Experiential Learning (Service-Learning/Co-Op)
advertisement

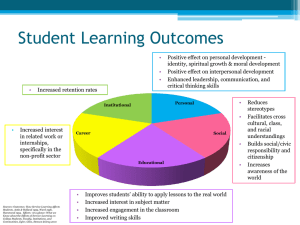
Service-Learning DENA SHONTS DIRECTOR OF SERVICE -LEARNING AUGUST 5, 2015 What is Service-Learning? Service-Learning is a teaching method that combines service to the community with academic instruction, it focuses on critical thinking and reflection. Types of Service-Learning Direct: Students complete service outside of the classroom at a agency approved by the instructor. Indirect: Students complete service during designated class time or on their own time for an agency that is approved by the instructor. Research Based: Students complete service during designated class time or on their own time for an agency that is approved by the instructor. Examples… Direct: Students in a Sustainability class partnered with Habitat for Humanity to perform blower door tests for residents in low income homes. Indirect: Students in a Graphic Design class developed a logo for The Crop Walk and Second Harvest. Research Based: Students in a Statistics class analyzed data for the Habitat for Humanity Critical Home Repair program. Examples… Combination of researched based and direct: Biology students researched science experiments and then preformed the experiments with 5th grade students at a local elementary school. English students partnered with residents in a nursing home to learn about their lives and then wrote their informative papers on the residents lives. Geology students researched the importance of planting trees along waterways, presented that information to students, and then participated in a tree planting project with the Charlotte Tree Fund. Common Threads: Elements that are essential to all Service-Learning projects: The project(s) address a learning objective for the course. Students are required to complete a reflection component that utilizes critical thinking skills. The Service-Learning assignment is part of the course work and not an add on or extra credit. Students are graded on the learning and not the service. Why Should You Offer ServiceLearning? Service-Learning enables the student to put theory into action. Service-Learning meets 2 of the core competencies: Critical Thinking and Personal Growth and Development. Studies show that students who participate in Service-Learning have a higher GPA (23%), are retained from semester to semester (15%)and earn more credentials than non service-learning students(17%). How Can We Help You? We build relationships with community agencies. Connect you with agencies your interested in for your course. Offer professional develop, conferences and workshops. Provide a orientation for your class. Provide placement support for your students. What's Next? Workshop Series: Service-Learning 101 (offered in an online format) Assessment Reflection Interested? Contact a Service-Learning representative: Central: Jenn Marts or Savannah Greer Overcash 257 Levine: Jessi Preussner Room 1402 on M, TH, F Cato: Savannah Greer Room 110 on T, TH Harper: Jessi Preussner Room 344, T, W Jill Lutz Executive Director Workplace Learning What is Workplace Learning? Apprenticeship Charlotte, Co-op & Internships Workplace Learning purpose “Matching Student Talent to Opportunities” Apprenticeship Charlotte Launched August 2012 Inspired by Apprenticeship 2000 Apprenticeship option for local companies Customizable approach Recruiting methods Interface with N.C. Dept. of Commerce Co-op/Work-based Learning Launched in 1986 Academic class (graded, college credit, semester-based) Over 40 programs of study Faculty involvement Eligibility Requirements Paid or Unpaid Why do Co-op / WBL? FTE Generator Employer Feedback About the student About your program Program Review Program Accreditation WBL in action Internships Launched Fall 2013 Non-credit bearing College Involvement Eligibility Requirements Curriculum, CCE, or recent grads Certificate of Completion Statistics Apprenticeship Charlotte 8 participating companies – 29 students 19 additional apprentices begin Fall 2015 Co-op/Work-based Learning 553 students 2014-15 academic year 350+ employer partners 96% completion rate Internships 73 students since launch Campus Locations Central Campus Cato Campus Terrell – 3rd floor Cato II, Room 160 Harper Campus Harris Campus Room 344 Harris II – by appointment Levine Campus Merancas Campus Room 2230 TS 203 www.cpcc.edu/workplacelearning (704) 330-6217 Terry O’Banion Discussion • Disruptive Innovation • Affective Education: Increased self-esteem, assertive in the classroom, practice learning and learning in the classroom • Project Based Learning: teaching method where students gain knowledge and skills by discovering answers to complex questions, problems and challenges. • Assessing and Accounting for Student Success/Completion • Meets 2 core competencies: – Personal Growth and Responsibility – Critical Thinking