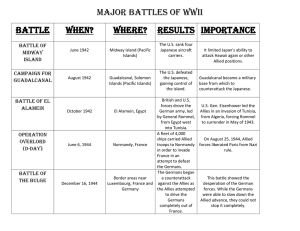
Unit Review
advertisement
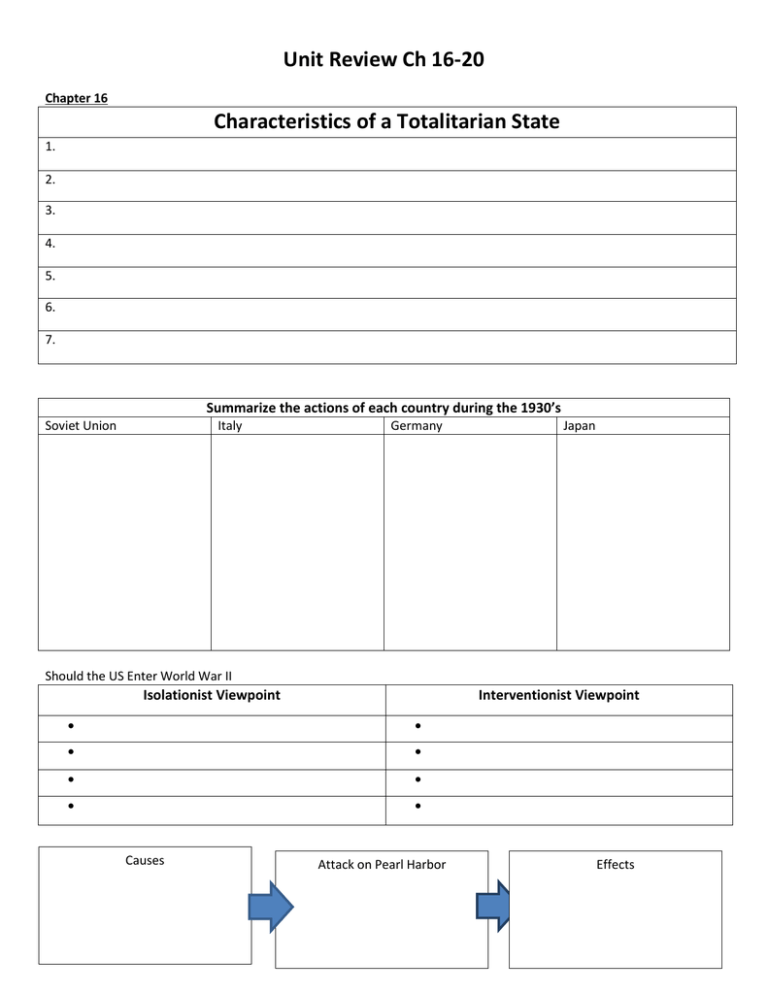
Unit Review Ch 16-20 Chapter 16 Characteristics of a Totalitarian State 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Summarize the actions of each country during the 1930’s Soviet Union Italy Germany Japan Should the US Enter World War II Isolationist Viewpoint Interventionist Viewpoint Causes Attack on Pearl Harbor Effects Allies Leaders Great Britain Joseph Stalin, communist dictator France United States Axis Powers Leaders Germany Italy Benito Mussolini, fascist dictator Japan Chapter 17 Home Front Economy Koresmatsu v. US (1944) The Facts Effects on Women The Issue Effects on Minorities The Decision Identify the steps that led to the Allied victory Europe The Pacific Allies Win World War II Identify different ways in which the US and other nations responded to the Holocaust Response to the Holocaust United States recognizes Israel Allied Leaders during World War II World Political U. S. Military Five Turning Points of World War II Year Event 1942 1942-43 1942 1944 1945 Chapter 18 Contrast the conflicting goals of the US and the Soviet Union American Goals Soviet Union Goals Arms Race Cold War Tactics List efforts taken to protect Americans from Communism and how these policies affected rights. Anti-Communist Policy Smith Act House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC) Blacklist Alger Hiss/Rosenbergs McCarthy Hearings Effect on Rights Loyalty Review Board Cold War at Home Duck and Cover Drills Chapter 20 Major Civil Rights Legislation Civil Rights Act of 1964 Twenty-Fourth Amendment (1964) Voting Rights Act of 1965 Fair Housing Act of 1968 Civil Rights Organizations Organization and Date Founded NAACP Nation of Islam Key People Key Features Congress of Racial Equality Southern Christian Leadership Conference Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee Black Panther Party