Chapter 11
advertisement

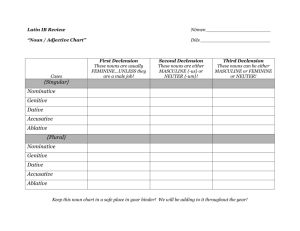
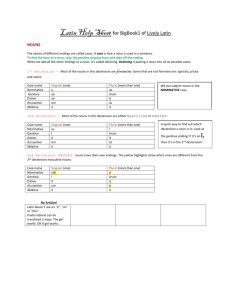
Chapter 11 I. Review - Cases Nominative: subject - person or thing that performs the action of the verb The goddess talks to the woman. Accusative: direct object receives the action of the verb directly or object of a preposition The god loves the nymph. Ablative: object of a preposition The tree is in the forest. Genitive case the of or possessive case The term possessive means that one noun, i.e., the possessor owns or possesses another noun, i.e., the possessed. In English you can show possession in one of two ways: 1. with an apostrophe the teacher’s book the girls’ father 2. with the word “of” followed by the possessor noun the book of the teacher the father of the girls In the class of Mrs. Duello we will always use of . . . there is no Latin word for "of" in this sense In Latin possession is shown by using the genitive case. liber magistri - the book of the teacher pater puellarum - the father of the girls st 1 nom: gen: dat: acc: abl: Declension Nouns singular -a -ae -ae -am -ā plural -ae -arum -is -as -is nd 2 nom: gen: dat: acc: abl: Declension Nouns singular plural -us -i -o -um -o -i -orum -is -os -is 3rd Declension Nouns nom: gen: dat: acc: abl: singular s-n-l-r-o-x -is -i -em -e plural -es -um -ibus -es -ibus In future vocabulary lists, the book will list the nominative and genitive along with the gender. puella,-ae, f. girl servus, -i, m. slave vox, vocis, f. voice The genitive singular indicates the declension to which the noun belongs: -ae = 1st declension -i = 2nd declension -is = 3rd declension The base of the noun is found by dropping the genitive singular ending puellae puell- servi serv- vocis voc- Activity 3: Decline the following nouns Latin singular English singular nom: gen: dat: acc: abl: area, areae - stem arevilicus, vilici - stem vilicpater, patris - stem patri- Latin plural English plural Activity 4: Fill in the blanks with Latin words to match the English cues. 1. Geta ________ non timent. (the master) 2. _______ dominus abest, servi saepe non laborant. (When) 3. Geta __________ vult. (to run away) 4. Nemo eum ______________. (hinders) 5. Geta ___________ parat. (food) 6. _______ __________ e villā furtim ambulat. (That night) 7. ________________ nox est, servus celeriter currit. (Although) 8. Servus _________ clamat ________ mussat. (neither . . . nor) 9. Geta in silvam ___________ arborum currit. (full) 10. In arbore ____ _________. (hides himself) Activity 5 - Translate the 10 sentences from 11b in your text on p. 82 using the family chart. 1. Marcus est frater Corneliae. 2. Cornelia est soror Marci. 3. Cornelius est vir Aureliae. 4. Aurelia est uxor Cornelii. 5. Marcus est filius Cornelii et Aureliae. 6. Cornelia est filia Cornelii et Aureliae. 7. Cornelius et Aurelia sunt parentes Marci et Corneliae. 8. Marcus et Cornelia sunt liberi Cornelii et Aureliae. 9. Aurelia est mater Marci et Corneliae. 10. Cornelius est pater Marci et Corneliae. How do you tell the difference between all the-ae and -i endings? 1. look at other words in the sentence 2. what makes sense 3. placement in the sentence Celeriter redeunt servi. The genitive usually forms a phrase with another noun. Since servi is the only noun in the sentence, it must be nominative plural. The slaves return quickly. Activity 6 – Identify the declension of the bold noun and supply the genitive end translate the sentence. 1. Liberi sunt in raedā senator_____ . declension: _______ 2. Marcus est frater Corneli_____. declension: _______ 3. Nuntius filium Corneli_____ salutat. declension: _______ 4. Servi iram vilic_____ timent. declension: _______ 5. Geta effugit et in ramis arbor_____ se celat. declension: _______ 6. Magna vox Dav_____ eum terret. declension: _______ 7. Davus, vilicus Corneli_____, Getam vidēre non potest. declension: _______ 8. Si Cornelius abest, Davus villam domin_____ curat. declension: _______ Pueri pater est senator Romanus. The word pueri could be genitive singular or nominative plural. It is only when we reach the word pater (which can only be nominative singular) and est (which is a singular verb) that we know that pueri must be genitive singular, forming a phrase with pater, i.e., "the father of the boy." The father of the boy is a Roman senator. In villā puellae sedent. Again, puellae could be genitive singular or nominative plural. Only the context will help you decide. The girls sit in the house. They sit in the house of the girl. How do you tell the difference between all the-ae and -i endings? 1. 2. look at other words in the sentence what makes sense 3. placement in the sentence Activity 7- Explain the clues that make you decide whether the nouns in boldface are genitive singular or nominative plural, then tra 1. Puellae sunt defessae. clue: ____________________________ 2. In agris pueri ambulant. clue: ___________________________ 3. Puellae et matres in villā sedent. clue: ___________________________ 4. Pueri epistulas scribunt. clue: ___________________________ 5. Pater Marci in villā sedet. clue: ___________________________ 6. Pater vocem puellae audit. clue: ___________________________ 7. Pueri vocem Marci audiunt. clue: ___________________________ 8. Fratres pueri sunt in horto. clue: ___________________________ 9. Servi in agris filium domini petunt. clue: ___________________________