates. Objectives E. 1. Educates patients and families in post oral and maxillofacial surgery care. 2. Demonstrates compassion for patients and families. 3. Provides adequate counseling and informed consent to patients. 4. Listens to patients and their families. 5. Assimilates data and information provided by other members of the health care team. 6. Charts and records accurate information. System Based Practice Goal: The resident will demonstrate an awareness of and responsiveness to the larger context and system of health care and the ability to effectively call on system resources to provide care that is of optimal value. Objectives F. 1. Coordinates all aspects of the oral and maxillofacial surgery care for patients. 2. Demonstrates knowledge of cost-effective oral and maxillofacial surgery care. 3. Advocates for patients within the health care system. 4. Refers patients to the appropriate practitioners and agencies. 5. Facilitates the timely discharge of same day surgery patients. 6. Works with primary care physicians, and other consultants such as cardiologists, toward the safe administration of anesthesia. Professionalism Goal: The resident will demonstrate a commitment to carrying out professional responsibilities, adherence to ethical principles, and sensitivity to a diverse patient population. Objectives 1. Develops a sensitivity of the unique stresses placed on families under care for surgical diagnoses. 2. Exhibits an unselfish regard for the welfare of surgical patients. 3. Demonstrates firm adherence to a code of moral and ethical values. 4. Is respectful to patients and their families, especially in times of stress to the family unit. 5. Respects and appropriately integrates other members of the health care team. 6. Provides appropriately prompt consultations when requested. 7. Demonstrates sensitivity to the individual patient’s profession, life goals, and cultural background as they apply to health care. 8. Is reliable, punctual, and accountable for own actions in the OR and clinic. 9. Understands the concepts of autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, justice, and respect for life. 10. Maintains patient confidentiality. Plastic Surgery U of C Red Service The U of C Red Service develops the resident’s knowledge base and management ability of complex wounds. The areas of focus on this service are head and neck reconstruction, burn wounds, genitalia reconstruction and hypertrophic-keloid scars. The primary faculty on this service are Lawrence Gottlieb and Raphael Lee. Red Service exposes our first year plastic surgery resident to the evaluation and treatment of patients needing complex head and neck reconstruction. Further, this month will provide the first year plastic surgery residents with the knowledge and tools required to evaluate and treat acute and chronic burn patients. Graduated responsibility for the management and surgical care of patients requiring complex head and neck reconstruction, acute and chronic burn patients will be provided. This will include outpatient evaluation and follow-up care, participation in microsurgical head and neck reconstruction and evaluation and treatment of the acute and chronic burn patient. The second year plastic surgery resident should have a working knowledge of the service and thus will be an integral member contributing to the diagnosis, assessment, surgical plan and care of the patient. Further, a disposition for each patient will be formulated by the second year resident with faculty oversight. The second year resident should also gain the skills necessary to understand and perform the index operations that the Red Service faculty engages in. A thorough knowledge base of head and neck anatomy and reconstructive techniques, care of the acute burn patient and burn reconstruction should be developed by the second year resident and the assessment of that knowledge will be based on the following. The third year plastic surgery resident (chief resident) should demonstrate competence in head and neck reconstruction, care of the acute burn patient, and burn reconstruction. With supervision, the third year resident should be able to diagnose, plan, execute and care for all the patients on the Red Service. Upon completion of the rotation, the third year resident should be able to demonstrate the skills and techniques required to practice safely and independently based upon the following parameters. A. Medical Knowledge Goal: The resident will achieve a detailed knowledge of the evaluation and management of burn patients. Also, the resident will achieve a detailed knowledge of the evaluation and management of patients requiring head and neck reconstruction after tumor extirpation. Objectives: 1. Discusses the techniques of resuscitation of major burns. B. 2. Recites the criteria for superficial and deep partial thickness, as well as full-thickness classification of burns. 3. Discusses the three zones of a burn wound. 4. Discusses the properties of split thickness vs. full thickness skin grafts, as meshed and sheet grafts. 5. Discusses the treatment of inhalation injuries. 6. Describes the resuscitation and management of electrical burns. 7. Describes the indications of fasciotomies and escharotomies. 8. Lists the details regarding the use of skin substitutes, biological dressings, and xenografts in the treatment of the burn patient. 9. Discusses the reconstruction for burn contractures. 10. Recites the use of pressure garments and silicone therapy in the prevention of abnormal scars. 11. Describes the pathology and management of thermal, chemical, and electrical injury and inhalation injury and relationship to mortality, morbidity, and course of patient recovery. 12. Outlines the principles of burn shock, immunologic alteration, and bacteriologic pathology of the burn wound. 13. Discusses the epidemiology, prevention, and socioeconomic and psychological impact of burns. 14. Recites the physiologic response to thermal, chemical, and electrical burn injuries, including the micro and macro disruption of normal skin anatomy and physiology. 15. Discusses the options for reconstruction of complex head and neck extirpative defects as it relates to form and function. 16. Participates with graduated responsibilities in all microsurgical operations for cervical esophagus, mandibular, facial and composite defects of the head and neck. Patient Care Goal: The resident will provide patient care that is compassionate, appropriate, and effective for the treatment of burn patients. Objectives 1. Evaluates the appearance of the burn wound in relation to its depth, bacteriologic condition, healing potential, and requirement for intervention. 2. Performs burn wound debridement and preparation for skin grafting. 3. Performs split thickness skin grafts. C. 4. Performs full thickness skin grafts. 5. Utilizes skin substitutes, biological dressings, and xenografts in the treatment of burn wounds. 6. Utilizes splinting and pressure garments to minimize scar formation and post burn contractures. 7. Performs the surgical treatment of post-burn contractures with releases, z-plasties, and grafting. 8. Participates in the acute resuscitation and care of the burned patient. 9. Treats patients who are victims of electrical burns. 10. Performs escharotomies and fasciotomies when indicated. 11. Evaluates the appearance of free tissue transfers and understands the physiology and appearance of both healthy and failing composite free tissue transfers. 12. Evaluates and performs with graduated responsibility local, regional and distant tissue transfers with appropriate supervision for level of residency and skill set. Practice Based Learning and Improvement Goal: The resident will investigate and evaluate his or her own patient care practices, appraise and assimilate scientific evidence, and improve patient care practices. Objectives 1. Uses information technology to prepare for surgical cases, bringing to the OR the knowledge of current modalities of care and the scientific evidence for that care. 2. Routinely analyzes the effectiveness of own practices in caring for burn patients. 3. Improves own practices in the care of burn patients by integrating appropriately gathered data and feedback. 4. Educates medical students and other healthcare professionals in the practices of burn surgery and reconstruction. 5. Functions independently with graduated advancement and appropriate faculty supervision. 6. Uses library sources to perform research and perform literature searches. 7. Understands the principles of clinical research and the application of biostatistics. D. Interpersonal and Communication Skills Goal: The resident will demonstrate interpersonal and communication skills that result in effective information exchange and teaming with patients, their families, and professional associates. Objectives E. 1. Educates patients and families in post operative and rehabilitative strategies for burn patients. 2. Demonstrates compassion for patients and families afflicted with trauma. 3. Provides adequate counseling and informed consent to patients. 4. Listens to patients and their families. 5. Assimilates data and information provided by other members of the health care team. 6. Charts and records accurate information. System Based Practice Goal: The resident will demonstrate an awareness of and responsiveness to the larger context and system of health care and the ability to effectively call on system resources to provide care that is of optimal value. Objectives 1. Coordinates all aspects of the rehabilitation of the burn surgery patient. 2. Directs the rehabilitation of burn surgery patients by partnering with the following: a. b. c. d. e. physical therapy occupational therapy PRM physicians social workers nutritionalists 3. Demonstrates knowledge of cost-effective burn surgery care. 4. Advocates for burn surgery patients within the health care system. 5. Refers orthopedic patients to the appropriate practitioners and agencies. 6. Facilitates the timely discharge of burn surgery patients. 7. Works with patients. paramedical professionals in the pre-hospital care of trauma F. Professionalism Goal: The resident will demonstrate a commitment to carrying out professional responsibilities, adherence to ethical principles, and sensitivity to a diverse patient population. Objectives 1. Develops a sensitivity of the unique stresses placed on families under care for burn injuries. 2. Exhibits an unselfish regard for the welfare of burn surgery patients. 3. Demonstrates firm adherence to a code of moral and ethical values. 4. Is respectful to burn patients and their families especially in times of trauma and stress to the family unit. 5. Respects and appropriately integrates other members of the burn surgery team. 6. Provides appropriately prompt consultations when requested. 7. Demonstrates sensitivity to the individual patient’s profession, life goals, and cultural background as they apply to burn care. 8. Is reliable, punctual, and accountable for own actions in the OR and clinic. 9. Understands the concepts of autonomy, beneficence, non-maleficence, justice, and respect for life. 10. Maintains patient confidentiality. Plastic Surgery U of C Blue Service The U of C Blue Service will provide the plastic surgery resident with a wide and varied exposure to the evaluation and management of reconstructive and aesthetic conditions of the cranium, face, hand and trunk. The primary focuses of the service will be craniofacial reconstruction (adult and pediatric), upper and lower extremity reconstruction, nasal reconstruction and body contouring. The teaching faculty of the Blue Service consists of Lawrence Zachary, Russell Reid, and Ginard Henry. The PSRY 1(PGY-4) resident will learn the principles and tenets of evaluating, diagnosing and treatment management of patients with reconstructive and aesthetic issues of the face, cranium, trunk, and extremities. Graduated responsibility for the management and surgical care of patients requiring hand/extremity and complex trunk reconstruction will be provided. This will include outpatient evaluation and follow-up care, participation in microsurgical reconstruction and evaluation and treatment of the complex neurological and vascular disorders of the extremities. The second year plastic surgery resident should have a working knowledge of the service and thus will be an integral member contributing to the diagnosis, assessment, surgical plan and care of the patient. Further a disposition for each patient will be formulated by the second year resident with faculty oversight. The second year resident should also gain the skills necessary to understand and perform the index operations that the Blue service faculty engages in. A thorough knowledge base of hand/extremity anatomy, reconstruction and trunk/chest wall reconstruction as well as post-bariatric patient care should be developed by the second year resident and the assessment of that knowledge will be based on the following. (A-F) The third year plastic surgery resident (chief resident) should demonstrate competence in hand/extremity reconstruction as well as trunk/chest wall reconstruction and care of the post-bariatric patient. With supervision, the third year resident should be able to diagnose, plan, execute and care for all the patients on the Blue Service. Upon completion of the rotation, the third year resident should be able to demonstrate the skills and techniques required to practice safely and independently based upon the following parameters. A. Medical Knowledge Goal: The resident will achieve a detailed knowledge of the techniques and practice of oral and craniomaxillofacial surgery, nasal reconstruction and aesthetic surgery. Objectives: 1. Discusses the embryology of the head and neck. 2. Recites the tenets of growth of the craniofacial skeleton. 3. Draws the anatomy of the head and neck with particular concern to the jaws and craniofacial skeleton. 4. Discusses the principles of odontogenesis 5. Recites the principles of and infiltration techniques of local anesthesia used in the head and neck. 6. Lists the principles of bone fixation and bony healing. 7. Discusses the general evaluation of the facial trauma patient. 8. Recites the techniques of the treatment of facial fractures, including: a. b. c. d. e. f. g. frontal sinus fractures orbital fractures nasal fractures NOE fractures midface and maxillary fractures mandibular fractures management of teeth in fractures 9. Discusses the unique treatment of pediatric facial fractures. 10. Describes the cephalometric analysis of maxillofacial surgery patients. 11. Discusses the common diagnoses in maxillofacial surgery and their management, including: a. b. c. d. 12. retrogenia mandibular excess and deficiency vertical maxillary excess maxillary deficiency Discusses the different kinds of occlusion, including: a. b. c. d. overjet overbite angle classification crossbites 13. Discusses the use of distraction osteogenesis in maxillofacial surgery. 14. Discusses maxillofacial surgery in the cleft patient. 15. Describes the acquired diseases of the TMJ and their management. 16. Describes the use of dento-facial prosthetics. B. Patient Care Goal: The resident will provide patient care that is compassionate, appropriate, and effective for the treatment of surgical problems. Objectives 1. Performs the various local anesthetic facial blocks for procedures done in oral and maxillofacial surgery. 2. Performs with graduated surgical independence bony fixation of the craniofacial skeleton. 3. Performs the head and neck exam in the facial trauma patient. 4. Performs the facial evaluation for orthognathic surgery patients. 5. Participates in the cephalometric analysis, prediction tracing, and preoperative surgical planning of maxillofacial surgery patients. 6. Performs a face-bow transfer. 7. Participates in preoperative model surgery. 8. Participates in common maxillofacial surgical procedures, including: a. b. c. d. e. 9. C. facial fractures genioplasties sagittal split mandibular osteotomies maxillary LeFort I osteotomies bimaxillary osteotomies Participates in the creation and application of dental splints in maxillofacial surgery. Practice Based Learning and Improvement Goal: The resident will investigate and evaluate his or her own patient care practices, appraise and assimilate scientific evidence, and improve patient care practices. Objectives: 1. Uses information technology to prepare for surgical cases, bringing to the OR the knowledge of current modalities of care and the scientific evidence for that care. 2. Routinely analyzes the effectiveness of own practices in caring for patient with abdominal wall and trunk plastic surgical diagnoses. 3. Improves own practices in the care of patient by integrating appropriately gathered data and feedback. 4. Educates medical students and other healthcare professionals in the practice of reconstructive surgery. 5. Functions independently with graduated advancement and appropriate faculty supervision. 6. D. Participates in and appreciates the value of outcome studies as they apply to abdominal wall and trunk plastic surgical reconstruction. Interpersonal and Communication Skills Goal: The resident will demonstrate interpersonal and communication skills that result in effective information exchange and teaming with patients, their families, and professional associates. Objectives: E. 1. Educates patients and families in post-operative strategies for reconstructive surgery. 2. Demonstrates compassion for patients and their families affected by breast cancer. 3. Provides adequate counseling and informed consent to patients. 4. Listens to patients and their families. 5. Assimilates data and information provided by general surgeons and other members of the breast care team. 6. Charts and records accurate information. 7. Demonstrates appreciation of the psychosocial aspects of breast surgery, breast deformity, and post mastectomy reconstruction. System Based Practice Goal: The resident will demonstrate an awareness of and responsiveness to the larger context and system of health care and ability to effectively call on system resources to provide care that is of optimal value. Objectives: 1. Directs the rehabilitation of pressure sore patients following surgery by partnering with the following: a. b. c. d. e. physical therapy occupational therapy prosthetic and orthotics specialists spina bifida clinic physical medicine and rehabilitation specialists. 2. Demonstrates knowledge of cost-effective breast reconstruction and other breast surgery. 3. Advocates for breast cancer patients within the health care system. 4. Refers breast cancer patients to the appropriate practitioners and agencies. 5. Facilitates the timely discharge of patients undergoing reconstructive plastic surgery. 6. Participates in all aspects of breast cancer care, partnering with general surgeons, radiation oncologists, and other breast care team members in the complete care of the breast cancer patient. F. Professionalism Goal: The resident will demonstrate a commitment to carrying out professional responsibilities, adherence to ethical principles, and sensitivity to a diverse patient population. Objectives: 1. Develops a sensitivity of the unique stress placed on families under care for breast cancer. 2. Exhibits an unselfish regard for the welfare of reconstructive patients. 3. Demonstrates firm adherence to a code of moral and ethical values. 4. Is respectful to breast cancer patients and their families, especially in times of stress to the family unit. 5. Respects and appropriately integrates other members of the breast care team. 6. Provides appropriately prompt reconstructive plastic surgery consultations when requested. 7. Demonstrates sensitivity to the individual patient’s profession, life goals, and cultural background as they apply to reconstructive plastic surgery. 8. Is reliable, punctual and accountable for own actions in the OR and outpatient clinic. Northshore Rotation For two months of each year, the PSRY 1-3 will rotate at the Northshore Medical Center. Residents will receive a comprehensive general plastic surgery training experience with a concentration focus on reconstructive surgery. The resident will learn evaluation and management of the full spectrum of plastic surgery issues, including breast reconstruction, trunk and back reconstruction, facial tumor and head and neck reconstruction and cosmetic surgery. Faculty of Northshore Medical Group are based at the Evanston Hospital and consist of Karol Gutowski, Michael Howard, Mark Sisco, Jeremy Warner, Laurie Casas and Bruce Bauer. A. Medical Knowledge Goal: The resident will achieve a detailed knowledge of the evaluation and management of the breast patient. I: 1. Discusses the evaluation, diagnosis, and surgical care of the breast mass 2. Describes the evaluation of non-palpable breast abnormalities 3. Discusses the appropriate use of mammography, ultrasound, fine needle aspiration, and stereotactic biopsies 4. Discusses the preoperative staging of breast cancer 5. Recites the use of preoperative chemotherapy and radiation therapy for breast cancer 6. Describes the indication for operative management of breast disease and selection of appropriate surgical procedures 7. Discusses the adjuvant treatment regimens and indications for their use in breast cancer 8. Describes the treatment of advanced breast cancer 9. Recites the screening for breast cancer 10. Discusses the genetic predisposition to breast cancer and prophylactic mastectomy Microsurgery Goal: The resident will demonstrate knowledge of the principles of microsurgery, and master basic microsurgery techniques, including microneural repair and microvascular anastomosis. Objectives: 1. Explains the use of the operating microscope and the technical aspects of microvascular anastomosis (artery and vein) and microneural repair 2. Discerns the indications for, the contraindications to, and the techniques for accomplishing replantation of amputated parts. Recognizes the techniques of monitoring the success of replantation 3. Discusses the varying types of blood supply to discrete units of tissue (including arterialized flap, musculocutaneous flap, fasciocutaneous flap) 4. Lists the terms and types of free tissue flaps – skin, skin/muscle, skin/muscle/bone, skin/tendon, muscle alone 5. Lists in detail the anatomy for harvesting the most common flaps, including latissimus dorsi, rectus abdominis, radial forearm 6. Discerns the indications for harvesting various flaps and matching donor sites to specific recipient site needs 7. Discusses radiologic techniques for evaluation of both donor and recipient sites 8. Discusses the mechanisms and consequences of the no-reflow phenomenon; knows how to treat a failing flap 9. Discusses the technologic, pharmacologic and physiologic principles of postoperative monitoring of free flaps 10. Recites the basic physiology of nerve injury (axontomesis, neurotomesis, neuropraxia, Wallerian degeneration) and of nerve healing 11. Draws the intraneural anatomy and anatomic relationships of structures of the major peripheral nerves 12. Explains the principles of repair of nerve injury, including need for nerve grafting, the anatomy of nerve graft donor sites, and the physiology, timing and techniques of primary, delayed primary and late nerve repair 13. Discusses the principles and techniques of hematologic manipulation of abnormal vascular flow characteristics 14. Discusses the technical aspects of microsurgery including: a. b. c. d. 15. microscopes – principles, usage sutures – types, indications microvascular coupling devices suturing techniques. Discusses the use of electrophysiologic tools in the evaluation of nerve injury (EMG, NCS) II: Implants/Biomaterials Goal: The resident will demonstrate knowledge of both biology and physiology of various implant materials, including bone, cartilage, and alloplasts Objectives: III: 1. Identifies the local wound factors which influence bone graft survival 2. Discusses the biologic differences between vascularized and non-vascularized bone grafts 3. Recites the influence of perichondrial and scoring on the warping of cartilage grafts 4. Discusses the various types of breast implants and the factors involved in implant choice, including surface content characteristics; is aware of the issues regarding silicone and is able to discuss these with a patient 5. Discerns the effects of breast implant surface characteristics on formation of capsular contracture 6. Discusses the various injectable materials for subcutaneous filling and the principles of their use 7. Discusses the processes of bone repair: incorporation, osteoconduction and osteoinduction 8. Discusses the difference in incorporation between cortical and cancellous bone grafts and membranous and endochondral autografts 9. Explains the immunology of bone and cartilage transplantation 10. Lists the chemistry and biocompatibility of the commonly implanted biomaterials, including silicone, methyl methacrylate, hydroxyapatite, tricalcium phosphate and proplast 11. Describes the factors involved in the choice of implant materials for varying reconstructive problems 12. Discusses the chemistry and biocompatibility of commonly injected materials including: collagen (bovine and human), fat, and others Special Techniques Goal: The resident will demonstrate knowledge of the principles of a variety of special techniques in plastic surgery, including: liposuction, tissue expansion, laser treatments and dermabrasion, and utilize the techniques effectively in appropriate clinical scenarios Objectives: 1. Discusses the basic principles, the common techniques and the instrumentation of suction lipectomy including tumescence, standard and ultrasonic liposuction IV: 2. Recites the indications for and contraindications to suction lipectomy, and is familiar with the principles of patient assessment; recognizes the limitations of liposuction 3. Explains the preoperative, intraoperative and postoperative management of the patient undergoing suction lipectomy; is familiar with the complications of liposuction and their management 4. Discusses the physiologic principles of tissue expansion 5. Discriminates the various techniques for tissue expansion and is familiar with the differing expansion devices 6. Discusses the principles of management of patients undergoing tissue expansion; recognizes and treats the complications of tissue expansion 7. Discusses the physiologic and pathologic principles of dermabrasion, chemical peel and laser resurfacing; recognizes the differences between the techniques and the indications for choice between the techniques 8. Recites the principles of pre- and postoperative management of patients undergoing facial resurfacing; recognizes the complications of the technique and its management 9. Explains the pharmacologic aspects and the techniques of chemical peel 10. Discriminates the biophysical properties of commonly used lasers, and chooses different lasers for different types of problems 11. Discusses the indications for and contraindications to laser treatments and techniques of laser use, and the various complications of laser therapy and their treatment Medicolegal and Psychiatric Aspects of Plastic Surgery Goal: The resident will demonstrate a clear understanding of medicolegal and psychiatric aspects of plastic surgery practice, regularly obtain informed consent from patients, and perform a basic psychological evaluation when appropriate Objectives: 1. Discusses the medical and legal perspectives of the contractual agreement between a physician and his/her patient 2. Discerns the concepts of informed consent and implied guarantee 3. Discusses the role of the medical record as a legal document 4. Discerns the impact physical deformity can have on patients and their families 5. Discusses techniques to explore the motivations of patients seeking cosmetic surgery, and how to distinguish acceptable, unacceptable, and pathological motivations 6. Recites the legal and ethical ways to sever the physician/patient relationship B. 7. Discusses the various types of malpractice insurance 8. Discusses the basic principles of risk management 9. Lists the psychiatric and psychological treatment options for patients with physical deformities and their families 10. Discusses the strategies to effectively treat the dissatisfied patient/family Patient Care Goal: The resident will provide patient care that is compassionate, appropriate, and effective for the treatment of reconstructive surgery Objectives: 1. Performs reconstructive surgery on the trunk, breast, and abdomen with increasing independence and surgical responsibility 2. Participates in treatment of patients with malignancy of the trunk, thorax and abdominal wall 3. Participates in the surgical management of thoracic and abdominal wall reconstruction with graduated independence, including: a. b. c. d. e. 4. reconstruction following sternal dehiscence and/or infection reconstruction after tumor resection utilizing flaps and grafts reconstruction of radiation injury of the thorax and trunk abdominal wall fascial reconstruction abdominal wound dehiscences and hernias utilizing prosthetic material, grafts, separation of parts Participates in surgical and nonsurgical management of pressure sores including: a. b. c. d. e. f. etiology and staging prevention nonsurgical considerations and management including patient compliance pressure sore surgery utilizing local flaps, muscle and myocutaneous flaps, and distant flaps complications of surgery rehabilitation 5. Participates in the surgical care of common developmental breast anomalies, with graduated surgical independence, including amastia, Poland’s syndrome, asymmetry, ectopic mammary tissue, virginal hypertrophy, and gynecomastia 6. Participates in the full spectrum of reconstructive surgery after breast carcinoma, including procedures on the opposite breast; participates in long-term treatment and follow-up of these patients 7. Evaluates and treats patients with premalignant diseases of the breast, including prophylactic mastectomy in selected patients 8. Evaluates and surgically treats patients with gynecomastia 9. Participates in breast reconstruction following mastectomy, including: a. b. c. d. e. f. tissue expanders implants flaps nipple reconstruction other procedures including tattooing management of contralateral breast 10. Participates in the evaluation and treatment of patients with post surgical breast deformities 11. Participates in the evaluation of patients with developmental breast abnormalities and performs diagnostic studies; interacts with appropriate consultants in allied areas 12. Performs perioperative care and surgery on patients with developmental and acquired breast abnormalities, including breast hypertrophy, asymmetry, tubular deformity, and Poland’s syndrome 13. Critically analyzes patients with developmental chest wall deformities for aesthetic and functional reconstruction 14. Participates in reconstructive surgery on patients with developmental chest deformities 15. Participates in the surgical care of posterior trunk lesions, including meningomyelocele, sacrococcygeal teratomas, etc. 16. Evaluates and participates in the multispecialty surgical evaluation of patients with congenital deformities of the posterior trunk 17. Participates in the reconstruction of posterior trunk congenital defects 18. Participates in the surgical care of congenital abdominal wall deformities such as gastroscesis, prune belly, and omphalocele 19. Participates in the evaluation and surgical planning (in concert with other surgical specialists) of congenital abdominal wall deformities C. Practice Based Learning and Improvement Goal: The resident will investigate and evaluate his or her own patient care practices, appraise and assimilate scientific evidence, and improve patient care practices. Objectives: 1. Uses information technology to prepare for surgical cases, bringing to the OR the knowledge of current modalities of care and the scientific evidence for that care 2. Routinely analyzes the effectiveness of own practices in caring for patients with abdominal wall and trunk plastic surgical diagnoses 3. Improves own practices in the care of patients by integrating appropriately gathered data and feedback D. 4. Educates medical students and other healthcare professionals in the practice of reconstructive surgery 5. Functions independently with graduated advancement and appropriate faculty supervision 6. Participates in and appreciates the value of outcome studies as they apply to abdominal wall and trunk plastic surgical reconstruction Interpersonal and Communication Skills Goal: The resident will demonstrate interpersonal and communication skills that result in effective information exchange and teaming with patients, their families, and professional associates. Objectives: E. 1. Educates patients and families in post-operative strategies for reconstructive surgery 2. Demonstrates compassion for patients and their families affected by breast cancer 3. Provides adequate counseling and informed consent to patients 4. Listens to patients and their families 5. Assimilates data and information provided by general surgeons and other members of the breast care team 6. Charts and records accurate information 7. Demonstrates appreciation of the psychosocial aspects of breast surgery, breast deformity, and post mastectomy reconstruction System Based Practice Goal: The resident will demonstrate an awareness of and responsiveness to the larger context and system of health care and ability to effectively call on system resources to provide care that is of optimal value Objectives: 1. Directs the rehabilitation of pressure sore patients following surgery by partnering with the following: a. b. c. d. e. physical therapy occupational therapy prosthetic and orthotics specialists spina bifida clinic physical medicine and rehabilitation specialists. 2. Demonstrates knowledge of cost-effective breast reconstruction and other breast surgery 3. Advocates for breast cancer patients within the health care system 4. Refers breast cancer patients to the appropriate practitioners and agencies F. 5. Facilitates the timely discharge of patients undergoing reconstructive plastic surgery 6. Participates in all aspects of breast cancer care, partnering with general surgeons, radiation oncologists, and other breast care team members in the complete care of the breast cancer patient Professionalism Goal: The resident will demonstrate a commitment to carrying out professional responsibilities, adherence to ethical principles, and sensitivity to a diverse patient population Objectives: 1. Develops a sensitivity of the unique stress placed on families under care for breast cancer 2. Exhibits an unselfish regard for the welfare of reconstructive patients 3. Demonstrates firm adherence to a code of moral and ethical values 4. Is respectful to breast cancer patients and their families, especially in times of stress to the family unit 5. Respects and appropriately integrates other members of the breast care team 6. Provides appropriately prompt reconstructive plastic surgery consultations when requested 7. Demonstrates sensitivity to the individual patient’s profession, life goals, and cultural background as they apply to reconstructive plastic surgery 8. Is reliable, punctual and accountable for own actions in the OR and outpatient clinic Plastic Surgery U of C Hand Service To expose our first year plastic surgery resident to the evaluation and treatment of patients needing hand and complex extremity reconstruction. Further, this rotation will provide the first year plastic surgery residents the knowledge and tools required to evaluate and treat both traumatic hand and upper extremity problems as well as complex functional reconstruction of the lower extremity after tumor extirpation. Drs. Mass and Birnie are orthopedic hand surgeons specializing in complex upper extremity reconstruction after trauma and/or tumor extirpative surgery. The second year plastic surgery resident should have a working knowledge of the service and thus will be an integral member contributing to the diagnosis, assessment, surgical plan and care of the patient. Further, a disposition for each patient will be formulated by the second year resident with faculty oversight. The second year resident should also gain the skills necessary to understand and perform the index operations that the Hand service faculty engages in. A thorough knowledge base of both traumatic hand and upper extremity problems as well as complex functional reconstruction of the lower extremity after tumor extirpation should be developed by the second year resident and the assessment of that knowledge will be based on the following. The third year plastic surgery resident (chief resident) should demonstrate competence in upper and lower extremity reconstruction and the management of the spectrum of clinical problems. With supervision, the third year resident should be able to diagnose, plan, execute and care for all the patients on the Hand service. Upon completion of the rotation, the third year resident should be able to demonstrate the skills and techniques required to practice safely and independently based upon the following parameters A. Medical Knowledge I: Anatomy/Physiology/Embryology Goal: The resident will achieve a detailed knowledge of the anatomy, physiology, and embryology of the upper and lower extremity and will utilize this knowledge in the complete management of the hand, arm, and brachial plexus as well as complex lower extremity reconstruction after tumor extirpation. Objectives: II: 1. Describes in detail the anatomy and physiology of the muscles, tendons, ligaments, and bones of the hand, upper and lower extremity. 2. Identifies in detail the anatomy of the vascular tree of the upper and lower extremity, including relationships to the surrounding structures. 3. Identifies in detail the anatomy of the major nerves and their branchings in the upper and lower extremity, including relationships to surrounding structures. 4. Draws the anatomy of the brachial plexus. 5. Demonstrate the detailed radiographic anatomy of the bony structures of the upper and lower extremity. 6. Utilizes the radiologic techniques, including plain films, CT scan, angiography and MRI of the upper and lower extremities. 7. Discriminates the principles of electrical evaluation and recites knowledge of the techniques of electrical examination of the upper and lower extremities including conduction studies and EMG evaluation. 8. Recites the principles of upper and lower extremity biomechanics. Congenital Disorders Goal: The resident will achieve familiarity with the spectrum of congenital abnormalities of the upper and lower extremity and perform comprehensive diagnostic evaluation and surgical management of such problems. Objectives: 1. Recites the classification system for congenital hand anomalies including: a. b. c. d. e. f. g. III. failure of part formation failure of differentiation duplication overgrowth undergrowth congenital bands generalized musculoskeletal anomalies 2. Describes the embryologic development and the physiologic theories which explain the etiology of hand anomalies. 3. Recites the operations, including timing and techniques used in the surgical management of hand anomalies. Benign and Malignant Tumors Goal: The resident will understand the principles of diagnosis and treatment of extremity tumors and undertake comprehensive management of a wide variety of such lesions. Objectives: 1. Describes the principles and techniques of management of upper and lower extremity tumors. 2. Describes the etiologic factors, epidemiology, and modalities of treatment for tumors of the upper and lower extremities. 3. Describes the clinical manifestations of both soft and hard tissue tumors of the extremities. 4. Describes the reconstructive principles and techniques for restoration of form and function after surgical resections. 5. Recites the indications and use of adjunctive therapy (i.e. radiation therapy and chemotherapy) in the management of and the prognosis for extremity tumors. 6. Describes the principles and techniques of management for extremity tumors, including reconstruction after surgical extirpation, for: a. b. c. d. e. 7. vascular tumors nerve tumors benign deep soft tissue tumors malignant deep soft tissue tumors primary bone tumors Rationalizes the utilization of radiotherapy, medical oncology, hand therapy, occupational therapy, and prosthetics where appropriate for patients with extremity tumors. IV: Trauma Goal: The resident will understand the principles of diagnosis and treatment of extremity trauma, and perform comprehensive management of acute injuries and other trauma-related problems of the hand and arm. Objectives: 1. Recites the principles and applications of diagnostic techniques for the evaluation of hand and upper extremity trauma. 2. Describes the techniques for operative management of traumatic injuries of the upper extremity, their indications and contraindications, and their possible complications and the treatment thereof. 3. Explains the indications for, contraindications to, and techniques in nonoperative management of traumatic injuries of the hand and upper extremity. 4. Describes the options for soft tissue coverage of upper extremities including: a. b. c. skin grafts local flaps free tissue transfer IV. Functional Problems of the Upper Extremities Goal: The resident will achieve familiarity with aesthetic and functional problems of the hand and arm, understand the principles of rehabilitation of the upper extremity and the management, including comprehensive rehabilitation of the upper extremity. Objectives: 1. Lists the surgical and nonsurgical treatment of nerve compression and entrapment syndromes of the upper extremity. 2. Draws the pathologic anatomy and physiology of upper extremity contractures and Dupuytren’s disease. 3. Recites the basic pathophysiology of rheumatoid and nonspecific arthritis of the upper extremity. 4. Describes with the pharmacological therapy of rheumatoid arthritis. 5. Demonstrates the surgical treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, timing of therapeutic treatment and interactions with medical therapy. 6. Describes the common circulatory disorders of the upper extremity including, but not limited to: arterial thromboses, aneurysms, embolic disorders, arteriovenous fistulae, vasospastic disease and scleroderma. 7. Describes the diagnosis and treatment of common pain syndromes including sympathetic dystrophy. 8. Recites the management of upper extremity lymphedema. V. Functional Problems of the Upper Extremities Goal: The resident will achieve familiarity with aesthetic and functional problems of the hand and arm, understand the principles of rehabilitation of the upper extremity and management, including comprehensive rehabilitation of the upper extremity. Objectives: 1. Lists the surgical and nonsurgical treatment of nerve compression and entrapment syndromes of the upper extremity. 2. Draws the pathologic anatomy and physiology of upper extremity contractures and Dupuytren’s disease. 3. Recites the basic pathophysiology of rheumatoid and nonspecific arthritis of the upper extremity. 4. Describes with the pharmacological therapy of rheumatoid arthritis. 5. Demonstrates the surgical treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, timing of therapeutic treatment and interactions with medical therapy. 6. Describes the common circulatory disorders of the upper extremity including, but not limited to: arterial thromboses, aneurysms, embolic disorders, arteriovenous fistulae, vasospastic disease and scleroderma. 7. Describes the diagnosis and treatment of common pain syndromes including sympathetic dystrophy. 8. Recites the management of upper extremity lymphedema. VI. Reconstruction Goal: The resident will understand the principles and techniques of upper extremity reconstruction and apply these to a variety of developmental, traumatic and acquired problems. Objectives: B. 1. Recites the diagnostic techniques for evaluation of function, including EMG and conduction studies, arteriography, CT scan, and MRI evaluation. 2. Recites the use of tendon transfers. Patient Care Goal: The resident will provide patient care that is compassionate, appropriate, and effective for the treatment of hand problems. Objectives 1. Performs the clinical techniques for physical examination of the hand and upper extremity. 2. Performs the surgical techniques used to treat congenital and developmental hand anomalies. 3. Performs postoperative care of patients with congenital and developmental anomalies of the upper extremity. 4. Applies casts and splints for the preoperative and postoperative care of hand patients. 5. Utilizes the diagnostic techniques for upper extremity tumors. 6. Demonstrates the techniques of management of extremity tumors. 7. Performs the procedures for the acute management and participates in the post-operative rehabilitation of traumatic injuries of the upper extremity including: a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. fractures and dislocations nerve injury including brachial plexus major amputation and avulsions joint injury tendon extensor and flexor injury of the hand muscle and tendon injury of the arm nail bed injuries infections fingertip and other minor injuries 8. Performs the surgical treatment options for contractures. 9. Performs treatment for tenosynovitis and tendon rupture. 10. Describes the indications for and perform the techniques of tendon reconstruction including tendon grafting – sources, methods, indications 11. Performs the management of nerve injuries including primary, delayed primary and secondary repair. 12. Performs the techniques for reconstruction of the amputated thumb including lengthening, pollicization, free toe to thumb, and free wrap-around techniques. 13. Performs the technical methods of soft tissue coverage including skin grafts, local flaps, distant flaps, and transfers. C. Practice Based Learning and Improvement Goal: The resident will investigate and evaluate his or her own patient care practices, appraise and assimilate scientific evidence, and improve patient care practices. Objectives 1. Uses information technology to prepare for surgical cases, bringing to the OR the knowledge of current modalities of care and the scientific evidence for that care. 2. Routinely analyzes the effectiveness of own practices in caring for hand patients. 3. Improves own practices in the care of hand patients by integrating appropriately gathered data and feedback. 4. Educates medical students and other healthcare professionals in the practices of hand surgery. 5. D. Functions independently with graduated advancement and appropriate faculty supervision. Interpersonal and Communication Skills Goal: The resident will demonstrate interpersonal and communication skills that result in effective information exchange and teaming with patients, their families, and professional associates. Objectives E. 1. Educates therapy. patients and families in post operative strategies for hand 2. Demonstrates compassion for patients and families with traumatic and congenital hand deformities. 3. Provides adequate counseling and informed consent to patients. 4. Listens to patients and their families. 5. Assimilates data and information provided by hand therapists and other members of the health care team. 6. Charts and records accurate information. System Based Practice Goal: The resident will demonstrate an awareness of and responsiveness to the larger context and system of health care and the ability to effectively call on system resources to provide care that is of optimal value. Objectives 1. Coordinates all aspects of hand and upper extremity rehabilitation, including splinting, prosthesis use, physical therapy, and sensory re-education. 2. Directs the rehabilitation of upper extremities following trauma by partnering with the following: a. b. c. physical therapy occupational therapy prosthetic and orthotic specialists 3. Demonstrates knowledge of cost-effective hand care. 4. Advocates for hand patients within the health care system. 5. Understands the basics of the Worker’s Compensation. 6. Refers hand patients to the appropriate practitioners and agencies. 7. Facilitates the timely discharge of hand patients. F. Professionalism Goal: The resident will demonstrate a commitment to carrying out professional responsibilities, adherence to ethical principles, and sensitivity to a diverse patient population. Objectives 1. Develops a sensitivity of the unique stresses placed on families under care for congenital anomalies of the hand. 2. Exhibits an unselfish regard for the welfare of hand patients. 3. Demonstrates firm adherence to a code of moral and ethical values. 4. Is respectful to hand patients and their families especially in times of trauma and stress to the family unit. 5. Respects and appropriately integrates other members of the hand care team. 6. Provides appropriately prompt hand consultations when requested. 7. Demonstrates sensitivity to the individual patient’s profession, life goals, and cultural background as they apply to hand surgery. 8. Is reliable, punctual, and accountable for own actions in the OR and hand clinic. Plastic Surgery Lutheran General Hospital To expose our PSRY 1 (PGY 4) residents to the spectrum of disease processes related to trauma in plastic and reconstructive surgery. Particular attention will be paid to craniomaxillofacial and extremity trauma. The resident will be an integral member of the plastic surgery team in the assessment, diagnosis and management of the patient on the plastic surgery service at Lutheran General Hospital. She/he will be responsible for the triage, diagnosis, treatment algorithm for all plastic surgery trauma patients and elective patients referred to the service under the direct guidance of Loren S. Schechter and Russell Reid. The resident will understand the spectrum of options related to the care of the trauma patient as it relates to plastic surgery. This will include: craniomaxillofacial trauma (blunt and penetrating), lower and upper extremity high velocity trauma (blunt and penetrating), general plastic surgery principles in the management and execution of local, regional and free tissue transfers as it relates to both traumatic injuries. Upon completion of the rotation, the resident will be proficient in the work-up, treatment and follow-up care of the general plastic surgery trauma patient and will be proficient in the communication and interaction with consultants and primary care givers of these patients. A. Medical Knowledge Goal: The resident will achieve a detailed knowledge of the pathophysiology of blunt and penetrating trauma and will develop the skills needed to treat the trauma patient . Objectives: 1. Describes the mechanisms of injury of blunt and penetrating injury. 2. Recites the steps of the primary, secondary, and tertiary surgery. 3. Discusses the diagnosis and treatment of abdominal injuries, including: a. b. c. 4. loss of domain after trauma laparotomy complex abdominal wounds related visceral injuries and their impact on abdominal reconstruction Discusses the diagnosis and treatment of maxillofacial injuries a. LeFort fractures b. fronto-naso-ethmoid fractures c. frontal sinus fractures d. blunt and penetrating mandibular fractures 5. Discusses the diagnosis and treatment of central nervous system injury: a. b. B. brain injury spinal cord injury 6. Discusses the diagnosis and treatment of orthopedic injuries. 7. Recites the steps in the treatment of hemorrhagic shock. 8. Recites the indications for and complications of blood product transfusion. Patient Care Goal: The resident will provide patient care that is compassionate, appropriate, and effective for the treatment of trauma problems. Objectives 1. Performs a primary, secondary, and tertiary survey for a trauma patient. 2. Performs the emergency treatment for airway obstruction 3. Participates in the operative treatment of thoracic and abdominal trauma as part of a plastic surgery consultant team. 4. Performs a complete CNS evaluation of the trauma patient and assign GCS scores. 5. Performs the evaluation and treatment of all blunt and penetrating fractures of the craniomaxillo-facial skeleton. 6. Performs the evaluation and treatment of lower and upper extremity traumatic injuries. C. Practice Based Learning and Improvement Goal: The resident will investigate and evaluate his or her own patient care practices, appraise and assimilate scientific evidence, and improve patient care practices. Objectives 1. Uses information technology to prepare for surgical cases, bringing to the OR the knowledge of current modalities of care and the scientific evidence for that care. 2. Routinely analyzes the effectiveness of own practices in caring for trauma patients. 3. Improves own practices in the care of trauma patients by integrating appropriately gathered data and feedback. 4. Educates medical students and other healthcare professionals in the practices of trauma surgery. 5. Functions independently with graduated advancement and appropriate faculty supervision. 6. Uses library sources to perform research and perform literature searches. 7. D. Understands biostatistics. the principles of clinical research and the application of Interpersonal and Communication Skills Goal: The resident will demonstrate interpersonal and communication skills that result in effective information exchange and teaming with patients, their families, and professional associates. Objectives E. 1. Educates patients and families in post operative and rehabilitative strategies for trauma patients. 2. Demonstrates compassion for patients and families afflicted with trauma. 3. Provides adequate counseling and informed consent to patients. 4. Listens to patients and their families. 5. Assimilates data and information provided by other members of the health care team. 6. Charts and records accurate information. System Based Practice Goal: The resident will demonstrate an awareness of and responsiveness to the larger context and system of health care and the ability to effectively call on system resources to provide care that is of optimal value. Objectives 1. Coordinates all aspects of the rehabilitation of the trauma patient. 2. Directs the rehabilitation of patients following trauma by partnering with the following: a. b. c. d. e. physical therapy occupational therapy PRM physicians social workers nutritionalists 3. Demonstrates knowledge of cost-effective trauma care. 4. Advocates for trauma patients within the health care system. 5. Refers trauma patients to the appropriate practitioners and agencies. 6. Facilitates the timely discharge of trauma patients 7. Works with paramedical professionals in the pre-hospital care of trauma patients. F. Professionalism Goal: The resident will demonstrate a commitment to carrying out professional responsibilities, adherence to ethical principles, and sensitivity to a diverse patient population. Objectives 1. Develops a sensitivity of the unique stresses placed on families under care for traumatic injuries. 2. Exhibits an unselfish regard for the welfare of trauma patients. 3. Demonstrates firm adherence to a code of moral and ethical values. 4. Is respectful to hand patients and their families especially in times of trauma and stress to the family unit. 5. Respects and appropriately integrates other members of the trauma team. 6. Provides appropriately prompt hand consultations when requested. 7. Demonstrates sensitivity to the individual patient’s profession, life goals, and cultural background as they apply to trauma care. 8. Is reliable, punctual, and accountable for own actions in the OR and hand clinic. 9. Understands the concepts of autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, justice, and respect for life. 10. Maintains patient confidentiality. Northshore Pediatric Rotation The Northshore Pediatric clinical experience will be a comprehensive exposure to the issues of complex pediatric plastic surgery conditions. This is a senior level experience limited to the PSRY 3 (PGY-6) resident. The goal is the mastery of evaluation and management of a spectrum of pediatric plastic surgery conditions including the diagnosis, management and surgical treatment of such entities as: congenital pigmented nevi, cleft lip/palate, craniosynostoses and rare facial clefts. During and after the rotation, the resident should understand and should be able to make the diagnosis of all congenital anomalies and the appropriate treatment algorithm. Further, she/he should be able to critically think about the respective operation and be able to execute the appropriate operation or set of interventions with graduated responsibility and oversight. She/he will be under the direct supervision of Bruce Bauer. The resident will be expected to communicate all patient related matters with stated faculty members and to organize and lead a pediatric plastic surgery team on rounds, in the operating theater and in the office/clinic setting. Upon completion of this rotation, the resident will be able to understand, discuss, and prepare diagnoses and treatment plans for the full spectrum of congenital and acquired problems associated with the pediatric plastic surgical patient. A. Medical Knowledge Goal: The resident will achieve a detailed knowledge of the techniques and practice of oral and maxillofacial surgery. Objectives: 1. Discusses the embryology of the head and neck. 2. Recites the tenets of growth of the craniofacial skeleton. 3. Draws the anatomy of the head and neck with particular concern to the jaws and craniofacial skeleton. 4. Discusses the principles of odontogenesis 5. Recites the principles of and infiltration techniques of local anesthesia used in the head and neck. 6. Lists the principles of bone fixation and bony healing. 7. Discusses the general evaluation of the facial trauma patient. 8. Recites the techniques of the treatment of facial fractures, including: a. b. c. d. e. f. g. 9. Discusses the unique treatment of pediatric facial fractures. 10. Describes the cephalometric analysis of maxillofacial surgery patients. 11. Discusses the common diagnoses in maxillofacial surgery and their management, including: a. b. c. d. 12. retrogenia mandibular excess and deficiency vertical maxillary excess maxillary deficiency Discusses the different kinds of occlusion, including: a. b. c. d. B. frontal sinus fractures orbital fractures nasal fractures NOE fractures midface and maxillary fractures mandibular fractures management of teeth in fractures overjet overbite Angle classification crossbites 13. Discusses the use of distraction osteogenesis in maxillofacial surgery. 14. Discusses maxillofacial surgery in the cleft patient. 15. Describes the acquired diseases of the TMJ and their management. 16. Describes the use of dento-facial prosthetics. Patient Care Goal: The resident will provide patient care that is compassionate, appropriate, and effective for the treatment of surgical problems. Objectives 1. Performs the various local anesthetic facial blocks for procedures done in oral and maxillofacial surgery. 2. Performs with graduated surgical independence bony fixation of the craniofacial skeleton. 3. Performs the head and neck exam in the facial trauma patient. 4. Performs the facial evaluation for orthognathic surgery patients. 5. Participates in the cephalometric analysis, prediction tracing, and preoperative surgical planning of maxillofacial surgery patients. 6. Performs a face-bow transfer. 7. Participates in preoperative model surgery. 8. Participates in common maxillofacial surgical procedures, including: a. b. c. d. e. 9. C. facial fractures genioplasties sagittal split mandibular osteotomies maxillary LeFort I osteotomies bimaxillary osteotomies Participates in the creation and application of dental splints in maxillofacial surgery. Practice Based Learning and Improvement Goal: The resident will investigate and evaluate his or her own patient care practices, appraise and assimilate scientific evidence, and improve patient care practices. Objectives D. 1. Uses information technology to prepare for cases, bringing to the OR the knowledge of current modalities of care and the scientific evidence for that care. 2. Routinely analyzes the effectiveness of own practices in caring for surgery patients. 3. Improves own practices in the care of patients by integrating appropriately gathered data and feedback. 4. Educates medical students and other healthcare professionals in the practices of oral and maxillofacial surgery. 5. Functions independently with graduated advancement and appropriate faculty supervision. 6. Uses library sources to perform research and perform literature searches. 7. Understands the principles of clinical research and the application of biostatistics. Interpersonal and Communication Skills Goal: The resident will demonstrate interpersonal and communication skills that result in effective information exchange and teaming with patients, their families, and professional associates. Objectives 1. Educates patients and families in post oral and maxillofacial surgery care. 2. Demonstrates compassion for patients and families. 3. Provides adequate counseling and informed consent to patients. 4. Listens to patients and their families. E. 5. Assimilates data and information provided by other members of the health care team. 6. Charts and records accurate information. System Based Practice Goal: The resident will demonstrate an awareness of and responsiveness to the larger context and system of health care and the ability to effectively call on system resources to provide care that is of optimal value. Objectives F. 1. Coordinates all aspects of the oral and maxillofacial surgery care for patients. 2. Demonstrates knowledge of cost-effective oral and maxillofacial surgery care. 3. Advocates for patients within the health care system. 4. Refers patients to the appropriate practitioners and agencies. 5. Facilitates the timely discharge of same day surgery patients 6. Works with primary care physicians, and other consultants such as cardiologists, toward the safe administration of anesthesia. Professionalism Goal: The resident will demonstrate a commitment to carrying out professional responsibilities, adherence to ethical principles, and sensitivity to a diverse patient population. Objectives 1. Develops a sensitivity of the unique stresses placed on families under care for surgical diagnoses. 2. Exhibits an unselfish regard for the welfare of surgical patients. 3. Demonstrates firm adherence to a code of moral and ethical values. 4. Is respectful to patients and their families especially in times of stress to the family unit. 5. Respects and appropriately integrates other members of the health care team. 6. Provides appropriately prompt consultations when requested. 7. Demonstrates sensitivity to the individual patient’s profession, life goals, and cultural background as they apply to health care. 8. Is reliable, punctual, and accountable for own actions in the OR and clinic. 9. Understands the concepts of autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, justice, and respect for life. 10. Maintains patient confidentiality. Cosmetic Surgery Rotation Cosmetic and aesthetic surgery exposure will be obtained primarily through a composite experience at several different surgical centers. The PSRY 1-2 (PGY 5-6) will gain experience at several different surgical center sites principled Gary Burget, Julius Few, David Teplica, and Peter Geldner. The resident will be exposed to the spectrum of Aesthetic surgery and interventions including: facial rejuvenation, dermal fillers, advanced techniques in rhytidectomy of the face neck, advanced techniques in eyelid and nasal surgery. The resident will gain critical knowledge in the diagnosis and treatment of facial aging, rhinoplasty, breast aesthetics and techniques in structural fat grafting and dermal fillers. Upon completion of the month, she/he will be proficient in understanding the cutting edge techniques in aesthetic surgery A. Medical Knowledge I. Aesthetic Surgery of the Breast and Trunk Goal: The resident will be thoroughly familiar with aesthetic surgery of the trunk and breast, and undertake comprehensive surgical management of such diagnoses. Objectives: 1. Draws the normal anatomy of the breast and axillae. 2. Describes the pathologic anatomy and histology of the breast as it relates to mammary hyperplasia and hypoplasia. 3. Discusses the various surgical techniques for breast reduction, the indications for and contraindications to the procedures. 4. Discusses the complications of breast reduction, their prevention and management. 5. Describes the various surgical techniques for breast augmentation, the indications for and contraindications to the procedures. 6. Discusses the complications of augmentation mammoplasty, their prevention and management. 7. Discusses the different types of breast implants and the reasons for choosing a particular type for a particular problem. 8. Describes the basic techniques for mastopexy, the indications for and contraindications to these procedures. 9. Discusses the complications of mastopexy, their prevention and management. 10. Discusses techniques for treatment of aesthetic trunk deformity such as panniculectomy and abdominoplasty, the indications for them and contraindications to the procedures. II. 11. Discusses the complications of panniculectomies and abdominoplasties and their prevention and management. 12. Discusses the treatment options for congenital breast anomalies such as Pollands syndrome. 13. Describes the techniques of suction lipectomy as applied to aesthetic deformities of the trunk, as well as anesthetic management for these procedures. 14. Recites the principles of selection of mastopexy vs. augmentation mammoplasty. 15. Recites the principles of selection of abdominoplasty vs. liposuction. 16. Explains the basic principles and techniques for treating other aesthetic deformities of the breast and drunk such as inverted nipples, localized lipodystrophy, tubular breast deformity, etc. 17. Lists the long-term consequences of augmentation mammoplasty such as capsular contraction and its treatment as well as methods for follow-up including special techniques for mammography. 18. Discusses the post-obesity deformity and the options for body contouring surgery. Aesthetic Surgery of the Head and Neck Goal: The resident will be familiar with aesthetic diagnoses of the head and neck and understand the principles of surgical treatment of such problems. Objectives: 1. Discusses the concepts of beauty and aesthetic principles of the facial structures. 2. Identifies the principles and techniques of aesthetic rhinoplasty as well as the differences in approach between primary and secondary rhinoplasty. 3. Recites the diagnostic and therapeutic techniques in the management of nasal airway obstruction. 4. Discusses the application of aesthetic principles to the cleft patient. 5. Explains the complications of rhinoplasty and septoplasty, their prevention and treatment. 6. Discusses the varying effects of aging and sun exposure on the facial structures. 7. Demonstrates the techniques of rhytidectomy, suction lipectomy, genioplasty, blepharoplasty, and other methods for treatment of the aging face. 8. Discusses the complications of facial aesthetic surgery, their prevention and treatment. 9. Draws the various aesthetic deformities of the ear and know the techniques of their correction. 10. Discusses the aesthetic and functional problems of the eyelid, including blepharochalasis and ptosis; knows the treatment for these diagnoses, complications and prevention. B. 11. Discusses the diagnostic methods and treatment options for the patient with facial palsy. 12. Describes the diagnostic principles and treatment techniques for alopecia pattern baldness including tissue expansion, scalp flaps, and hair transplantation. 13. Discusses the principles and techniques of orthognathic surgery for the treatment of craniofacial skeletal dysharmony. 14. Discusses the various ancillary techniques for management of the aging face, including chemical peel, Retin A, dermabrasion, collagen injection, laser resurfacing, injection of filling material, botulinum toxin, hydroxyapatite, hyaluronic acid, and skin care products. 15. Discusses the use of lasers for the treatment of unwanted hair, tattoo removal, and facial resurfacing, include laser biophysics and safety. 16. Discusses the various techniques used for face lifting, including the role of platysma, SMAS, subperiosteal, deep plan, composite, etc. 17. Discusses the different types and appropriate uses of liposuction. Patient Care Goal: need a goal Objectives: 1. Performs complete assessment of patients presenting for facial plastic surgery. 2. Performs the following breast surgeries with graduated operative independence including: a. b. c. 3. reduction mammoplasty augmentation mammoplasty ptosis correction and mastopexy. Performs the following surgeries including pre-operative markings with graduated operative independence, including: a. b. c. d. e. f. suction lipectomy panniculectomy abdominoplasty body lifts brachioplasties thigh lifts 4. Performs preoperative markings for reduction mammoplasty. 5. Performs a comprehensive (internal/external) nasal exam and participate in surgery of the nose including: a. b. c. d. primary and secondary rhinoplasty cleft lip nasal deformity airway obstruction septoplasty. 6. Participates in facial aesthetic surgery including: a. b. c. d. e. f. 7. Performs both open and endoscopic surgical therapy for patients with aging face including rhytidectomy and brow lift. 8. Performs ancillary procedures for the aging face such as chemical peels, skin care, injection of fillers and botox, etc. 9. Participates in the treatment of patients with facial nerve palsy including: a. b. c. d. e. 10. C. rhytidectomy brow lift facial liposuction Blepharoplasty gennioplasty jaw disharmony nerve grafts placement of gold weights suspensory static procedures dynamic procedures free tissue transfer. Evaluates the psychosocial status of the patient presenting for aesthetic plastic surgery and determine whether the patient is an appropriate candidate for surgery. Practice Based Learning and Improvement Goal: The resident will investigate and evaluate his or her own patient care practices, appraise and assimilate scientific evidence, and improve patient care practices. Objectives: D. 1. Uses information technology to prepare for surgical cases, bringing to the OR the knowledge of current modalities of care and the scientific evidence for that care. 2. Routinely analyzes the effectiveness of own practices in caring for aesthetic and breast patients. 3. Improves own practices in the care of aesthetic and breast patients by integrating appropriately gathered data and feedback. 4. Educates medical students and other healthcare professionals in the practices of aesthetic and breast surgery. 5. Functions independently with graduated advancement and appropriate faculty supervision. 6. Continues to keep apprised of new techniques used in facial aesthetic surgery. Interpersonal and Communication Skills Goal: The resident will demonstrate interpersonal and communication skills that result in effective information exchange and teaming with patients, their families, and professional associates. Objectives: E. 1. Educates patients and families in operative strategies for aesthetic surgery. 2. Provides adequate counseling and informed consent to patients. 3. Listens to patients and their families. 4. Charts and records accurate information. 5. Accurately assess patient’s expectations of aesthetic plastic surgery and honestly educates them on appropriate surgical intervention. System Based Practice Goal: The resident will demonstrate an awareness of and responsiveness to the larger context and system of health care and the ability to effectively call on system resources to provide care that is of optimal value. Objectives: 1. Demonstrates knowledge of cost-effective strategies for breast surgery. 2. Facilitates the timely discharge of aesthetic and breast patients. 3. Understands the state, local and specialty requirements for outpatient surgical centers utilized in the care of aesthetic surgery patients. F. Professionalism Goal: The resident will demonstrate a commitment to carrying out professional responsibilities, adherence to ethical principles and sensitivity to a diverse patient population. Objectives: 1. Exhibits an unselfish regard for the welfare of patients presenting for cosmetic surgery. 2. Demonstrates firm adherence to a code of moral and ethical values. 3. Respects and appropriately integrates other members of the breast care team. 4. Demonstrates sensitivity to the individual patient’s profession, life goals, and cultural background as they apply to aesthetic and breast surgery. 5. Is reliable, punctual, and accountable for own actions in the OR and clinic. 6. Provides non-biased consultations for patients presenting for aesthetic surgery. 7. Understands the impact of psychological issues, such as body dysmorphic disorder and psychosocial stressors, in patients who present for cosmetic surgery. 8. Participates in the Chief Resident’s Aesthetic Clinic, adhering to strict ethical principles and professionalism specifically with respect to advertising, recruiting, educating and treating patients. 9. Appreciates the potential conflict of interest that exists in the practice of aesthetic plastic surgery with respect to patient’s surgical needs and expectations and the surgeon’s financial rewards. * Taken from Plastic Surgery Curriculum AACPS website