Rain garden overview (ppt)
advertisement

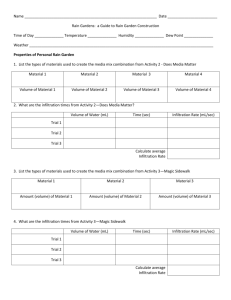
Bioretention, Raingardens & Improved Swales Frank Henning fhenning@uga.edu What is a Rain Garden? • A shallow depression in a landscape that captures water and holds it a short time • Runoff water is captured & infiltrated into soil • An attractive addition to a landscape Benefits of Rain Gardens • Attractive landscape feature • Increases infiltration of rainwater in landscapes with impervious surfaces • Reduces runoff volume and temperature • Creates habitat in the landscape Rainfall Rice Creek Watershed District Storage Infiltration Basic Rain Garden Components Overflow Evaporation Ponding Area Engineered soil Infiltration Runoff In Water Quality - Expected BMP Performance Georgia Stormwater Management Manual ARC, 2001 Credit: GA CSS Nutrients – Chapel Hill, NC 0.7 0.6 0.5 Mass 0.4 (Kg) 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 In Out TN NO3-N TKN TP Hydrology Burnsville, MN Neighborhood Rain Garden Study Barr Engineering Locating the Rain Garden • Where does water come from ? • Where is it going or collecting? Garden Location – Between runoff source & destination – Avoid wet locations – >10 feet from house foundation or well – > 25 ft from septic system components – Avoid TV, phone, utility lines – In full to partial sun is best Quick Soil Infiltration Test • Hole about as deep as garden (>4 feet) • Fill with water • Allow infiltration & refill hole • Calculate infiltration rate (in/hr, ft/hr) Beware of Clay Soils • Gray soil colors indicate extended saturated soil conditions • Typical rain garden plants may not establish well Options: 1) Try another location. 2) Consider a wetland 3) Install an under drain. Rain Garden Design Steps to sizing a rain garden: 1. Estimate watershed drainage area (<5ac). 2. Estimate area of imperviousness. 3. Choose a ponding depth, mulch depth, media depth and gravel depth (ft). 4. Determine media and native soil hydraulic conductivity, or K (in/hr) 5. Determine media & gravel porosity. 6. Determine required size for rain garden. Estimate area of imperviousness Impervious areas include roof tops, sidewalks, and driveways. www.nifty-stuff.com thedailygreen..com Thehomegarden.blogspot.com Choose a rain event, ponding depth & media Design Rain Event: The rainfall that you want the rain garden to treat; usually 1.2 inches for Georgia Ponding depth: the depth to which water will pond in the rain garden before overflowing; usually 9 inches or less © NCSU, 2009 Media pore space & infiltration rate Raingarden Size Bioretention Ponding Zone - Full Drain Time <48hrs 2’ below surface Draw - Down Time? 24 – 48 Hours After the Storm Weir (10 year peak flow) -Use TR55 -Generate Q(cfs) for 10 year storm -Calculate weir length Rain garden Installation & Construction Construction Timing: • Install rain garden last – Sediment! • Site must be stabilized and erosion-free! • Use a forebay: runoff filtered and slowed before entering garden Underground Utilities??? Call Your State’s One Call Center 811 Digging Your Rain Garden • Necessary when under-drains are required • Don’t forget about spoil Pretreatment Inlet (forebay, verge, etc.) Rain Garden – Underdrain Runoff Engineered Media Primarily Sand Under-drain pipe Under drain System Clay - Underdrain Installation Inlets Outlet • Under-drains are a necessity where clay soils or compaction cause water infiltration rates to be low • Increases cost - $5 sq. ft Underdrain Installation Outlet Inlets • Backfilling with an engineered soil (mineral material) and a perforated pipe with protective ‘sock’ • Drain is about 1 foot off bottom to allow ponding and encourage infiltration Media Spoil Upturned Elbow 2-3 inches of hardwood mulch Cover the berm Stable Weir or Spillway Choosing Plants • Tolerant of moisture and drought • Adapted to site conditions • Moisture levels within rain garden vary depending on location Consider Native Species!! • Accustomed to the climate • No invasive issues • Beautiful selections http://www.bae.ncsu.edu/programs/extension/wqg/srp/riparian.html Maintenance Irrigate -First Year -During Drought Lime -Soil test Fertilization -Never Weed -often www.bae.ncsu.edu/topic/raingarden http://stormwater.uga.edu/ Cistern to Raingarden Improved Swales Infiltration Trench - Similar to RG -Gravel is Media Enhanced Swales * Convey 25-year event with >6” freeboard -Dry swale: maximum infiltration rate = 0.75 in/hr , max ponding depth = 1.5’, filter WQv within 48 hours (linear bioretention with constraints) -Wet swale: Must hold the WQv (linear wetland)-